目录
🍓本文出现如此多草莓的原因是,我昨天晚上吃了好多草莓,并且现在还想吃。
🍓接下来要更新链表这儿的题解咯~
正文开始@边通书
0. 引
上文提到,带头双向循环链表 ——
- 结构最复杂,一般用在单独存储数据。实际中使用的链表数据结构,都是带头双向循环链表。
- 另外这个结构虽然复杂,却也是无死角的结构,用代码实现时会发现结构会带来很多优势,非常爽,后面我们代码实现了就知道了。
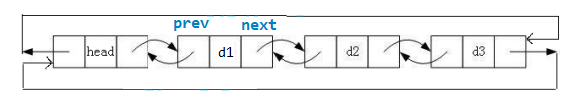
代码实现的简单归功于它复杂的结构,以下这几点都是在写的过程中感受到的 ——
🍓 带头
- 这样使得尾插尾删头插头删不必传二级指针,因为pList这个带哨兵位头节点的地址不会发生改变
- 尾删时,只剩一个节点和普遍情况(>=2个节点)可以合并
🍓 双向
方便找上一个下一个
🍓 循环
使找尾变得简单
1. 双向循环链表实现
1.1 创建、销毁、申请新节点、打印
1.1.1 创建
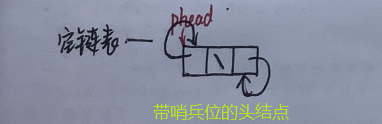
🍓 对于pList即这个链表地址的分配我们完全可以直接写,但还是推荐写成接口函数
🍓 初始化函数, 对于pList这个实参的改变,我们同样可以采取以往的办法传二级指针(即pList的地址类型,为
LTNode**
)
🍓 这里采取返回值的办法,返回地址,赋给pList
LTNode*ListInit(){//哨兵位的头结点
LTNode* phead =(LTNode*)malloc(sizeof(LTNode));if(phead ==NULL){printf("malloc failed\n");exit(-1);}
phead->prev = phead;
phead->next = phead;return phead;}
test.c
中是这样调用的
LTNode* pList =ListInit();
1.1.2 销毁
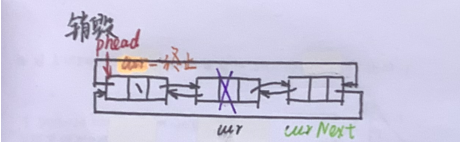
voidListDestroy(LTNode* phead){assert(phead);
LTNode* cur = phead->next;while(cur != phead){
LTNode* curNext = cur->next;free(cur);
cur = curNext;}free(phead);//phead = NULL;}
注意这里的
phead = NULL;
很有必要,但这样写没有发挥实际作用(所以我也把它注释掉了),因为phead是形参,形参改变不会影响实参,也就是pList不会改变。
这就导致了野指针的问题 —— 虽然pList仍保持着原来的地址,但是phead已经被释放了,此时pList就是一个野指针。(可以传二级,实际上传二级就不会有这些问题,但为了保持接口一致性用一级比较好)
因此,我们需要在外面,即
test.c
文件中把它置空 ——
ListDestroy(pList);
pList =NULL;//外面置空,就跟free一样
1.1.3 申请新节点
LTNode*BuyListNode(LTDataType x){
LTNode* newnode =(LTNode*)malloc(sizeof(LTNode));if(newnode ==NULL){printf("malloc failed\n");exit(-1);}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->prev =NULL;
newnode->next =NULL;return newnode;}
1.1.4 打印
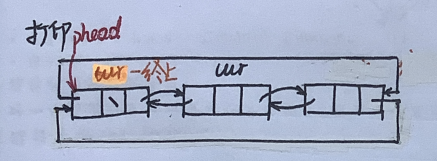
voidListPrint(LTNode* phead){assert(phead);
LTNode* cur = phead->next;while(cur != phead){printf("%d ", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;}printf("\n");}
1.2 尾插、尾删
1.2.1 尾插
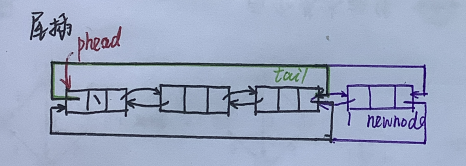
🍓 相比于单链表
- 不必再传二级指针,因为phead不用更改
- 完美处理空链表,无需再把链表为空时的插入单拎出来解决
- 找尾也很方便*O(1)*,不必像单链表一样找尾找得好辛苦
voidListPushBack(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x){assert(phead);
LTNode* newnode =BuyListNode(x);
LTNode* tail = phead->prev;
tail->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = tail;
newnode->next = phead;
phead->prev = newnode;}
1.2.2 尾删
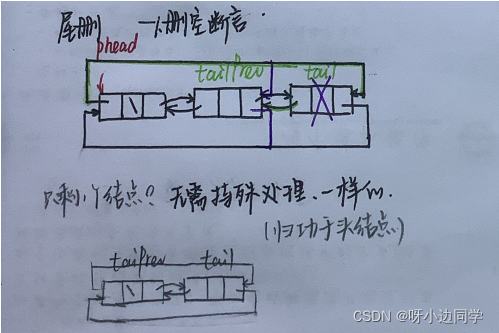
🍓 与单链表相比
- 不必再传二级指针,因为phead不用更改
- 不用单拎出来解决只剩一个节点时的情况,它的结构保证了tail不会为空,就不会被错误的解引用
voidListPopBack(LTNode* phead){assert(phead);assert(phead->next != phead);//1.删空了
LTNode* tail = phead->prev;
LTNode* tailPrev = tail->prev;free(tail);//链接
phead->prev = tailPrev;
tailPrev->next = phead;}
1.3 头插、头删
1.3.1头插
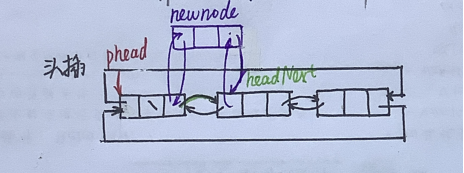
🍓 与单链表相比
- 不必再传二级指针,因为phead不用更改
- 链表为空?也没事。其实这在单链表那儿也没事,就是情不自禁要想一下
voidListPushFront(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x){assert(phead);
LTNode* newnode =BuyListNode(x);
LTNode* headNext = phead->next;//链接
phead->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = phead;
newnode->next = headNext;
headNext->prev = newnode;}
1.3.2 头删
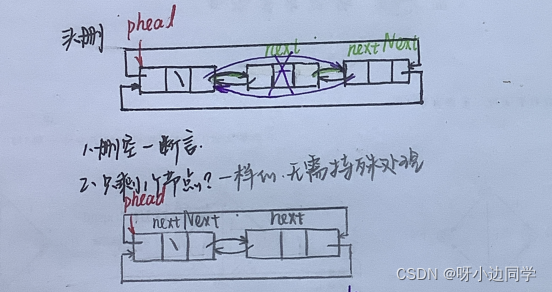
🍓 与单链表相比
- 不必再传二级指针,因为phead不用更改
- 只剩一个节点?也没事。其实这在单链表那儿也没事,就是情不自禁要想一下
voidListPopFront(LTNode* phead){assert(phead);assert(phead->next != phead);//删空时断言
LTNode* next = phead->next;
LTNode* nextNext = next->next;free(next);//链接
phead->next = nextNext;
nextNext->prev = phead;}
1.4 查找、任意位置插入、任意位置删除
1.4.1 查找
和打印类似
LTNode*ListFind(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x){assert(phead);//空链表if(phead->next == phead){returnNULL;}
LTNode* cur = phead->next;while(cur != phead){if(cur->data == x){return cur;}
cur = cur->next;}returnNULL;}
1.4.2 任意位置插入
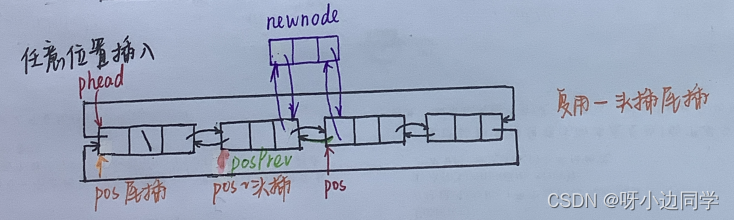
voidListInsert(LTNode* pos, LTDataType x){assert(pos);
LTNode* newnode =BuyListNode(x);
LTNode* posPrev = pos->prev;//链接
posPrev->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = posPrev;
newnode->next = pos;
pos->prev = newnode;}
1.4.3 任意位置删除
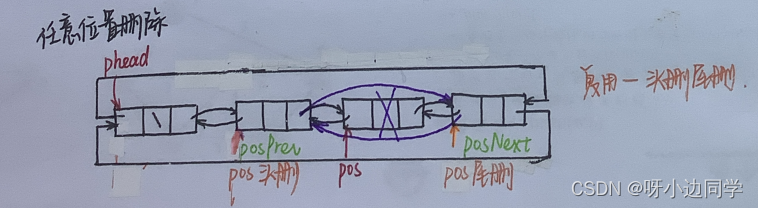
voidListErase(LTNode* pos){//按理说应该断言一下pos是pList的情况,但是为了这个再增加一个参数,得不偿失assert(pos);
LTNode* posPrev = pos->prev;
LTNode* posNext = pos->next;free(pos);//链接
posPrev->next = posNext;
posNext->prev = posPrev;}
1.4.4 复用
有了上面的任意位置插入删除,就可以快速写出头插头删、尾插尾删。
//尾插voidListPushBack(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x){assert(phead);ListInsert(phead, x);}//尾删voidListPopBack(LTNode* phead){assert(phead);assert(phead->next != phead);//1.删空了ListErase(phead->prev);}//头插voidListPushFront(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x){assert(phead);
LTNode* newnode =BuyListNode(x);ListInsert(phead->next, x);}//头删voidListPopFront(LTNode* phead){assert(phead);assert(phead->next != phead);//删空时断言ListErase(phead->next);}
2. 顺序表和链表的比较
这两个结构各有优势,很难说谁更优,它们是相辅相成的结构。
顺序表链表(带头双向循环链表)优点1. 支持随机访问,需要随机访问支持的结构可以很好地适用1. 任意位置插入删除效率高*O(1)*2. CPU高速缓存命中率高2. 按需申请释放空间缺点1. 头部、中间插入效率低1. 不支持随机访问(即下标访问,如要访问第5个)2. 连续的物理空间,空间不够了需要增容2. 链表存储一个值,同时要存储两个指针,有一定消耗a. 增容有一定程度的消耗3. CPU高速缓存命中率低b. 为了避免频繁增容,一般按倍数去增,用不完存在一定空间浪费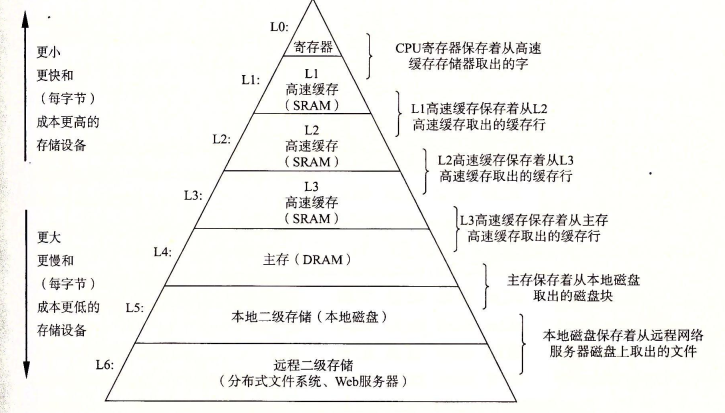
关于CPU高速缓存命中率,请阅读陈皓的文章与程序员相关的CPU缓存知识 | 酷 壳 - CoolShell,我顺便也读了,没法完全的懂,另外我还被他的其他文章拽走了,太有意思了,但还是解释一下CPU高速缓存命中率。
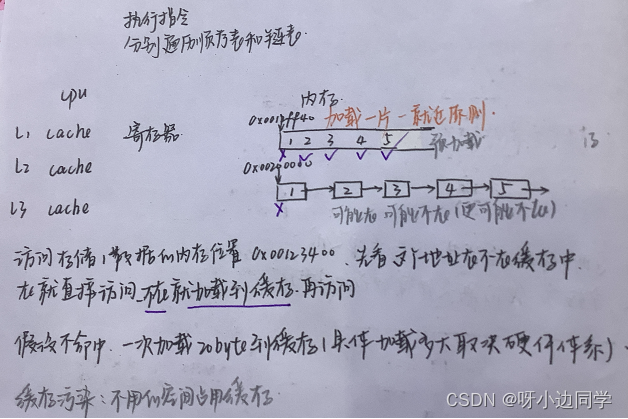
附:
List.h
#pragmaonce#include<stdio.h>#include<stdlib.h>#include<assert.h>typedefint LTDataType;//带头双向循环---非常棒的结构typedefstructListNode{
LTDataType data;structListNode* prev;structListNode* next;}LTNode;//初始化
LTNode*ListInit();//链表打印voidListPrint(LTNode* phead);//销毁voidListDestroy(LTNode* phead);//尾插voidListPushBack(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x);//尾删voidListPopBack(LTNode* phead);//头插voidListPushFront(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x);//头删voidListPopFront(LTNode* phead);//查找
LTNode*ListFind(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x);//任意位置插入voidListInsert(LTNode* pos, LTDataType x);//任意位置删除voidListErase(LTNode* pos);
List.c
#define_CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS1#include"List.h"
LTNode*BuyListNode(LTDataType x){
LTNode* newnode =(LTNode*)malloc(sizeof(LTNode));if(newnode ==NULL){printf("malloc failed\n");exit(-1);}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->prev =NULL;
newnode->next =NULL;return newnode;}
LTNode*ListInit(){//哨兵位的头结点
LTNode* phead =(LTNode*)malloc(sizeof(LTNode));if(phead ==NULL){printf("malloc failed\n");exit(-1);}
phead->prev = phead;
phead->next = phead;return phead;}voidListDestroy(LTNode* phead){assert(phead);
LTNode* cur = phead->next;while(cur != phead){
LTNode* curNext = cur->next;free(cur);
cur = curNext;}free(phead);//phead = NULL;}voidListPrint(LTNode* phead){assert(phead);
LTNode* cur = phead->next;while(cur != phead){printf("%d ", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;}printf("\n");}voidListPushBack(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x){assert(phead);
LTNode* newnode =BuyListNode(x);
LTNode* tail = phead->prev;//链接
tail->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = tail;
newnode->next = phead;
phead->prev = newnode;//ListInsert(phead, x);}voidListPopBack(LTNode* phead){assert(phead);assert(phead->next != phead);//1.删空了
LTNode* tail = phead->prev;
LTNode* tailPrev = tail->prev;free(tail);//链接
phead->prev = tailPrev;
tailPrev->next = phead;//ListErase(phead->prev);}voidListPushFront(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x){assert(phead);
LTNode* newnode =BuyListNode(x);
LTNode* headNext = phead->next;//链接
phead->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = phead;
newnode->next = headNext;
headNext->prev = newnode;//ListInsert(phead->next, x);}voidListPopFront(LTNode* phead){assert(phead);assert(phead->next != phead);//删空时断言
LTNode* next = phead->next;
LTNode* nextNext = next->next;free(next);//链接
phead->next = nextNext;
nextNext->prev = phead;//ListErase(phead->next);}
LTNode*ListFind(LTNode* phead, LTDataType x){assert(phead);//空链表if(phead->next == phead){returnNULL;}
LTNode* cur = phead->next;while(cur != phead){if(cur->data == x){return cur;}
cur = cur->next;}returnNULL;}voidListInsert(LTNode* pos, LTDataType x){assert(pos);
LTNode* newnode =BuyListNode(x);
LTNode* posPrev = pos->prev;//链接
posPrev->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = posPrev;
newnode->next = pos;
pos->prev = newnode;}voidListErase(LTNode* pos){//按理说应该断言一下pos是pList的情况,但是为了这个再增加一个参数,得不偿失assert(pos);
LTNode* posPrev = pos->prev;
LTNode* posNext = pos->next;free(pos);//链接
posPrev->next = posNext;
posNext->prev = posPrev;}
test.c
#define_CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS1#include"List.h"//测试尾插尾删voidtestList1(){
LTNode* pList =ListInit();ListPushBack(pList,1);ListPushBack(pList,2);ListPushBack(pList,3);ListPrint(pList);ListPopBack(pList);//ListPopBack(pList);/*ListPopBack(pList);
ListPopBack(pList);*/ListPrint(pList);ListDestroy(pList);
pList =NULL;}//测试头插头删voidtestList2(){
LTNode* pList =ListInit();ListPushFront(pList,1);ListPushFront(pList,2);ListPushFront(pList,3);ListPrint(pList);ListPopFront(pList);/*ListPopFront(pList);
ListPopFront(pList);
ListPopFront(pList);*/ListPrint(pList);ListDestroy(pList);
pList =NULL;}//测试查找、任意位置插入、任意位置插入voidtestList3(){
LTNode* pList =ListInit();ListPushBack(pList,1);ListPushBack(pList,2);ListPushBack(pList,4);ListPushBack(pList,5);ListPrint(pList);
LTNode* ret =ListFind(pList,4);if(ret ==NULL){printf("not found\n");}else{printf("%d\n", ret->data);}ListInsert(ret,3);ListPrint(pList);ListErase(ret);ListPrint(pList);ListDestroy(pList);
pList =NULL;}intmain(){//testList1();testList2();//testList3();return0;}
本文完@边通书
版权归原作者 呀小边同学 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。