这段时间因为毕设的需求,接触学习了一下用Android app连接MQTT服务器,然后对下位机(STM32/ESP8266)进行数据通讯的一个小设计,本篇文章介绍app+MQTT服务器这一段。
实现原理:
这里设计的是一个监测控制智能风扇的APP,可以实时监测当前温度、湿度及下位机的传感器、控制器件的一些状态。
一、设计流程:
- Android app项目创建;
- UI控制界面设计;
- 导入MQTT jar包;
- 配置联网权限;
- 配置MQTT服务器连接参数;
- MQTT.fx实现联调;
二、设计实现
1、Android app项目创建
项目创建这里就不过多赘述了!
2、UI控制界面设计
我这里主要是以毕设的需求设计的,所以比较简单;
模拟器界面
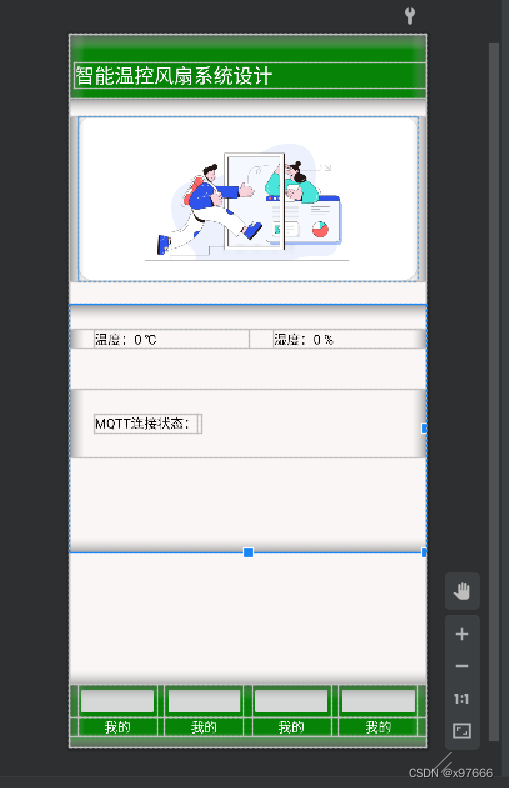
手机app界面

这个显示界面代码相对简单,有需要的可以参考一下,代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:background="#078307"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="78dp">
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:text="智能温控风扇系统设计"
android:textSize="24sp"
android:layout_marginLeft="6dp"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:textColor="@color/white"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:background="#FAF6F6"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_height="710dp">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<androidx.cardview.widget.CardView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:layout_marginRight="10dp"
app:cardCornerRadius="20dp">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/m_im_1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/img_3"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</androidx.cardview.widget.CardView>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_marginTop="30dp"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_height="300dp">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_marginTop="30sp"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/m_temp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:text="温度:0 ℃"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:layout_marginLeft="30dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/m_humi"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:text="湿度:0 %"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:layout_marginLeft="30dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_marginTop="50dp"
android:padding="30dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:text="MQTT连接状态:"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/m_mqtt"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:text=" "
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<ImageButton
android:layout_width="30dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:layout_marginRight="10dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_height="40dp"/>
<ImageButton
android:layout_width="30dp"
android:layout_marginRight="10dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_height="40dp"/>
<ImageButton
android:layout_width="30dp"
android:layout_marginRight="10dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_height="40dp"/>
<ImageButton
android:layout_width="30dp"
android:layout_marginRight="10dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_height="40dp"/>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:text="我的"
android:gravity="center"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:textColor="@color/white"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:text="我的"
android:gravity="center"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:textColor="@color/white"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:text="我的"
android:gravity="center"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:textColor="@color/white"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:text="我的"
android:gravity="center"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_marginRight="10dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:textColor="@color/white"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
3、导入MQTT jar包
进入正题,开始导入MQTT所需要的jar包:
jar包链接 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1hLt1xiL67dhbJ3v3MKfUlw
提取码:wmmh
下载jar包后直接复制这个jar包
然后给粘贴至libs目录下
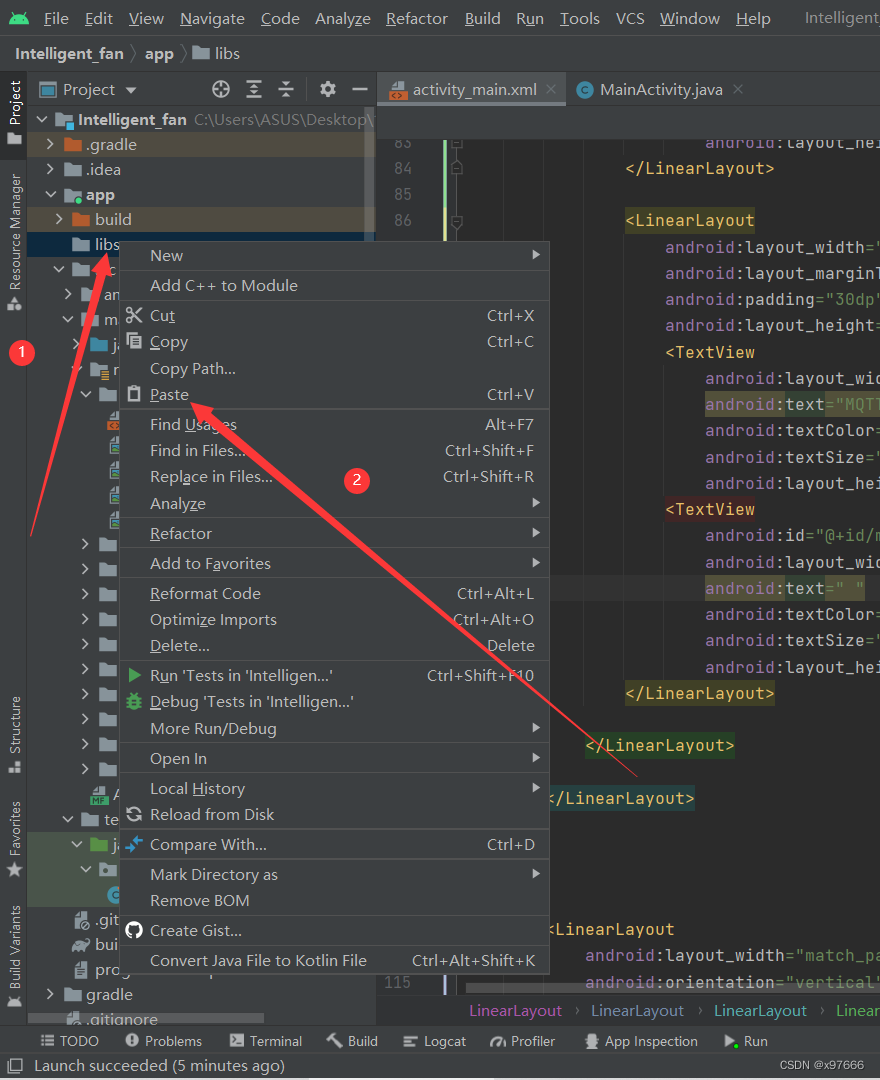
点击OK即可
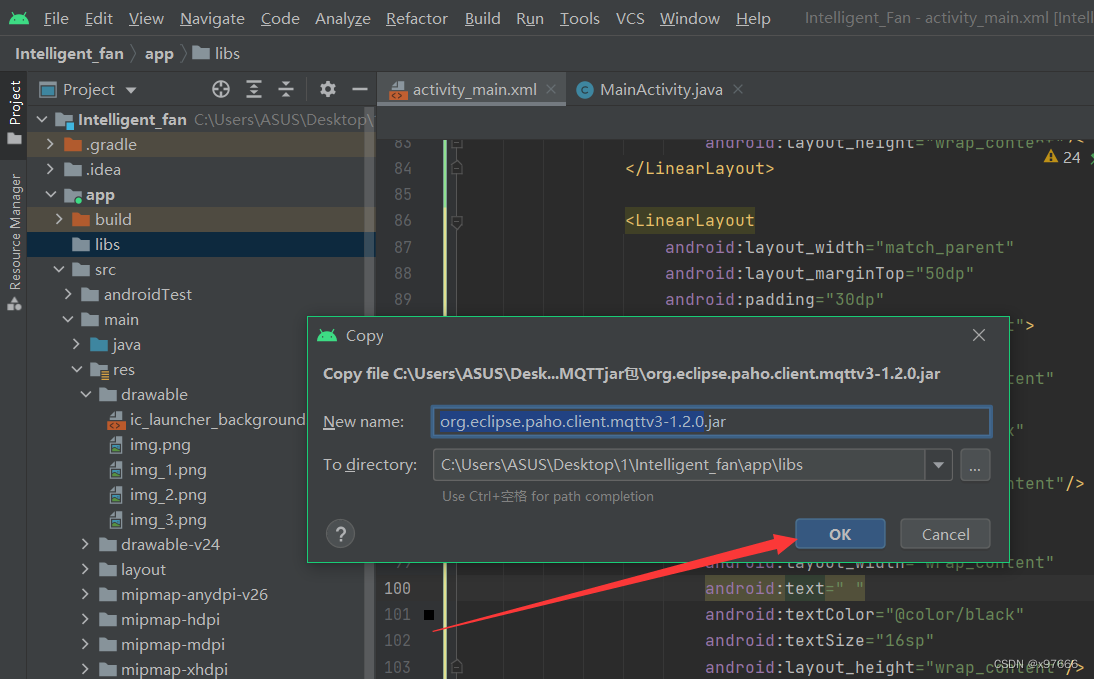
导入
然后鼠标右键给它添加依赖
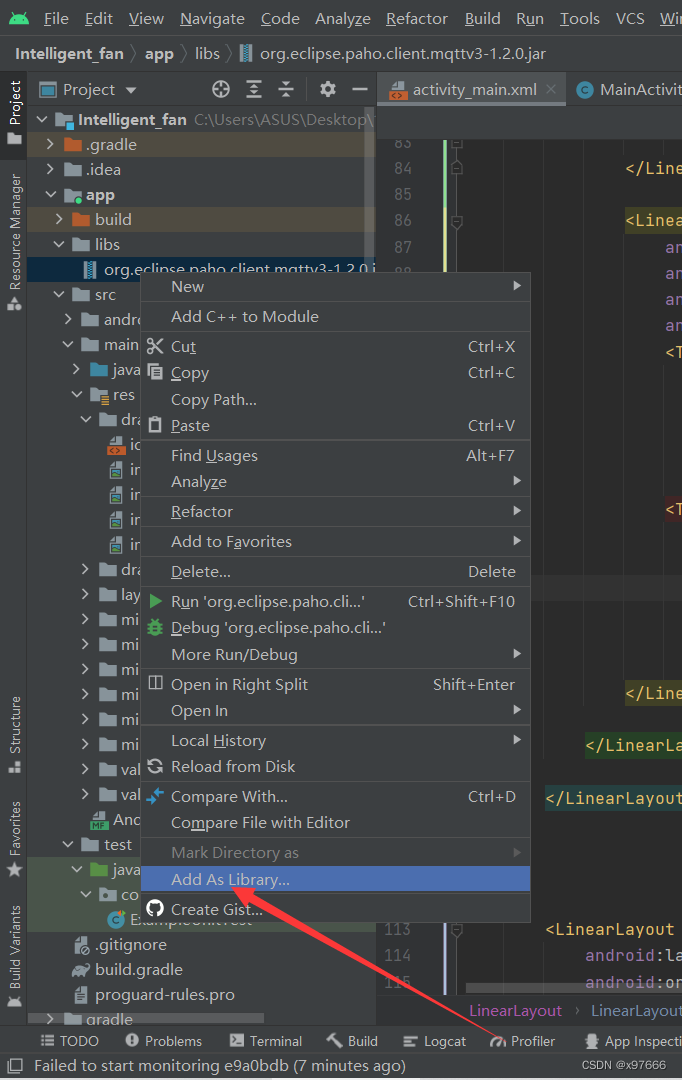
点击OK
等待构建完成即可.
此时我们来到java代码界面敲MQTT就可以看到很多方法
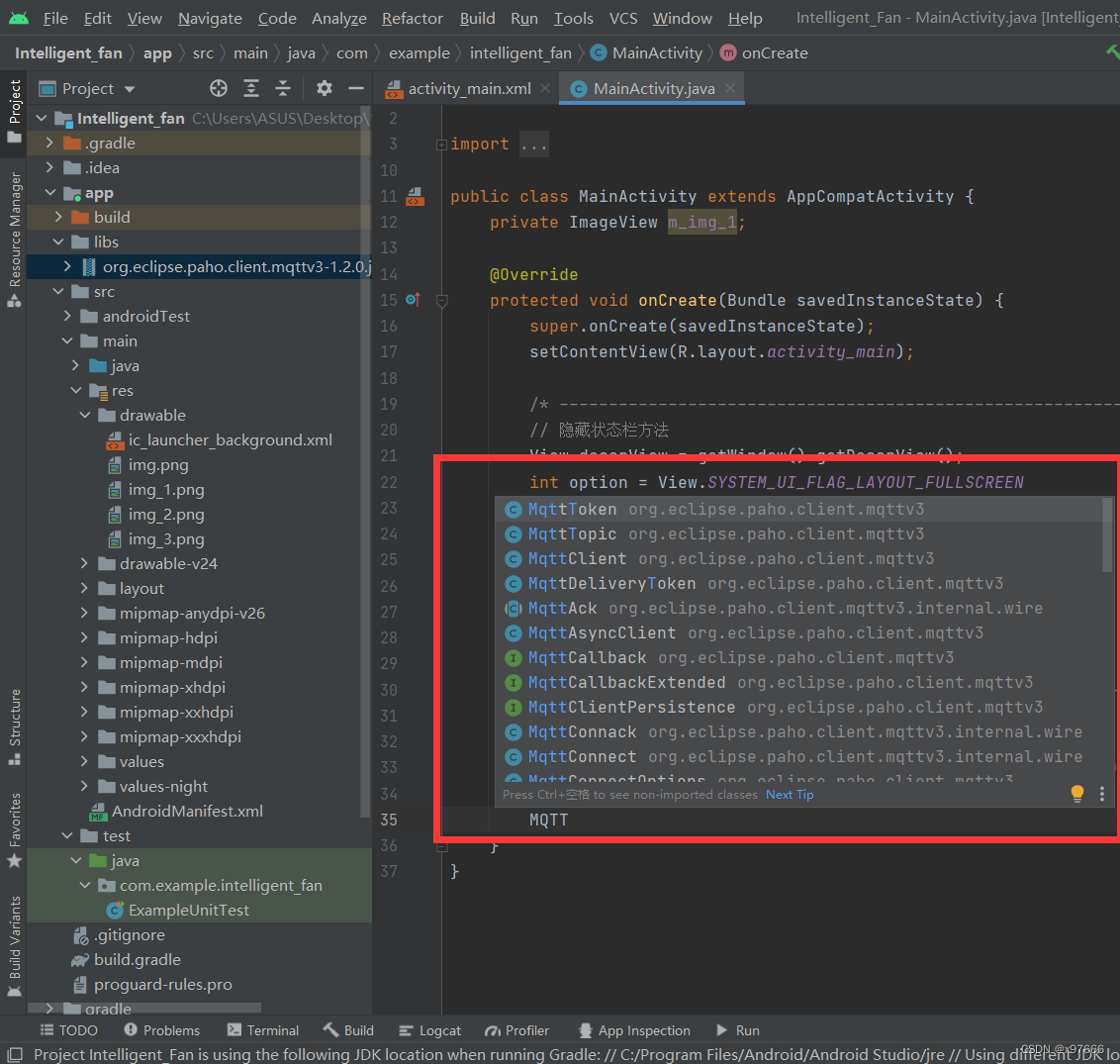
好,到了这一步就可以添加MQTT的配置代码了
在onCreate后面添加下列代码
添加代码
// MQTT初始化
private void Mqtt_init()
{
try {
//host为主机名,test为clientid即连接MQTT的客户端ID,一般以客户端唯一标识符表示,MemoryPersistence设置clientid的保存形式,默认为以内存保存
client = new MqttClient(host, mqtt_id,
new MemoryPersistence());
//MQTT的连接设置
MqttConnectOptions options = new MqttConnectOptions();
//设置是否清空session,这里如果设置为false表示服务器会保留客户端的连接记录,这里设置为true表示每次连接到服务器都以新的身份连接
options.setCleanSession(false);
//设置连接的用户名
options.setUserName(userName);
//设置连接的密码
options.setPassword(passWord.toCharArray());
// 设置超时时间 单位为秒
options.setConnectionTimeout(10);
// 设置会话心跳时间 单位为秒 服务器会每隔1.5*20秒的时间向客户端发送个消息判断客户端是否在线,但这个方法并没有重连的机制
options.setKeepAliveInterval(20);
//设置回调
client.setCallback(new MqttCallback() {
@Override
public void connectionLost(Throwable cause) {
//连接丢失后,一般在这里面进行重连
System.out.println("connectionLost----------");
//startReconnect();
}
@Override
public void deliveryComplete(IMqttDeliveryToken token) {
//publish后会执行到这里
System.out.println("deliveryComplete---------"
+ token.isComplete());
}
@Override
public void messageArrived(String topicName, MqttMessage message)
throws Exception {
//subscribe后得到的消息会执行到这里面
System.out.println("messageArrived----------");
Message msg = new Message();
msg.what = 3; //收到消息标志位
// msg.obj = topicName + "---" +message.toString();
msg.obj = message.toString();
handler.sendMessage(msg); // hander 回传
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// MQTT连接函数
private void Mqtt_connect() {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
if(!(client.isConnected()) ) //如果还未连接
{
MqttConnectOptions options = null;
client.connect(options);
Message msg = new Message();
msg.what = 31;
handler.sendMessage(msg);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
Message msg = new Message();
msg.what = 30;
handler.sendMessage(msg);
}
}
}).start();
}
// MQTT重新连接函数
private void startReconnect() {
scheduler = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor();
scheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (!client.isConnected()) {
Mqtt_connect();
}
}
}, 0*1000, 10 * 1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
// 订阅函数 (下发任务/命令)
private void publishmessageplus(String topic,String message2)
{
if (client == null || !client.isConnected()) {
return;
}
MqttMessage message = new MqttMessage();
message.setPayload(message2.getBytes());
try {
client.publish(topic,message);
} catch (MqttException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/* ========================================================================================== */
不出意外,这里会出现一堆报红
不用慌,这是因为有一些方法还没构建,有一些参数还没声明,我们一步一步来;
光标放置后按alt+Enter后,有部分参数就会自动构建,开干
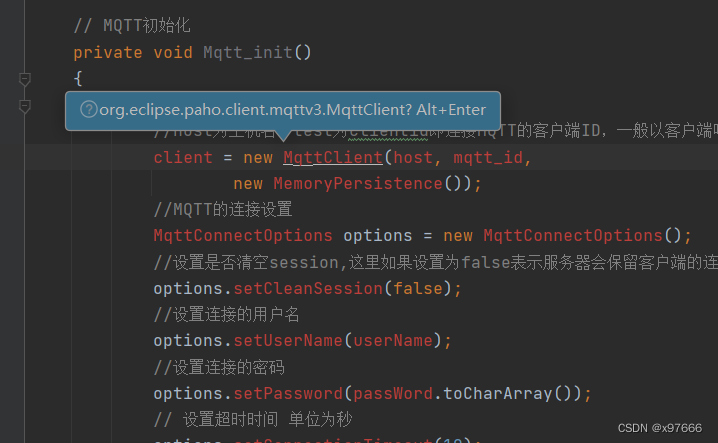
然后把下列处理代码添加至主函数(这个位置)
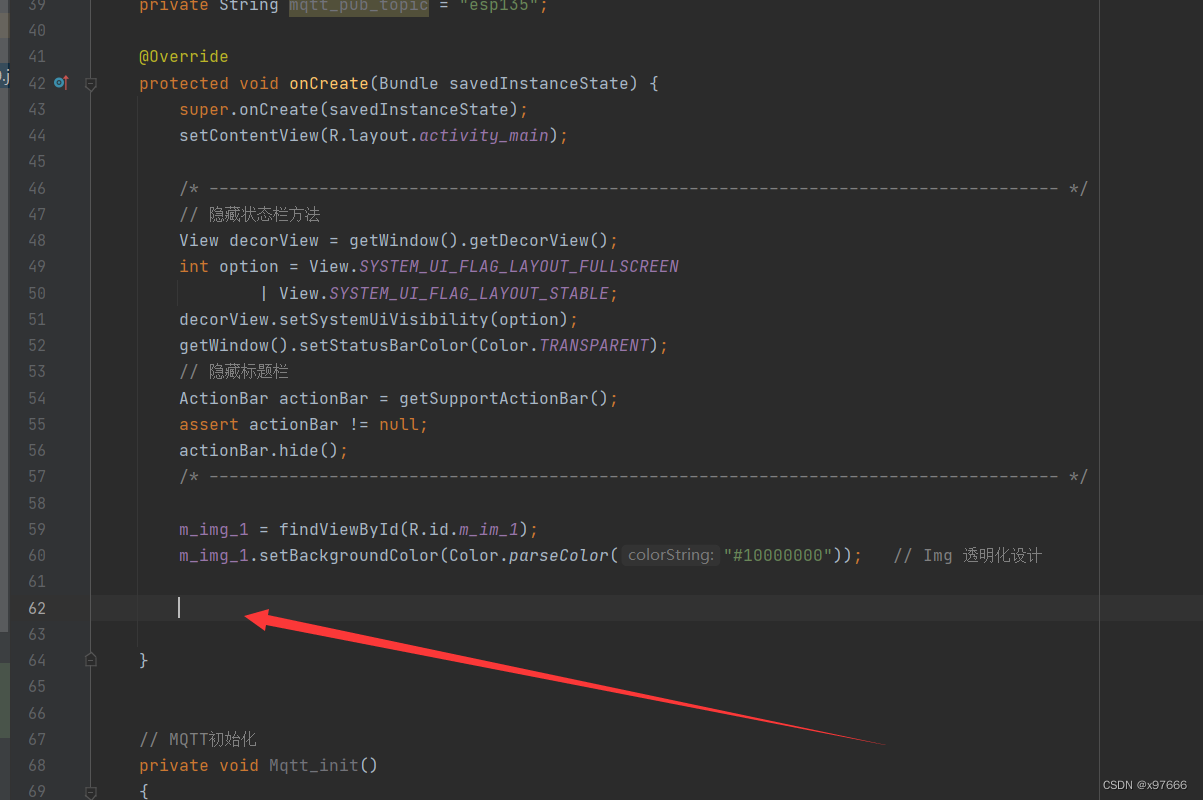
Mqtt_init();
startReconnect();
handler = new Handler(Looper.myLooper()) {
@SuppressLint("SetTextI18n")
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
super.handleMessage(msg);
switch (msg.what){
case 1: //开机校验更新回传
break;
case 2: // 反馈回传
break;
case 3: //MQTT 收到消息回传 UTF8Buffer msg=new UTF8Buffer(object.toString());
System.out.println(msg.obj.toString()); // 显示MQTT数据
break;
case 30: //连接失败
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,"连接失败" ,Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
case 31: //连接成功
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,"连接成功" ,Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
try {
client.subscribe(mqtt_sub_topic,1);
} catch (MqttException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
};
/* -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
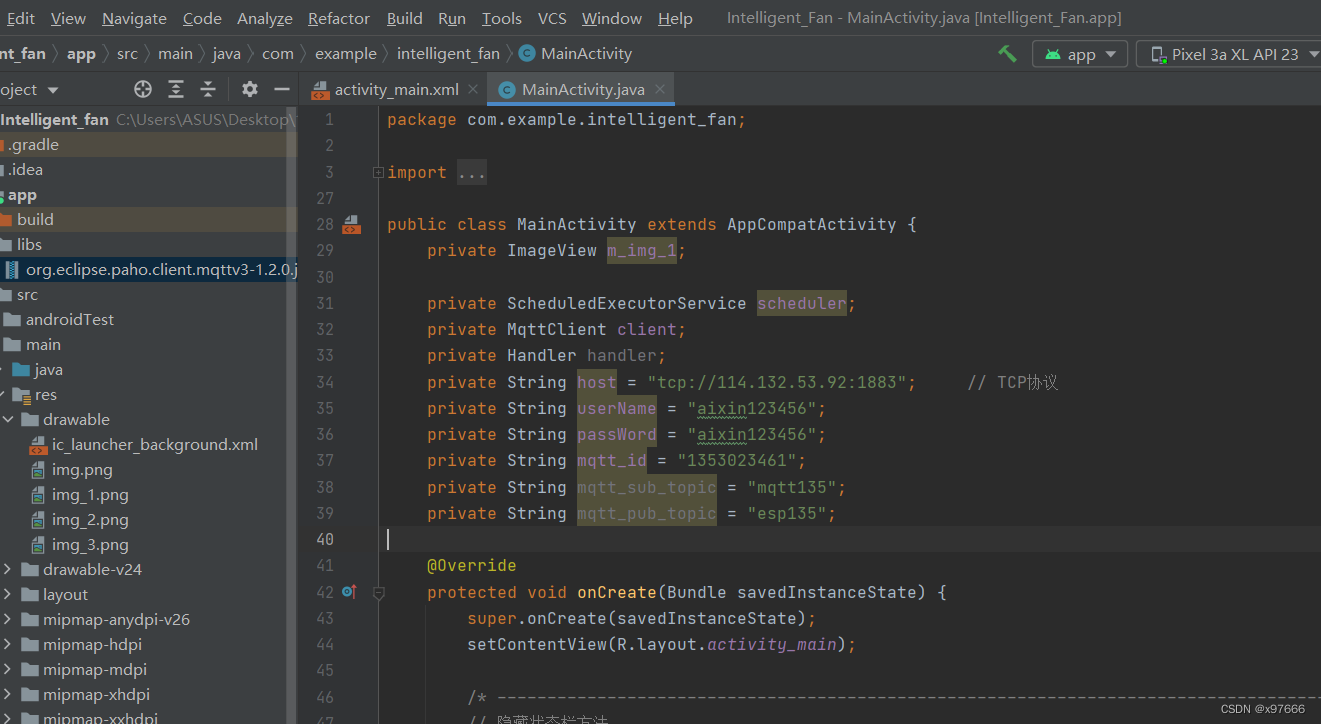
好,把这个配置代码加上去
private ScheduledExecutorService scheduler;
private MqttClient client;
private Handler handler;
private String host = "tcp://114.132.53.92:1883"; // TCP协议
private String userName = "aixin123456";
private String passWord = "aixin123456";
private String mqtt_id = "1353023461";
private String mqtt_sub_topic = "mqtt135";
private String mqtt_pub_topic = "esp135";
那么到达这一步就不会有报错了! 解决
4、配置联网权限
在事件清单中添加联网权限
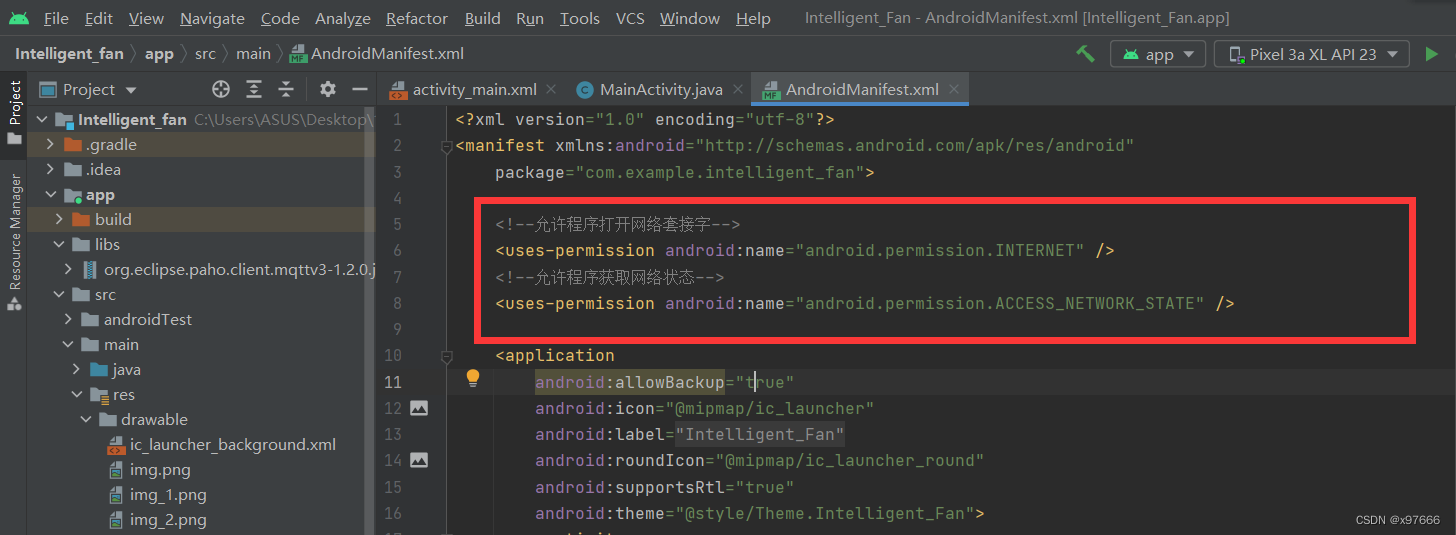
<!--允许程序打开网络套接字-->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<!--允许程序获取网络状态-->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" />
5、配置服务器参数
这里的服务器连接的参数注意一定要修改,这里连接服务器地址可以填写我的服务器地址(“tcp://114.132.53.92:1883”),当然也可以使用官方公用的MQTT服务器地址或者用别人的都是可以的;然后就是用户名和密码,一定不要用这里我填写的这个,可以用自己的QQ加上一些英文,或者自定义一些内容都是可以的,**注意不要用我这里填写的这个!!! **然后就是订阅和发布号可以随意起,建议不用下面这些!
private String host = "tcp://114.132.53.92:1883"; // TCP协议 private String userName = "aixin123456"; private String passWord = "aixin123456"; private String mqtt_id = "1353023461"; private String mqtt_sub_topic = "mqtt135"; private String mqtt_pub_topic = "esp135";
好!配置完以上步骤之后,咱们就可以下载到模拟机或者真机测试一下了,这里我用的真机测试,不用慌!直接下载运行,弹窗弹出连接成功!完美
真机运行画面

那么到这里我们的app已经成功连接了MQTT服务器了!
6、MQTT.fx实现联调
这里需要使用到一个测试软件 MQTT.fx
这里不提供软件安装包(我的找不到按转包在哪了),网上有教程,也可以去官网下载
这里的连接服务器地址填114.132.53.92或者是你自己app中连接的地址,端口1883,clientld_ID可以自己填
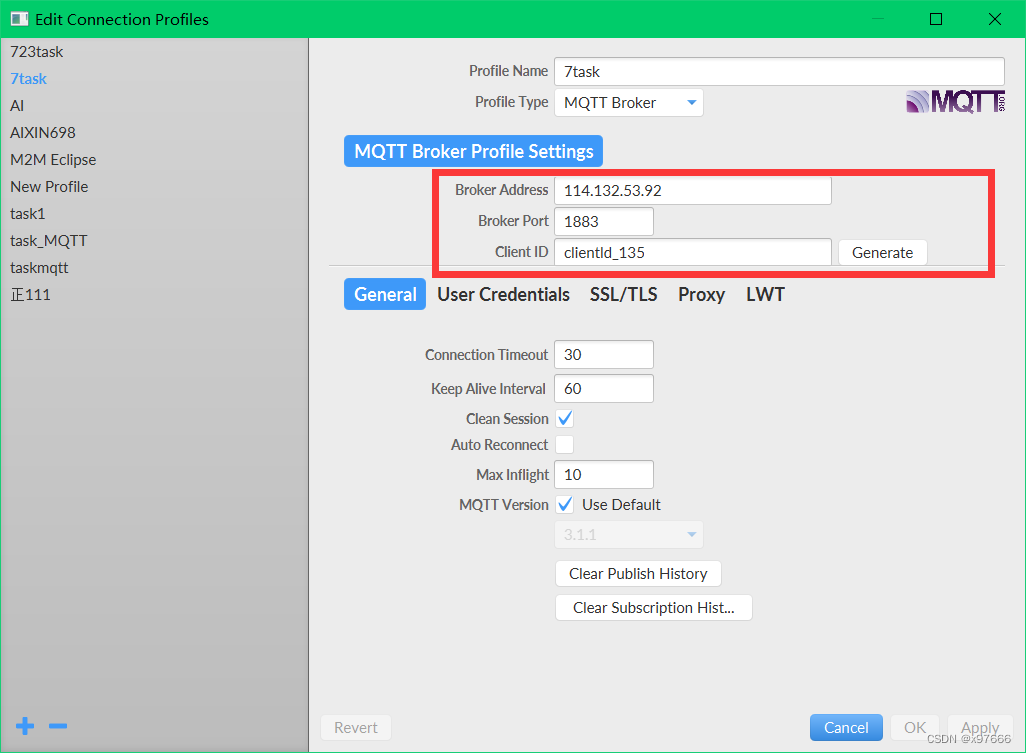
用户名和密码也可以自己填写(需要注意的是,这里填写的这些其实是模拟你下位机的连接用户信息,也就是你STM32通过ESP8266连接MQTT服务器的信息)
点击这里,填写发布号以及填写要发往app中的信息,点击Publish
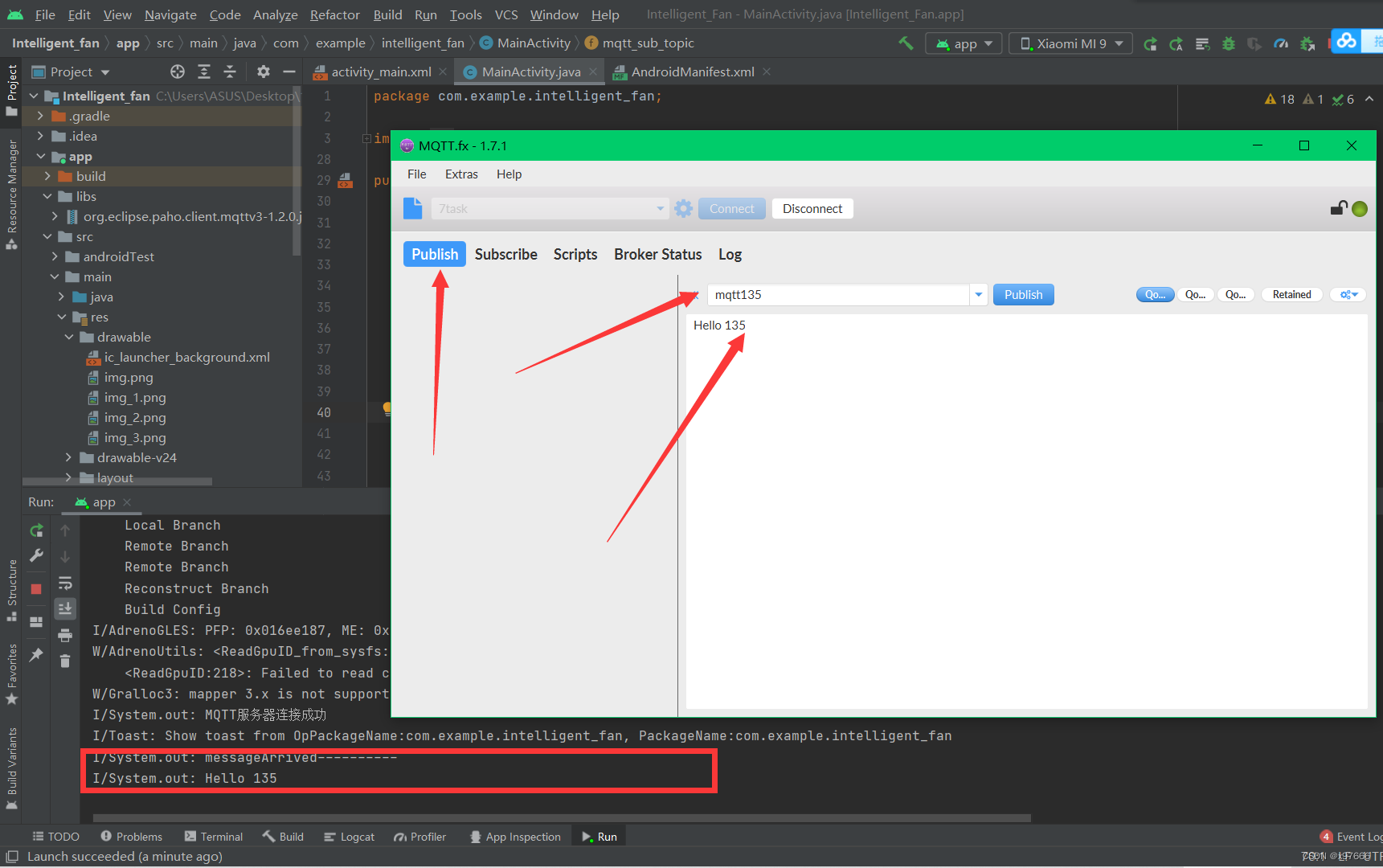
然后就可以看的到Android Studio调试台下的接收到了数据,到了这里是不是就实现了下位机上传数据至MQTT服务器至客户端手机APP
这里再介绍一种简单的Json格式数据处理吧!
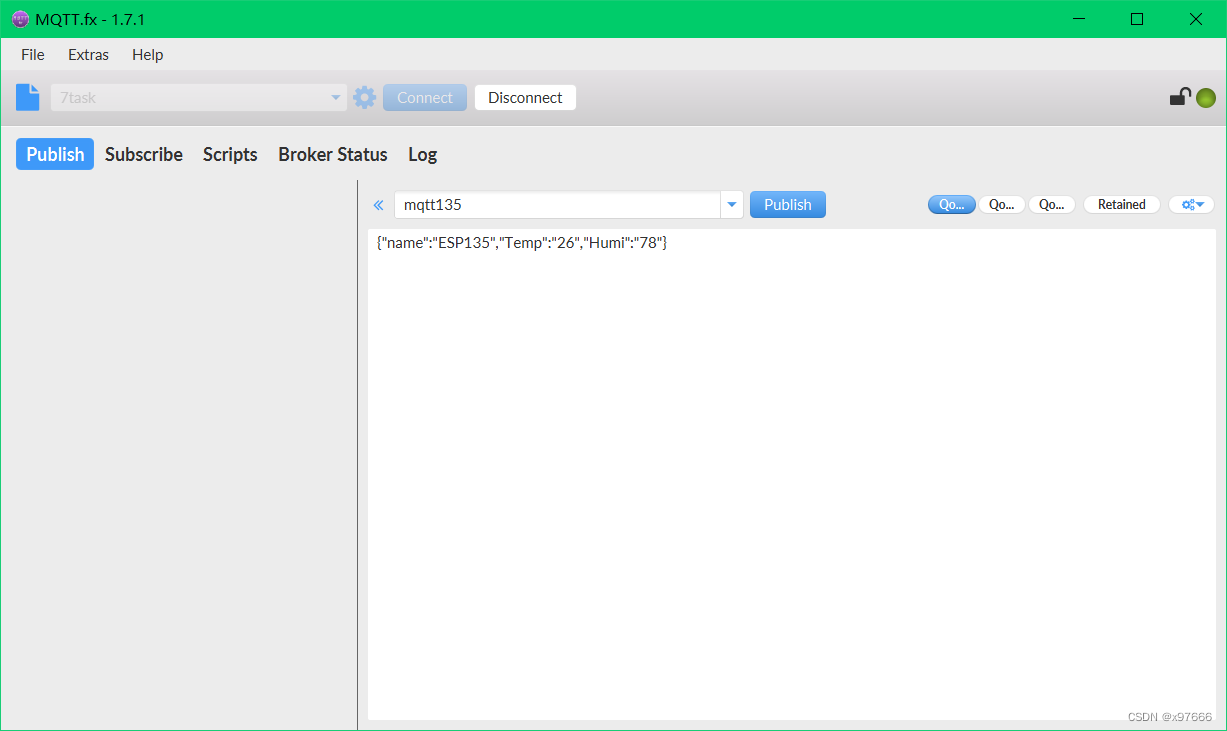
简单的Json数据格式模拟下位机数据
{"name":"ESP135","Temp":"26","Humi":"78"}
这里我们就要在app中添加一个Json数据处理的函数,形参就是需要处理的字符串
// Json数据解析
private void parseJsonobj(String jsonobj){
// 解析json
try {
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject(jsonobj);
String name = jsonObject.getString("name");
String temp = jsonObject.getString("Temp");
String humi = jsonObject.getString("Humi");
m_temp.setText("温度: "+temp+" ℃ ");
m_humi.setText("湿度: "+humi+" % ");
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
app中接收到的数据
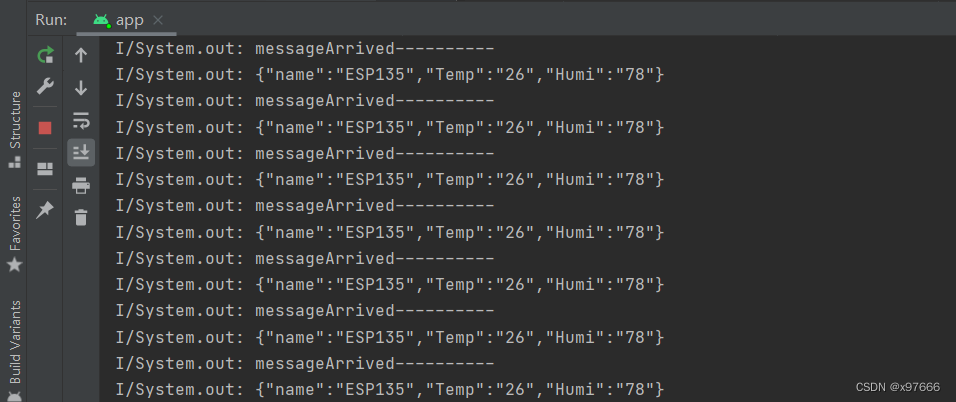
经过处理后就可以在我们app的控件中以指定格式显示

这样是不是感觉就出来了!好到此那么我们上位机数据接收就差不多了
嗯,那么app向下位机发送数据呢!其实也就是订阅号与STM32+ESP的信息关联后,经过一个函数就可以下发数据了,下一篇下位机(STM32+ESP)再详细介绍吧!发送的函数已经添加在上述的代码中了;这里贴出来一个示例代码,简单介绍一下,一个按键然后下发数据 publishmessageplus(mqtt_pub_topic,"{"set_curtain": "fB}");
// 关闭控件点击事件
private void button_guan(View v){
if(curtain_flag == 0){
curtain_flag = 1;
// 发送指令让下位机关闭窗帘
publishmessageplus(mqtt_pub_topic,"{\"set_curtain\": \"fB}");
}
mtv_1.setText("关闭");
}
最后,嗯就这样!第一次写这么长篇的学习记录,也是对自己所学内容的一种巩固,希望能帮到有需要的同志,如果有错误的地方还请多多见谅!谢谢!!!
版权归原作者 x97666 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。