前言
现在搭建部署环境基本都是用Docker进行,学会Docker指令相当重要。在我的Docker系列文章中我们已经进行了很多准备工作,我是在云服务器上面进行部署的工作,大大省去了虚拟机环境配置时间,大家可以用用看:
云服务器Centos8.2SSH登陆、安装部署图形化界面以及VNC连接一文详解
云服务器CentOS8.2安装部署Docker一文详解
云服务器CentOS8.2Docker图形化管理工具Portainer安装部署
下面仍旧还是使用SecureCRT进行指令演示。
很多学Python伙伴问题有没有体系的面试题?
今天为大家推荐一款刷题神奇哦 :刷题面试神器牛客
各大互联网大厂面试真题。从基础到入阶乃至原理刨析类面试题 应有尽有,赶快来装备自己吧!助你面试稳操胜券,solo全场面试官
一、Docker基础命令
1.启动docker
systemctl start docker
2.查看状态
systemctl status docker

3.关闭docker
systemctl stop docker

4.开机自启
systemctl enable docker
5.查看版本信息
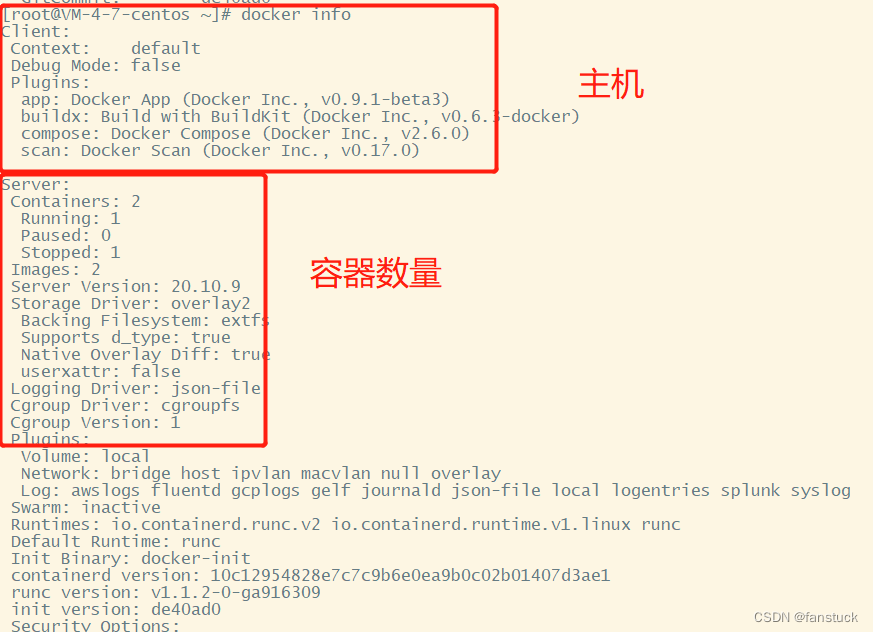
docker version
docker info
6.查看帮助
docker --help
若忘记了某个指令的功能可以在后面加上help查看功能:
docker 指令参数 --help

二、Docker镜像命令
1.查看docker镜像
docker images

可以通过--help查看每一个Image命令的详细信息。
docker image ls --help

显示所有镜像(默认隐藏中间图像)
docker image ls -a

docker images
、
docker image ls
和
docker image ls -a
是一样的效果。
docker image ls -q
仅输出image的IMAGE ID。

2.搜索镜像
docker search 镜像名
比如:

docker search [OPTIONS] TERM
其中OPTIONS有:
- --automated:弃用,只列出自动构建类型的镜像
- --filter , -f:基于给定条件过滤输出
- --format:使用模板格式化显示输出
- --limit:Max number of search results ,默认值25
- --no-trunc:禁止截断输出
- --stars , -s:弃用,只显示收藏数不小于几颗星的镜像,移到--filter中使用
代码如下(示例):
搜索不小于10000星的busybox的镜像
docker search --filter=stars=10000 mysql
format格式化输出
- .Description 镜像描述
- .StarCount star数量
- .IsOfficial “OK” 表示官方镜像
- .IsAutomated “OK” 表示自动构建
docker search --format "{{.Name}}:{{.StarCount}}" mysql

docker search --format "table {{.Name}}\t{{.IsAutomated}}\t{{.IsOfficial}}" redis

限制搜索输出个数
docker search redis --filter=stars=500 --limit 3

禁止截断输出
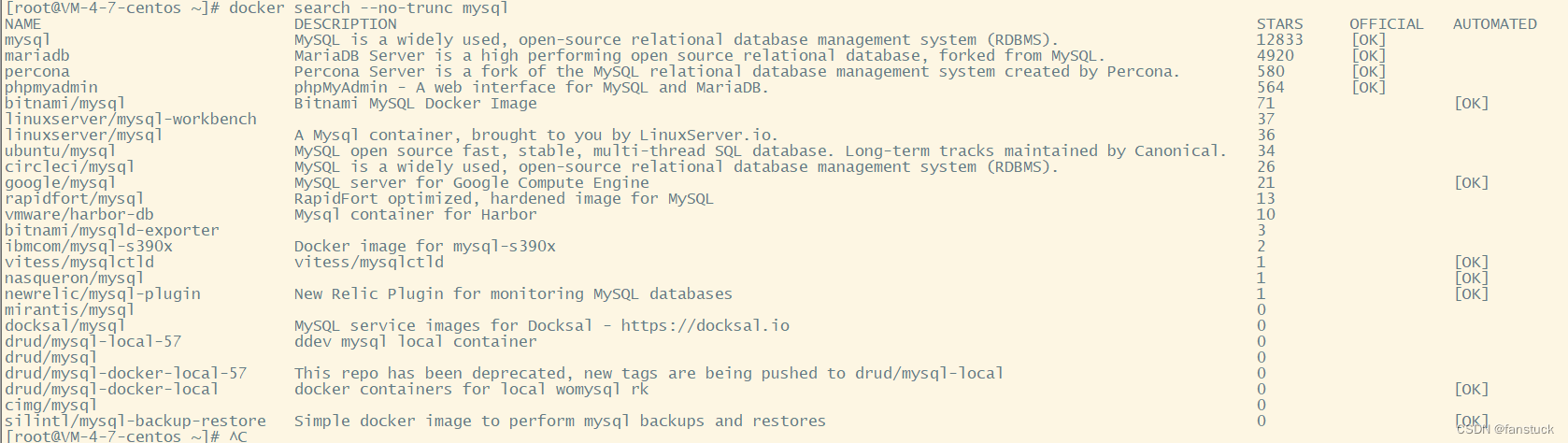
docker search --no-trunc mysql
3.拉取镜像
代码如下(示例):
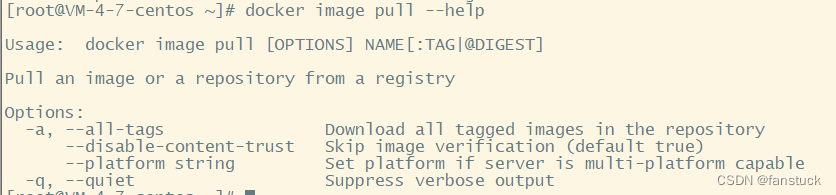
docker image pull
参数可以选有两个:
例如拉取一个最新的redis:
docker image pull redis

拉取完后docker images查看:

4.删除所有镜像
代码如下:
docker image prune [OPTIONS]
 5.删除指定镜像
5.删除指定镜像
docker image rm [OPTIONS] IMAGE [IMAGE...]

删除TAG为latest最新版本的redis:
docker image rm redis:latest


6.TAG修改生成新镜像
docker image tag SOURCE_IMAGE[:TAG] TARGET_IMAGE[:TAG]

docker image tag hello-world:latest hello-world:v.1.0

7.保存镜像
docker image save [OPTIONS] IMAGE [IMAGE...]

docker image save hello-world:v.1.0 > hw.tar

保存到指定目录:
docker image save hello-worl:v.1.0 -o /usr/local/hw.tar
8.加载镜像
docker image load [OPTIONS]

我们一开始是把hello-world的v.1.0的版本给删了,现在我们可以把通过本地保存的hello-world给放到image里面去:
docker image load <hw.tar


加载指定路径的镜像源:
docker load -i /usr/local/hw.tar # 指定加载镜像的源
9.显示历史镜像操作
docker image history [OPTIONS] IMAGE

docker image history hello-world:v.1.0

10.显示镜像的详细信息
docker image inspect [OPTIONS] IMAGE [IMAGE...]
例如我们查看hello-world镜像的详细信息会发现:
docker image inspect hello-world
一大串JSON文件格式:
11.从归档文件中创建镜像
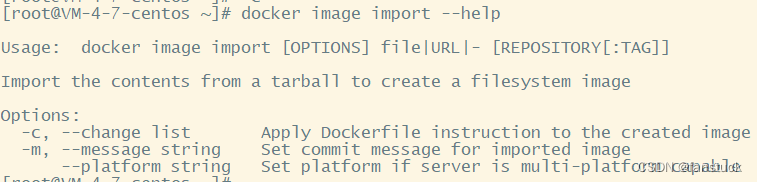
docker image import [OPTIONS] file|URL|- [REPOSITORY[:TAG]]
docker image import hw.tar # 一般需要指定镜像名字
12.上传镜像
docker image push [OPTIONS] NAME[:TAG]

这样就是上传成功了可以在dockerhub上看到自己上传的镜像:
docker push fanstuck/my-private-repo:hellow-world


13.创建镜像
docker image build [OPTIONS] PATH | URL | -
bulid属于制作镜像是一个较为复杂且需要编写程序的过程,因此参数相应的会比较复杂:
Usage: docker [OPTIONS] COMMAND
A self-sufficient runtime for containers
Options:
--config string Location of client config files (default "/root/.docker")
-c, --context string Name of the context to use to connect to the daemon
(overrides DOCKER_HOST env var and default context set
with "docker context use")
-D, --debug Enable debug mode
-H, --host list Daemon socket(s) to connect to
-l, --log-level string Set the logging level
("debug"|"info"|"warn"|"error"|"fatal") (default "info")
--tls Use TLS; implied by --tlsverify
--tlscacert string Trust certs signed only by this CA (default
"/root/.docker/ca.pem")
--tlscert string Path to TLS certificate file (default
"/root/.docker/cert.pem")
--tlskey string Path to TLS key file (default "/root/.docker/key.pem")
--tlsverify Use TLS and verify the remote
-v, --version Print version information and quit
Management Commands:
app* Docker App (Docker Inc., v0.9.1-beta3)
builder Manage builds
buildx* Build with BuildKit (Docker Inc., v0.6.3-docker)
compose* Docker Compose (Docker Inc., v2.6.0)
config Manage Docker configs
container Manage containers
context Manage contexts
image Manage images
manifest Manage Docker image manifests and manifest lists
network Manage networks
node Manage Swarm nodes
plugin Manage plugins
scan* Docker Scan (Docker Inc., v0.17.0)
secret Manage Docker secrets
service Manage services
stack Manage Docker stacks
swarm Manage Swarm
system Manage Docker
trust Manage trust on Docker images
volume Manage volumes
Commands:
attach Attach local standard input, output, and error streams to a running container
build Build an image from a Dockerfile
commit Create a new image from a container's changes
cp Copy files/folders between a container and the local filesystem
create Create a new container
diff Inspect changes to files or directories on a container's filesystem
events Get real time events from the server
exec Run a command in a running container
export Export a container's filesystem as a tar archive
history Show the history of an image
images List images
import Import the contents from a tarball to create a filesystem image
info Display system-wide information
inspect Return low-level information on Docker objects
kill Kill one or more running containers
load Load an image from a tar archive or STDIN
login Log in to a Docker registry
logout Log out from a Docker registry
logs Fetch the logs of a container
pause Pause all processes within one or more containers
port List port mappings or a specific mapping for the container
ps List containers
pull Pull an image or a repository from a registry
push Push an image or a repository to a registry
rename Rename a container
restart Restart one or more containers
rm Remove one or more containers
rmi Remove one or more images
run Run a command in a new container
save Save one or more images to a tar archive (streamed to STDOUT by default)
search Search the Docker Hub for images
start Start one or more stopped containers
stats Display a live stream of container(s) resource usage statistics
stop Stop one or more running containers
tag Create a tag TARGET_IMAGE that refers to SOURCE_IMAGE
top Display the running processes of a container
unpause Unpause all processes within one or more containers
update Update configuration of one or more containers
version Show the Docker version information
wait Block until one or more containers stop, then print their exit codes
Run 'docker COMMAND --help' for more information on a command.
这里参数十分丰富,以后将独自写一期docker bulid来详细介绍该功能的使用,属于制作镜像一块的,是比较大的一块docker内容。
14.运行镜像
创建一个新的容器并运行一个命令
docker run [OPTIONS] IMAGE [COMMAND] [ARG...]
相应的参数也是十分的多的:
Usage: docker run [OPTIONS] IMAGE [COMMAND] [ARG...]
Run a command in a new container
Options:
--add-host list Add a custom host-to-IP mapping (host:ip)
-a, --attach list Attach to STDIN, STDOUT or STDERR
--blkio-weight uint16 Block IO (relative weight), between 10 and
1000, or 0 to disable (default 0)
--blkio-weight-device list Block IO weight (relative device weight)
(default [])
--cap-add list Add Linux capabilities
--cap-drop list Drop Linux capabilities
--cgroup-parent string Optional parent cgroup for the container
--cgroupns string Cgroup namespace to use (host|private)
'host': Run the container in the Docker
host's cgroup namespace
'private': Run the container in its own
private cgroup namespace
'': Use the cgroup namespace as
configured by the
default-cgroupns-mode option on
the daemon (default)
--cidfile string Write the container ID to the file
--cpu-period int Limit CPU CFS (Completely Fair Scheduler) period
--cpu-quota int Limit CPU CFS (Completely Fair Scheduler) quota
--cpu-rt-period int Limit CPU real-time period in microseconds
--cpu-rt-runtime int Limit CPU real-time runtime in microseconds
-c, --cpu-shares int CPU shares (relative weight)
--cpus decimal Number of CPUs
--cpuset-cpus string CPUs in which to allow execution (0-3, 0,1)
--cpuset-mems string MEMs in which to allow execution (0-3, 0,1)
-d, --detach Run container in background and print container ID
--detach-keys string Override the key sequence for detaching a
container
--device list Add a host device to the container
--device-cgroup-rule list Add a rule to the cgroup allowed devices list
--device-read-bps list Limit read rate (bytes per second) from a
device (default [])
--device-read-iops list Limit read rate (IO per second) from a device
(default [])
--device-write-bps list Limit write rate (bytes per second) to a
device (default [])
--device-write-iops list Limit write rate (IO per second) to a device
(default [])
--disable-content-trust Skip image verification (default true)
--dns list Set custom DNS servers
--dns-option list Set DNS options
--dns-search list Set custom DNS search domains
--domainname string Container NIS domain name
--entrypoint string Overwrite the default ENTRYPOINT of the image
-e, --env list Set environment variables
--env-file list Read in a file of environment variables
--expose list Expose a port or a range of ports
--gpus gpu-request GPU devices to add to the container ('all' to
pass all GPUs)
--group-add list Add additional groups to join
--health-cmd string Command to run to check health
--health-interval duration Time between running the check (ms|s|m|h)
(default 0s)
--health-retries int Consecutive failures needed to report unhealthy
--health-start-period duration Start period for the container to initialize
before starting health-retries countdown
(ms|s|m|h) (default 0s)
--health-timeout duration Maximum time to allow one check to run
(ms|s|m|h) (default 0s)
--help Print usage
-h, --hostname string Container host name
--init Run an init inside the container that
forwards signals and reaps processes
-i, --interactive Keep STDIN open even if not attached
--ip string IPv4 address (e.g., 172.30.100.104)
--ip6 string IPv6 address (e.g., 2001:db8::33)
--ipc string IPC mode to use
--isolation string Container isolation technology
--kernel-memory bytes Kernel memory limit
-l, --label list Set meta data on a container
--label-file list Read in a line delimited file of labels
--link list Add link to another container
--link-local-ip list Container IPv4/IPv6 link-local addresses
--log-driver string Logging driver for the container
--log-opt list Log driver options
--mac-address string Container MAC address (e.g., 92:d0:c6:0a:29:33)
-m, --memory bytes Memory limit
--memory-reservation bytes Memory soft limit
--memory-swap bytes Swap limit equal to memory plus swap: '-1' to
enable unlimited swap
--memory-swappiness int Tune container memory swappiness (0 to 100)
(default -1)
--mount mount Attach a filesystem mount to the container
--name string Assign a name to the container
--network network Connect a container to a network
--network-alias list Add network-scoped alias for the container
--no-healthcheck Disable any container-specified HEALTHCHECK
--oom-kill-disable Disable OOM Killer
--oom-score-adj int Tune host's OOM preferences (-1000 to 1000)
--pid string PID namespace to use
--pids-limit int Tune container pids limit (set -1 for unlimited)
--platform string Set platform if server is multi-platform capable
--privileged Give extended privileges to this container
-p, --publish list Publish a container's port(s) to the host
-P, --publish-all Publish all exposed ports to random ports
--pull string Pull image before running
("always"|"missing"|"never") (default "missing")
--read-only Mount the container's root filesystem as read only
--restart string Restart policy to apply when a container
exits (default "no")
--rm Automatically remove the container when it exits
--runtime string Runtime to use for this container
--security-opt list Security Options
--shm-size bytes Size of /dev/shm
--sig-proxy Proxy received signals to the process
(default true)
--stop-signal string Signal to stop a container (default "SIGTERM")
--stop-timeout int Timeout (in seconds) to stop a container
--storage-opt list Storage driver options for the container
--sysctl map Sysctl options (default map[])
--tmpfs list Mount a tmpfs directory
-t, --tty Allocate a pseudo-TTY
--ulimit ulimit Ulimit options (default [])
-u, --user string Username or UID (format: <name|uid>[:<group|gid>])
--userns string User namespace to use
--uts string UTS namespace to use
-v, --volume list Bind mount a volume
--volume-driver string Optional volume driver for the container
--volumes-from list Mount volumes from the specified container(s)
-w, --workdir string Working directory inside the container
run的执行流程为:

三、docker容器命令
1.查看正在运行容器列表
docker ps [OPTIONS]
Usage: docker ps [OPTIONS]
List containers
Options:
-a, --all Show all containers (default shows just running)
-f, --filter filter Filter output based on conditions provided
--format string Pretty-print containers using a Go template
-n, --last int Show n last created containers (includes all states) (default -1)
-l, --latest Show the latest created container (includes all states)
--no-trunc Don't truncate output
-q, --quiet Only display container IDs
-s, --size Display total file sizes
-a 查看所有容器
docker ps -a
-n 个数 列出最近创建的容器
docker ps -n 2

-aq 显示所有运行过的容器的id
docker ps -aq

2.删除容器
rm -f 容器id 删除容器
docker rm -f 0150f4c51f21
rm -f $(docker ps -aq) 删除所有docker容器
docker ps -aq|xargs docker rm -f 也可以删除所有的容器
docker rm -f $(docker ps -aq)
docker ps -aq|xargs docker rm -f
3.启动容器
start 容器id 启动容器
docker start e8sdzx524
restart 容器id 重启容器
docker restart e8sdzx524
stop 容器id 停止容器
docker stop e8sdzx524
当使用docker stop 无法停止时,可以使用docker kill 直接杀掉
docker kill ec8626df668c
4. 查看日志命令
docker logs [OPTIONS] CONTAINER
Usage: docker logs [OPTIONS] CONTAINER
Fetch the logs of a container
Options:
--details Show extra details provided to logs
-f, --follow Follow log output
--since string Show logs since timestamp (e.g. 2013-01-02T13:23:37Z) or
relative (e.g. 42m for 42 minutes)
-n, --tail string Number of lines to show from the end of the logs (default
"all")
-t, --timestamps Show timestamps
--until string Show logs before a timestamp (e.g. 2013-01-02T13:23:37Z)
or relative (e.g. 42m for 42 minutes)
查看启动容器的最新num行的日志
docker logs -tf --tail num 容器id
例如:
docker logs -tf --tail 10 ec8626df668c
5. 查看容器的进程信息
docker top 容器id

6.重新打开一个终端的方式进入docker
docker exec [OPTIONS] CONTAINER COMMAND [ARG...]
Usage: docker exec [OPTIONS] CONTAINER COMMAND [ARG...]
Run a command in a running container
Options:
-d, --detach Detached mode: run command in the background
--detach-keys string Override the key sequence for detaching a container
-e, --env list Set environment variables
--env-file list Read in a file of environment variables
-i, --interactive Keep STDIN open even if not attached
--privileged Give extended privileges to the command
-t, --tty Allocate a pseudo-TTY
-u, --user string Username or UID (format: <name|uid>[:<group|gid>])
-w, --workdir string Working directory inside the container
7.进入容器中正在运行的终端
docker attach [OPTIONS] CONTAINER
Usage: docker attach [OPTIONS] CONTAINER
Attach local standard input, output, and error streams to a running container
Options:
--detach-keys string Override the key sequence for detaching a container
--no-stdin Do not attach STDIN
--sig-proxy Proxy all received signals to the process (default true)
8.从容器内拷贝文件到主机上
docker cp 容器id:容器文件路径 本地文件路径
例如:
docker cp ec8626df668c:/opt/test.txt /opt/test.txt
很多学Python伙伴问题有没有体系的面试题?
今天为大家推荐一款刷题神奇哦 :刷题面试神器牛客
各大互联网大厂面试真题。从基础到入阶乃至原理刨析类面试题 应有尽有,赶快来装备自己吧!助你面试稳操胜券,solo全场面试官
点关注,防走丢,如有纰漏之处,请留言指教,非常感谢
以上就是本期全部内容。我是fanstuck ,有问题大家随时留言讨论 ,我们下期见。
参阅
docker 常用命令大全
Docker Image 命令详解
Docker - Docker Image及Image命令详解
Docker----Docker容器操作常用命令
版权归原作者 fanstuck 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。