SpringBoot常用注解
1.常用注解介绍
1.1 SpringMvc的实现原理
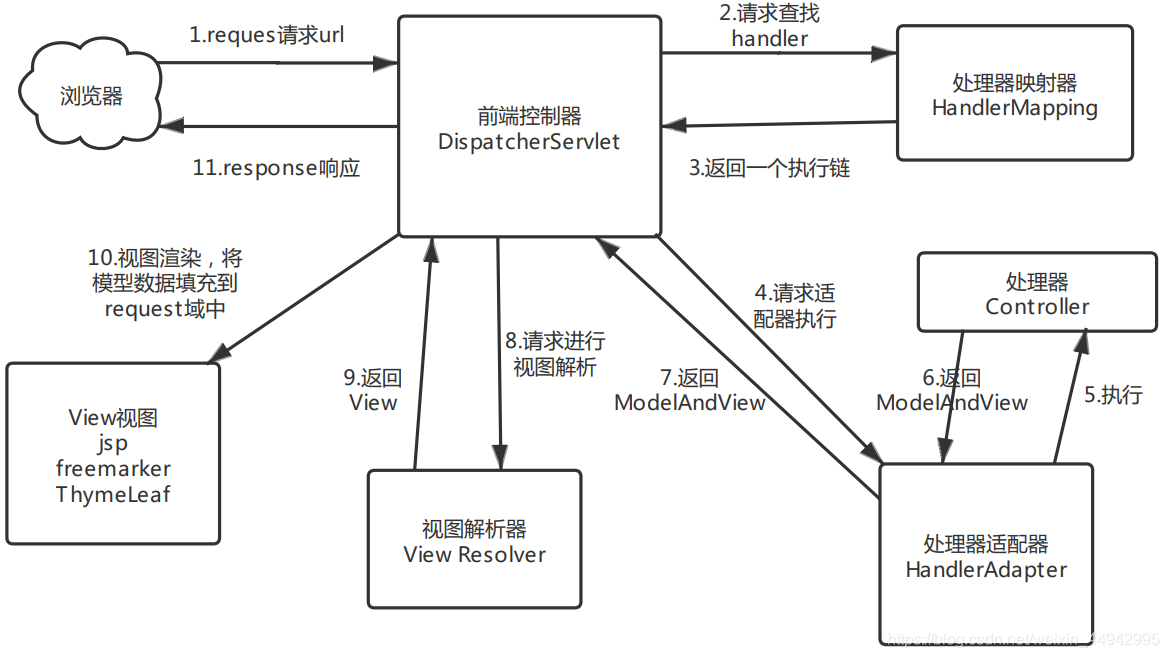
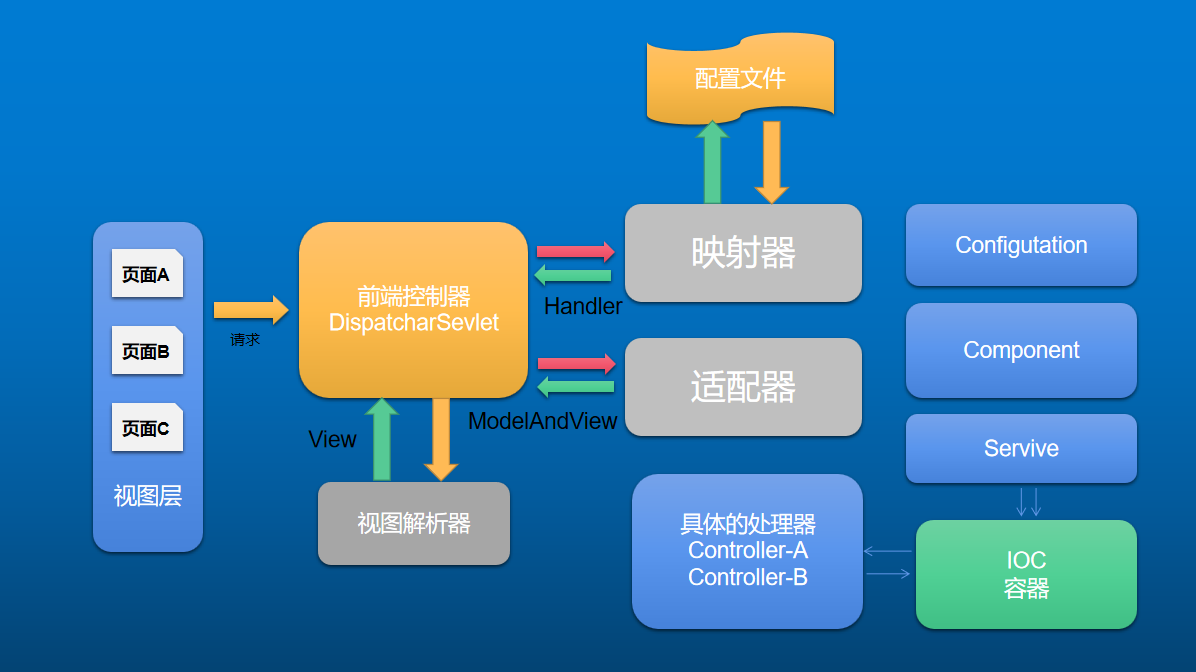
1.2 常用的注解介绍
常用注解分类有如下:
1.项目配置注解
@SpringBootApplication@ServletComponentScan@MapperScan
2.Controller的表现层注解:
@controller@Autowired@CrossOrigin@PathVariable@RequestParam@EnablCaching@RestController@RequestMapping@ResponseBody@GetMapping@PutMapping@PostMapping@DeleteMapping
3.servcie业务层注解
@Service@Resource
4.持久层注解
@Repository@Component@Transactional
5.其他相关注解
@ControllerAdvice@Configuration@Bean@Value
1.3 前言介绍
在spring boot中,摒弃了spring以往项目中大量繁琐的配置,遵循约定大于配置的原则,通过自身默认配置,极大的降低了项目搭建的复杂度。同样在spring boot中,大量注解的使用,使得代码看起来更加简洁,提高开发的效率。这些注解不光包括spring boot自有,也有一些是继承自spring的。
2.配置文件相关注解
2.2 @SpringBootApplication
@SpringBootApplication
是一个复合注解,包含了
@SpringBootConfiguration
,
@EnableAutoConfiguration
,
@ComponentScan
这三个注解这三个注解的作用分别为:
@SpringBootConfiguration:标注当前类是配置类,这个注解继承自@Configuration。并会将当前类内声明的一个或多个以@Bean注解标记的方法的实例纳入到srping容器中,并且实例名就是方法名。@EnableAutoConfiguration:是自动配置的注解,这个注解会根据我们添加的组件jar来完成一些默认配置,我们做微服时会添加spring-boot-starter-web这个组件jar的pom依赖,这样配置会默认配置springmvc 和tomcat。@ComponentScan:扫描当前包及其子包下被@Component,@Controller,@Service,@Repository注解标记的类并纳入到spring容器中进行管理。等价于context:component-scan的xml配置文件中的配置项
@SpringBootApplicationpublicclassSpringboot2Application{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){SpringApplication.run(Springboot2Application.class, args);}}
2.3 @ServletComponentScan
Servlet、Filter、Listener 可以直接通过
@WebServlet、@WebFilter、@WebListener
注解自动注册,这样通过注解servlet ,拦截器,监听器的功能而无需其他配置,所以这次相中使用到了filter的实现,用到了这个注解
2.4 @MapperScan
spring-boot支持mybatis组件的一个注解,通过此注解指定
mybatis接口类的路径
,即可完成对mybatis接口的扫描。
@MapperScan("com.example.mapper")@SpringBootApplicationpublicclassSpringboot2Application{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){SpringApplication.run(Springboot2Application.class, args);}}
3.Controller层相关注解
3.1 @controller
表明这个类是一个控制器类,和
@RequestMapping
来配合使用拦截请求
@ControllerpublicclassUserController{@RequestMapping("/view")publicStringview(){return"view";}}
3.2 @Autowired
是spring的自动装配,这个个注解可以用到构造器,变量域,方法,注解类型上。
当我们需要从bean 工厂中获取一个bean时,Spring会自动为我们装配该bean
中标记为@Autowired的元素
publicclassUserController{@AutowiredprivateUserService userService;@RequestMapping("/view")publicStringview(){
userService.save();return"view";}}
3.3 @CrossOrigin
@CrossOrigin(origins = “”, maxAge = 1000)
这个注解主要是为了解决跨域访问的问题。这个注解可以为整个controller配置启用跨域,也可以在方法级别启用
3.4 @PathVariable
路径变量注解,
@RequestMapping中用{}
来定义url部分的变量名
privatestaticfinalString PAGE ="param";// @PathVariable的用法// 这里是@PathVariable注解的单个值路径使用方法@RequestMapping("/path/{id}")publicModelAndViewpathTest1(@PathVariable(value ="id",required =false)int id){ModelAndView modelAndView =newModelAndView();
modelAndView.setViewName(PAGE);return modelAndView;}// 这里是@PathVariable注解的多个值路径使用方法@RequestMapping("/path/{id}/{username}/{password}")publicModelAndViewpathTest2(@PathVariable(value ="id",required =false)int id,@PathVariable(value ="username",required =false)String username,@PathVariable(value ="password",required =false)String password){ModelAndView modelAndView =newModelAndView();
modelAndView.setViewName(PAGE);return modelAndView;}
3.5 @RequestParam
用于将指定的请求参数赋值给方法中的形参。
有三个属性:
value:请求参数名(必须配置)required:是否必需,默认为 true,即 请求中必须包含该参数,如果没有包含,将会抛出异常(可选配置)defaultValue:默认值,如果设置了该值,required 将自动设为 false,无论你是否配置了required,配置了什么值,都是 false(可选配置)
privatestaticfinalString PAGE ="param";// @RequestParam 的多参数方式使用@RequestMapping("/param")publicModelAndViewparamTest(@RequestParam(value ="id",required =false,defaultValue ="0")int id,@RequestParam(value ="username",required =false,defaultValue ="zhangsan")String username,@RequestParam(value ="password",required =false,defaultValue ="123456")String password){ModelAndView modelAndView =newModelAndView();
modelAndView.addObject("id",id);
modelAndView.addObject("username",username);
modelAndView.addObject("password",password);
modelAndView.setViewName(PAGE);return modelAndView;// 访问的时候使用 http://localhost:8080/param?id=1&username=zhangsan&password=123456}
3.6 @EnablCaching
@EnableCaching: 这个注解是spring framework中的注解驱动的缓存管理功能。自spring版本3.1起加入了该注解。其作用相当于spring配置文件中的cache manager标签。
3.7 @RestController
@RestController
是
@Controller
和
@ResponseBody
的结合,以json数据格式返回数据,一个类被加上@RestController 注解,数据接口中就不再需要添加@ResponseBody。更加简洁。
@RestController// @Controller + @ResponseBody@RequestMapping("/request")publicclassRestUserController{@GetMapping("/get")publicUserrestTest(){User user =newUser(1,"zhangsan",20,"男");return user;}
3.8 @RequestMapping
第一种使用
1.用来拦截请求,默认拦截get和post请求
@RequestMapping("/adminDetele/{id}")
或
@RequestMapping(value="/adminDetele/{id}", method=RequestMethod.GET )
2.详细使用方法:
@RestController// @Controller + @ResponseBody@RequestMapping("/request")publicclassRestUserController{@RequestMapper("/data1")publicStringsave(){return"Hello Word"}}
第二种使用
1.导入Freemarker的坐标
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-freemarker</artifactId></dependency>
2.配置application.yml的配置文件
# 配置视图解析器spring:mvc:view:prefix: /
suffix: .html
# 配置freemarker插件 后缀freemarker:suffix: .html
template-loader-path: classpath:/static/
3.使用@GetMapping注解配合视图解析器
@RestControllerpublicclassUserController{@RequestMapping("/view")publicStringview(){return"view";}}
3.9 @ResponseBody
后端如果要返回json数据的话,需要配合@ResponseBody注解来完成
3.10 @GetMapping
用于将HTTP GET请求映射到特定处理程序方法的注释。具体来说,
@GetMapping
是一个作为快捷方式的组合注释
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
。
@RestController@RequestMapping("/request")publicclassRestUserController{@GetMapping("/get")publicUserrestTest(){User user =newUser(1,"zhangsan",20,"男");return user;}}
3.11 @PostMapping
用于将HTTP POST请求映射到特定处理程序方法的注释。具体来说,
@PostMapping
是一个作为快捷方式的组合注释
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
。
@RestController@RequestMapping("/request")publicclassRestUserController{@PostMapping("/addUser")publicUseraddUser(@RequestBodyUser user){System.out.println(user);return user;}}
类似的组合注解还有
@PutMapping、@DeleteMapping、@PatchMapping
4.业务层相关注解
4.1@Service
这个注解用来标记业务层的组件,我们会将业务逻辑处理的类都会加上这个注解交给spring容器管理,在需要使用的地方可使用
@Autowired自动装配
@ServicepublicclassArticleServiceImplimplementsArticleService{}@ControllerpublicclassArticleController{@AutowiredArticleService articleService;}
4.2 @Resource
@Resource和@Autowired一样都可以用来装配bean,都可以标注字段上,或者方法上。 @resource注解不是spring提供的,是属J2EE规范的注解。两个之前的区别就是匹配方式上有点不同,@Resource默认按照名称方式进行bean匹配,@Autowired默认按照类型方式进行bean匹配
@Service("userService")publicclassUserServiceImplimplementsUserService{}@RestControllerpublicclassUserController{@Autowired@Qualifier("userService")@Resource(name ="userService")privateUserService userService;}
5. 持久层注解
5.1 @Repository
作为DAO对象,管理操作数据库的对象。@Component, @Service, @Controller, @Repository是spring注解,注解后可以被spring框架所扫描并注入到spring容器来进行管理
@RepositorypublicinterfaceUserDao{}
5.2 @Component
通用注解,其他三个注解是这个注解的拓展,并且具有了特定的功能。通过这些注解的分层管理,就能将请求处理,义务逻辑处理,数据库操作处理分离出来,为代码解耦,也方便了以后项目的维护和开发
@ComponentpublicclassRedisUtils{@AutowiredRedisTemplate<String,String> redisTemplate;publicObjectget(String key){return redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);}}
5.3 @Transactional
声明事务,可以添加在类上或者方法上。在spring boot中 不用再单独配置事务管理,一般情况是我们会在servcie层添加了事务注解,即可开启事务。要注意的是,事务的开启只能在public 方法上
//尽量放在业务层上@Transactional@RequestMapping("/test")publicStringtest(Upload upload){}
6. 其他相关注解
6.1 ControllerAdvice
@ControllerAdvice 和 @ExceptionHandler
配合完成统一异常拦截处理
@RestControllerAdvice 是 @ControllerAdvice 和 @ResponseBody的合集,可以将异常以json的格式返回数据。
@ControllerAdvicepublicclassGlobalExceptionHandler{@AutowiredRedisUtils redisUtils;@ExceptionHandler(value =Exception.class)publicModelAndViewdefaultErrorHandler(HttpServletRequest req,Exception e)throwsException{ModelAndView mav =newModelAndView();
mav.addObject("exception", e);
mav.addObject("url", req.getRequestURL());// mav.addObject("admin", redisUtils.get(Constant.USER));
mav.setViewName("error");return mav;}}
6.2 @Configuration
声明当前类为配置类,配合
@Bean
注解一起使用,可以作为导入插件。
@ConfigurationpublicclassMybatiPlusConfig{@BeanpublicMybatisPlusInterceptormybatisPlusInterceptor(){MybatisPlusInterceptor interceptor =newMybatisPlusInterceptor();
interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(newOptimisticLockerInnerInterceptor());return interceptor;}}
版权归原作者 CN-ZHANG 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。