写在前面
本篇文章是在下面这个B站课程里学的,作为我的学习记录同时也希望能帮助到大家。
【SQL SERVER数据库_D丝学编程】 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1XV411C7TP/?p=2&share_source=copy_web&vd_source=02052d2fc18088b96251f0ac88221db6
废话少说,现在就开始学习吧!
01-SQL SERVER 数据库基础
SQL SERVER介绍
数据库:数据库是“按照数据结构来组织、存储和管理数据的仓库”,是一个长期存储在计算机内的、有组织的、可共享的、统一管理的大量数据的集合。
应用场景:在软件系统中无处不在,几乎所有的软件系统背后都有数据库,例如(淘宝、QQ、游戏等)。
数据表现形式:(二维表)
学号姓名性别电话邮箱001刘备男13558789854liubei@qq.com
002
孙尚香女13665878523susnhangxiang@163.com003关羽男13223569852guanyu@163.com004张飞男1343720083zhangfei@163.com
主流关系型数据库:SQL SERVER、MySQL、ORACLE等。
SQL SERVER官网:SQL Server 下载 | Microsoft
SQL SERVER界面
打开数据库:
(1)启动服务:
【1】命令行启动;【2】SQL SERVER配置管理器;【3】Windows服务;
(2)打开SQL SERVER Management Studio,使用工具连接到数据库。
【1】Windows身份验证;【2】SQL SERVER身份验证;
数据库基本操作:
(1)建库;(2)建表;(3)数据维护。
(1)建库:右键数据库 新建数据库

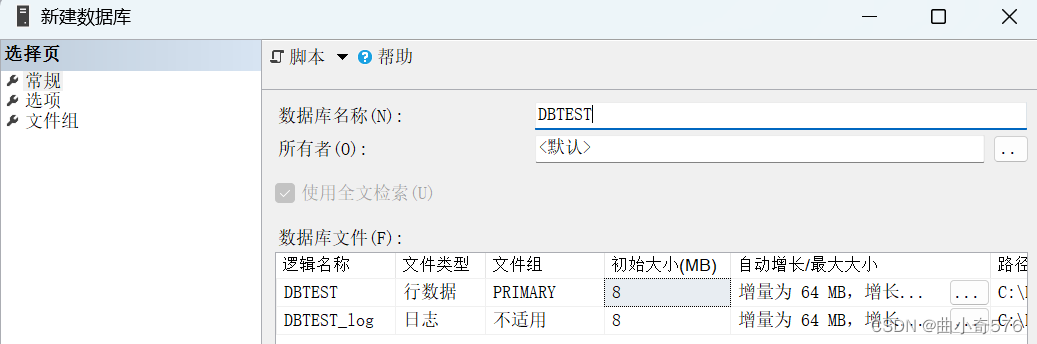
DBTEST是数据文件,DBTEST_log是日志文件。
(2)建表
把StuNo(学号)设置为主键,唯一标识一个人。
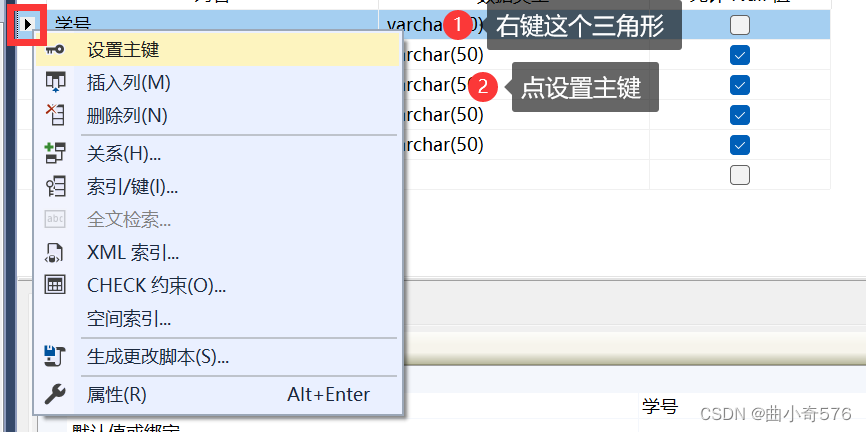
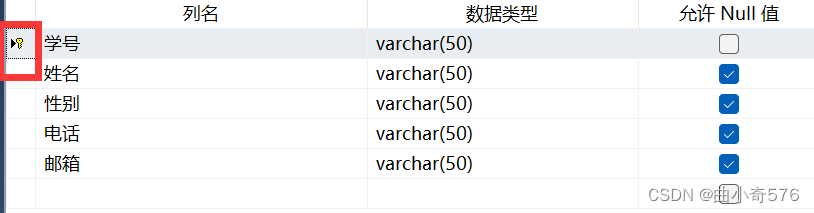
设置好之后,刷新表就能看到刚才新建的表了。
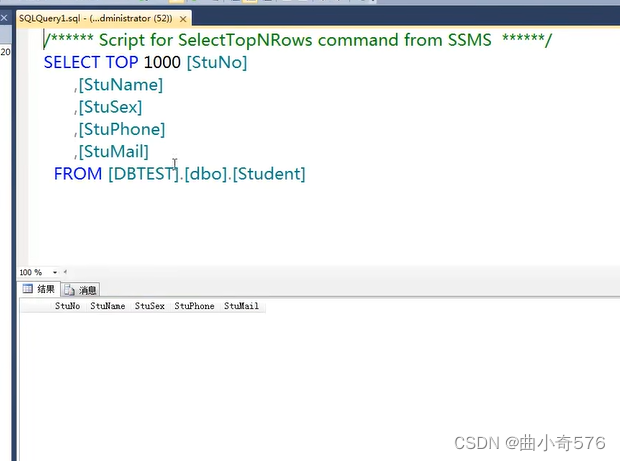
选择前1000行可以查询数据,刚建的表还没有插入数据,所以现在是查询不到信息的。
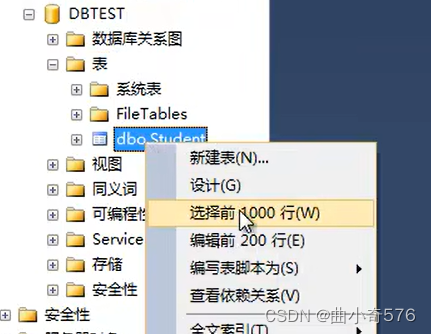
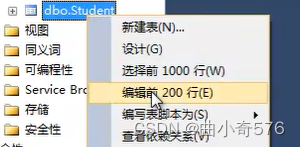
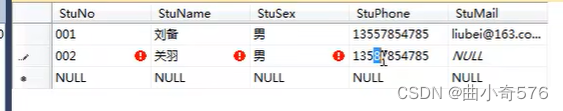
编辑数据:编辑前200行,可以插入、修改、删除数据。
删除数据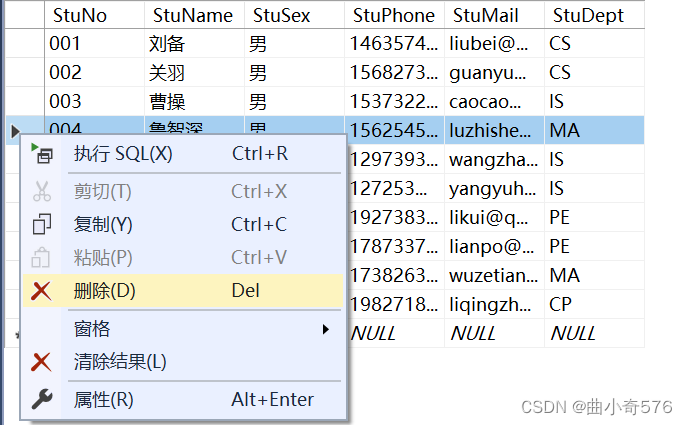
数据库的迁移:
(1)数据库的分离、附加;(分离和删除的区别在于硬盘上是否还留存有数据库文件)
(2)数据库的备份、还原;
(3)数据库脚本的保存。
02_01-创建数据库
--drop database DBTEST 当前数据库如果已经存在DBTEST 就先删掉再创建
--创建数据库
/*if exists (select * from sys.databases where name = 'DBTEST')
drop database DBTEST*/
--危险操作
create database DBTEST
on --数据文件
(
name = 'DBTEST',--逻辑名称 在数据库里字符串放在单引号‘’里
filename = 'D:\DATA\DBTEST.mdf' , --物理路径和名称
size = 5MB,--文件的初始大小
filerowth = 2MB--文件增长可以写大小,也可以写百分比
)
log on --日志文件
(
name = 'DBTEST_log',--逻辑名称 在数据库里字符串放在单引号‘’里
filename = 'D:\DATA\DBTEST_log.ldf' , --物理路径和名称
size = 5MB,--文件的初始大小
filerowth = 2MB--文件增长可以写大小,也可以写百分比
)
02_02-创建数据表
建表(部门表、职级表、员工表)
--默认情况下,建表会建在master库里
--切换数据库
use DBTEST
--创建表基本语法
/*
create table 表名
(
列名1 数据类型,
列名2 数据类型,
列名3 数据类型
)
*/
--判断表是否存在
if exists(select * from sys.objects where name = 'Department'and type='U')
drop table Department
--建表(部门表、职级表、员工表)
create table Department
(--部门表
--部门编号 primary:主键,唯一标识一行;identity:自动增长,初始值为1,增长步长也为1
DepartmentId int PRIMARY KEY identity(1,1),--设置为主键之后编号不能重复。
--部门名称
DepartmentName nvarchar(50) not null,--nvarchar代表字符串,nvarchar(50)表示最多不能超过50个字符
--部门描述
DepartmentRemark text
)
/* char\varchar\text\nchar\nvarchar\ntext的区别
①char 定长,char(10),无论存储的数据是否真的有10字节,都要占用10字节;
char(10)存储'ab',仍然占用10字节。
②varchar 变长,varchar(10),最多占10字节;
varcahr(10)存储'ab',占用2字节。
③text 长文本,可以存储几千几万个字节的数据
④char、varchar、text前面加n:存储Unicode字符,对中文友好。
varchar(100):存储100个字母或者50个汉字,一个汉字占两个字节
nvarchar(100):存储100个字母或者100个汉字。
*/
create table [Rank]
(--职级表
--职级编号 primary:主键,唯一标识一行;identity:自动增长,初始值为1,增长步长也为1
RankId int PRIMARY KEY identity(1,1),--设置为主键之后编号不能重复。
--职级名称
RankName nvarchar(50) not null,--nvarchar代表字符串,nvarchar(50)表示最多不能超过50个字符
--职级描述
RankRemark text
)
create table People
(--员工表
--员工编号 primary:主键,唯一标识一行;identity:自动增长,初始值为1,增长步长也为1
PeopleId int PRIMARY KEY identity(1,1),--设置为主键之后编号不能重复。
--部门 references:引用外键,将其他表的主键作为这个表的字段(一列)
DepartmentId int references Department(DepartmentId) ,
--职级 加了references之后,添加外键字段时会自动检测输入的字段是否正确
RankId int references [Rank](RankId),
--员工姓名
PeopleName nvarchar(50) not null,--nvarchar代表字符串,nvarchar(50)表示最多不能超过50个字符
--员工性别 用default('男')设置默认情况下员工性别为男,
--check(PeopleSex='男' or PeopleSex='女')约束性别只能是男或者女
PeopleSex nvarchar(1) default('男') check(PeopleSex='男' or PeopleSex='女'),
--员工生日 datetime类型能存储年月日时分秒,date类型只能存储年月日,smalldaetime只能存储最近的一段时间
PeopleBirth smalldatetime not null,
--员工薪资 decimal(12,2) 12:长度最长为12,2:精确到小数点后2位
PeopleSalary decimal(12,2) check(PeopleSalary >= 1000 and PeopleSalary<=1000000) not null,
--员工号码 unique表示每个PeoplePhone必须是唯一的 unique也是一个约束条件
PeoplePhnoe varchar(20) unique not null,
--员工住址
PeopleAddress varchar(300),
--添加时间 系统添加员工信息的时间
PeopleAddTime smalldatetime default(getdate())
)
02_03-表结构和约束的维护
修改表的结构有三种情况:(1)添加列、(2)删除列、(3) 修改列。
(1)添加列
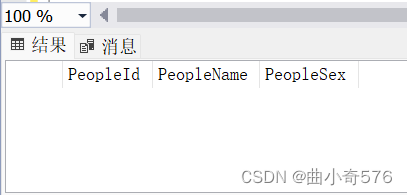
在员工表中添加员工邮箱PeopleMail
--(1)添加列 alter table 表名 add 新列名 数据类型
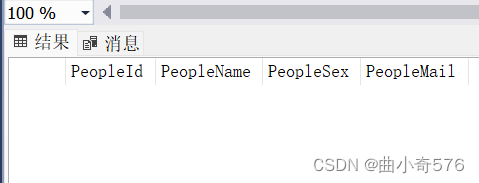
alter table People add PeopleMail varchar(30)
添加PeopleMail之前
添加PeopleMail之后
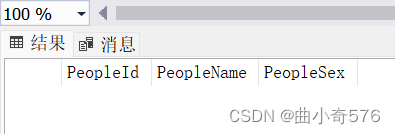
(2)删除列
删除员工表中刚刚新加的PeopleMail列
--(2)删除列 alter table 表名 drop column 列名
alter table People drop column PeopleMail
删除PeopleMail列之后
(3)修改列
--(3) 修改列 alter table 表名 alter column 列名 数据类型
--修改People表中的PeopleAddress的长度300-->200
alter table People alter column PeopleAddress varchar(200)
注意:在做具体设计或者项目的时候,要尽量少的使用alter语句,因为当我们修改表的结构的时候很有可能整个软件或者系统都要跟着一起修改,会造成很大的麻烦。
维护约束
约束名查找


--修改表的结构--------------------------------------------
--(1)添加列 alter table 表名 add 新列名 数据类型
alter table People add PeopleMail varchar(30)--添加PeopleMail列
--(2)删除列 alter table 表名 drop column 列名
alter table People drop column PeopleMail--删除PeopleMail列
--(3) 修改列 alter table 表名 alter column 列名 数据类型
--修改People表中的PeopleAddress的长度300-->200
alter table People alter column PeopleAddress varchar(200)
--删除添加约束--------------------------------------------
--(1)删除约束 (本质上也是修改表,修改表的约束
--alter table 表名 drop constraint 约束名
--删除PeopleSalary的约束
alter table People drop constraint CK_PeoPleSa_34C8D9D1
--(2)添加约束
--alter table 表名 add constraint 约束名 check(表达式)
--添加check约束 添加工资约束 工资范围:1000~1000000
alter table People add constraint CK_PeoPleSa1 check(PeopleSalary >= 1000 and PeopleSalary<=1000000)
--添加主键约束 primary key
alter table 表名 add constraint 约束名 primary key 列名
--添加唯一约束 unique
alter table 表名 add constraint 约束名 unique 列名
--添加默认约束 default
alter table 表名 add constraint 约束名 default 默认值 for 列名
--添加外键
alter table 表名 add constraint 约束名 foreign key 列名
references 关联表名(列名)
03-插入数据
--插入数据
--向部门表中插入数据
--完整语法 字段和具体的值一一对应
insert into Department (DepartmentName,DepartmentRemark)
values ('市场部','..........')
insert into Department (DepartmentName,DepartmentRemark)
values ('软件部','..........')
insert into Department (DepartmentName,DepartmentRemark)
values ('企划部','..........')
--简写 最好不要这样写因为字段顺序如果换了,这样直接插入可能会出错
insert into Department values ('硬件部','..........')
--一次性插入多行数据
insert into Department(DepartmentName,DepartmentRemark)
select '测试部','......'union
select '网络部','......'union
select '宣传部','......'union
select '公关部','......'
select * from Department
--向职级表中插入数据
insert into Rank1(RankName,RankRemark)
values ('初级','......')
insert into Rank1(RankName,RankRemark)
values ('高级','......')
insert into Rank1(RankName,RankRemark)
values ('中级','......')
insert into Rank1(RankName,RankRemark)
values ('初级','......')
insert into Rank1(RankName,RankRemark)
values ('高级','......')
insert into Rank1(RankName,RankRemark)
values ('高级','......')
insert into Rank1(RankName,RankRemark)
values ('中级','......')
insert into Rank1(RankName,RankRemark)
values ('初级','......')
select * from Rank1
--向员工表中插入数据
insert into People(DepartmentId,RankId ,PeopleName,PeopleSex,PeopleBirth,PeopleSalary,PeoplePhone,PeopleAddress)
values (8,1,'刘备','男','1988-8-8',100000,'13859038502','中国')
select *from People
04-数据的修改和删除
--数据库的修改和删除
select * from Department
select * from Rank1
select * from People
--修改-------------------------------------------------------
--语法: updete 表名 set 字段1=值1,字段2=值2 where 条件
--在People中做工资调整
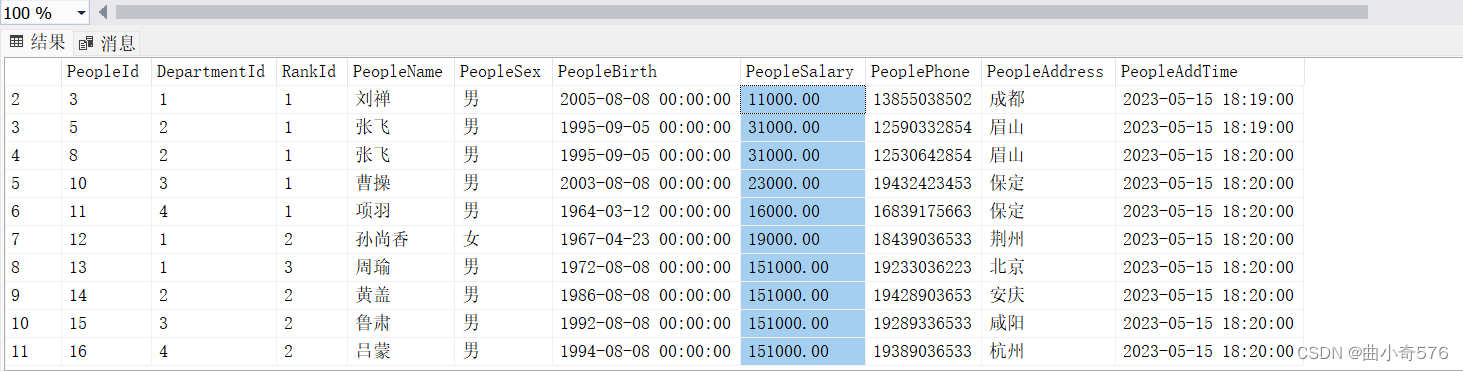
update People set PeopleSalary=PeopleSalary+1000 --没有加where条件就会修改people表中的每一项PeopleSalary
--给员工编号为14的员工加工资
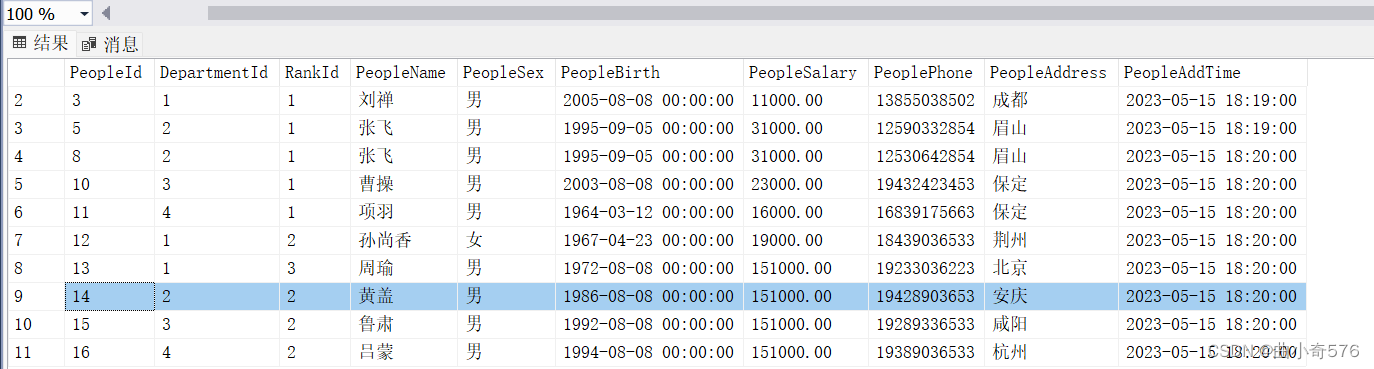
update People set PeopleSalary=PeopleSalary+2000
where PeopleId ='14'
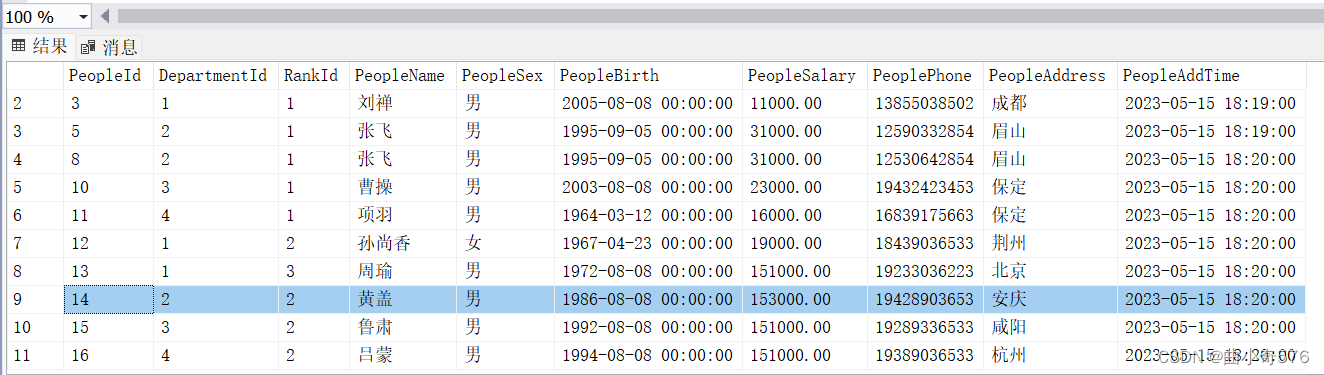
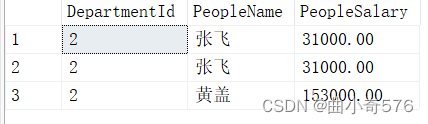
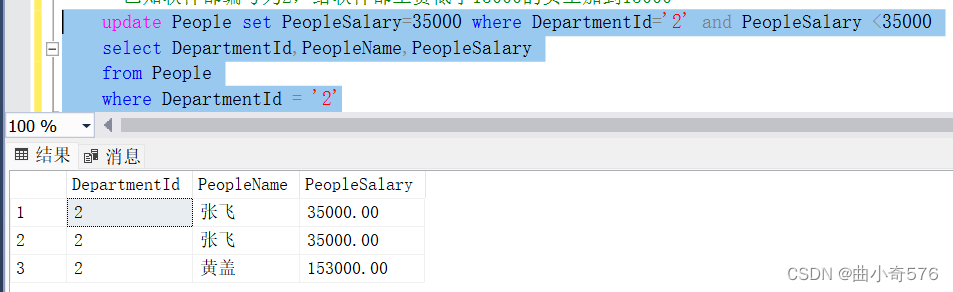
--已知软件部编号为2,给软件部工资低于35000的员工加到35000
update People set PeopleSalary=35000
where DepartmentId='2' and PeopleSalary <35000 --或:or、||
select DepartmentId,PeopleName,PeopleSalary
from People
where DepartmentId = '2'
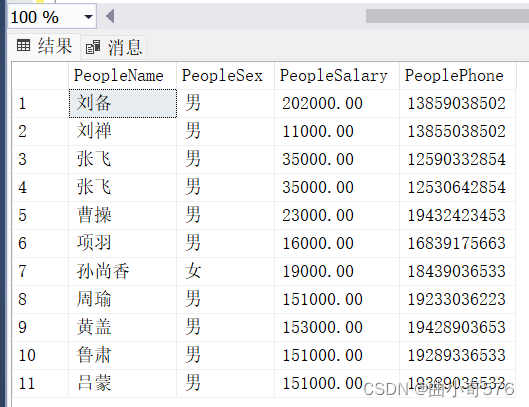
--多字段修改
--修改刘备的工资为原来的2倍,并且把刘备的地址改成北京
update People set PeopleSalary = 2*PeopleSalary,PeopleAddress='北京'
where PeopleName = '刘备'
select * from People
--删除-------------------------------------------------------
--语法: delete from 表名 where 条件
--删除员工表所有记录
/*delete from People*/ --这一句就不执行了 举个例子
--删除市场部(部门编号1)中工资大于1万的人
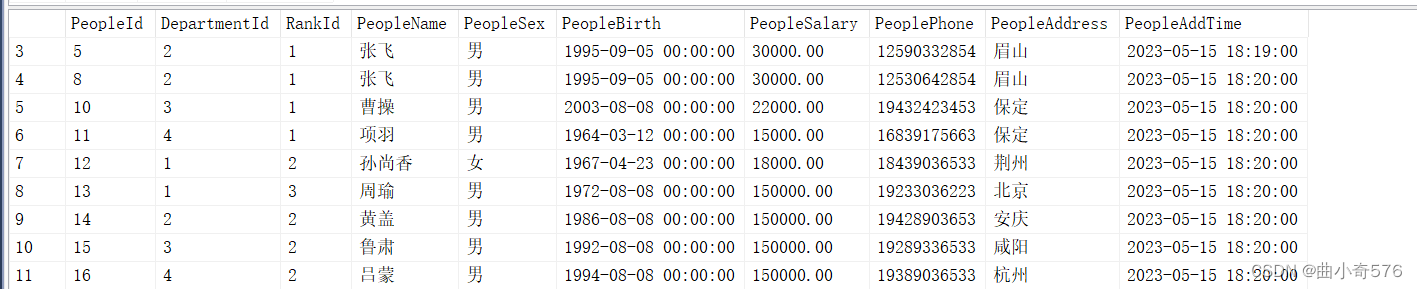
delete from People where DepartmentId = '1' and PeopleSalary>10000
--关于删除(drop、truncate、delete)
/*
drop table People --删除表对象,表和数据一起被删掉
truncate table People --删除数据(清空数据),表对象及表结构依然存在
delete table People --删除所有数据,表对象及表结构依然存在
truncate和delete的区别
①truncate清空所有数据,不能有条件;delete可以删除所有数据也可以删除符合条件的数据
②自动编号:假设表中自动编号为1,2,3,4,5
使用truncate清空数据之后再添加数据,编号依然是1,2,3,4,5....
使用delete删除数据,删除的自动编号就永远不存在了,会在原来的编号后面续写6,7,8,9,10....
*/
05-基本查询
--基础查询
--查询所有列、所有行
select * from Department
select * from Rank1
select * from People
--查询指定列(姓名,性别,月薪,电话)
select PeopleName,PeopleSex,PeopleSalary,PeoplePhone
from People
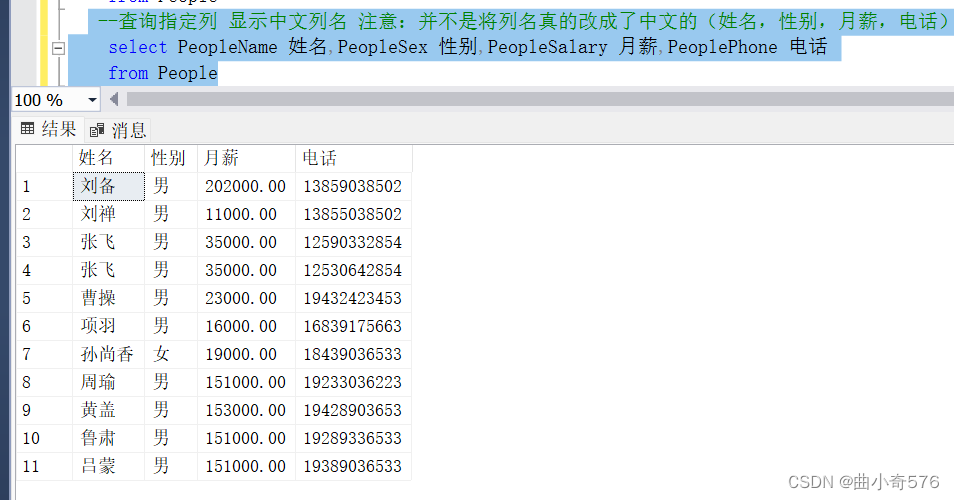
--查询指定列 显示中文列名 注意:并不是将列名真的改成了中文的(姓名,性别,月薪,电话)
select PeopleName 姓名,PeopleSex 性别,PeopleSalary 月薪,PeoplePhone 电话
from People
--查询员工所在城市
select PeopleAddress
from People
--查询员工所在城市(删除重复值:distinct)
select distinct PeopleAddress
from People
--假设准备加工资(上调20%),想查询出加工资后的员工数据
select PeopleName,PeopleSex,PeopleSalary*1.2 加薪后的工资,PeopleSalary 原始工资
from People

06_01-条件查询一
SQL中的常用运算符
常用运算符含义=等于,比较是否相等及赋值!=比较不等于>大于<小于>=大于等于<=小于等于IS NULL比较是否为空IS NOT NULL比较是否不为空
in
比较是否在其中like模糊查询BETWEEN...AND...比较是否在两者之间AND逻辑与(两个条件同时成立时表达式成立)OR逻辑或(两个条件有一个成立时表达式成立)NOT逻辑非(条件成立,表达式则不成立;条件不成立,表达式则成立)
--条件查询
select *from People
--查询性别为女的员工信息
select * from People where PeopleSex='女'
--查询工资大于等于10000元的员工信息
select * from people where PeopleSalary>= 10000
--多条件|查询出性别为女且大于等于10000元的员工信息
select * from People where PeopleSex='女' and PeopleSalary>= 10000
--查询出月薪大于等于10000的员工或者月薪大于等于8000的女员工
select * from People where PeopleSalary >= 10000 or (PeopleSalary>=8000 and PeopleSex='女')
--查询出出生年月在1980-1-1之后,且月薪大于等于10000的女员工
select * from People where PeopleBirth >='1980-1-1'and (PeopleSalary>=10000 and PeopleSex='女' )
--查询月薪在10000-20000之间的员工信息
select * from People where PeopleSalary >= 10000 and PeopleSalary <= 20000
select * from People where PeopleSalary between 10000 and 20000 --用between and也可以
--查询出地址在'成都'或者'北京'
select * from People where PeopleAddress = '成都' or PeopleAddress = '北京'
select * from People where PeopleAddress in ('成都','北京') --用in
--排序 asc升序(默认) desc降序
--查询所有的员工信息,按工资排序,降序
select * from People order by PeopleSalary desc
--查询所有的员工信息,按名字长度排序,降序
select * from People order by len(PeopleName) desc
--查询出工资最高的五个人的信息
select top 5 * from People order by PeopleSalary desc
--查询出工资最高的10%的员工的信息
select top 10 percent * from People order by PeopleSalary desc
--null:空值
insert into People(DepartmentID,RankID,PeopleName,PeopleSex,PeopleBirth,PeopleSalary,PeoplePhone,PeopleAddTime)
values(1,1,'花木兰','女','1995-3-2',30000,'`18393225556',GETDATE())
select * from People
--查询出没有填写地址的员工信息
select * from People where PeopleAddress is null
--查询出已经填写了地址的员工信息
select * from People where PeopleAddress is not null
06_02-条件查询二
--查询出80后的员工信息
select * from People where PeopleBirth >= '1980-1-1' and PeopleBirth<= '1989-12-31'
select * from People where PeopleBirth between '1980-1-1' and '1989-12-31'
select * from People where year(PeopleBirth) between 1980 and 1989 --year(PeopleBirth)把PeopleBirth的年份取出来
--查询30到40岁之间,并且工资在15000~30000之间的员工信息
select * from People where
year(getdate())-year(PeopleBirth) between 30 and 40
and
PeopleSalary between 15000 and 30000
--查询星座是巨蟹座的员工信息(6.22~7.22)
select * from People where
month(PeopleBirth)=1 and day(PeopleBirth) >= 22--如果是6月要大于22
or
month(PeopleBirth)= 7 and day(PeopleBirth) <= 22--如果是7月要小于22
--查询出工资比刘禅高的员工信息
select * from People where PeopleSalary >
(select PeopleSalary from People where PeopleName = '刘禅')
--查询出和刘禅在同一个城市的员工信息
select * from People where PeopleAddress >
(select PeopleAddress from People where PeopleName = '刘禅')
--查询出生肖是'鼠'的员工信息
--鼠、牛、虎、兔、龙、蛇、马、羊、猴、鸡、狗、猪
--4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 0 1 2 3
select * from People where year(PeopleBirth)%12=4
--查询所有的员工信息,添加一列,显示生肖
select *,
case
when year(PeopleBirth)%12=4 then '鼠'
when year(PeopleBirth)%12=5 then '牛'
when year(PeopleBirth)%12=6 then '虎'
when year(PeopleBirth)%12=7 then '兔'
when year(PeopleBirth)%12=8 then '龙'
when year(PeopleBirth)%12=9 then '蛇'
when year(PeopleBirth)%12=10 then '马'
when year(PeopleBirth)%12=11 then '羊'
when year(PeopleBirth)%12=0 then '猴'
when year(PeopleBirth)%12=1 then '鸡'
when year(PeopleBirth)%12=2 then '狗'
when year(PeopleBirth)%12=3 then '猪'
else ''
end 生肖
from People
--简化
select *,
case year(PeopleBirth)%12
when 4 then '鼠'
when 5 then '牛'
when 6 then '虎'
when 7 then '兔'
when 8 then '龙'
when 9 then '蛇'
when 10 then '马'
when 11 then '羊'
when 0 then '猴'
when 1 then '鸡'
when 2 then '狗'
when 3 then '猪'
else ''
end 生肖
from People
07-模糊查询
--模糊查询 like
/*
模糊查询使用like关键字和通配符结合来实现,通配符的具体含义如下:
% :代表匹0个字符,1个字符或者多个字符
_ :代表匹配有且只有1个字符
[] :代表匹配范围内
[^]:代表匹配不在范围内
*/
--(1)查询姓刘的员工信息
select * from People where PeopleName like '刘%'
--(2)查询名字中含有'尚'的员工信息
select * from People where PeopleName like '%尚%'
--(3)显示名字中含有'尚'或者'兰'的员工信息
select * from People where PeopleName like '%尚%' or PeopleName like '%兰%'
--(4)查询姓刘的员工,名字是2个字
select * from People where PeopleName like '刘_'
select SUBSTRING('hello word',3,4)
--SUBSTRING函数取字符串里的值,第一个参数代表要操作的字符,第二个参数代表从第几个字符串开始取,第三个参数代表取几个字符
select * from People where SUBSTRING(PeopleName,1,1)= '刘' and len(PeopleName) = 2
--(5)查询出名字最后一个字是'香',名字一共是三个字的员工信息
select * from People where PeopleName like '__香'
select * from People where SUBSTRING(PeopleName,3,1)= '香' and len(PeopleName) = 3
--(6)查询出电话号码开头为138的员工信息
select * from People where PeoplePhone like '138%'
--(7)查询出电话号码为192的,第4位是3或者8,最后一个号码是3的员工信息
select * from People where PeoplePhone like '1923%3' or PeoplePhone like '1928%3'
--(8)查询出电话号码为192的,第4位是2-5之间,最后一个号码不是5和6
select * from People where PeoplePhone like '192[2,3,4,5]%[^5,6]'
select * from People where PeoplePhone like '192[2-5]%[^5,6]'

08-聚集函数
SQL SERVER 中聚集函数主要有:
count:求数量
max:求最大值
min:求最小值
avg:求平均值
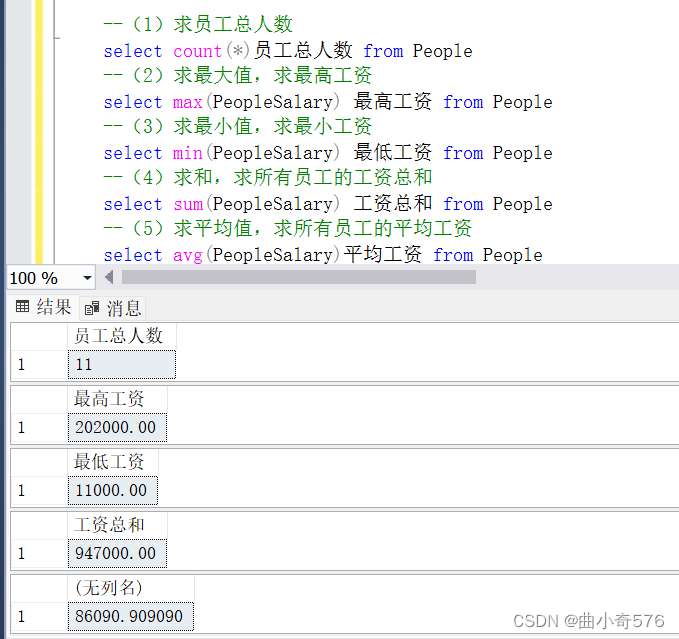
--(1)求员工总人数
select count(*)员工总人数 from People
--(2)求最大值,求最高工资
select max(PeopleSalary) 最高工资 from People
--(3)求最小值,求最小工资
select min(PeopleSalary) 最低工资 from People
--(4)求和,求所有员工的工资总和
select sum(PeopleSalary) 工资总和 from People
--(5)求平均值,求所有员工的平均工资
select avg(PeopleSalary)平均工资 from People
用AVG函数求所有员工的工资平均值
--(5)求平均值,求所有员工的平均工资
select avg(PeopleSalary)平均工资 from People
/*
select round(a,b,c) from 表名
round函数 a:要处理的数据 b:保留到小数点后b位 c:0就四舍五入,c是其他数字直接把后面的数值删掉
如果要四舍五入,第三个参数可以省略,因为ground默认是0。
*/
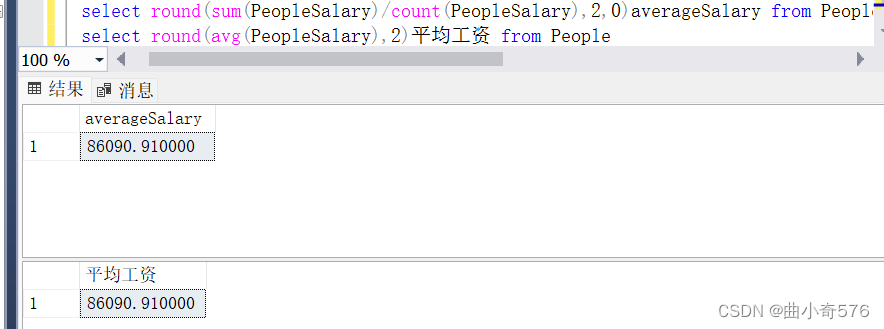
select round(sum(PeopleSalary)/count(PeopleSalary),2,0)averageSalary from People
select round(avg(PeopleSalary),2)平均工资 from People
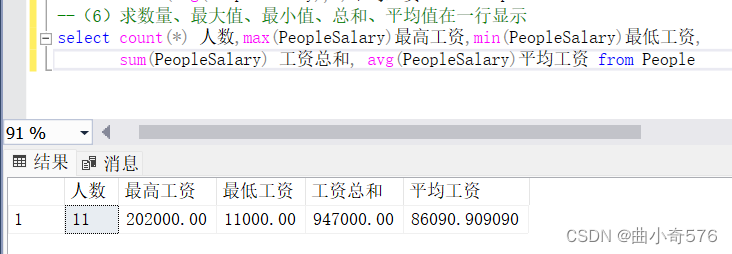
--(6)求数量、最大值、最小值、总和、平均值在一行显示
select count(*) 人数,max(PeopleSalary)最高工资,min(PeopleSalary)最低工资,
sum(PeopleSalary) 工资总和, avg(PeopleSalary)平均工资 from People
--在聚集函数的基础上加上条件查询
--(7)查询出保定地区的员工人数、总工资、最高工资、最低工资和平均工资
select count(*)员工人数,sum(PeopleSalary)总工资,max(PeopleSalary)最高工资,
min(PeopleSalary)最低工资,avg(PeopleSalary)平均工资
from People
where PeopleAddress = '保定'
--(8)求出工资比平均工资高的人员信息
select * from People where PeopleSalary >
(select round(avg(PeopleSalary),2) 平均工资
from People)

--(9)求数量,年龄最大值,年龄最小值,年龄总和,年龄平均值,在一行显示
select *,year(getdate())-year(PeopleBirth) 年龄 from People --①通过year()求年龄
select datediff(year,PeopleBirth,getdate()) from People --②通过datediff()求时间差datediff(a,b,c) a:结果的单位,有year、month、day 时间差=c-b
select Count(*) 数量,
Max(year(getdate())-year(PeopleBirth)) 年龄最大值,
Min(year(getdate())-year(PeopleBirth)) 年龄最小值,
sum(year(getdate())-year(PeopleBirth)) 年龄总和,
avg(year(getdate())-year(PeopleBirth)) 年龄平均值
from People
select Count(*) 数量,
Max(datediff(year,PeopleBirth,getdate())) 年龄最大值,
Min(datediff(year,PeopleBirth,getdate())) 年龄最小值,
sum(datediff(year,PeopleBirth,getdate())) 年龄总和,
avg(datediff(year,PeopleBirth,getdate())) 年龄平均值
from People

--聚集函数
/*
count:求数量
max:求最大值
min:求最小值
sum :求和
avg:求平均值
*/
--(1)求员工总人数
select count(*)员工总人数 from People
--(2)求最大值,求最高工资
select max(PeopleSalary) 最高工资 from People
--(3)求最小值,求最小工资
select min(PeopleSalary) 最低工资 from People
--(4)求和,求所有员工的工资总和
select sum(PeopleSalary) 工资总和 from People
--(5)求平均值,求所有员工的平均工资
select avg(PeopleSalary)平均工资 from People
/*
select round(a,b,c) from 表名
round函数 a:要处理的数据 b:保留到小数点后b位 c:0就四舍五入,c是其他数字直接把后面的数值删掉
如果要四舍五入,第三个参数可以省略,因为ground默认是0。
*/
select round(sum(PeopleSalary)/count(PeopleSalary),2,0)averageSalary from People
select round(avg(PeopleSalary),2)平均工资 from People
--(6)求数量、最大值、最小值、总和、平均值在一行显示
select count(*) 人数,max(PeopleSalary)最高工资,min(PeopleSalary)最低工资,
sum(PeopleSalary) 工资总和, avg(PeopleSalary)平均工资 from People
--在聚集函数的基础上加上条件查询
--(7)查询出保定地区的员工人数、总工资、最高工资、最低工资和平均工资
select count(*)员工人数,sum(PeopleSalary)总工资,max(PeopleSalary)最高工资,
min(PeopleSalary)最低工资,avg(PeopleSalary)平均工资
from People
where PeopleAddress = '保定'
--(8)求出工资比平均工资高的人员信息
select * from People where PeopleSalary >
(select round(avg(PeopleSalary),2)
from People)
--(9)求数量,年龄最大值,年龄最小值,年龄总和,年龄平均值,在一行显示
select *,year(getdate())-year(PeopleBirth) 年龄 from People --①通过year()求年龄
select datediff(year,PeopleBirth,getdate()) from People --②通过datediff()求时间差datediff(a,b,c) a:结果的单位,有year、month、day 时间差=c-b
--year()
select Count(*) 数量,
Max(year(getdate())-year(PeopleBirth)) 年龄最大值,
Min(year(getdate())-year(PeopleBirth)) 年龄最小值,
sum(year(getdate())-year(PeopleBirth)) 年龄总和,
avg(year(getdate())-year(PeopleBirth)) 年龄平均值
from People
--datediff()
select Count(*) 数量,
Max(datediff(year,PeopleBirth,getdate())) 年龄最大值,
Min(datediff(year,PeopleBirth,getdate())) 年龄最小值,
sum(datediff(year,PeopleBirth,getdate())) 年龄总和,
avg(datediff(year,PeopleBirth,getdate())) 年龄平均值
from People
--(10)计算出月薪在10000以上的男性员工的人数、最大年龄,最小年龄和平均年龄
select COUNT(*) 数量,
Max(datediff(year,PeopleBirth,getdate())) 年龄最大值,
Min(datediff(year,PeopleBirth,getdate())) 年龄最小值,
avg(datediff(year,PeopleBirth,getdate())) 年龄平均值
from People
where PeopleSalary >=10000 and PeopleSex = '男'
--(11)统计出所在地在'荆州'或在'安庆'的女员工的人数、最大年龄,最小年龄和平均年龄
select COUNT(*) 数量,
Max(datediff(year,PeopleBirth,getdate())) 年龄最大值,
Min(datediff(year,PeopleBirth,getdate())) 年龄最小值,
avg(datediff(year,PeopleBirth,getdate())) 年龄平均值
from People
where PeopleSex = '女' and PeopleAddress in('荆州','安庆')
--(12)求出年龄比平均年龄高的人员信息
select * from People where year(getdate()-year(PeopleBirth))>
(select avg(year(getdate())-year(PeopleBirth))from People)
09-分组查询
--分组查询
--(1)根据员工所在地区分组统计员工人数、员工工资总和、平均成绩、最高成绩和最低工资
--方案一:使用union,union是把多个查询结果进行合并 (不推荐:①代码多;②必须要找到有那些地区才可以查询,很繁琐)
--(此方案需要知道所有的地区,分别查询出所有地区的数据,然后使用union拼接起来。)
select '保定' 地区,count(*) 数量,MAX(PeopleSalary) 最高工资,MIN(PeopleSalary) 最低工资,SUM(PeopleSalary)工资总和,AVG(PeopleSalary) 平均工资
from People
where PeopleAddress = '保定' union
select '北京' 地区,count(*) 数量,MAX(PeopleSalary) 最高工资,MIN(PeopleSalary) 最低工资,SUM(PeopleSalary)工资总和,AVG(PeopleSalary) 平均工资
from People
where PeopleAddress = '北京'
--方案二:group by分组
select PeopleAddress 地区, count(*) 员工人数,MAX(PeopleSalary) 最高工资,MIN(PeopleSalary) 最低工资,SUM(PeopleSalary)工资总和,AVG(PeopleSalary) 平均工资
from People
group by PeopleAddress
--选择列表中的列只能是包含在聚集函数中的或者gruop by子句中,这里 PeopleName、PeopleId不可以加在选择列表里
--(2)根据员工所在地区分组统计员工人数,员工工资总和,平均工资,最高工资和最低工资,1985年及以后出生的员工不参与统计
select PeopleAddress 地区, count(*) 员工人数,MAX(PeopleSalary) 最高工资,MIN(PeopleSalary) 最低工资,SUM(PeopleSalary)工资总和,AVG(PeopleSalary) 平均工资
from People
where PeopleBirth < '1985-1-1'
group by PeopleAddress
--(3)根据根据员工所在地区分组统计员工人数,员工工资总和,平均工资,最高工资和最低工资,要求筛选出员工人数至少在2人以上的记录,并且1985年及以后出生的员工不参与统计
select PeopleAddress 地区, count(*) 员工人数,MAX(PeopleSalary) 最高工资,MIN(PeopleSalary) 最低工资,SUM(PeopleSalary)工资总和,AVG(PeopleSalary) 平均工资
from People
where PeopleBirth < '1985-1-1'--一般语句写在group by前面
group by PeopleAddress
having count(*)>=2 --聚合函数条件写在group by后面,用having语句

10-多表查询一
--多表查询
select * from Department
select * from People
--笛卡尔乘积
select * from People,Department
--查询结果将Department所有记录和People表所有记录依次排列组合形成新的表
--简单多表查询
--查询员工信息,显示部门名称
select * from People,Department
where People.DepartmentId=Department.DepartmentId
--查询员工信息,显示职级名称
select * from People,Rank1
where People.RankId=Rank1.RankId
--查询员工信息,显示部门名称和显示职级名称
select * from People,Department,Rank1
where People.DepartmentId=Department.DepartmentId
and People.RankId=Rank1.RankId
--内连接查询
--查询员工信息,显示部门名称
select * from People
inner join Department on People.DepartmentId=Department.DepartmentId
--查询员工信息,显示职级名称
select * from People
inner join Rank1 on People.RankId=Rank1.RankId
--查询员工信息,显示部门名称和显示职级名称
select * from People
inner join Department on People.DepartmentId=Department.DepartmentId
inner join Rank1 on People.RankId=Rank1.RankId
--简单多表查询和内连接共同的特点:不符合主外键关系的数据不会被显示出来
select * from People
select * from Department
insert into People(DepartmentId,RankId,PeopleName,PeopleSex,PeopleBirth,PeopleSalary,PeoplePhone,PeopleAddress,PeopleAddTime )
values (99,99,'张良','男','1975-8-9',8000,'13454432205','香港',getdate())
--这条语句是不能插入到People表里面的,因为不符合主外键关系,DepartmentId和RankId不存在99号
--外连接(左外连接、右外连接、全外连接)
--左外连接:以左表为主表进行数据的显示,主外键关系找不到的数据用null取代
--查询员工信息,显示部门名称
select * from People
left join Department on People.DepartmentId=Department.DepartmentId
--左连接 People在左边,显示所有的员工
--查询员工信息,显示职级名称
select * from People
left join Rank1 on People.RankId=Rank1.RankId
--查询员工信息,显示部门名称和显示职级名称
select * from People
left join Department on People.DepartmentId=Department.DepartmentId
left join Rank1 on People.RankId=Rank1.RankId
--右连:A left join B = B right join A
--下面两个查询含义相同
select * from People
left join Department on People.DepartmentId=Department.DepartmentId
select * from Department
right join People on People.DepartmentId=Department.DepartmentId
--右连接 People在右边,显示所有的员工信息
--全外连接:两张表的数据,无论是否符合关系,都要显示
select * from People
full join Department on People.DepartmentId=Department.DepartmentId
--所有的员工和所有的部门都要显示
11-多表查询二
欲知后事如何,且听下回分解。
持续更新......
版权归原作者 yosh'joy!! 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。
