Clicknium 是一个Python UI自动化库,主要用来自动化Windows桌面应用和网页应用。由于Clicknium没中文文档, 本文将系统的介绍一下Clicknium的使用方法。
1、基本概念
Clicknium通过录制鼠标点击UI元素,自动生成Locator,其中存储了该UI元素的各种属性,使Clicknium可以通过locator重新定位到对应的UI元素。 定位到UI元素后,Clicknium提供了各种常见的操作UI的方法,比如输入(set_text)、鼠标点击(Click)等,就能轻松完成UI自动化脚本。
Clicknium开发套件
Clicknium Python SDK是Clicknium的自动化核心, 围绕这一核心,Clicknium还提供了一系列插件协助开发自动化脚本:
- Clicknium VS Code 插件:管理、调试locator,提供Python代码补全和智能提示。
- Clicknium 浏览器插件:加强网页自动化能力,支持Chrome、Firefox、Edge、Brave、Vivaldi。
- Clicknium Recorder:支持录制UI元素,生成locator。
Clicknium Python SDK 可通过pip install clicknium安装。 在VS Code 中搜索Clicknium安装拓展后,可以在拓展中管理Clicknium的各种插件和SDK的安装和升级。
2. 开发环境配置
需在Windows环境下:
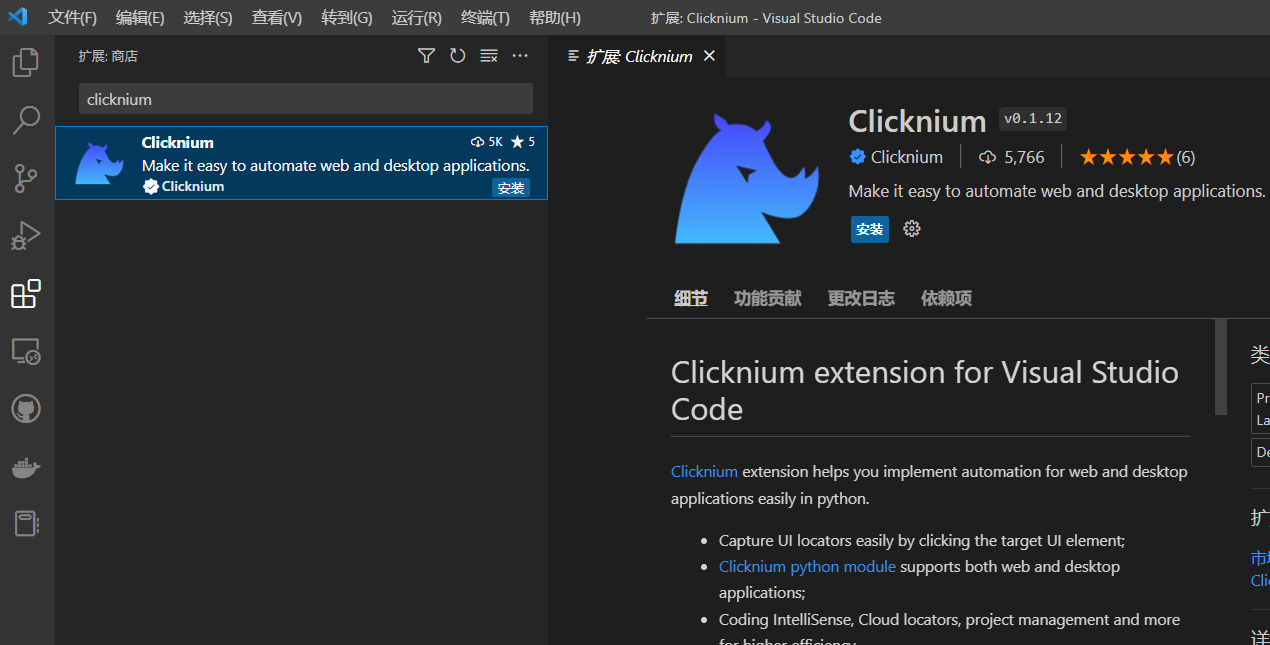
在VS Code 扩展中搜索Clicknium并安装:
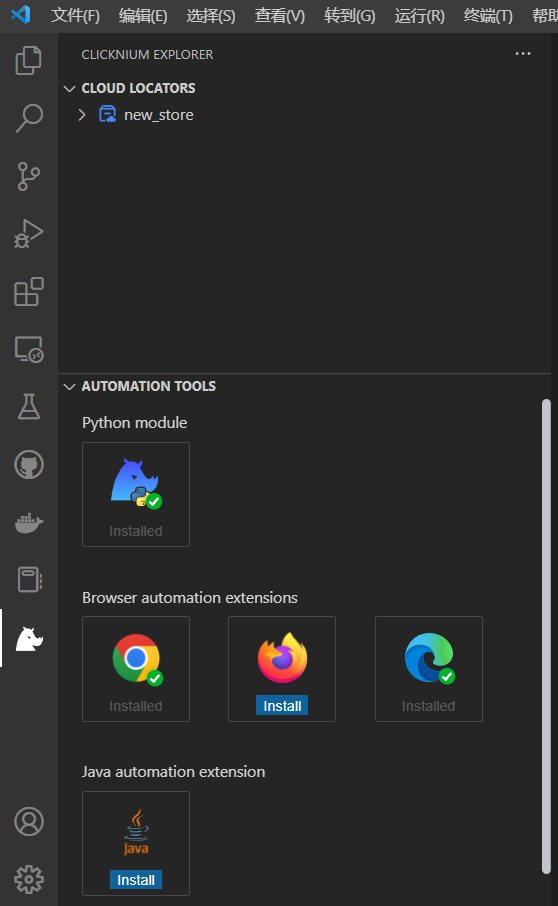
在Clicknium explorer中安装Python module和需要的插件:
Python module也可通过:pip install clicknium安装。 安装较慢的同学,可以将pypi切换为清华源
3.自动化脚本开发流程
3.1 sample脚本
首先看一下示例的sample。打开VS Code,Ctrl+shift+P输入Clicknium: Sample 然后选择一个新建一个空目录用来存放sample project。
这时候我们得到了下面的sample project,按F5运行,Ctrl+F5调试。
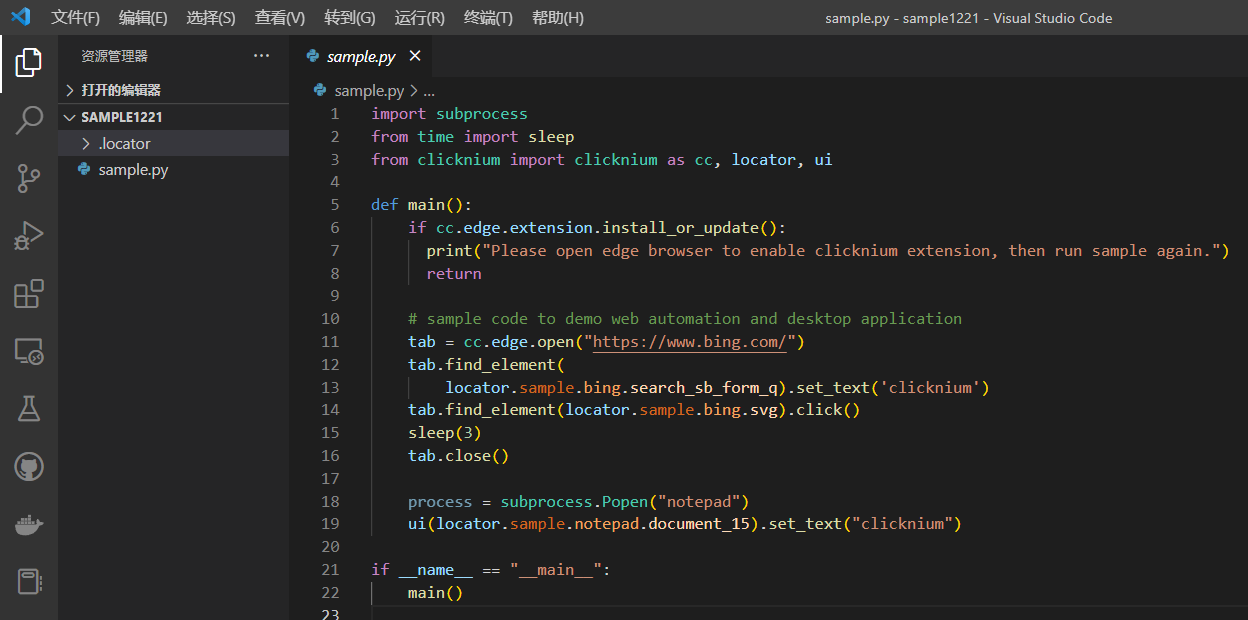
sample project目录结构:
/.locator locator信息
/.locator/sample_img是locator的快照
/.locator/sample.cnstore是locator store里面存放这locator的属性
代码分析:
- 第一部分:安装浏览器插件
if cc.edge.extension.install_or_update():
print("Please open edge browser to enable clicknium extension, then run sample again.")
很好理解自动安装edge浏览器的插件。自动化浏览器需要安装对应的浏览器插件。
- 第二部分:网页自动化,自动打开浏览器,进入bing搜索,在输入框中输入clicknium并点击搜索按钮。
tab = cc.edge.open("https://www.bing.com/")
tab.find_element(locator.sample.bing.search_sb_form_q).set_text('clicknium')
tab.find_element(locator.sample.bing.svg).click()
sleep(3)
tab.close()
第一行:利用clicknium调用edge浏览器打开bing首页,返回对应浏览器tab。
第二行:在tab内调用find_element,在参数中传入输入框locator,调用set_text API传入文本信息。
第三行:在tab内调用find_element,在参数中传入搜索按钮的locator,调用click函数。
第四、五行:等待3秒钟,关闭对应的tab。
通过这部分代码,可以大致理解clicknium的逻辑。 Clicknium提供了诸如find_element等函数,接受locator参数获取到UI元素。同时提供了一些操作UI的通用方法,比如set_text, click等来模拟人工操作。
- 第三部分:Windows桌面端自动化。打开记事本(notepad),并输入clicknium
process = subprocess.Popen("notepad")
ui(locator.sample.notepad.document_15).set_text("clicknium")
接口与网页端自动化类似。
- Clicknium的核心,Locator:
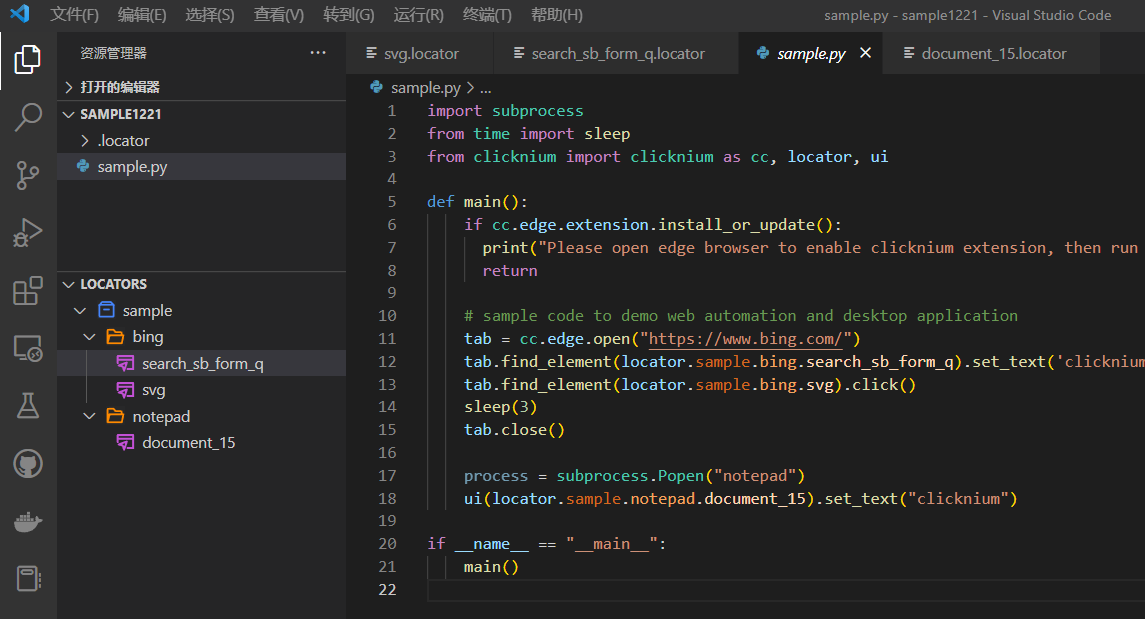
因为sample中没有录制的过程, 你可能不知道locator为什么要这么写。 在上图中, VS Code 左下方有一个Locator tab下。
3.2 从0开发自己的自动化脚本
从0开始用Chrome浏览器搜索Clicknium网站,自动注册一个账号。
- 创建项目
创建一个文件夹ClickniumSample来存放Python Project,用VS Code打开文件夹,并创建Python文件Sample.py。
打开百度的首页,创建第一个locator搜索框。
进入VS Code,在LOCATOR旁边找到Capture按钮,启动Clicknium Recorder。
打开Clicknium官网The best python automation module | Clicknium
按住Ctrl +鼠标点击Sign Up按钮:
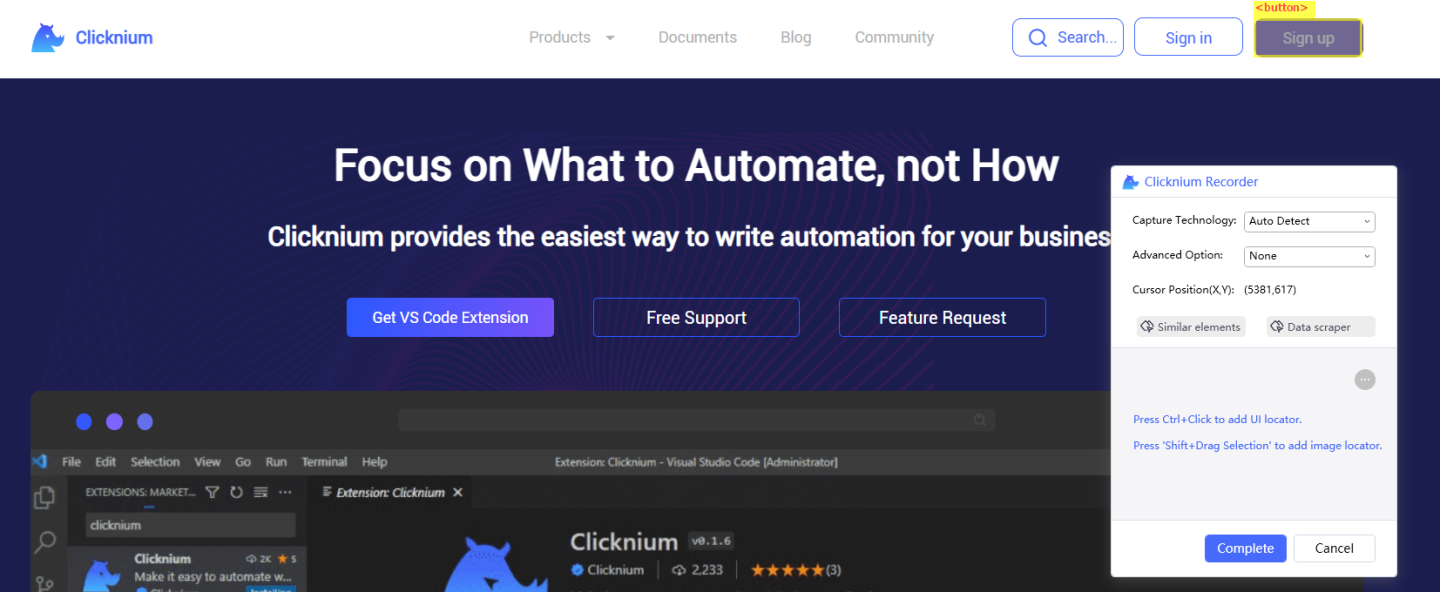
成功后就获得了注册按钮的locator.
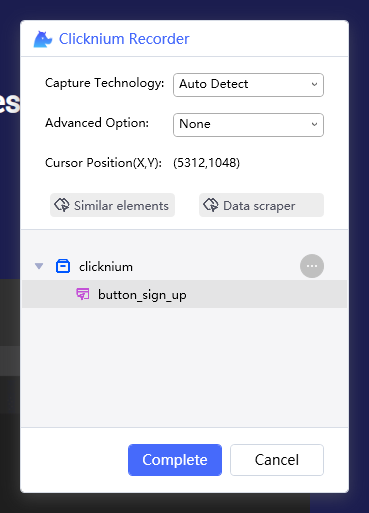
locator可以用文件夹的形式整理,也可以自己重命名。结构类似namespace的形式,所以locator的名字中不能出现空格等特殊字符。
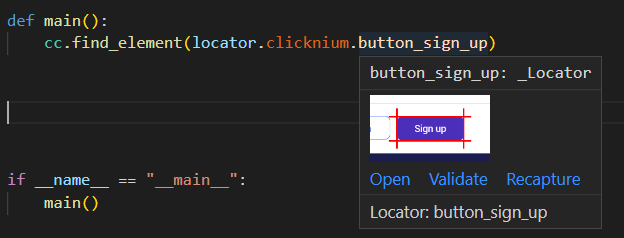
生成locator后,我们可以用方法find_element定位到Locator对应的UI元素。 在输入locator.后会有智能提示:
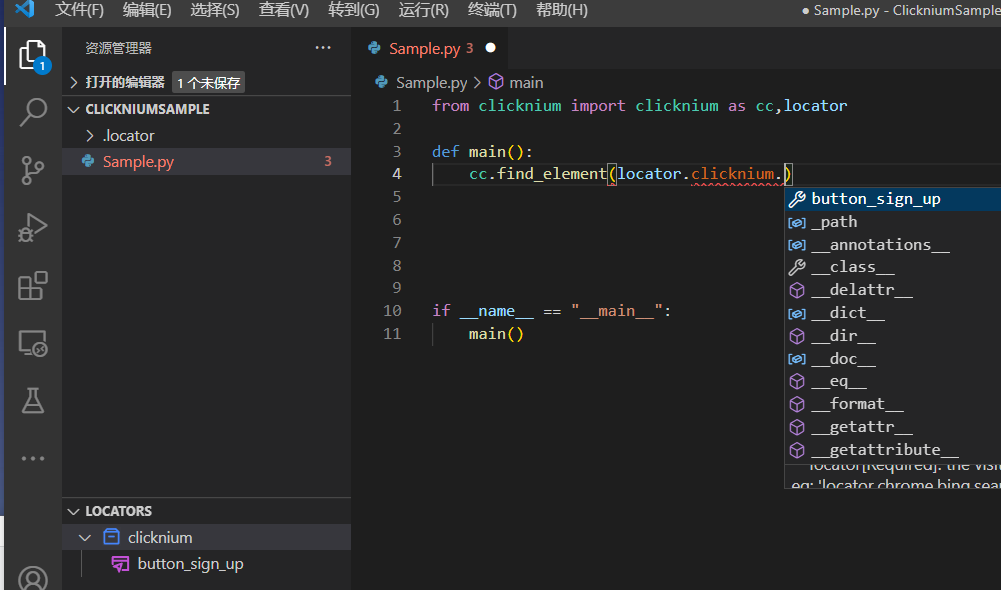
当鼠标放置在locator上时,会有locator快照出现,帮你辨认locator对应的UI元素,同时也可以做验证和重新录制。
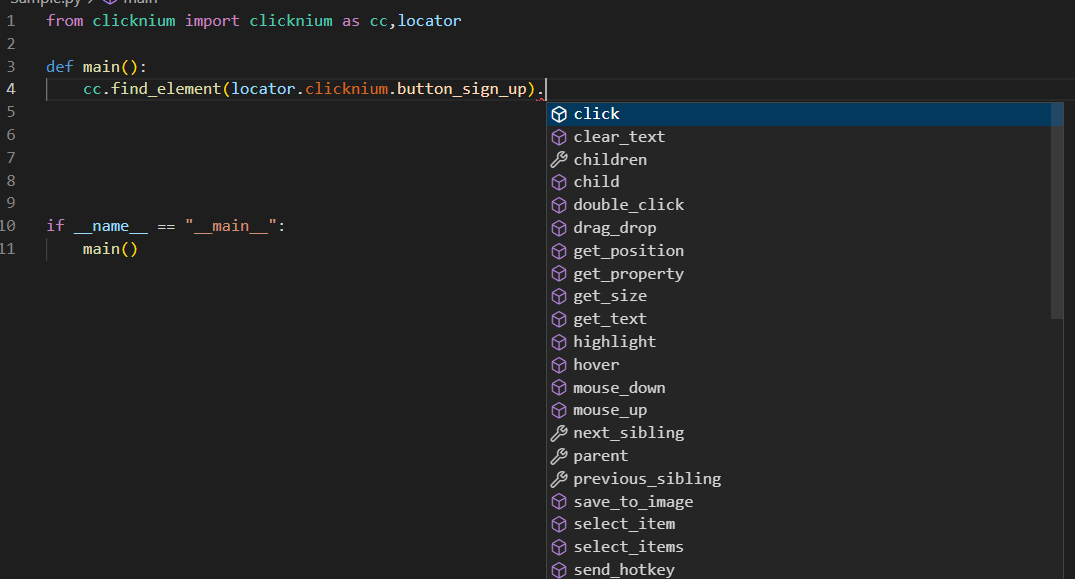
定位到UI元素后,就支持一系列的操作。操作对象是一个按钮,所以我们选择click单击:
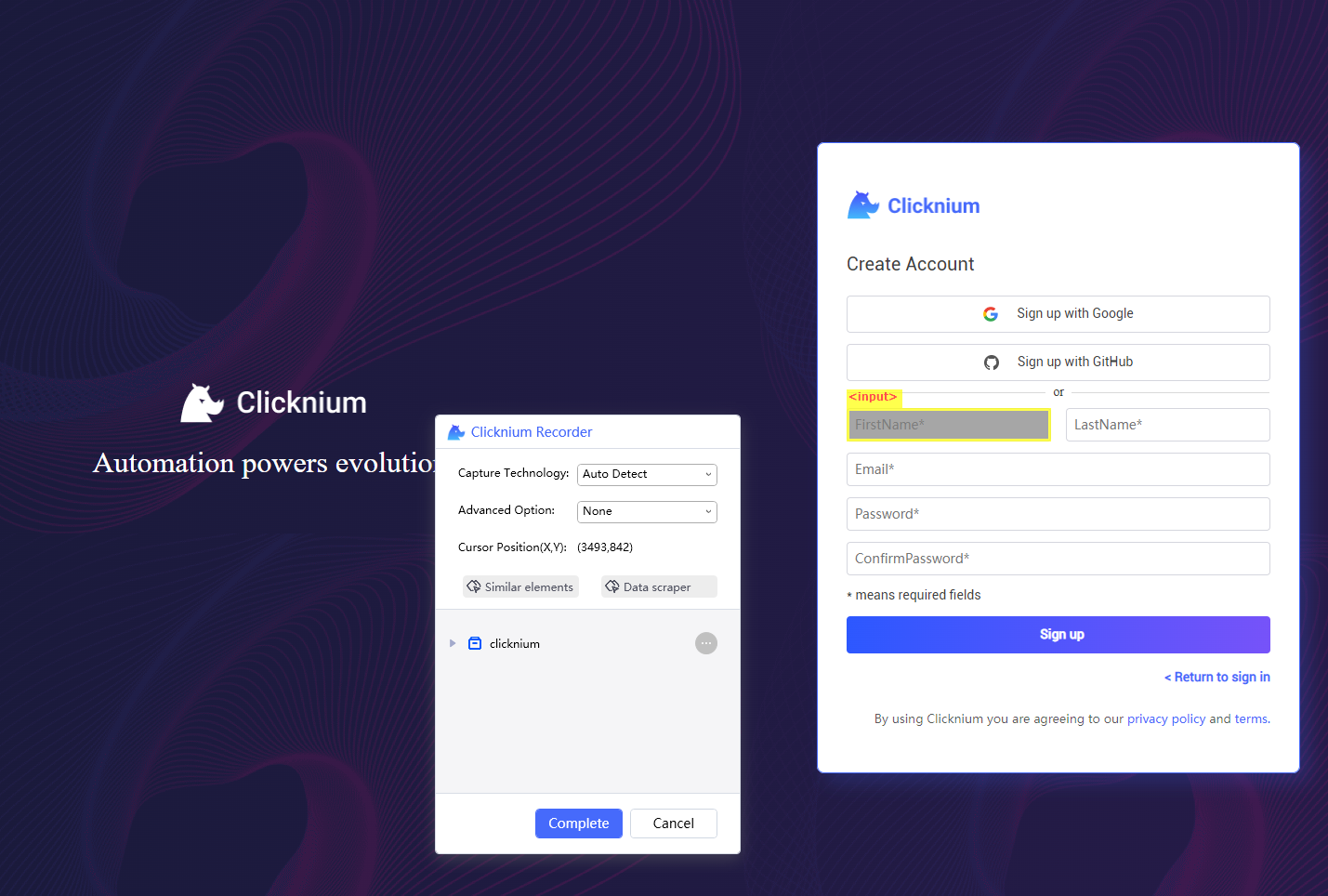
同样的方法,再录制注册页面的5个输入框和一个按钮:
按钮采用Click方法, 输入框采用set_text。同样的方法,完成数据填入和点击按钮,使用F5运行,查看效果。
from clicknium import clicknium as cc,locator
from time import sleep
def main():
cc.chrome.open("https://www.clicknium.com/")
cc.find_element(locator.clicknium.button_sign_up).click()
sleep(5)
firstName = "Kay"
lastName = "Whitlock"
email = "[email protected]"
password = "youpassword"
cc.find_element(locator.clicknium.auth.text_firstname).set_text(firstName)
cc.find_element(locator.clicknium.auth.text_lastname).set_text(lastName)
cc.find_element(locator.clicknium.auth.text_email).set_text(email)
cc.find_element(locator.clicknium.auth.password_password).set_text(password)
cc.find_element(locator.clicknium.auth.password_confirmpassword).set_text(password)
cc.find_element(locator.clicknium.button_sign_up).click()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
4. 鼠标、键盘输入
Clicknium的文档中,对鼠标、键盘支持的操作有比较详细的描述,这里简单做一下介绍。
鼠标输入:
Clicknium支持的鼠标操作可以在Mouse下看到,以最简单的单击(single click)为例,看一下click支持的参数:
def click(
self,
mouse_button: Literal["left", "middle", "right"] = MouseButton.Left,
mouse_location: MouseLocation = MouseLocation(),
by: Union[Literal["default", "mouse-emulation", "control-invocation"], MouseActionBy] = MouseActionBy.Default,
modifier_key: Literal["nonekey", "alt", "ctrl", "shift","win"] = ModifierKey.NoneKey,
timeout: int = 30
) -> None:
"""
Single click the target element.
Parameters:
mouse_button: The available values are: 'left', 'right' and 'center', default is 'left'.
mouse_location: it is set to define the position where the element to be clicked. Default position is center of element.
by: Defines the method to click the UI element.
mouse-emulation: click the target UI element by simulating mouse.
control-invocation: click the target UI element by invoking its UI method. It may not be supported if it is a Windows desktop element.
default: automatically choose method per element type. For Web element, use `control-invocation`; for Window element, use `mouse-emulation`.
modifier_key: The modifier key("alt", "ctrl", "shift", "win") to be pressed along with click, and default is none.
timeout: timeout for the operation, the unit is second, and default is set to 30 seconds.
Returns:
None
"""
mouse_button:鼠标左键,或右键。
mouselocation:绝对位置或者相对位置
by: 有两种模式mouse-emulation和control-invocation。看名字比较抽象。其实前者就是模拟鼠标的行为,移动鼠标过去点击,control-invocation则是使用类似系统调用的方式。 简单说来,模拟鼠标mouse-emulation成功概率高,方法调用control-invocation性能好。 一般桌面端自动化,优先选择模拟鼠标,浏览器端优先方法调用,没效果再尝试模拟鼠标。
modifier_key:达到按住特殊按钮如alt、ctrl、shift点击鼠标的效果。
键盘输入
常用的键盘输入有两种:
- 输入文字
- 按下特殊按钮
输入文字一般用set_text方法:
def set_text(
self,
text: str,
by: Union[Literal["default", "set-text", "sendkey-after-click", "sendkey-after-focus"], InputTextBy]= InputTextBy.Default,
overwrite: bool = True,
timeout: int = 30
) -> None:
"""
Set text for the target element, it can be used to input text to a system.
Parameters:
text[Requried]: text string to be input.
by: the method to perform the text input operation.
set-text: call system method to set text to the target element. Some Windows application elements may not be supported.
sendkey-after-click: simulate mouse click to activate the element, then send keys by simulating keyboard.
sendkey-after-focus: set the target element to focused state, then send keys by simulating keyboard.
default: using different methods per target element type. `set-text` for web element and `sendkey-after-click` for desktop element.
overwrite: whether overwrite or append the text on the target element, default is True.
timeout: timeout for the operation. The unit of parameter is seconds. Default is set to 30 seconds
Returns:
No
参数部分:
text:需要输入的字符串。
by:set-text为系统调用,性能最好,一般在使用在浏览器场景下。
sendkey-after-click:模拟鼠标点击这个UI元素,然后通过模拟键盘的方式输入。
sendkey-after-focus:将目标UI元素设置为focus然后模拟键盘输入。
overwrite: 可以选择是append或是直接覆盖。
sendkey-after-click是一个很常用的选项,因为目前输入框经常需要鼠标单击后变为激活状态接受输入,在非激活状态下是无法接受输入的。 这也自动化过程中,输入操作经常失败的原因。 需要注意的是,这个方法经常会被输入法劫持,所以采用这个参数时,要讲输入关闭,切换为英文输入。
按下特殊按钮:
主要使用send_hotkey方法:
def send_hotkey(hotkey: str) -> None:
"""
Send hotkey to the cursor's current position.
Parameters:
hotkey[Requried]: hotkey string represents one key or combined keys. For example, to represent the letter A, input string "A". To represent the letters A, B, and C, input paremeter "ABC". For special keys, please refer to [hotkeys](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-au/dotnet/api/system.windows.forms.sendkeys?view=windowsdesktop-6.0#remarks).
Returns:
None
"""
这个方法接受一个string作为hotkey的代码:具体按键对应的hotkey code可以查微软的hotkey列表 举个例子,需要按下回车,查表可得enter的代码为{ENTER}
cc.send_hotkey("{ENTER}")
5. Locator
Locator是Clicknium用来定位UI元素的核心。Clicknium Recorder在录制过程中会读取UI元素的各种属性和结构,然后根据算法,选择出能够帮助定位出UI元素的属性。
回到Sample中的目录结构,Python项目目录下会出现一个.locator文件夹,就是存储Locator数据的。VS Code会读取Locator数据并在LOCATORS tab下展示出来:
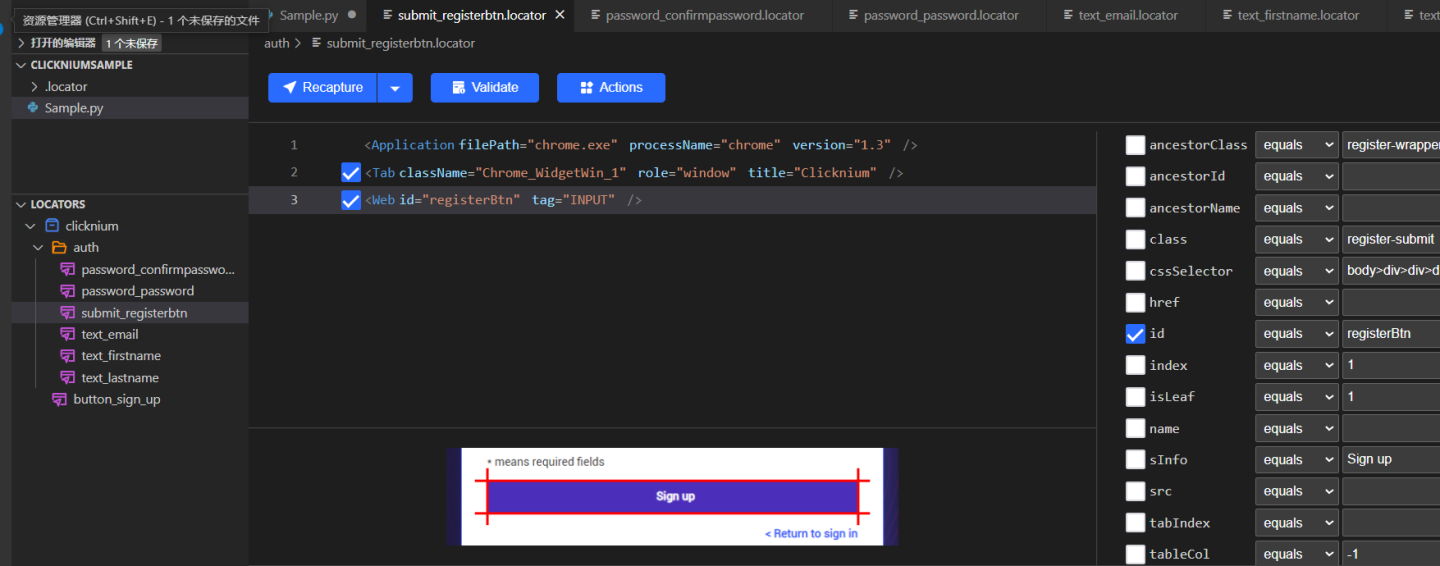
上图为locator界面,在LOCATORS tab下选择对应的locator就能进入locator的详情页。
右侧上部分有三个按钮,Recapture, Validation, Action:
Recapture:主要用于locator失效后重新录制,其还有一个选择是recapture&compare用来做比较,尤其是locator失效后,重新录制,可以看出是哪些属性发生变化导致locator定位失效。
Validation:测试locator是否能定位出对应的UI元素。注意,对应的UI元素的网页或app需要处于打开状态,Validation不会主动打开陈旭。
Action:主要用于测试Locator的可用性, 做一些常见的UI操作,如点击click,获取文本get_text,设置文本set_text。
5.1 Locator Attributes
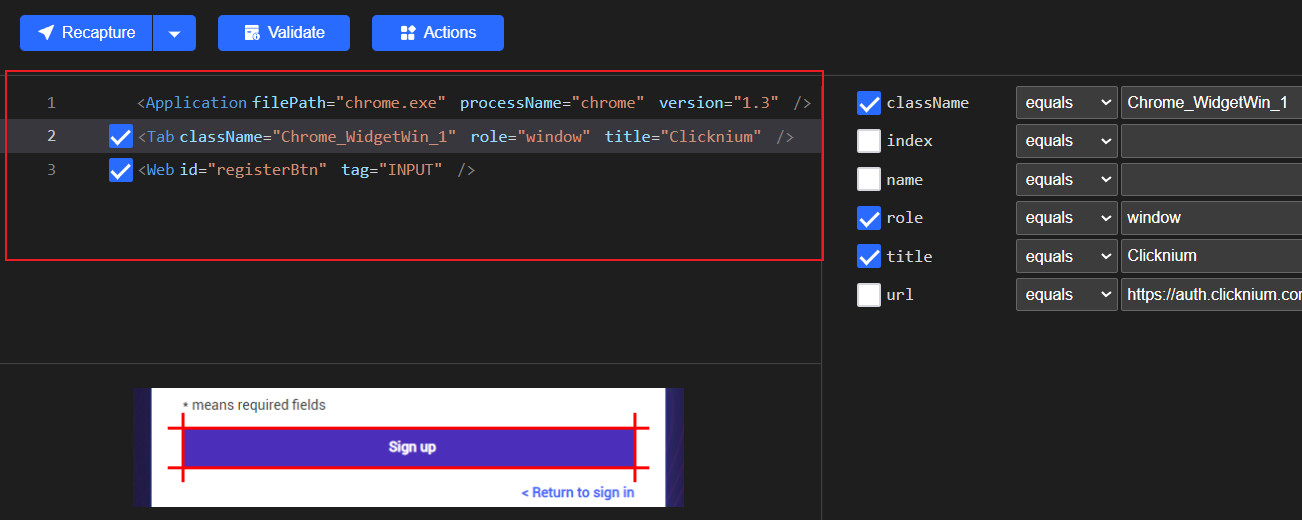
Locator attributes实际上就是locator的内容。 Clicknium Recorder在抓取元素时,会自动获取元素的属性,然后选择利用哪些属性来定位UI元素。 在locator三个快捷操作按钮下方的红框中的内容就是locator attributes。在上图的例子中, attributes的内容从上到下一共有三行。 Clicknium是通过层级结构找到对应的UI元素,attributes中三行属性实际上是层级关系。第一行是chrome.exe应用,在定位到chrome应用后, 第二行是浏览器tab,第三行通过web属性定位按钮。
5.2 Locator Atrributes修改
在绝大多数情况下,Clicknium自动选择的属性都能成功定位到UI元素,但少数情况下,我们还是需要对locator attribute进行微调,已更好的匹配UI元素:首先是对层级关系的选择, 如果判断某一层属性不需要,可以通过点击属性前的蓝色方框取消勾选,该层级的属性就不会参与定位元素。 用鼠标单击层级属性后, 右侧会对该层属性进行展开。对于层级内属性,同样支持选择是否参与定位。同时为了提高泛化能力,属性值的匹配规则支持equals,startWith,endWith,regex四种模式。
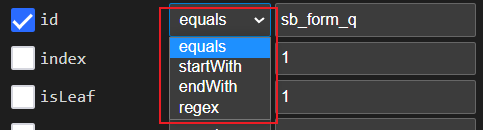
在匹配模式为equals时,还支持通配符。 例如 name='test?_node 其中?匹配1个字符,* 匹配0个或多个字符。
5.3 参数化Locator (Parametric Locator):
对于多个同类型的UI元素,大部分locator attributes都是相同的,仅仅一个或几个属性值不同的情况下, 创建大量locator是不显示的,尤其很多场景下,元素的数量还不固定,这个时候使用参数化locator就很合适。
在locator中使用参数:
- 采用Mustache style 在locator attribute中使用两个花括号+变量名的方式声明一个参数: {{variable}},可以将整个属性值设置为一个变量:
<Web ancestorId="{{id}}" tag="A" />
或将部分值设置为变量:
<Web ancestorId="video-{{id}}" tag="A" />
在Python项目中,采用下面的方式传入变量的值:
from clicknium import clicknium as cc, locator, ui
# replace variable'id' in parametric locator during runtime
variables = {"id":"test"}
ui(locator.chrome.bing.search_sb_form_q, variables)
举个例子:
示例网页中有一个列表:List group · Bootstrap v5.1
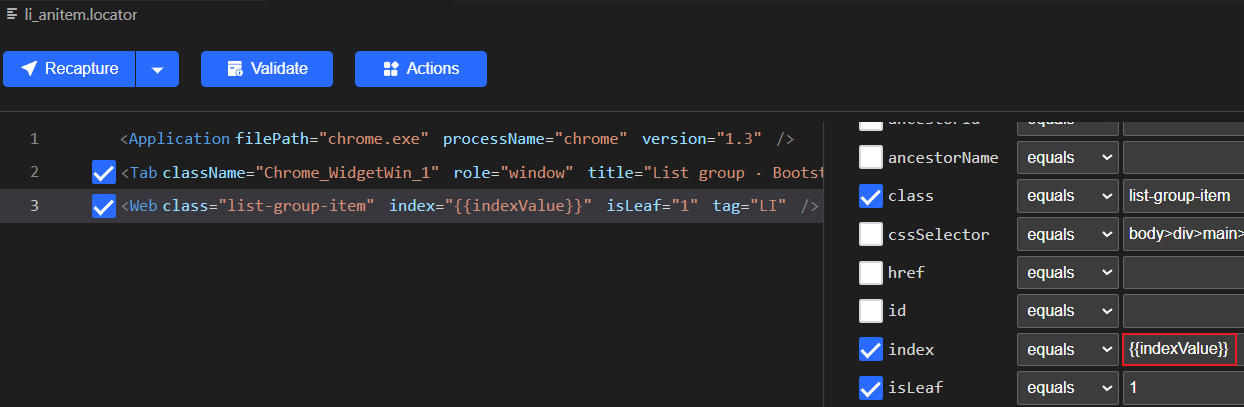
使用Recorder录制列表中的第一个item后,得到下面的locator:
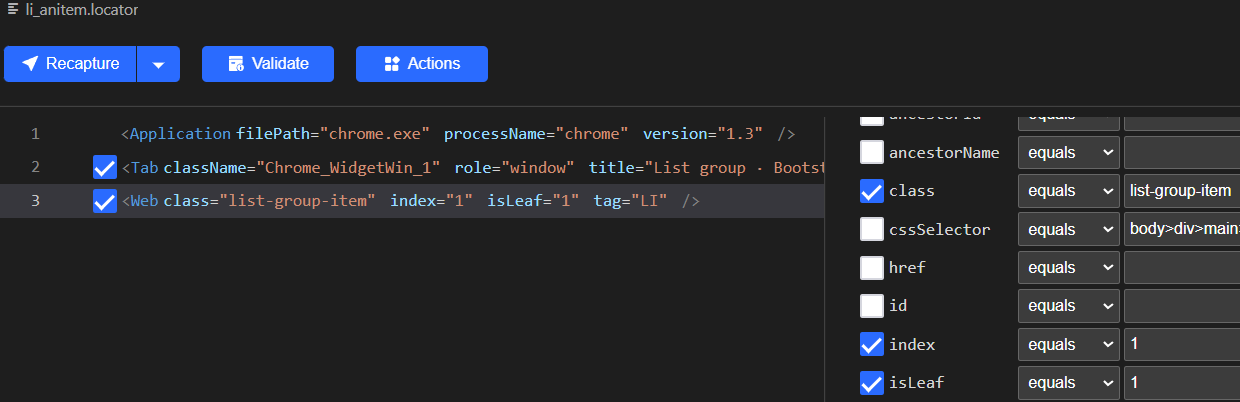
我们修改index的值,使用双花括号创建一个变量{{indexValue}},然后在代码中用一个循环遍历每个item
from clicknium import clicknium as cc, locator, ui
index = 1
driver = cc.chrome.open("https://getbootstrap.com/docs/5.1/components/list-group/")
while True:
variables = {"indexValue":index}
if driver.is_existing(locator.chrome.getbootstrap.li_anitem, variables):
text = driver.find_element(locator.chrome.getbootstrap.li_anitem, variables).get_text()
print(text)
index += 1
else:
break
5.4 获取Locator attribute中的某个属性值
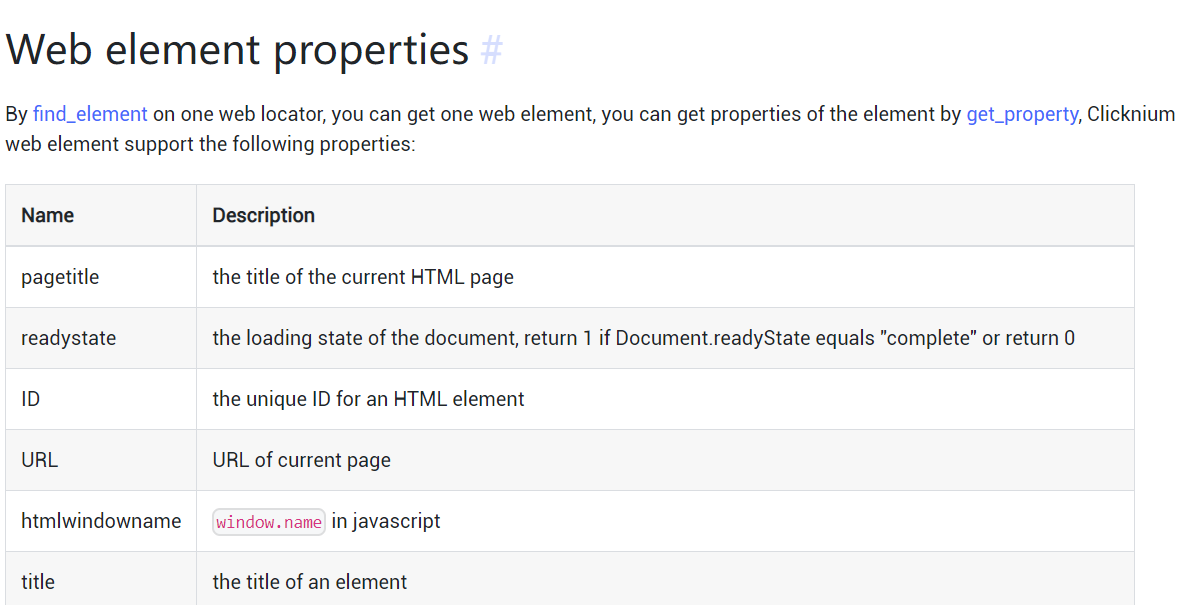
get_text方法会自动判断对应的UI元素中展示的文字。当我们需要获取UI元素的其他属性值时,可以采用get_property方法。 Clicknium支持多种自动化技术(参考Automation Concepts页面)不同自动化技术会生成不同的locator。 其中Web对应浏览器,UIA和IA对应Windows桌面应用。针对Web元素, 在Web automation页面中, 可以找到属性列表(Web element properties)。
from clicknium import clicknium as cc, locator, ui
#获取当前页面的URL
tag = ui(locator.chrome.bing.search_sb_form_q).get_property("URL")
#获取该元素的title
tag = ui(locator.chrome.bing.search_sb_form_q).get_property("title")
版权归原作者 潜水摸鱼Kay 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。