🍊 Java学习:Java从入门到精通总结
🍊 深入浅出RocketMQ设计思想:深入浅出RocketMQ设计思想
🍊 绝对不一样的职场干货:大厂最佳实践经验指南
📆 最近更新:2022年10月15日
🍊 个人简介:通信工程本硕💪、Java程序员🌕。做过科研paper,发过专利,优秀的程序员不应该只是CRUD
🍊 点赞 👍 收藏 ⭐留言 📝 都是我最大的动力!
文章目录
平均分配算法
这也是消息消费时候的默认算法,所谓平均,就是同一个
Topic
主题下的所有队列被同一个消费者组中的所有Consumer平均消费掉。
例如有5个队列和2和Consumer,就会根据下面的步骤进行分配:
- 5除以2不能整除,所以队列无法均分
- 每个消费者先分到2个队列
- 多出来的1个队列按照顺序分配给了第一个Consumer

具体的源码如下:
publicclassAllocateMessageQueueAveragelyimplementsAllocateMessageQueueStrategy{privatefinalInternalLogger log =ClientLogger.getLog();@OverridepublicList<MessageQueue>allocate(String consumerGroup,String currentCID,List<MessageQueue> mqAll,List<String> cidAll){if(currentCID ==null|| currentCID.length()<1){thrownewIllegalArgumentException("currentCID is empty");}if(mqAll ==null|| mqAll.isEmpty()){thrownewIllegalArgumentException("mqAll is null or mqAll empty");}if(cidAll ==null|| cidAll.isEmpty()){thrownewIllegalArgumentException("cidAll is null or cidAll empty");}List<MessageQueue> result =newArrayList<MessageQueue>();if(!cidAll.contains(currentCID)){
log.info("[BUG] ConsumerGroup: {} The consumerId: {} not in cidAll: {}",
consumerGroup,
currentCID,
cidAll);return result;}// 当前分配到的Consumer的索引int index = cidAll.indexOf(currentCID);// 余数int mod = mqAll.size()% cidAll.size();// 队列总数小于Consumer总数时,给当前Consumer分配一个队列消费// 不能均分且当前编号小于余数时,需要给当前Consumer分配x + 1个队列,否则分配x个队列int averageSize =
mqAll.size()<= cidAll.size()?1:(mod >0&& index < mod ? mqAll.size()/ cidAll.size()+1: mqAll.size()/ cidAll.size());int startIndex =(mod >0&& index < mod)? index * averageSize : index * averageSize + mod;// 取min的原因是,如果Consumer多,队列少,多出来的Consumer分配不到队列int range =Math.min(averageSize, mqAll.size()- startIndex);for(int i =0; i < range; i++){
result.add(mqAll.get((startIndex + i)% mqAll.size()));}return result;}@OverridepublicStringgetName(){return"AVG";}}
环形平均分配算法
使用方法:
consumer.setAllocateMessageQueueStrategy(newAllocateMessageQueueAveragelyByCircle());
也可以自定义消费策略:
consumer.setAllocateMessageQueueStrategy(newAllocateMessageQueueStrategy(){@OverridepublicList<MessageQueue>allocate(String consumerGroup,String currentCID,List<MessageQueue> mqAll,List<String> cidAll){// 自定义负载策略returnnull;}@OverridepublicStringgetName(){returnnull;}});
所谓环形分配算法,就是把消息队列按照环形进行排列,然后同一个组下的所有Consumer按照顺序进行匹配即可,如下图所示:
上图中
Topic
下共有10个消息队列,假设消费者组里有4个Consumer,分配过程如下:
- 对所有的消息队列和Consumer分别排序
- 按照顺序让Consumer和消息队列进行匹配
第一轮分配Queue1到Queue4,第二轮分配Queue5到Queue8,第三轮分配Queue9和Queue10。经过3轮分配完毕
具体源码如下所示:
publicclassAllocateMessageQueueAveragelyByCircleimplementsAllocateMessageQueueStrategy{privatefinalInternalLogger log =ClientLogger.getLog();@OverridepublicList<MessageQueue>allocate(String consumerGroup,String currentCID,List<MessageQueue> mqAll,List<String> cidAll){if(currentCID ==null|| currentCID.length()<1){thrownewIllegalArgumentException("currentCID is empty");}if(mqAll ==null|| mqAll.isEmpty()){thrownewIllegalArgumentException("mqAll is null or mqAll empty");}if(cidAll ==null|| cidAll.isEmpty()){thrownewIllegalArgumentException("cidAll is null or cidAll empty");}List<MessageQueue> result =newArrayList<MessageQueue>();if(!cidAll.contains(currentCID)){
log.info("[BUG] ConsumerGroup: {} The consumerId: {} not in cidAll: {}",
consumerGroup,
currentCID,
cidAll);return result;}int index = cidAll.indexOf(currentCID);for(int i = index; i < mqAll.size(); i++){if(i % cidAll.size()== index){
result.add(mqAll.get(i));}}return result;}@OverridepublicStringgetName(){return"AVG_BY_CIRCLE";}}
一致性哈希算法
首先先介绍一下一致性哈希算法:
hash算法带来的问题:
假设后台有多个服务器,我们就可以做负载均衡将前端来的请求“平均”分配到各个服务器上来处理,如果是按照用户id对服务器个数N取模来计算hash的话,如果有一台服务器宕机,之前所有的求模计算都要重来,开销较大。
一致性哈希的思路就是:用户按照顺时针方向做排列,离哪个节点近,就去访问哪个节点。
用户按照顺时针方向,离哪个节点近,就去访问哪个节点。
此时如果有服务器宕机,直接顺着找下一个服务器节点就可以了。 如果要增加节点:
如果要增加节点: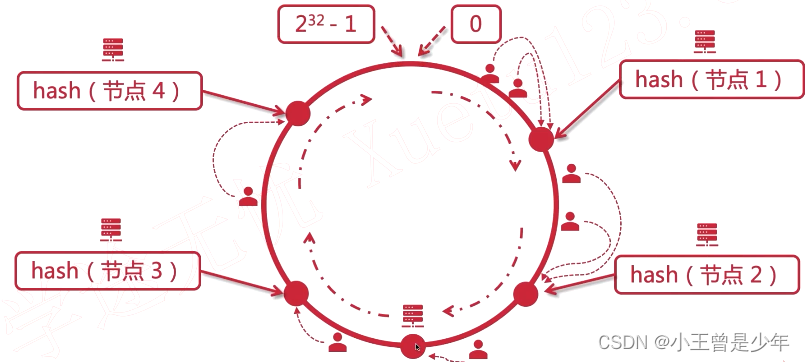
RocketMQ中对于一致性哈希的源码级实现:
publicclassAllocateMessageQueueConsistentHashimplementsAllocateMessageQueueStrategy{privatefinalInternalLogger log =ClientLogger.getLog();privatefinalint virtualNodeCnt;privatefinalHashFunction customHashFunction;publicAllocateMessageQueueConsistentHash(){this(10);}// 设计虚拟节点数量publicAllocateMessageQueueConsistentHash(int virtualNodeCnt){this(virtualNodeCnt,null);}publicAllocateMessageQueueConsistentHash(int virtualNodeCnt,HashFunction customHashFunction){if(virtualNodeCnt <0){thrownewIllegalArgumentException("illegal virtualNodeCnt :"+ virtualNodeCnt);}this.virtualNodeCnt = virtualNodeCnt;this.customHashFunction = customHashFunction;}// 负载均衡算法主要实现@OverridepublicList<MessageQueue>allocate(String consumerGroup,String currentCID,List<MessageQueue> mqAll,List<String> cidAll){if(currentCID ==null|| currentCID.length()<1){thrownewIllegalArgumentException("currentCID is empty");}if(mqAll ==null|| mqAll.isEmpty()){thrownewIllegalArgumentException("mqAll is null or mqAll empty");}if(cidAll ==null|| cidAll.isEmpty()){thrownewIllegalArgumentException("cidAll is null or cidAll empty");}List<MessageQueue> result =newArrayList<MessageQueue>();if(!cidAll.contains(currentCID)){
log.info("[BUG] ConsumerGroup: {} The consumerId: {} not in cidAll: {}",
consumerGroup,
currentCID,
cidAll);return result;}// 把所有消费者放到一个List里Collection<ClientNode> cidNodes =newArrayList<ClientNode>();for(String cid : cidAll){
cidNodes.add(newClientNode(cid));}// 创建hash环形结构finalConsistentHashRouter<ClientNode> router;//for building hash ringif(customHashFunction !=null){
router =newConsistentHashRouter<ClientNode>(cidNodes, virtualNodeCnt, customHashFunction);}else{
router =newConsistentHashRouter<ClientNode>(cidNodes, virtualNodeCnt);}// 根据一致性hash算法,基于客户端节点,把分配到当前消费者组的MQ添加到集合里并返回List<MessageQueue> results =newArrayList<MessageQueue>();for(MessageQueue mq : mqAll){ClientNode clientNode = router.routeNode(mq.toString());if(clientNode !=null&& currentCID.equals(clientNode.getKey())){
results.add(mq);}}return results;}@OverridepublicStringgetName(){return"CONSISTENT_HASH";}privatestaticclassClientNodeimplementsNode{privatefinalString clientID;publicClientNode(String clientID){this.clientID = clientID;}@OverridepublicStringgetKey(){return clientID;}}}
上面代码在
ConsistentHashRouter
中创建了hash环,算法的主要流程是在这个类中实现的,主要是基于
TreeMap
,感兴趣的小伙伴可以深入研究一下它的源码~
指定机房算法
假设有两个机房,则对应的消费关系如下图:
指定机房分配算法先根据MQ所述的Broker找出有效的机房里的所有MQ,然后再平分给所有的Consumer
publicclassAllocateMessageQueueByMachineRoomimplementsAllocateMessageQueueStrategy{privateSet<String> consumeridcs;@OverridepublicList<MessageQueue>allocate(String consumerGroup,String currentCID,List<MessageQueue> mqAll,List<String> cidAll){List<MessageQueue> result =newArrayList<MessageQueue>();// 计算出当前消费者ID在消费者集合中的具体位置int currentIndex = cidAll.indexOf(currentCID);if(currentIndex <0){return result;}// 拿出BrokerName下的所有MQList<MessageQueue> premqAll =newArrayList<MessageQueue>();for(MessageQueue mq : mqAll){String[] temp = mq.getBrokerName().split("@");if(temp.length ==2&& consumeridcs.contains(temp[0])){
premqAll.add(mq);}}// 队列长度除以客户端长度int mod = premqAll.size()/ cidAll.size();// 队列长度mod客户端长度int rem = premqAll.size()% cidAll.size();// 给Consumer分配MQint startIndex = mod * currentIndex;int endIndex = startIndex + mod;for(int i = startIndex; i < endIndex; i++){
result.add(premqAll.get(i));}if(rem > currentIndex){
result.add(premqAll.get(currentIndex + mod * cidAll.size()));}return result;}@OverridepublicStringgetName(){return"MACHINE_ROOM";}publicSet<String>getConsumeridcs(){return consumeridcs;}publicvoidsetConsumeridcs(Set<String> consumeridcs){this.consumeridcs = consumeridcs;}}
就进机房算法
顾名思义,就近机房分配策略是一种基于
Consumer
和机房距离来分配的策略。部署在同一个机房的MQ会被先分配给同一个机房里的
Consumer
。
具体步骤是先统计
Consumer
与
Broker
所在的机房,之后再将
Broker
中的MQ分配给同机房的
Consumer
消费,如果本机房里没有
Consumer
,则再尝试分配给其他机房的
Consumer

publicclassAllocateMachineRoomNearbyimplementsAllocateMessageQueueStrategy{privatefinalInternalLogger log =ClientLogger.getLog();privatefinalAllocateMessageQueueStrategy allocateMessageQueueStrategy;//actual allocate strategyprivatefinalMachineRoomResolver machineRoomResolver;publicAllocateMachineRoomNearby(AllocateMessageQueueStrategy allocateMessageQueueStrategy,MachineRoomResolver machineRoomResolver)throwsNullPointerException{if(allocateMessageQueueStrategy ==null){thrownewNullPointerException("allocateMessageQueueStrategy is null");}if(machineRoomResolver ==null){thrownewNullPointerException("machineRoomResolver is null");}this.allocateMessageQueueStrategy = allocateMessageQueueStrategy;this.machineRoomResolver = machineRoomResolver;}@OverridepublicList<MessageQueue>allocate(String consumerGroup,String currentCID,List<MessageQueue> mqAll,List<String> cidAll){if(currentCID ==null|| currentCID.length()<1){thrownewIllegalArgumentException("currentCID is empty");}if(mqAll ==null|| mqAll.isEmpty()){thrownewIllegalArgumentException("mqAll is null or mqAll empty");}if(cidAll ==null|| cidAll.isEmpty()){thrownewIllegalArgumentException("cidAll is null or cidAll empty");}List<MessageQueue> result =newArrayList<MessageQueue>();if(!cidAll.contains(currentCID)){
log.info("[BUG] ConsumerGroup: {} The consumerId: {} not in cidAll: {}",
consumerGroup,
currentCID,
cidAll);return result;}// 将MQ按照不同的机房归纳Map<String/*machine room */,List<MessageQueue>> mr2Mq =newTreeMap<String,List<MessageQueue>>();for(MessageQueue mq : mqAll){String brokerMachineRoom = machineRoomResolver.brokerDeployIn(mq);if(StringUtils.isNoneEmpty(brokerMachineRoom)){if(mr2Mq.get(brokerMachineRoom)==null){
mr2Mq.put(brokerMachineRoom,newArrayList<MessageQueue>());}
mr2Mq.get(brokerMachineRoom).add(mq);}else{thrownewIllegalArgumentException("Machine room is null for mq "+ mq);}}// 将consumer按照不同的机房归纳Map<String/*machine room */,List<String/*clientId*/>> mr2c =newTreeMap<String,List<String>>();for(String cid : cidAll){String consumerMachineRoom = machineRoomResolver.consumerDeployIn(cid);if(StringUtils.isNoneEmpty(consumerMachineRoom)){if(mr2c.get(consumerMachineRoom)==null){
mr2c.put(consumerMachineRoom,newArrayList<String>());}
mr2c.get(consumerMachineRoom).add(cid);}else{thrownewIllegalArgumentException("Machine room is null for consumer id "+ cid);}}List<MessageQueue> allocateResults =newArrayList<MessageQueue>();// 1. 分配与当前消费者部署在同一机房的MQString currentMachineRoom = machineRoomResolver.consumerDeployIn(currentCID);List<MessageQueue> mqInThisMachineRoom = mr2Mq.remove(currentMachineRoom);List<String> consumerInThisMachineRoom = mr2c.get(currentMachineRoom);if(mqInThisMachineRoom !=null&&!mqInThisMachineRoom.isEmpty()){
allocateResults.addAll(allocateMessageQueueStrategy.allocate(consumerGroup, currentCID, mqInThisMachineRoom, consumerInThisMachineRoom));}//2.如果机房没有活着的消费者,则将其MQ分配给每个其他的机房for(String machineRoom : mr2Mq.keySet()){if(!mr2c.containsKey(machineRoom)){// no alive consumer in the corresponding machine room, so all consumers share these queues
allocateResults.addAll(allocateMessageQueueStrategy.allocate(consumerGroup, currentCID, mr2Mq.get(machineRoom), cidAll));}}return allocateResults;}@OverridepublicStringgetName(){return"MACHINE_ROOM_NEARBY"+"-"+ allocateMessageQueueStrategy.getName();}/**
* 一个解析器对象,用于确定消息队列或客户端部署在哪个机房。
*
* AllocateMachineRoomNearby将使用该结果按机房对消息队列和客户端进行分组。
*
* 返回值不能为null
*/publicinterfaceMachineRoomResolver{StringbrokerDeployIn(MessageQueue messageQueue);StringconsumerDeployIn(String clientID);}}
手动配置负载均衡参数
除了使用内置的负载均衡算法以外,还可以手动配置相关的参数,例如设置消费的队列、消费的
Topic
、消费的机器等,在消费端直接设置消费队列即可:
consumer.setAllocateMessageQueueStrategy(newAllocateMessageQueueByConfig(){{this.setMessageQueueList(Collections.<MessageQueue>singletonList(newMessageQueue(){{this.setQueueId(0);this.setTopic("Topic name");this.setBrokerName("Broker name");}}));}});
上面的代码里,手动指定了消费队列的索引,Topic和Broker服务器的名称,之后Consumer就会在指定的服务器中进行消费,源码如下:
publicclassAllocateMessageQueueByConfigimplementsAllocateMessageQueueStrategy{privateList<MessageQueue> messageQueueList;@OverridepublicList<MessageQueue>allocate(String consumerGroup,String currentCID,List<MessageQueue> mqAll,List<String> cidAll){returnthis.messageQueueList;}@OverridepublicStringgetName(){return"CONFIG";}publicList<MessageQueue>getMessageQueueList(){return messageQueueList;}publicvoidsetMessageQueueList(List<MessageQueue> messageQueueList){this.messageQueueList = messageQueueList;}}
可以看到源码里只提供了一个消息队列集合,就是我们上面传入的自定义配置的MQ列表,配置完成之后就可以进行负载均衡及消费。
版权归原作者 小王曾是少年 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。