
概念
Java中的Properties文件是一种配置文件,主要用于表达配置信息,格式是文本文件。该类主要用于读取Java的配置文件,也可以对properties文件进行修改
属性配置:以“键=值”的方式书写一个属性的配置信息
注 释:在properties文件中,可以用“#”来注释
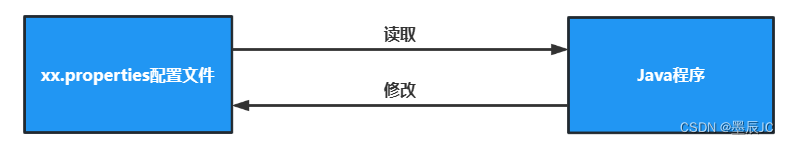
为什么需要Properties类?
将一些固定修改的内容放到Properties文件,如果我们将这些内容放到程序里面(比如:账号、密码),假如说这些内容需要改变,意味着需要对源程序进行修改(修改源码);当再次运行的时候,需要进行重新编译或运行在第三方(当程序工程量大的时候,会浪费大量资源,灵活性差)
Properties类可以很轻松的理解和修改它们
传统的方法(不使用Properties类)
split方法是String类中,用于分割字符串,将分割的字符串变成字符串数组
test.Properties文件的内容
ip=192.168.1.100
user=root
pwd=123456
读取test.properties文件,并获取相应的ip user pwd
importjava.io.BufferedReader;importjava.io.FileReader;importjava.io.IOException;publicclassProperties01{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){BufferedReader bufferedReader =null;try{
bufferedReader =newBufferedReader(newFileReader("src\\test.properties"));String line ="";while((line = bufferedReader.readLine())!=null){String[] split = line.split("=");System.out.println(split[0]+"值是:"+split[1]);}}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();}finally{try{
bufferedReader.close();}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();}}}}
控制台输出如下:
ip值是:192.168.1.100
user值是:root
pwd值是:123456
传统方法解决并不是很方便,需要遍历循环,如果要获取文件中指定的某个内容,这时候需要用到Properties类
Properties
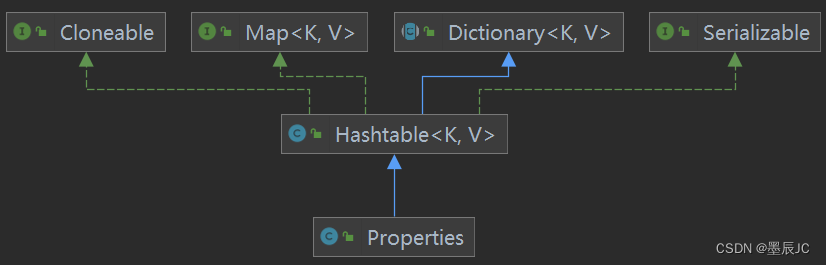
Properties 继承于 Hashtable。表示一个持久的属性集.属性列表中每个键及其对应值都是一个字符串。
- 专门用于读取配置文件的集合类 配置文件格式: 键=值 键=值
- 键值对不需要由空格,值不需要用引号括起来,默认类型是String
该类提供了两个构造器
常见Properties调用方法
- load:加载配置文件的键值对到Properties对象

- list:将数据显示到指定设备

- getProperties(key):根据键获取值
- setProperties(key,value):设置键值对到Properties对象
- store:将Properties中的键值对存储到配置文件中(如果已存在则覆盖),在IDEA编译器中,保存信息到配置文件,如果含有中文,会存储Unicode编码格式

编码查询工具网站
更多具体方法可在JDK文档或百度进行查看
示例
1.演示使用Properties类读取test.properties文件的内容
importjava.io.FileReader;importjava.io.IOException;importjava.util.Properties;publicclassProperties02{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){//创建Properties对象Properties properties =newProperties();//加载指定的配置文件try{
properties.load(newFileReader("src\\test.properties"));//把键值对显示到控制台
properties.list(System.out);System.out.println("===根据键获取对应的值===");System.out.println(properties.getProperty("ip"));}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();}}}
– listing properties –
user=root
pwd=123456
ip=192.168.1.100
=根据键获取对应的值=
192.168.1.100
2.使用Properties类添加键值对到文件test.properties中
importjava.io.FileWriter;importjava.io.IOException;importjava.util.Properties;publicclassProperties03{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){Properties properties =newProperties();
properties.setProperty("charset","UTF-8");
properties.setProperty("user","jack");
properties.setProperty("pwd","123456");try{
properties.store(newFileWriter("src\\test.properties"),null);//第二个参数,表示注释信息(null表示没有注释)System.out.println("保存配置文件成功");}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();}}}
此时test.properties文件的内容为
#Tue Jan 17 18:31:36 CST 2023
user=jack
pwd=123456
charset=UTF-8
注意:如果保存的内容是中文,则存放的格式是Unicode编码
3.完成对test.properties文件的读取,并修改某个键值对
注意:使用setProperty方法,如果key不存在则创建,反之存在,则修改
importjava.io.FileWriter;importjava.io.IOException;importjava.util.Properties;publicclassProperties04{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){Properties properties =newProperties();
properties.setProperty("charset","UTF-8");
properties.setProperty("user","jack");
properties.setProperty("pwd","123456");
properties.setProperty("user","tom");
properties.setProperty("pwd","888888");try{
properties.store(newFileWriter("src\\test.properties"),null);System.out.println("保存配置文件成功");}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();}}}
此时文件内容为:
#Tue Jan 17 18:45:04 CST 2023
user=tom
pwd=888888
charset=UTF-8
setProperty操作时底层源码(父类Hashtable中的方法,可忽略)
publicsynchronizedVput(K key,V value){// Make sure the value is not nullif(value ==null){thrownewNullPointerException();}// Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.Entry<?,?> tab[]= table;int hash = key.hashCode();int index =(hash &0x7FFFFFFF)% tab.length;@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")Entry<K,V> entry =(Entry<K,V>)tab[index];for(; entry !=null; entry = entry.next){if((entry.hash == hash)&& entry.key.equals(key)){V old = entry.value;
entry.value = value;return old;}}addEntry(hash, key, value, index);returnnull;}
版权归原作者 墨辰JC 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。