文章目录
四个数据结构
dictEntry
dictEntry 的结构如下(Redis 7.0):
typedefstructdictEntry{void*key;// 键union{void*val;uint64_t u64;int64_t s64;double d;} v;// 值structdictEntry*next;/* Next entry in the same hash bucket.即下一个节点 */void*metadata[];/* An arbitrary number of bytes (starting at a
* pointer-aligned address) of size as returned
* by dictType's dictEntryMetadataBytes(). */} dictEntry;
可以对比 《Redis 设计与实现》中的 dictEntry 结构,发现联合结构 v 中多了一个 double 的浮点数表示,metadata 是一块任意长度的数据,具体的长度由 dictType 中的 dictEntryMetadataBytes() 返回,作用相当于 privdata
dictType
dictType 是一系列操作字典的键和值的操作:
typedefstructdictType{uint64_t(*hashFunction)(constvoid*key);// 哈希函数void*(*keyDup)(dict *d,constvoid*key);// 复制键的函数void*(*valDup)(dict *d,constvoid*obj);// 复制值的函数int(*keyCompare)(dict *d,constvoid*key1,constvoid*key2);// 键的比较void(*keyDestructor)(dict *d,void*key);// 键的销毁void(*valDestructor)(dict *d,void*obj);// 值的销毁int(*expandAllowed)(size_t moreMem,double usedRatio);// 字典里的哈希表是否允许扩容/* Allow a dictEntry to carry extra caller-defined metadata. The
* extra memory is initialized to 0 when a dictEntry is allocated. *//* 允许调用者向条目 (dictEntry) 中添加额外的元信息.
* 这段额外信息的内存会在条目分配时被零初始化. */size_t(*dictEntryMetadataBytes)(dict *d);} dictType;
该结构是为了实现字典的多态。
dict
7.0 版本的字典结构如下:
structdict{
dictType *type;
dictEntry **ht_table[2];unsignedlong ht_used[2];long rehashidx;/* rehashing not in progress if rehashidx == -1 *//* Keep small vars at end for optimal (minimal) struct padding */int16_t pauserehash;/* If >0 rehashing is paused (<0 indicates coding error) */signedchar ht_size_exp[2];/* exponent of size. (size = 1<<exp) */};
相比于 《Redis 设计与实现》中的字典实现,改动较大,7.0中去掉了 dictht 结构,即去掉了哈希结构。接下来介绍每个成员:
/* type 上面已经解释过了;
* ht_table 即哈希表数组
* ht_used 分别表示哈希表数组中各自已经存放键值对的个数
* rehashidx 是 rehash 时用的,没有 rehash 时值为1
* pauserehash 则是表示 rehash 的状态,大于0时表示 rehash 暂停了,小于0表示出错了
* ht_size_exp 则是表示两个哈希表数组的大小,通过 1 << ht_size_exp[0/1] 来计算
*/
我们可以看到一行注释:
/* Keep small vars at end for optimal (minimal) struct padding */
,将小变量放在结构体的后面,为了最佳或最小的填充,即节省空间。
dictIterator
dictIterator 是字典的迭代器
/* If safe is set to 1 this is a safe iterator, that means, you can call
* dictAdd, dictFind, and other functions against the dictionary even while
* iterating. Otherwise it is a non safe iterator, and only dictNext()
* should be called while iterating. */typedefstructdictIterator{
dict *d;long index;int table, safe;
dictEntry *entry,*nextEntry;/* unsafe iterator fingerprint for misuse detection. */unsignedlonglong fingerprint;} dictIterator;
解释其成员:
/* d 指向当前迭代的字典
* index 表示指向的键值对索引
* table 是哈希表的号码,ht[0]/ht[1]
* safe 表示该迭代器是否安全。安全时可以掉用 dictAdd,dictFind等等其他函数,不安全时只能调用 dictNext
* entry 指向迭代器所指的键值对,nextEntry 指向下一个键值对
* fingerprint 指纹, 用于检查不安全迭代器的误用
*/
常量与一系列宏
首先是关于哈希表初始化的两个常量:
/* This is the initial size of every hash table */#defineDICT_HT_INITIAL_EXP2#defineDICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE(1<<(DICT_HT_INITIAL_EXP))
很明显,哈希表的初始大小为 4
dictFreeVal
释放 val
#definedictFreeVal(d, entry)\if((d)->type->valDestructor)\(d)->type->valDestructor((d),(entry)->v.val)
调用 dictType 中提供的 valDestructor 函数释放 val
dictSetVal
设置 val 的值
#definedictSetVal(d, entry, _val_)do{\if((d)->type->valDup)\(entry)->v.val =(d)->type->valDup((d), _val_);\else\(entry)->v.val =(_val_);\}while(0)
如果 dictType 提供了设置 val 值的方法则调用,没有则直接赋值
dictSetSignedIntegerVal
设置有符号的整型 val 值
#definedictSetSignedIntegerVal(entry, _val_)\do{(entry)->v.s64 = _val_;}while(0)
当然还有设置 无符号的整型值、double 值
dictFreeKey
释放 key
#definedictFreeKey(d, entry)\if((d)->type->keyDestructor)\(d)->type->keyDestructor((d),(entry)->key)
dictSetKey
设置 key 的值
#definedictSetKey(d, entry, _key_)do{\if((d)->type->keyDup)\(entry)->key =(d)->type->keyDup((d), _key_);\else\(entry)->key =(_key_);\}while(0)
dictCompareKeys
key 的比较
#definedictCompareKeys(d, key1, key2)\(((d)->type->keyCompare)?\(d)->type->keyCompare((d), key1, key2):\(key1)==(key2))
如果 dictType 中的 keyCompare 指针不为空,则调用它进行比较,否则直接用
==
比较
dictMetadata
获取用户提供的元数据
#definedictMetadata(entry)(&(entry)->metadata)
dictMetadataSize
获取用户提供的元数据的长度
#definedictMetadataSize(d)((d)->type->dictEntryMetadataBytes \?(d)->type->dictEntryMetadataBytes(d):0)
获取 key 和 val 的宏
#definedictHashKey(d, key)(d)->type->hashFunction(key)// 获取 key 的哈希值#definedictGetKey(he)((he)->key)#definedictGetVal(he)((he)->v.val)#definedictGetSignedIntegerVal(he)((he)->v.s64)#definedictGetUnsignedIntegerVal(he)((he)->v.u64)#definedictGetDoubleVal(he)((he)->v.d)
关于哈希表大小的宏
// 获取哈希表的大小#defineDICTHT_SIZE(exp)((exp)==-1?0:(unsignedlong)1<<(exp))// 哈希表的掩码(size - 1)#defineDICTHT_SIZE_MASK(exp)((exp)==-1?0:(DICTHT_SIZE(exp))-1)
dictSlots
// 获取字典的总大小#definedictSlots(d)(DICTHT_SIZE((d)->ht_size_exp[0])+DICTHT_SIZE((d)->ht_size_exp[1]))
dictSize
// 获取字典保存键值对的总数#definedictSize(d)((d)->ht_used[0]+(d)->ht_used[1])
关于 rehash 的宏
// 判断当前是否在 rehash#definedictIsRehashing(d)((d)->rehashidx !=-1)// 暂停 rehash#definedictPauseRehashing(d)(d)->pauserehash++// 恢复 rehash#definedictResumeRehashing(d)(d)->pauserehash--
创建/销毁/修改字典
创建字典
创建字典的接口是 dictCreate
dictCreate 为字典结构分配空间,并调用 _dictInit 进行初始化
在 _dictinit 中,又调用了 _dicrReset 进行成员设置
/* Create a new hash table */
dict *dictCreate(dictType *type){
dict *d =zmalloc(sizeof(*d));_dictInit(d,type);return d;}/* Initialize the hash table */int_dictInit(dict *d, dictType *type){_dictReset(d,0);_dictReset(d,1);
d->type = type;
d->rehashidx =-1;
d->pauserehash =0;return DICT_OK;}/* Reset hash table parameters already initialized with _dictInit()*/staticvoid_dictReset(dict *d,int htidx){
d->ht_table[htidx]=NULL;
d->ht_size_exp[htidx]=-1;
d->ht_used[htidx]=0;}
在 _dictInit 中有一个宏 DICT_OK,它的定义为:
#defineDICT_OK0#defineDICT_ERR1
用来标识操作是否成功完成
修改字典
一般修改字典都是为 rehash 做准备,或者扩大容量或者缩小容量。
dictResize
缩小字典大小,前提是当前没有在进行 rehash 以及 dict_can_resize 变量不为 0
dict_can_resize 是 dict.c 中定义的一个全局变量,用来指示 resize 能否进行
staticint dict_can_resize =1;
什么时候 dict_can_resize 会为0呢?
当 redis 在后台进行持久化时, 为了最大化地利用系统的 copy on write 机制,会暂时地将 dict_can_resize 设置为0,避免执行自然 rehash,从而减少程序对内存的碰撞。持久化任务完成后,dict_can_resize 又会设置为1
/* Resize the table to the minimal size that contains all the elements,
* but with the invariant of a USED/BUCKETS ratio near to <= 1 */intdictResize(dict *d){unsignedlong minimal;if(!dict_can_resize ||dictIsRehashing(d))return DICT_ERR;
minimal = d->ht_used[0];if(minimal < DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE)
minimal = DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE;returndictExpand(d, minimal);}
缩小哈希表的大小,新的容量刚好能容纳已有元素。minimal 等于已有元素的数量,然后在 _dictExpand 中,会将新容量的大小设置为刚好大于等于 minimal 的 2 的幂。
dictExpand
再来看 dictExpand,调用 _dictExpand 进行实际的扩容。
/* return DICT_ERR if expand was not performed */intdictExpand(dict *d,unsignedlong size){return_dictExpand(d, size,NULL);}/* Expand or create the hash table,
* when malloc_failed is non-NULL, it'll avoid panic if malloc fails (in which case it'll be set to 1).
* Returns DICT_OK if expand was performed, and DICT_ERR if skipped. */int_dictExpand(dict *d,unsignedlong size,int* malloc_failed){if(malloc_failed)*malloc_failed =0;/* the size is invalid if it is smaller than the number of
* elements already inside the hash table */if(dictIsRehashing(d)|| d->ht_used[0]> size)return DICT_ERR;/* the new hash table */
dictEntry **new_ht_table;unsignedlong new_ht_used;signedchar new_ht_size_exp =_dictNextExp(size);/* Detect overflows */size_t newsize =1ul<<new_ht_size_exp;if(newsize < size || newsize *sizeof(dictEntry*)< newsize)return DICT_ERR;/* Rehashing to the same table size is not useful. */if(new_ht_size_exp == d->ht_size_exp[0])return DICT_ERR;/* Allocate the new hash table and initialize all pointers to NULL */if(malloc_failed){
new_ht_table =ztrycalloc(newsize*sizeof(dictEntry*));*malloc_failed = new_ht_table ==NULL;if(*malloc_failed)return DICT_ERR;}else
new_ht_table =zcalloc(newsize*sizeof(dictEntry*));
new_ht_used =0;/* Is this the first initialization? If so it's not really a rehashing
* we just set the first hash table so that it can accept keys. */if(d->ht_table[0]==NULL){
d->ht_size_exp[0]= new_ht_size_exp;
d->ht_used[0]= new_ht_used;
d->ht_table[0]= new_ht_table;return DICT_OK;}/* Prepare a second hash table for incremental rehashing */
d->ht_size_exp[1]= new_ht_size_exp;
d->ht_used[1]= new_ht_used;
d->ht_table[1]= new_ht_table;
d->rehashidx =0;return DICT_OK;}
_dictExpand 函数不是只为了 rehash,还可以初始化字典。 _dictExpand 函数判断是否是 rehash 是通过判断 ht_table[0] 是否为空来判断的。也就是说如果调用 _dictExpand 的字典是非空的,则增容后的哈希表是放在 ht_table[1] 中的,所以需要调用者手动释放 ht_table[0],将 ht_table[1] 放到 ht_table[0] 位置上。
Rehash
rehash 扩容分为两种:
- 自然 rehash:used / size >= 1 时且
dict_can_resize为1 - 强制 rehash:used / size >
dict_force_resize_ratio该版本中dict_force_resize_ratio的值为5
另外,当哈希表的负载因子小于 0.1 时,程序自动开始对哈希表执行收缩操作。
Rehash 过程:创建一个新的哈希表 ht[1],rehashidx 变成0,根据 rehashidx 指向的桶进行数据的迁移。当所有数据迁移完毕时,释放 ht[0],将 ht[1] 迁移到 ht[0],ht[1] 置为空。
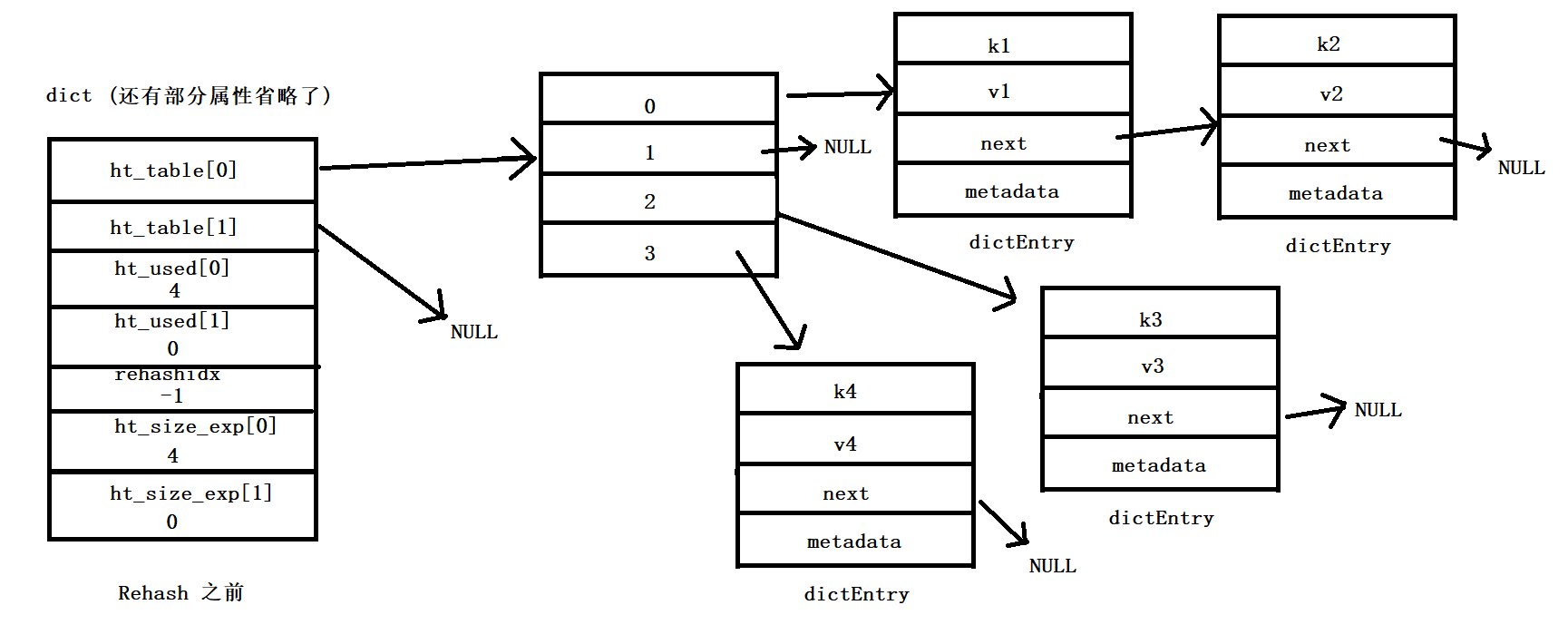
下面是 Rehash 的一个简单示例:
Rehash 之前:
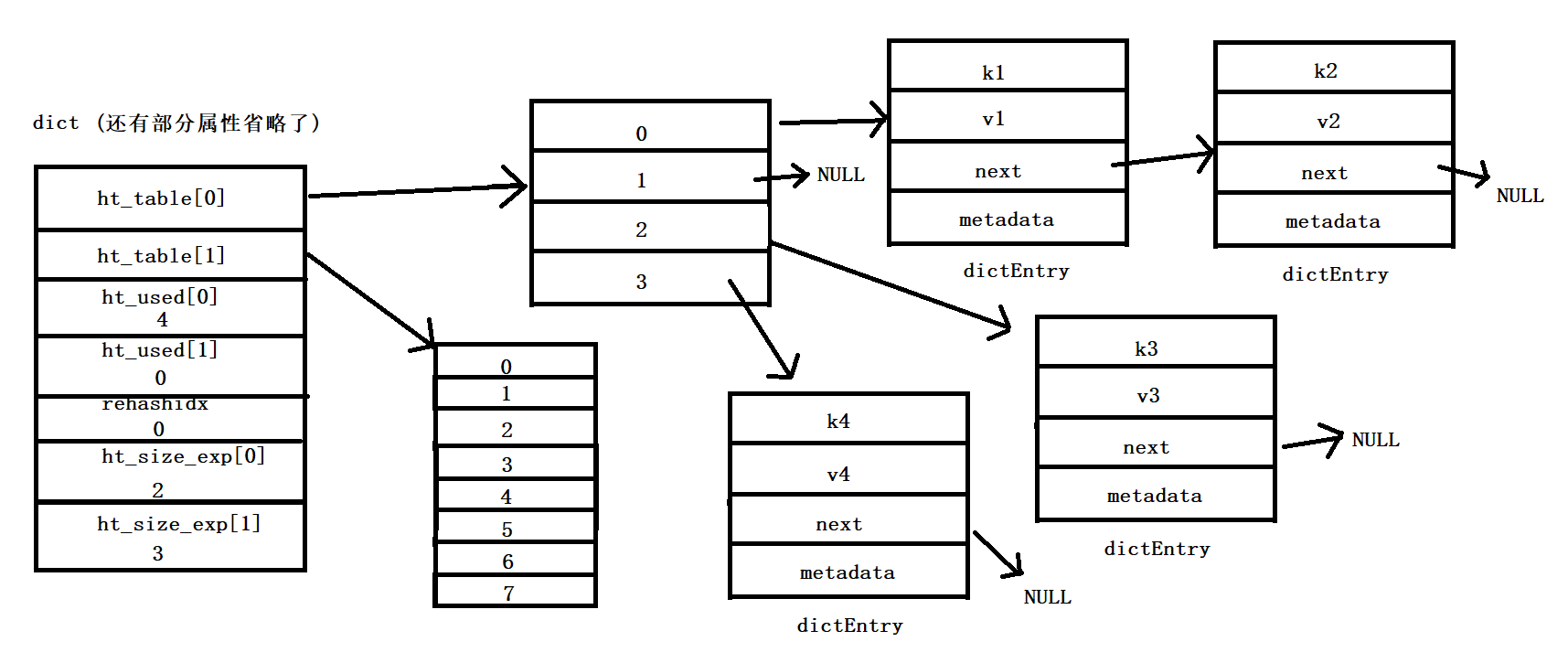
Rehash 开始:
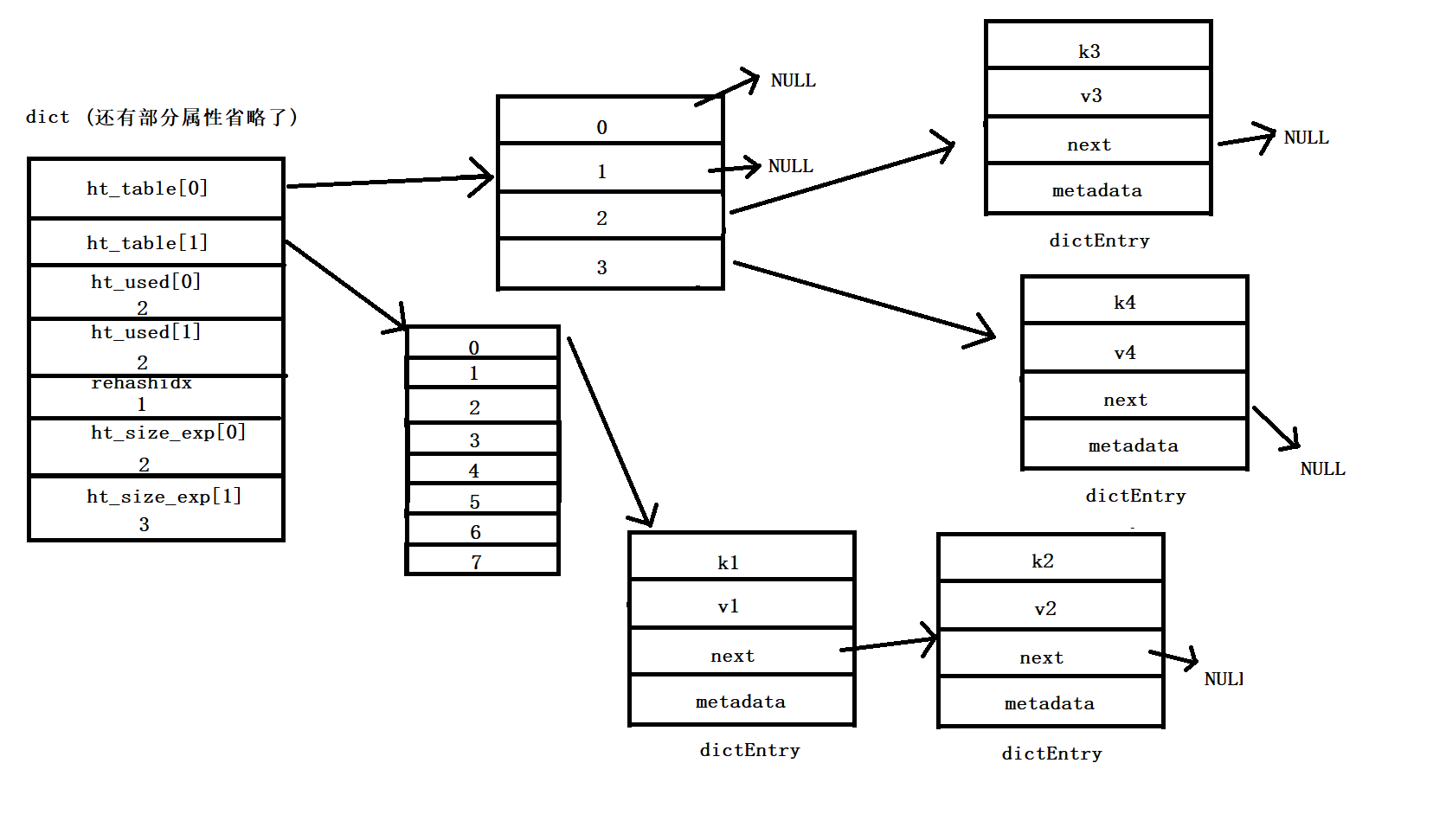
所有元素重新映射到 ht_table[1] :
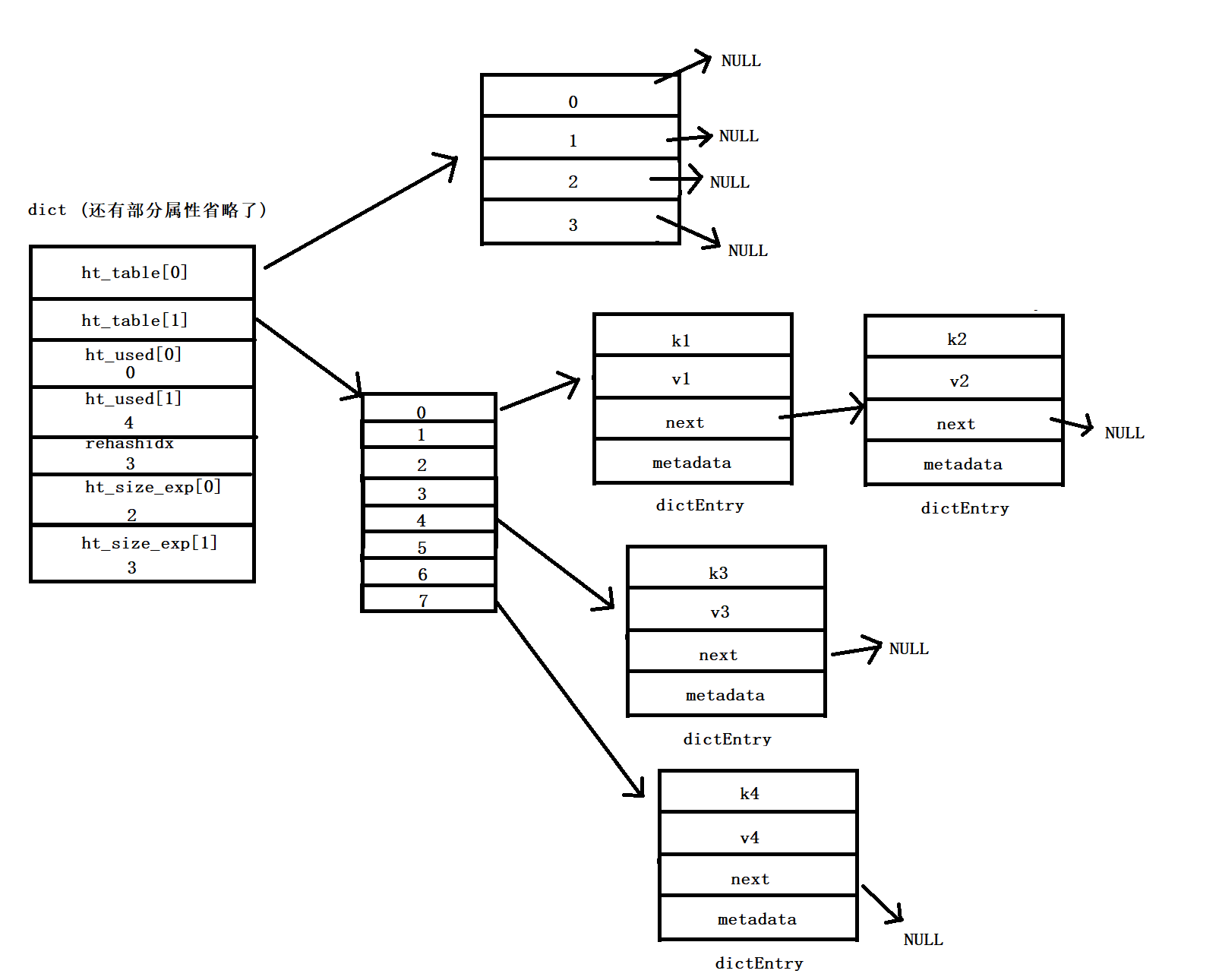
表的转移,完成 Rehash:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-oOmONTWE-1652675352252)(C:\Users\晏思俊\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20220516122546788.png)]
Rehash 不是一步就完成的,否则数据量特别大时,迁移数据会是一个很大的工程,可能会导致服务器暂停服务来迁移数据,Rehash 是渐进式的,数据的迁移发生在对数据的增删改查时,这样就将迁移平摊在每个增删改查的操作上。
如果在 rehash 期间要执行添加键的操作,都是在 ht[1] 中进行的,而进行删改查等操作,会同时在两张表中进行。
每次 rehash 都是以 n 个桶为单位的,将每个桶上的链都移到新的哈希表上。一次 rehash 完成以后,如果之后还有桶要 rehash,则返回1,如果 rehash 完成,则返回0。但是实际上,rehashidx 指向的桶可能是空桶,所以为了效率,一次 rehash 最多要遍历 10*n 个空桶,遍历完了 10 * n 个空桶就会返回。
intdictRehash(dict *d,int n){int empty_visits = n*10;/* Max number of empty buckets to visit. */if(!dictIsRehashing(d))return0;while(n--&& d->ht_used[0]!=0){
dictEntry *de,*nextde;/* Note that rehashidx can't overflow as we are sure there are more
* elements because ht[0].used != 0 */assert(DICTHT_SIZE(d->ht_size_exp[0])>(unsignedlong)d->rehashidx);while(d->ht_table[0][d->rehashidx]==NULL){
d->rehashidx++;if(--empty_visits ==0)return1;}
de = d->ht_table[0][d->rehashidx];/* Move all the keys in this bucket from the old to the new hash HT */while(de){uint64_t h;
nextde = de->next;/* Get the index in the new hash table */
h =dictHashKey(d, de->key)&DICTHT_SIZE_MASK(d->ht_size_exp[1]);
de->next = d->ht_table[1][h];
d->ht_table[1][h]= de;
d->ht_used[0]--;
d->ht_used[1]++;
de = nextde;}
d->ht_table[0][d->rehashidx]=NULL;
d->rehashidx++;}/* Check if we already rehashed the whole table... */if(d->ht_used[0]==0){zfree(d->ht_table[0]);/* Copy the new ht onto the old one */
d->ht_table[0]= d->ht_table[1];
d->ht_used[0]= d->ht_used[1];
d->ht_size_exp[0]= d->ht_size_exp[1];_dictReset(d,1);
d->rehashidx =-1;return0;}/* More to rehash... */return1;}
销毁字典
销毁字典的接口是dictRelease
dictRelease 调用_dictClear 来释放两个哈希表,并最后释放字典空间
/* Destroy an entire dictionary */int_dictClear(dict *d,int htidx,void(callback)(dict*)){unsignedlong i;/* Free all the elements */for(i =0; i <DICTHT_SIZE(d->ht_size_exp[htidx])&& d->ht_used[htidx]>0; i++){
dictEntry *he,*nextHe;if(callback &&(i &65535)==0)callback(d);if((he = d->ht_table[htidx][i])==NULL)continue;while(he){
nextHe = he->next;dictFreeKey(d, he);dictFreeVal(d, he);zfree(he);
d->ht_used[htidx]--;
he = nextHe;}}/* Free the table and the allocated cache structure */zfree(d->ht_table[htidx]);/* Re-initialize the table */_dictReset(d, htidx);return DICT_OK;/* never fails */}/* Clear & Release the hash table */voiddictRelease(dict *d){_dictClear(d,0,NULL);_dictClear(d,1,NULL);zfree(d);}
_dictClear 的第三个参数是一个函数指针,但 dictRelease 在这里都传了空指针,所以暂且不管。 _dictClear 遍历所有的索引,当该索引上有键值对时,则释放该索引上的整条链表。释放完所有键值对之后,再释放该哈希表并重置其成员。
键的操作
dictAdd
添加一个键值对到指定哈希表中
/* Add an element to the target hash table */intdictAdd(dict *d,void*key,void*val){
dictEntry *entry =dictAddRaw(d,key,NULL);if(!entry)return DICT_ERR;dictSetVal(d, entry, val);return DICT_OK;}
该函数调用了 dictAddRaw 函数,下面是 dictAddRaw 函数的定义:
/* Low level add or find:
* This function adds the entry but instead of setting a value returns the
* dictEntry structure to the user, that will make sure to fill the value
* field as they wish.
*
* This function is also directly exposed to the user API to be called
* mainly in order to store non-pointers inside the hash value, example:
*
* entry = dictAddRaw(dict,mykey,NULL);
* if (entry != NULL) dictSetSignedIntegerVal(entry,1000);
*
* Return values:
*
* If key already exists NULL is returned, and "*existing" is populated
* with the existing entry if existing is not NULL.
*
* If key was added, the hash entry is returned to be manipulated by the caller.
*/
dictEntry *dictAddRaw(dict *d,void*key, dictEntry **existing){long index;
dictEntry *entry;int htidx;if(dictIsRehashing(d))_dictRehashStep(d);/* Get the index of the new element, or -1 if
* the element already exists. */if((index =_dictKeyIndex(d, key,dictHashKey(d,key), existing))==-1)returnNULL;/* Allocate the memory and store the new entry.
* Insert the element in top, with the assumption that in a database
* system it is more likely that recently added entries are accessed
* more frequently. */
htidx =dictIsRehashing(d)?1:0;size_t metasize =dictMetadataSize(d);
entry =zmalloc(sizeof(*entry)+ metasize);if(metasize >0){memset(dictMetadata(entry),0, metasize);}
entry->next = d->ht_table[htidx][index];
d->ht_table[htidx][index]= entry;
d->ht_used[htidx]++;/* Set the hash entry fields. */dictSetKey(d, entry, key);return entry;}
该函数上面有一串注释,意思是:该函数添加一个 dictEntry 到哈希表中,但并不会设置值,将该结构返回给用户,将值的设置交给用户。 这个函数也直接暴露给要调用的用户API,主要是为了在哈希值内部存储非指针。
返回值:如果键已经存在,则返回 NULL,并填充“*existing” 如果 existing 不为 NULL,则使用现有条目。如果成功添加了键,则返回哈希条目(dictEntry)以供调用者操作
我们分析函数的一个实现细节:可以看到函数首先会判断当前的哈希表是否在 rehash,如果在 rehash,则进行一次只迁移一个桶的 rehash。
_dictRehashStep
是完成一次只迁移一个桶的 rehash。
所以现在我们就知道。dictAdd 调用 dictAddRaw,获取一个已插入的 dictEntry,然后完成值的设置。
在该函数中还调用了
_dictKeyIndex
函数,该函数实现如下:
函数返回 key 在哈希表中的索引,如果哈希表中存在该 key,则返回 -1,可选的输出参数 existing 会被填充成对应的 dictEntry。
需要注意的是,如果当前哈希表正在 rehash,则返回的索引始终是第二张哈希表的索引。
staticlong_dictKeyIndex(dict *d,constvoid*key,uint64_t hash, dictEntry **existing){unsignedlong idx, table;
dictEntry *he;if(existing)*existing =NULL;/* Expand the hash table if needed */if(_dictExpandIfNeeded(d)== DICT_ERR)return-1;for(table =0; table <=1; table++){
idx = hash &DICTHT_SIZE_MASK(d->ht_size_exp[table]);/* Search if this slot does not already contain the given key */
he = d->ht_table[table][idx];while(he){if(key==he->key ||dictCompareKeys(d, key, he->key)){if(existing)*existing = he;return-1;}
he = he->next;}if(!dictIsRehashing(d))break;}return idx;}
dictReplace
如果 key 不存在,则添加 key,并设置 value,函数返回1。如果 key 已经存在,则更新 value 值,函数返回0
intdictReplace(dict *d,void*key,void*val){
dictEntry *entry,*existing, auxentry;/* Try to add the element. If the key
* does not exists dictAdd will succeed. */
entry =dictAddRaw(d,key,&existing);if(entry){dictSetVal(d, entry, val);return1;}/* Set the new value and free the old one. Note that it is important
* to do that in this order, as the value may just be exactly the same
* as the previous one. In this context, think to reference counting,
* you want to increment (set), and then decrement (free), and not the
* reverse. */
auxentry =*existing;dictSetVal(d, existing, val);dictFreeVal(d,&auxentry);return0;}
首先调用 dictAddRaw 函数,根据返回值判断 key 是否已经在哈希表中,如果不存在,则 entry 不为空,设置 val 值并返回1。如果 entry 为空,则进行值的更新。但要遵循先设置新值再释放旧值的顺序。因为新值和旧值可能相同,这种情况就需要考虑引用计数,我们应该先增加计数,再减少计数。
dictAddOrFind
该函数总是返回一个 指定key 的 dictEntry。如果 key 已经存在,则将其 dictEntry 返回;如果不存在,则将其添加并返回。
dictEntry *dictAddOrFind(dict *d,void*key){
dictEntry *entry,*existing;
entry =dictAddRaw(d,key,&existing);return entry ? entry : existing;}
dictDelete
删除元素
/* Remove an element, returning DICT_OK on success or DICT_ERR if the
* element was not found. */intdictDelete(dict *ht,constvoid*key){returndictGenericDelete(ht,key,0)? DICT_OK : DICT_ERR;}
dictDelete
通过
dictGenericDelete
来删除哈希表中的元素。
如果没找到要删除的元素则返回 NULL,找到了则返回已经释放的 dictEntry。
/* Search and remove an element. This is a helper function for
* dictDelete() and dictUnlink(), please check the top comment
* of those functions. */static dictEntry *dictGenericDelete(dict *d,constvoid*key,int nofree){uint64_t h, idx;
dictEntry *he,*prevHe;int table;/* dict is empty */if(dictSize(d)==0)returnNULL;if(dictIsRehashing(d))_dictRehashStep(d);
h =dictHashKey(d, key);for(table =0; table <=1; table++){
idx = h &DICTHT_SIZE_MASK(d->ht_size_exp[table]);
he = d->ht_table[table][idx];
prevHe =NULL;while(he){if(key==he->key ||dictCompareKeys(d, key, he->key)){/* Unlink the element from the list */if(prevHe)
prevHe->next = he->next;else
d->ht_table[table][idx]= he->next;if(!nofree){dictFreeUnlinkedEntry(d, he);}
d->ht_used[table]--;return he;}
prevHe = he;
he = he->next;}if(!dictIsRehashing(d))break;}returnNULL;/* not found */}
dictUnlink
与
dictFreeUnlinkedEntry
dictUnlink
函数是从哈希表中删除 key,但 key,value 和 dictEntry 并没有被释放,需要调用
dictFreeUnlinkedEntry
函数来释放这些资源。如果 key 在哈希表中找到了,则返回对应的 dictEntry,如果没找到则返回 NULL
dictEntry *dictUnlink(dict *d,constvoid*key){returndictGenericDelete(d,key,1);}
/* You need to call this function to really free the entry after a call
* to dictUnlink(). It's safe to call this function with 'he' = NULL. */voiddictFreeUnlinkedEntry(dict *d, dictEntry *he){if(he ==NULL)return;dictFreeKey(d, he);dictFreeVal(d, he);zfree(he);}
dictFind
查找 key,找到了返回其 dictEntry;否则返回 NULL
dictEntry *dictFind(dict *d,constvoid*key){
dictEntry *he;uint64_t h, idx, table;if(dictSize(d)==0)returnNULL;/* dict is empty */if(dictIsRehashing(d))_dictRehashStep(d);
h =dictHashKey(d, key);for(table =0; table <=1; table++){
idx = h &DICTHT_SIZE_MASK(d->ht_size_exp[table]);
he = d->ht_table[table][idx];while(he){if(key==he->key ||dictCompareKeys(d, key, he->key))return he;
he = he->next;}if(!dictIsRehashing(d))returnNULL;}returnNULL;}
版权归原作者 WoLannnnn 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。