优质博文:IT-BLOG-CN
**【1】
x.sh
文件内容编写:** 固定开头:
#!/bin/sh
;
【2】学习的第一个命令就是
echo
输出的意思;
【3】其实
shell
脚本也就是在文件中写命令,但是我们要写的是绝对路径:
eg:/bin/pwd
;
【4】运行
shell
脚本:**
sh
文件名**;
【5】通过下面脚本进行学习:
#!/bin/sh
/bin/date +%F >>/test/shelldir/ex2.info #data +%F是将日期格式化。>>追加输出
echo "disk info:">>/test/shelldir/ex2.info
/bin/df -h >>/test/shelldir/ex2.info
echo >>/test/shelldir/ex2.info
echo "online users:">>/test/shelldir/ex2.info
/usr/bin/who |/bin/grep -v root >>/test/shelldir/ex2.info #使用的命令主要来自两个地方:①、/bin/ ②、/usr/bin/-v:表示排除
echo "memory info:">>/test/shelldir/ex2.info
/usr/bin/free -m >>/test/shelldir/ex2.info
echo >>/test/shelldir/ex2.info
#writeroot/usr/bin/write root </test/shelldir/ex2.info &&/bin/rm /test/shelldir/ex2.info
crontab -e #定时执行命令
09**1-5/bin /sh /test/ex2.sh #表示:每周一到周五的9点执行该脚本。
【6】变量: 是
shell
传递数据的一种方式,用来代表每个取值的符号。
Shell的变量有两种:①、永久变量 ②、临时变量。临时变量是
shell
程序内部定义的,其使用范围只限于定义它的程序,其它程序不可见。包括程序自定义变量、位置变量。永久变量是环境变量。其值不随 shell脚本的执行结束而消失。
【永久变量】: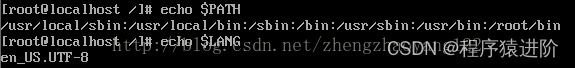
【自定义变量】: 在使用变量时,要在变量前面加前缀:
$
,一般变量使用大写字母表示,并且是英文字母开头,赋值号“=”两边没有空格,如:
NUM=5
、
STR="A string"
。可以将一个命令的执行结果赋值给一个变量:但需要使用命令替换符。
NUM=data
注意单引号和双引号之间的区别,“”是会将里面的变量值进行输出,‘’会将里面的内容原封不动的进行输出,不会识别里面的变量。使用
set
查看所有变量。查询
$
变量。使用
unset
命令删除指定的变量。
【7】占位变量: 在
shell
中还有两种常用的变量,一种是占位变量,还有一种是特殊变量,在编写
shell
到的时候特别常用:
【位置变量】:
ls -l file1 file2 file3...
(
n
范围=
1-9
)在代码里使用
$0-9
进行替换。也就是说查看
file1
目录地下的所有文件信息。
#!/bin/sh
DATE=`/bin/date +%Y%m%d`
echo "TODAY IS $DATE"/bin/ls -l $1/bin/ls -l $2/bin/ls -l $3
在命令行输入:
sh
文件名
/test /usr/bin /home
。解释:就是让命令中的
/test
替换脚本中的
$1........
【8】特殊变量:
■
$*
这个程序的所有参数;
■
$#
这个程序的参数个数;
■
$$
这个程序的
PID
;
■
$!
执行上一个程序的
PID
;
■
$?
执行上一个命令的返回值;
■
$(0-9)
显示位置变量;
【9】
read
:键盘输入,命令:
read
从键盘读取数据,赋给变量。
#!/bin/sh
read f s t
echo "the first is $f"
echo "the second is $s"
echo "the third is $t"
执行命令:
sh
文件名先执行,在输入变量。如果输入:
sh -x
文件名执行
shell
脚本,当执行到
read
时会弹出:
read f s t
,然后我们根据需求输入,例如:
10 20 30
;
**【10】
shell
的运算:**
expr
命令,对整数进行运算。注意点:
①、
expr
的计算必须用空格隔开;
②、
\*
表示转义字符;
③、保持先算乘除后算加减,如果需要优先算法需要加命令替换符;
④、可以对变量进行运算;
**【11】
test
测试命令:** 使用
test
命令可以对文件、字符串等进行测试,一般配合控制语句使用,不应该单独使用。
【12】
if
语句,语法格式:
if[-d $1]
then
else
fi
【实例展示】
#!/bin/sh
#iftest $1 then ...else... fiif[-d $1]
then
echo "this is a directory!"else
echo "this is not a directory!"
fi
【
if elif
语法】
#!/bin/sh
#iftest then ... elif test then ...else... fiif[-d $1]
then
echo "is a directory!"
elif [-f $1]
then
echo "is a file!"else
echo "error!"
fi
【逻辑 与
-a
和 或
-o
】
#!/bin/sh
# -a -o
if[ $1-eq $2-a $1=1]
then
echo "param1 == param2 and param1 = 1"
elif [ $1-ne $2-o $1=2]
then
echo "param1 != param2 or param1 = 2"else
echo "others"
fi
【
for
循环】
#!/bin/sh
#forvar in [params]do... donefor var in 12345678910do
echo "number is $var"
done
【
select
循环】
#!/bin/sh
#selectvar in [params]do... done
select var in "java""c++""php""linux""python""ruby""c#"dobreak
done
echo "you selected $var"
【
case
循环】
#!/bin/sh
read op
case $op in
a)
echo "you selected a";;
b)
echo "you selected b";;
c)
echo "you selected c";;*)
echo "error"
esac
【
while
循环】
#!/bin/sh
#whiletest do... done
num=1
sum=0while[ $num -le 100] #le表示小于等于
do
sum=`expr $sum + $num`
num=`expr $num +1`
done
#sleep5
echo $sum
版权归原作者 程序猿进阶 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。