一、对象的创建方式
Spring会帮助我们创建bean,那么它底层是调用什么方法进行创建的呢?有以下三种方法
- 使用构造方法
- 使用工厂类方法
- 使用工厂类的静态方法
接下来详细讲解这三种方法。
1. 使用构造方法
Spring默认使用类的空参构造方法创建bean,假如类没有空参构造方法,将无法完成bean的创建,接下来我们可以测试一下。
package com.example.dao;
import com.example.pojo.Student;
public class StudentDaoImpl1 implements StudentDao{
/*public StudentDaoImpl1() {
}*/
public StudentDaoImpl1(int a){};
@Override
public Student findById(int id){
return new Student(id,"程序员","北京");
}
}

错误原因:Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt: org.springframework.beans.factory.UnsatisfiedDependencyException: Error creating bean with name 'studentDao' defined in class path resource [bean.xml]: Unsatisfied dependency expressed through constructor parameter 0; nested exception is org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException: No qualifying bean of type 'int' available: expected at least 1 bean which qualifies as autowire candidate. Dependency annotations: {}
翻译:上下文初始化过程中遇到异常-取消刷新尝试:org.springframework.beans.factory.UnsatisfiedDependencyException:创建类路径资源[bean.xml]中定义的名称为“studentDao”的bean时出错:通过构造函数参数0表示的不满足依赖关系;嵌套异常为org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException:没有可用的类型为“int”的符合条件的bean:应至少有1个符合自动连线候选条件的bean。依赖项注释:{}
其实就是没有空的构造函数,加上一个就好了
2. 使用工厂类方法
Spring可以调用工厂类的方法创建bean:创建工厂类,工厂类提供创建对象的方法,在配置文件中配置创建bean的方式为工厂方式。
工厂类StudentDaoFactory:
package com.example.dao;
public class StudentDaoFactory {
public StudentDao getStudentDao(){
return new StudentDaoImpl1(1);
}
}
bean.xml的配置:
<!-- id: 工厂对象的id,class:工厂类 -->
<bean id="studentDaoFactory" class="com.example.dao.StudentDaoFactory" />
<!-- id:bean对象的id,factory-bean:工厂对象的id,factory-method:工厂方法 -->
<bean id="studentDao" factory-bean="studentDaoFactory" factory-method="getStudentDao"></bean>
**测试方法: **
@Test
public void t2(){
// 创建spring容器
ApplicationContext ac = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("C:\\JavaProjects\\06SSM_Projects\\springdemo\\spring_ioc1\\src\\main\\resources\\bean.xml");
// 从容器中获取对象
StudentDao userDao = ac.getBean("studentDao",StudentDao.class);
System.out.println(userDao);
System.out.println(userDao.findById(1));;
}
**测试结果: **
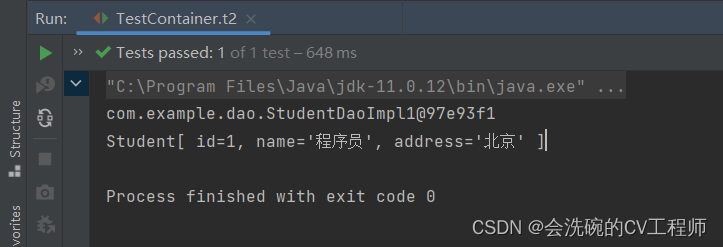
OK,确实成功写出来了
3. 使用工厂类的静态方法
Spring可以调用工厂类的静态方法创建bean,创建工厂类,工厂提供创建对象的静态方法,在配置文件中配置创建bean的方式为工厂静态方法。
工厂类StudentDaoFactory2
package com.example.dao;
public class StudentDaoFactory2 {
public static StudentDao getStudentDao2() {
return new StudentDaoImpl2();
}
}
**bean.xml的配置 **
<!-- id:bean的id class:工厂全类名 factory-method:工厂静态方法 -->
<bean id="studentDao" class="com.example.dao.StudentDaoFactory2" factory-method="getStudentDao2"/>
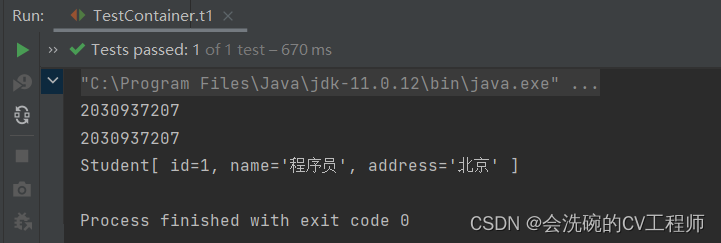
都是可以成功运行的。
二、对象的创建策略
scope属性设置对象的创建策略。Spring通过配置 <bean> 中的 scope 属性设置对象的创建策略,共有两种种创建策略。
1. 单例策略
singleton:单例,默认策略。整个项目只会创建一个对象,通过 <bean> 中的 lazy-init 属性可以设置单例对象的创建时机:lazy-init="false"(默认):立即创建,在容器启动时会创建配置文件中的所有Bean对象。lazy-init="true":延迟创建,第一次使用Bean对象时才会创建。下面测试获取对象后的哈希值是否一样就可以知道是否配置单例策略了
**bean.xml的配置 **
<bean id="studentDao" class="com.example.dao.StudentDaoImpl2" scope="singleton" lazy-init="true" />
**测试方法 **
@Test
public void t3(){
// 创建Spring容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
// 从容器获取对象
StudentDao studentDao1 = ac.getBean("studentDao",StudentDao.class);
StudentDao studentDao2 = ac.getBean("studentDao",StudentDao.class);
StudentDao studentDao3 = ac.getBean("studentDao",StudentDao.class);
System.out.println(studentDao1.hashCode());
System.out.println(studentDao2.hashCode());
System.out.println(studentDao3.hashCode());
}
**运行结果 **
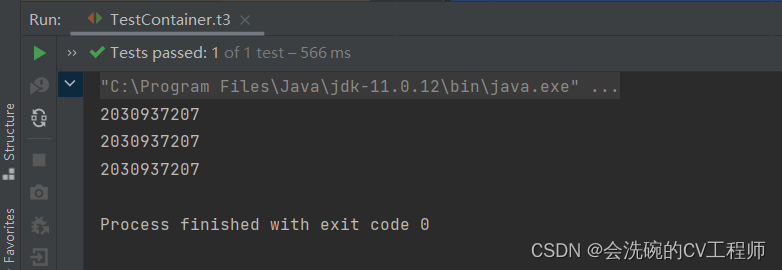
OK,得到的对象都是同一个哈希值,说明确实是同一个对象也就是说成功配置了单例模式。
2. 多例策略
prototype:多例,每次从容器中获取时都会创建对象。
**bean.xml配置 **
<!-- 配置多例策略 -->
<bean id="studentDao" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl2" scope="prototype"></bean>
**测试结果 **

得到的哈希值不一样,说明得到的是不同的对象,确实是多例策略 。
request:每次请求创建一个对象,只在web环境有效。
session:每次会话创建一个对象,只在web环境有效。
gloabal-session:一次集群环境的会话创建一个对象,只在web环境有效。
三、对象的销毁时机
对象的创建策略不同,销毁时机也不同:
- singleton:对象随着容器的销毁而销毁。
- prototype:使用JAVA垃圾回收机制销毁对象。
- request:当处理请求结束,bean实例将被销毁。
- session:当HTTP Session最终被废弃的时候,bean也会被销毁掉。
- gloabal-session:集群环境下的session销毁,bean实例也将被销毁。
四、生命周期方法
Bean对象的生命周期包含创建——使用——销毁,Spring可以配置Bean对象在创建和销毁时自动执行的方法:
1. 定义生命周期方法
在StudentDaoImpl2中新增生命周期方法
// 创建时自动执行的方法
public void init(){
System.out.println("使用StudentDaoImpl2创建对象"+this.hashCode());
}
// 销毁时自动执行的方法
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("销毁StudentDaoImpl2创建的对象"+this.hashCode());
}
2. 配置生命周期方法
<!-- init-method:创建对象时执行的方法 destroy-method:销毁对象时执行的方法 -->
<bean id="studentDao" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl2" scope="singleton" init-method="init" destroy-method="destory"></bean>
3. 测试
测试方法
@Test
public void t3(){
// 创建Spring容器
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml");
// 销毁Spring容器,ClassPathXmlApplicationContext才有销毁容器的方法
ac.close();
}
**测试结果 **

也确实可以
五、获取Bean对象的方式
1. 通过id/name获取
获取对象的时候是这样:
StudentDao studentDao = (StudentDao) ac.getBean("studentDao");
2. 通过类型获取
获取对象的时候是这样:
StudentDao studentDao2 = ac.getBean(StudentDao.class);不需要进行类型强转
3. 通过类型+id/name获取
虽然使用类型获取不需要强转,但如果在容器中有一个接口的多个实现类对象,则获取时会报错,此时需要使用类型+id/name获取,获取对象是这样:StudentDao studentDao2 = ac.getBean("studentDao",StudentDao.class);
往期专栏&文章相关导读
大家如果对于本期内容有什么不了解的话也可以去看看往期的内容,下面列出了博主往期精心制作的Maven,Mybatis等专栏系列文章,走过路过不要错过哎!如果对您有所帮助的话就点点赞,收藏一下啪。其中Spring专栏有些正在更,所以无法查看,但是当博主全部更完之后就可以看啦。
Maven系列专栏文章Maven系列专栏Maven工程开发Maven聚合开发【实例详解---5555字】Mybatis系列专栏文章Mybatis系列专栏MyBatis入门配置Mybatis入门案例【超详细】MyBatis配置文件 —— 相关标签详解Mybatis模糊查询——三种定义参数方法和聚合查询、主键回填Mybatis动态SQL查询 --(附实战案例--8888个字--88质量分)Mybatis分页查询——四种传参方式Mybatis一级缓存和二级缓存(带测试方法)Mybatis分解式查询Mybatis关联查询【附实战案例】MyBatis注解开发---实现增删查改和动态SQLMyBatis注解开发---实现自定义映射关系和关联查询Spring系列专栏文章Spring系列专栏Spring IOC 入门简介【自定义容器实例】IOC使用Spring实现附实例详解Spring IOC之对象的创建方式、策略及销毁时机和生命周期且获取方式Spring DI简介及依赖注入方式和依赖注入类型Spring IOC相关注解运用——上篇Spring IOC相关注解运用——下篇Spring AOP简介及相关案例注解、原生Spring、SchemaBased三种方式实现AOP【附详细案例】Spring事务简介及相关案例Spring 事务管理方案和事务管理器及事务控制的APISpring 事务的相关配置、传播行为、隔离级别及注解配置声明式事务
版权归原作者 会洗碗的CV工程师 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。