文章目录
1. MongoDB简介
MongDB是一款性能极强的文档数据库,可以充分利用系统的内存资源,会充分使用系统内存作为缓存。
在MongoDB中,
指定索引插入
比
不指定
慢很多,这是因为,MongoDB里每一条数据的_id值都是唯一的。
- 当在不指定_id插入数据的时候,其_id是系统自动计算生成的。MongoDB通过计算机
特征值、时间、进程ID与随机数来确保生成的_id是唯一的。 - 而在指定_id插入时,MongoDB每插一条数据,都需要检查此_id可不可用,当数据库中数据条数太多的时候,这一步的查询开销会拖慢整个数据库的插入速度
MongoDB不指定_id插入 > MySQL不指定主键插入 > MySQL指定主键插入 > MongoDB指定_id插入
2. Go连接MongoDB
驱动:
go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo
- 定义一个mongoDB的一个client
var MongoDBClient *mongo.Client
- 连接mongoDB
clientOptions := options.Client().ApplyURI("mongodb://"+"localhost"+":"+"27017")var err error
MongoDBClient, err = mongo.Connect(context.TODO(), clientOptions)// 链接if err !=nil{
fmt.Println(err)}
err = MongoDBClient.Ping(context.TODO(),nil)// 测试连接if err !=nil{
fmt.Println(err)}
- 链接MongoDB数据库
var Collection *mongo.Collection // 声明一个集合
Collection = MongoDBClient.Database("practice").Collection("user")// 链接practice这个数据库中的user集合
MongoDB数据库 —> MySQL数据库
MongoDB的Collection集合 —> MySQL表
注意一点:这时候如果MongoDB中没有这个数据库和这个集合的话,就会自动创建的,无需我们自己再去创建集合

3. insert 插入
- 定义一个类型
type PersonInfo struct{
Name string
Age float64
Major string}
3.1 插入单条数据
- 定义数据
fan := PersonInfo{"FanOne",17.99,"Big Data"}
- 插入
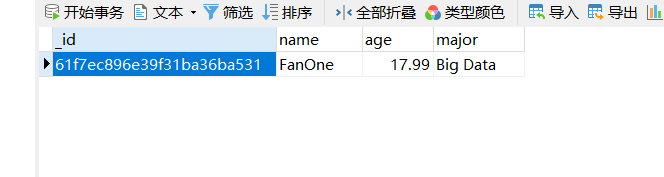
insertResult, err := Collection.InsertOne(context.TODO(), fan)
- 查看插入结果的id
fmt.Println(insertResult.InsertedID)
3.2 插入多条数据
在MongoDB中我们看到这个
InsertMany
的函数的实际上是要传入一个
[]interface{}
类型的
- 声明数据类型
var fans []interface{}
- bson.M{}
在go.mongodb中有两种族来使用bson数据,分别是
D
和
RAW
。
D族是使用原生Go形式来构造一个BSON对象。这个对于使用命令来操作mongoDB是十分有用的。
D()由下面4种类型:
- D:一个BSON文档,这个是有序的。
- M:一个无序的map。它除了无序之外和D是一样的(可以理解为map和bson是可以转换)。
- A:一个BSON形式的数组。
- E:一个D里面的单独元素。(就是文档里的一个元素)
RAW族是被用来判断是否为bytes的一个slice。
你也可以用look up()方法从RAW取得一个元素。这可以在你将BSON转化为另一个形式的数 据时是十分有用的(原文大概意思是可以节省你转化数据时的开销)。
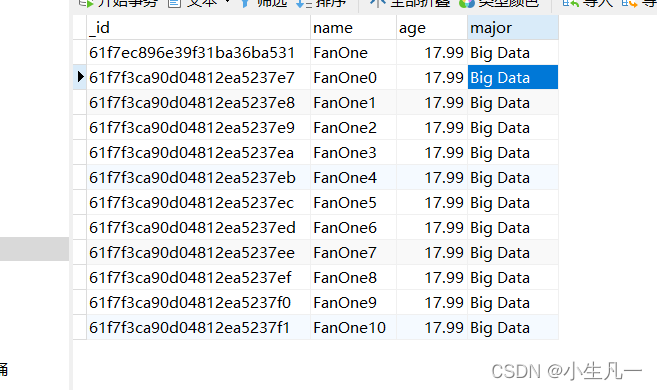
for i :=0; i <=10; i++{
fan := PersonInfo{"FanOne",17.99,"Big Data"}
fan.Name = fan.Name + strconv.Itoa(i)
fans =append(fans, bson.M{"name": fan.Name,"age": fan.Age,"major": fan.Major})}
insertResult, err := Collection.InsertMany(context.TODO(), fans)// 插入多条数据if err !=nil{
fmt.Println(err)}
fmt.Println(insertResult.InsertedIDs)
4. find 查询
4.1 单条查询
- 定义查询结果
var result PersonInfo
- 定义筛选条件
filter := bson.D{{"name","FanOne0"}}
- 选择
err := Collection.FindOne(context.TODO(), filter).Decode(&result)// 将结果Decode到result中if err !=nil{
log.Fatal(err)}
fmt.Printf("Found a single document: %+v\n", result)
- 结果

4.2 多条查询
- 定义查询结果
var result []PersonInfo
- 定义过滤器
filter := bson.D{{"major","Big Data"}}
- 数据库查询
res,err := Collection.Find(context.TODO(), filter)
- 结果赋值
_= res.All(context.TODO(),&result)
- 结果

4.3 复合查询
4.3.1 $regex 模糊查询
查询名字包含1的数据
filter := bson.M{"name": bson.M{"$regex":"1"}}
查询
res,err := Collection.Find(context.TODO(), filter)if err !=nil{
log.Fatal(err)}_= res.All(context.TODO(),&result)
fmt.Printf("result : %+v\n", result)
查询结果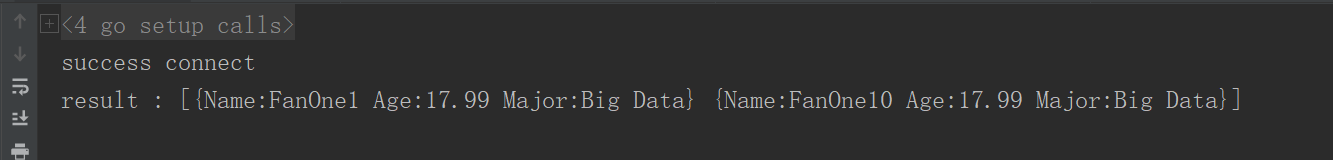
4.3.2 in($in)
查询
name字段
中有
FanOne1
和
FanOne2
的数据字段
filter := bson.M{"name": bson.M{"$in":[]string{"FanOne1","FanOne2"}}}
查询字段
如果是查询不存在就用 **no in
($nin)
** 关键字 进行查询
4.3.3 各种比较函数
!=($ne)>($gt)<($lt)>=($gte)<=($lte)
例子:
filter := bson.M{"age": bson.M{"$gt":1}}
选出age>1的数据
4.3.4 复合查询
- and($and)
查询
name是FanOne2
和
age是4
的数据
res, err := Collection.Find(context.TODO(), bson.M{"$and":[]bson.M{{"name":"FanOne2"},{"age":4}}})
结果
- or($or)
查询
name是FanOne2
或者
age是2
的数据
res, err := Collection.Find(context.TODO(), bson.M{"$or":[]bson.M{{"name":"FanOne2"},{"age":2}}})
结果
4.3.5 聚类
表达式描述实例$sum计算总和bson.D{{“KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: …son.D{{"_id", "major”},{“sum”, bson.D{{"$sum", 1},}},}},}$avg计算平均值bson.D{{“KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: …bson.D{{"_id","major”},{“ageAvg”,bson.D{{"$ avg","$age"},}},}},}$min获取集合中所有文档对应值得最小值。bson.D{{“KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: …bson.D{{"_id","major”},{“minAvg”,bson.D{{“
m
i
n
"
,
"
min","
min","age”}}}}}}$max获取集合中所有文档对应值得最大值。bson.D{{“KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: …bson.D{{"_id","major”},{“maxAvg”,bson.D{{“
m
a
x
"
,
"
max","
max","age”}}}}}}$push在结果文档中插入值到一个数组中。bson.D{{“KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: …son.D{{"_id", "name”}, {“num”, bson.D{{"$push", “test”}}}}}}$addToSet在结果文档中插入值到一个数组中,但不创建副本。bson.D{{“KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: …son.D{{"_id", "name”}, {“num”, bson.D{{"$addToSet", “test”}}}}}}$first根据资源文档的排序获取第一个文档数据。bson.D{{“KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: …son.D{{"_id", "major”}, {“first”, bson.D{{“
f
i
r
s
t
"
,
"
first", "
first","name”}}}}}}$last根据资源文档的排序获取最后一个文档数据bson.D{{“KaTeX parse error: Expected '}', got 'EOF' at end of input: …son.D{{"_id", "major”}, {“first”, bson.D{{“
l
a
s
t
"
,
"
last", "
last","name”}}}}}}
类似:
select by_user, count(*) from mycol group by by_user
查看
Aggregate
的源码可知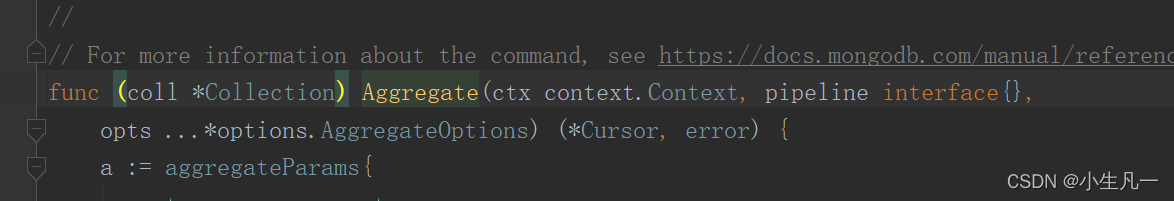
$sum
例子:
- 定义最大时间
opts := options.Aggregate().SetMaxTime(2* time.Second)
- 定义查询语句
通过major字段进行划分,每一个sum变1
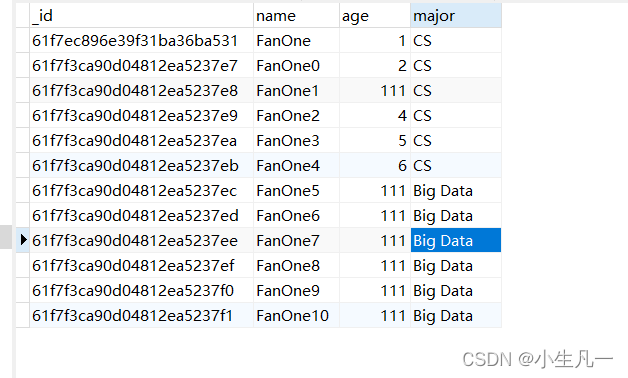
groupStage := bson.D{{"$group", bson.D{{"_id","$major"},{"sum", bson.D{{"$sum",1},}},}},}
- 查询
result, err := Collection.Aggregate(context.TODO(), mongo.Pipeline{groupStage}, opts)
- 赋值,注意这里类型可以自己定义,也可以直接用
bson.M
var results []bson.M
if err = result.All(context.TODO(),&results); err !=nil{
log.Fatal(err)}
fmt.Printf("results : %+v\n", results)
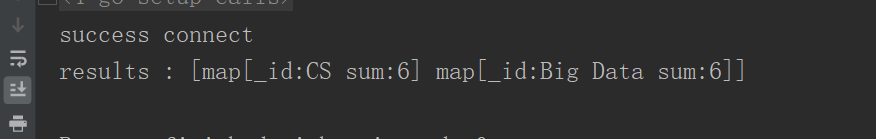
$avg
例子
- 定义一个过滤条件
计算各个
major
的
平均age
字段
groupStage := bson.D{{"$group",bson.D{{"_id","$major"},{"ageAvg",bson.D{{"$avg","$age"},}},}},}
数据库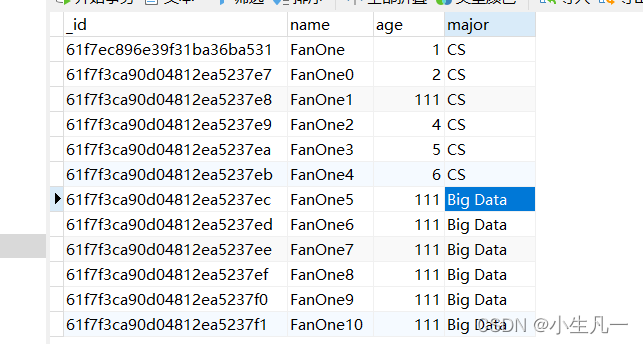
结果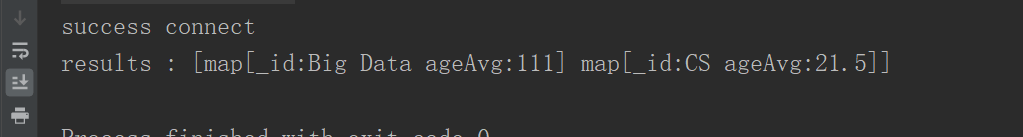
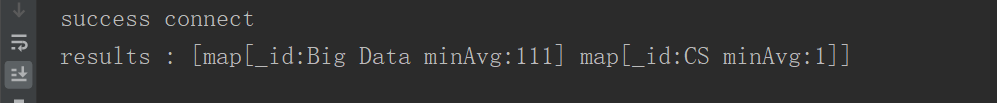
$min例子
找到以major为分组,各组最小的age
groupStage := bson.D{{"$group",bson.D{{"_id","$major"},{"minAvg",bson.D{{"$min","$age"}}}}}}
5. update 更新
5.1 更新单条
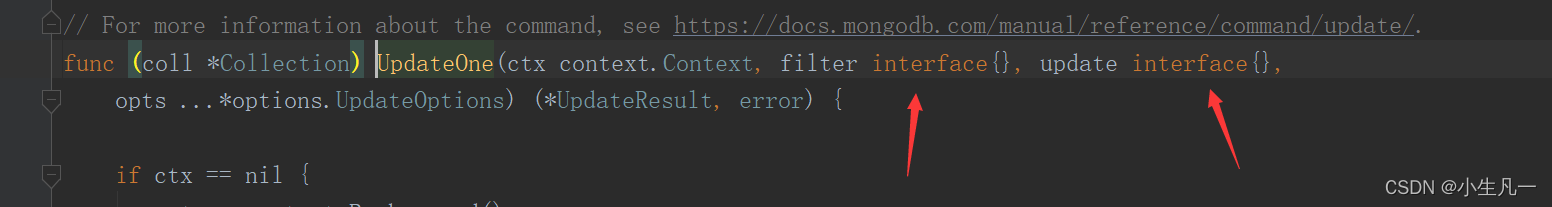
第一个是filter,选出哪个更新,第二个是传进去的更新的东西,要传
$set
res, err := Collection.UpdateOne(context.TODO(), bson.M{"name":"FanOne1"}, bson.M{"$set": bson.M{"age":111}})
- 结果

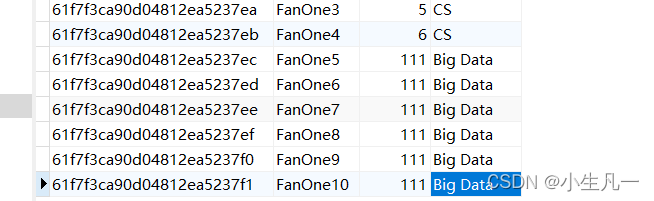
5.2 更新多条
UpdateMany
找到字段major是BigData的,然后把age变成111。
res, err := Collection.UpdateMany(context.TODO(), bson.M{"major":"Big Data"}, bson.M{"$set": bson.M{"age":111}})
- 结果
6. delete 删除
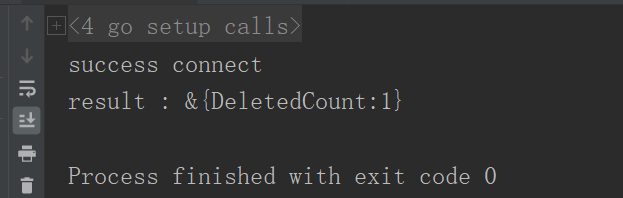
6.1 删除单条
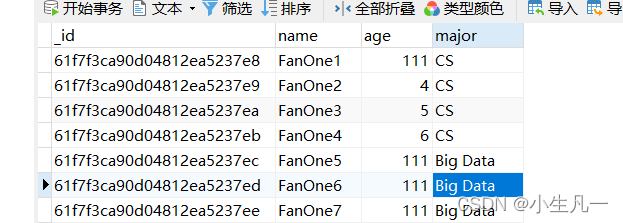
res, err := Collection.DeleteOne(context.TODO(), bson.M{"name":"FanOne0"})if err !=nil{
log.Fatal(err)}
fmt.Printf("result : %+v\n", res)
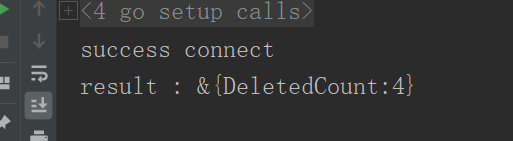
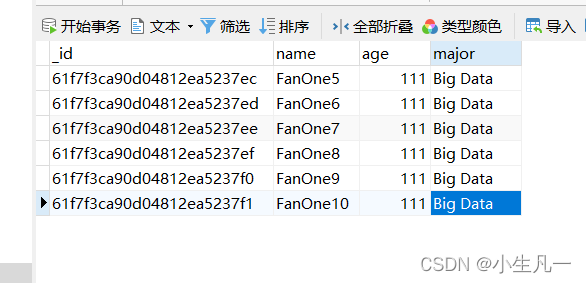
6.2 删除多条
res, err := Collection.DeleteMany(context.TODO(), bson.M{"major":"CS"})if err !=nil{
log.Fatal(err)}
fmt.Printf("result : %+v\n", res)
版权归原作者 小生凡一 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。