数据结构就是定义出某种结构:像数组结构、链表结构、树形结构等,实现数据结构就是我们主动去管理增删查改的实现函数
二叉搜索树的概念
二叉搜索树又称二叉排序树,它或者是一棵空树,或者是具有以下性质的二叉树
非空左子树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值,右子树上所有节点的值都大于根节点的值
二叉搜索树的定义
template<class K>//搜索二叉树
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode<K>* _left;//左孩子指针
BSTreeNode<K>* _right;//右孩子指针
K _key;//节点数据值
//构造函数
BSTreeNode(const K& key):_left(nullptr),_right(nullptr),_key(key)
{}
};
先来了解一下文件BinnarySearchTree.h中的接口
template<class K>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node; //重命名上面的定义
public
//递归查找
bool FindR(const K& key)
{
return _FindR(_root, key);
}
//递归插入
bool InsertR(const K& key)
{
return _InsertR(_root, key);
}
//递归删除
bool EraseR(const K& key)
{
return _EraseR(_root, key);
}
//中序遍历 类内调用拿root
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
//构造函数
BSTree() = default;
//拷贝构造
BSTree(const BSTree<K>& t);
//赋值函数
BSTree<K>& operator=(BSTree<K> t);
//析构函数
~BSTree();
private:
//类部子函数不继承的话通常私有
bool _EraseR(Node*& root,const K& key);//递归删除
bool _InsertR(Node*& root,const K& key);//递归插入
bool _FindR(Node* root,const K& key);//递归查找
void _InOrder(Node* root);//中序遍历函数
void DestroyTree(Node* root)//置空函数
Node* CopyTree(Node* root)//树的拷贝
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};
下面我们来详细学习函数接口的具体实现
递归插入函数的定义
//递归插入函数
bool _InsertR(Node*& root,const K& key)//递归插入
{
if (root == nullptr)//为空就申请节点插入数据
{
root = new Node(key);//注意上面传指针引用 可以直接连接
return true;
}
if (key > root->_key)//插入的值大于根 往右走
{
return _InsertR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (key < root->_key)//插入的值小于根 往右走
{
return _InsertR(root->_left, key);
}
else
{
return false;//相等说明数据已经有了
}
}
递归删除函数的定义
bool _EraseR(Node*& root,const K& key)//递归删除
{
//先找到要删除的节点
if (root == nullptr)//为空返回false
{
return false;
}
if (key > root->_key)//要删除的大于根
{
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);//递归右树找
}
else if (key < root->_key)//要删除的小于根
{
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);//递归左树找
}
//走到这里说明已经找到要删除的数据
else
{
//1.删除一个孩子 左为空或右为空 托孤
Node* del = root;//先保存要删除的节点
if (root->_left == nullptr)//左为空 让父亲指向右
{
root = root->_right;//引用
}
else if (root->_right == nullptr)右为空 让父亲指向左
{
root = root->_left;
}
//2.删除2个孩子左右都不为空 替换法
else
{
Node* minRight = root->_right;//
while (minRight->_left)
{
minRight = minRight->_left;
}
swap(root->_key, minRight->_key);//交换数据
//此时要删除的已经换下来 再去右树递归删除
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);//指定树
}
delete del;
return true;
}
}
中序遍历函数的定义
//中序遍历
void _InOrder(Node* root) 左子树 根 右子树
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_InOrder(root->_left);//先走左边
cout << root->_key << " "; 打印数据
_InOrder(root->_right);//后走右边
}
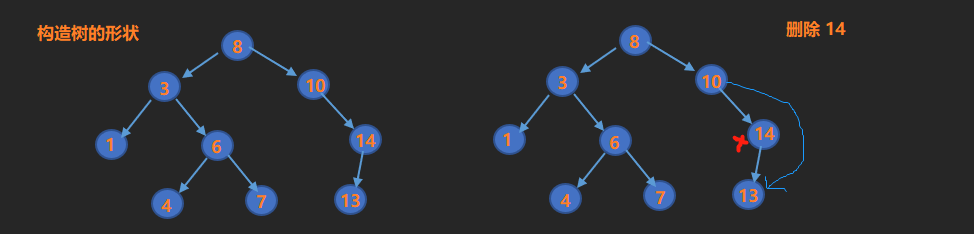
我们先用以上接口实现图中二叉树的插入和删除测试案例TestBSTree
//递归插入测试
void TestBSTree1()
{
//
BSTree<int> t;
int a[] = { 8,3,1,10,6,4,7,14,13, };
for (auto e : a)
{
t.InsertR(e);//依次插入 默认去重
}
t.InOrder();//遍历打印 1 3 4 6 7 8 10 13 14
}
//递归删除测试
void TestBSTree2()
{
//
BSTree<int> t;
int a[] = { 8,3,1,10,6,4,7,14,13, };
for (auto e : a)
{
t.InsertR(e);//依次插入 默认去重
}
t.InOrder();//打印1 3 4 6 7 8 10 13 14
t.EraseR(14);//删除14
t.InOrder();//打印1 3 4 6 7 8 10 13
}
int main()
{
TestBSTree1();//递归插入
TestBSTree2();//递归删除
return 0;
}
递归查找函数的定义
从根开始比较查找,比根大则往右边查找,比根小则往左边查找
bool _FindR(Node* root,const K& key)//递归查找
{
if (root == nullptr)
return false;
if (key > root->_key)//
{
return _FindR(root->_right, key);
}
else if(key < root->_key)
{
return _FindR(root->_left, key);
}
else
{
return true;//相等就找到了
}
}
置空函数定义
置空函数一般会放在我们进行插入或删除的函数最后,释放我们在堆上申请的空间,将其还给操作系统,另外也会相应的进行检查越界等问题
void DestroyTree(Node* root)//置空函数
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
DestroyTree(root->_left);
DestroyTree(root->_right);
delete root;
}
析构函数定义
~BSTree()//析构函数
{
DestroyTree(_root);//调用置空函数
_root = nullptr;
}
赋值函数定义
BSTree<K>& operator=(BSTree<K> t)//赋值函数
{
swap(_root, t._root);
return *this;
}
树的拷贝函数定义
Node* CopyTree(Node* root)//拷贝树
{
if (root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
Node* copynode = new Node(root->_key);
copynode->_left = CopyTree(root->_left);//递归创建左树
copynode->_right = CopyTree(root->_right);//递归创建右树
return copynode;
}
拷贝构造函数定义
BSTree(const BSTree<K>& t)//拷贝构造
{
_root = CopyTree(t._root);//调用下方树的拷贝函数
cout << "调用拷贝构造" << endl;
}
我们再用上面这几个接口实现第3个测试案例TestBSTree3
//赋值函数测试
void TestBSTree3()
{
//
BSTree<int> t;
int a[] = { 8,3,1,10,6,4,7,14,13, };
for (auto e : a)
{
t.InsertR(e);//依次插入 默认去重
}
t.InOrder();//遍历打印 1 3 4 6 7 8 10 13 14
BSTree<int> t1;
t1 = t;//赋值函数 调用拷贝构造
t.InOrder();//遍历打印1 3 4 6 7 8 10 13 14
}
int main()
{
TestBSTree3();//赋值函数测试
return 0;
}
最后这里放一下整个二叉搜索树递归版本代码的实现,方便大家观察理解
#pragma once
template<class K>//搜索二叉树
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode<K>* _left;
BSTreeNode<K>* _right;
K _key;
//构造函数
BSTreeNode(const K& key):_left(nullptr),_right(nullptr),_key(key)
{}
};
template<class K>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node;
public:
//默认构造
BSTree() = default;
//拷贝构造
BSTree(const BSTree<K>& t)
{
_root = CopyTree(t._root);
cout << "调用拷贝构造" << endl;
}
//赋值函数
BSTree<K>& operator=(BSTree<K> t)
{
swap(_root, t._root);
return *this;
}
//析构函数
~BSTree()
{
DestroyTree(_root);
_root = nullptr;
}
//递归查找
bool FindR(const K& key)
{
return _FindR(_root, key);
}
//递归插入
bool InsertR(const K& key)
{
return _InsertR(_root, key);
}
//递归删除
bool EraseR(const K& key)
{
return _EraseR(_root, key);
}
//中序遍历 类内调用拿root
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
private://类部子函数不继承的话通常私有
//递归删除
bool _EraseR(Node*& root,const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return false;
}
if (key > root->_key)//
{
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (key < root->_key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
}
else
{
Node* del = root;//保存要删除的节点
//相等说明可以删除了 三种情况
if (root->_left == nullptr)
{
root = root->_right;//引用
}
else if (root->_right == nullptr)
{
root = root->_left;
}
else//左右都不为空 替换法
{
Node* minRight = root->_right;
while (minRight->_left)
{
minRight = minRight->_left;
}
swap(root->_key, minRight->_key);//交换数据
//此时要删除的已经换下来 再去右树递归删除
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);//指定树
}
delete del;
return true;
}
}
bool _InsertR(Node*& root,const K& key)//递归插入
{
if (root == nullptr)//为空就申请节点插入数据
{
root = new Node(key);//注意上面传指针引用 可以直接连接
return true;
}
if (key > root->_key)//插入的值大于根 往右走
{
return _InsertR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (key < root->_key)//插入的值小于根 往右走
{
return _InsertR(root->_left, key);
}
else
{
return false;//相等说明数据已经有了
}
}
bool _FindR(Node* root,const K& key)//递归查找
{
//
if (root == nullptr)
return false;
if (key > root->_key)//
{
return _FindR(root->_right, key);
}
else if(key < root->_key)
{
return _FindR(root->_left, key);
}
else
{
return true;//相等就找到了
}
}
void _InOrder(Node* root)//中序遍历
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
void DestroyTree(Node* root)//置空函数
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
DestroyTree(root->_left);
DestroyTree(root->_right);
delete root;
}
Node* CopyTree(Node* root)//拷贝树
{
if (root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
Node* copynode = new Node(root->_key);
copynode->_left = CopyTree(root->_left);//递归创建左树
copynode->_right = CopyTree(root->_right);//递归创建右树
return copynode;
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};
//递归插入测试
void TestBSTree1()
{
BSTree<int> t;
int a[] = { 8,3,1,10,6,4,7,14,13, };
for (auto e : a)
{
t.InsertR(e);//依次插入 默认去重
}
t.InOrder();//遍历
}
//递归删除测试
void TestBSTree2()
{
BSTree<int> t;
int a[] = { 8,3,1,10,6,4,7,14,13, };
for (auto e : a)
{
t.InsertR(e);//依次插入 默认去重
}
t.InOrder();//打印 1 3 4 6 7 8 10 13 14
t.EraseR(8);//删除8
t.EraseR(3);//删除3
t.InOrder();//打印 1 4 6 7 10 13 14
}
//赋值函数测试
void TestBSTree3()
{
BSTree<int> t;
int a[] = { 8,3,1,10,6,4,7,14,13, };
for (auto e : a)
{
t.InsertR(e);//依次插入 默认去重
}
t.InOrder();//遍历打印 1 3 4 6 7 8 10 13 14
BSTree<int> t1;
t1 = t;//赋值函数 调用拷贝构造
t.InOrder();//遍历打印1 3 4 6 7 8 10 13 14
}
int main()
{
TestBSTree1();//插入函数测试
TestBSTree2();//删除函数测试
TestBSTree3();//赋值函数测试
return 0;
}
在Java和C++的学习当中,前期学习数据结构当中的顺序表、链表、二叉树等便于我们后面更好的学习容器,后面会继续分享红黑树和排序的实现
希望这篇文章大家有所收获,我们下篇见
版权归原作者 小圣编程 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。