目录
AVL树的概念
二叉搜索树虽可以缩短查找的效率,但如果数据有序或接近有序二叉搜索树将退化为单支树,查找元素相当于在顺序表中搜索元素,效率低下。因此,两位俄罗斯的数学家G.M.Adelson-Velskii和E.M.Landis在1962年发明了一种解决上述问题的方法:当向二叉搜索树中插入新结点后,如果能保证每个结点的左右子树高度之差的绝对值不超过1(需要对树中的结点进行调整),即可降低树的高度,从而减少平均搜索长度。
一棵AVL树或者是空树,或者是具有以下性质的二叉搜索树:
- 它的左右子树都是AVL树
- 左右子树高度之差(简称平衡因子)的绝对值不超过1(-1/0/1)
- 平衡因子的计算是右子树的高度减去左子树的高度的差值结果
如果一棵二叉搜索树是高度平衡的,它就是AVL树。如果它有n个结点,其高度可保持在O(log N) ,搜索时间复杂度O( log N)。
AVL树节点的定义
template<class K, class V>structAVLTreeNode{
AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _left;//左孩子
AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _right;//右孩子
AVLTreeNode<K, V>* _parent;//父亲结点
pair<K, V> _Kv;//键值int _bf;//平衡因子//构造函数AVLTreeNode(const pair<K, V>& Kv):_left(nullptr),_right(nullptr),_parent(nullptr),_Kv(Kv),_bf(0){}};
AVL树的定义
template<classK,classV>classAVLTree{typedef AVLTreeNode<K, V> Node;public:AVLTree():_root(nullptr){}private:
Node* _root;};
AVL树的插入
AVL树就是在二叉搜索树的基础上引入了平衡因子,因此AVL树也可以看成是二叉搜索树。那么AVL树的插入
过程可以分为两步:
按照二叉搜索树的方式插入新节点
与根结点比较如果比根大就往右子树插入,如果比根小就往左子树插入,直到走到合适的位置就插入,由于这里是三叉链所以需要处理结点之间的关联关系
boolInsert(const pair<K, V>&kv){if(!_root) _root =newNode(kv);//初始根节点
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = _root;while(cur){
K key = cur->_Kv.first;if(key > kv.first)//比根结点的key值小,{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;}elseif(key < kv.first)//比根结点的key值大,{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;}else{returnfalse;//插入失败}}//开始插入
cur =newNode(kv);
Node* newNode = cur;if(parent->_Kv.first > newNode->_Kv.first)//新插入的结点key值比根节点小就插入到左子树{
parent->_left = newNode;
newNode->_parent = parent;}else//新插入的结点key值比根节点大就插入到右子树{
parent->_right = newNode;
newNode->_parent = parent;}}
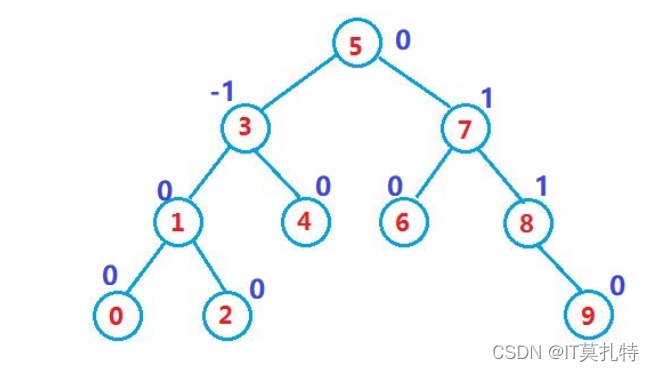
调整节点的平衡因子
当左右子树的高度发生了变化,那么就需要对父亲及祖先路径上的所有结点的平衡因子进行调整
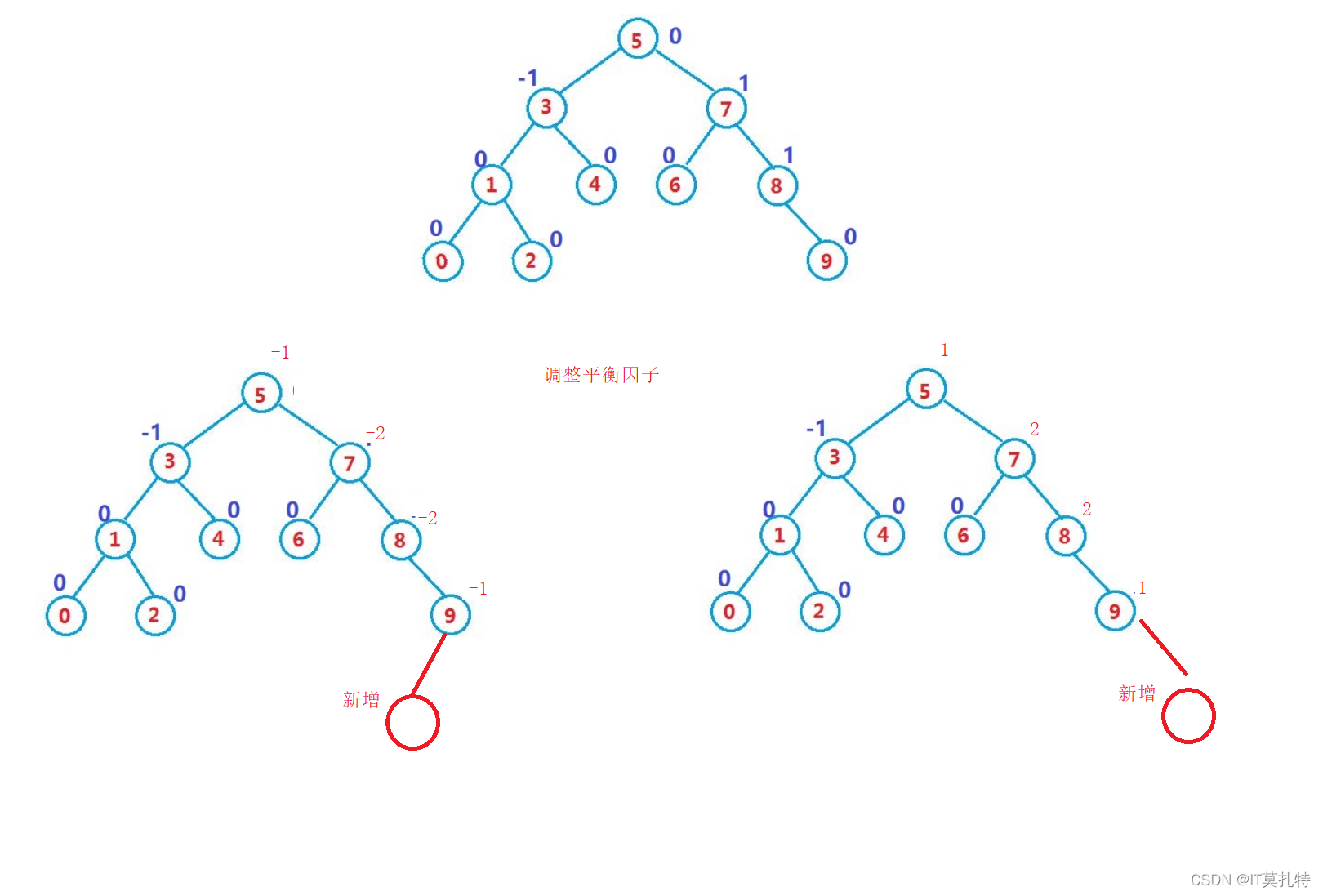
//更新祖先路径的所以结点的平衡因子/*
总结五种情况:
1、新增结点出现在父结点的左边,平衡因子减减
2、新增结点出现在父结点的右边,平衡因子加加
3、父亲的平衡因子为0就不再调整
4、父亲结点的平衡因子为1或者-1继续调整
5、父亲结点的平衡因子为2或者-2那就旋转
*/while(parent){if(parent->_left == cur) parent->_bf--;//1、if(parent->_right == cur) parent++;//2、if(parent->_bf ==0)break;//3、if(parent->_bf ==-1|| parent->_bf ==1)//4、 {
cur = parent;
parent = parent->_parent;}if(parent->_bf ==-2|| parent->_bf ==2)//5、{//旋转if(parent->_bf ==-2){if(cur->_bf ==-1)RotateR(parent);//左边高,右单旋elseRotateLR(parent);//左右双旋}else//右 parent->_bf == 2{if(cur->_bf ==1)RotateL(parent);//右边高左单旋转elseRotateRL(parent);//右左双旋}break;}}
AVL树的四种旋转
旋转的原则是遵循搜索树的规则,尽量让两边平衡
如果在一棵原本是平衡的AVL树中插入一个新节点,可能造成不平衡,此时必须调整树的结构,使之平衡化。根据节点插入位置的不同,AVL树的旋转分为四种:
右单旋
新节点插入较高左子树的左侧—左左:右单旋

不管是哪种单旋都得考虑两种情况:
1、局部旋转,如果parent并不是树的_root结点,那么就需要调整subL和根结点的关系
2、独立旋转,parent就是树的_root结点,那么subL就是旋转后的根节点了
3、subLR有可能为null
//右单旋voidRotateR(Node* parent){
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
parent->_left = subLR;if(subLR) subLR->_parent = parent;//防止subLR为nullptr
subL->_right = parent;
Node* parent_parent = parent->_p arent;//指针备份
parent->_parent = subL;if(_root == parent)//如果parent就是树的根 {
_root = subL;//subL取代parent
_root->_parent =nullptr;}else//如果parent并不是树的根{if(parent_parent->_left == parent) parent->_left = subL;else parent_parent->_right = subL;
subL->_parent = parent_parent;//subL去做parent_parent的孩子}//调节平衡因子
subL->_bf = parent->_bf =0;}
左单旋
新节点插入较高右子树的右侧—右右:左单旋
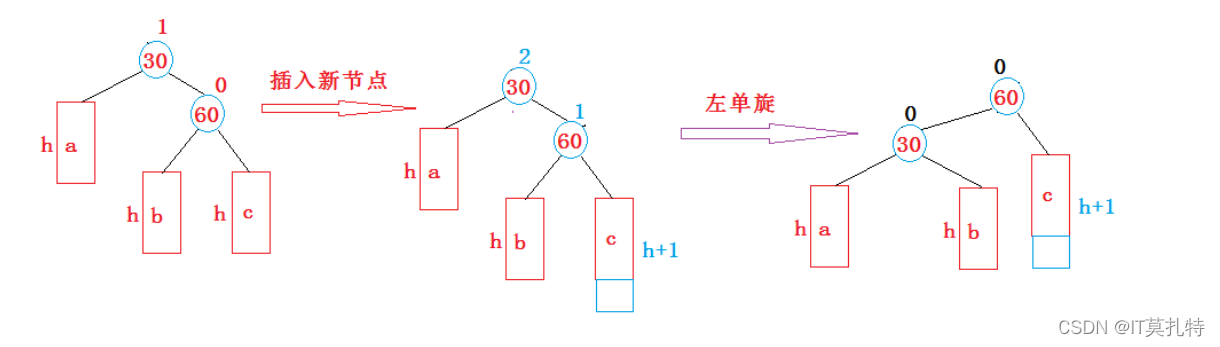
跟右单旋几乎是一样的做法
1、局部旋转,如果parent并不是树的_root结点,那么就需要调整subL和根结点的关系
2、独立旋转,parent就是树的_root结点,那么subL就是旋转后的根节点了
3、subRL有可能为null
//左单旋voidRotateL(Node* parent){
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
parent->_right = subRL;if(subRL) subRL->_parent = parent;
subR->_left = parent;
Node* parent_parent = parent->_parent;
parent->_parent = subR;if(_root == parent){
_root = subR;
_root->_parent =nullptr;}else{if(parent_parent->_left == parent) parent_parent->_left = subR;else parent_parent->_right = subR;
subR->_parent = parent_parent;}
subR->_bf = parent->_bf =0;}
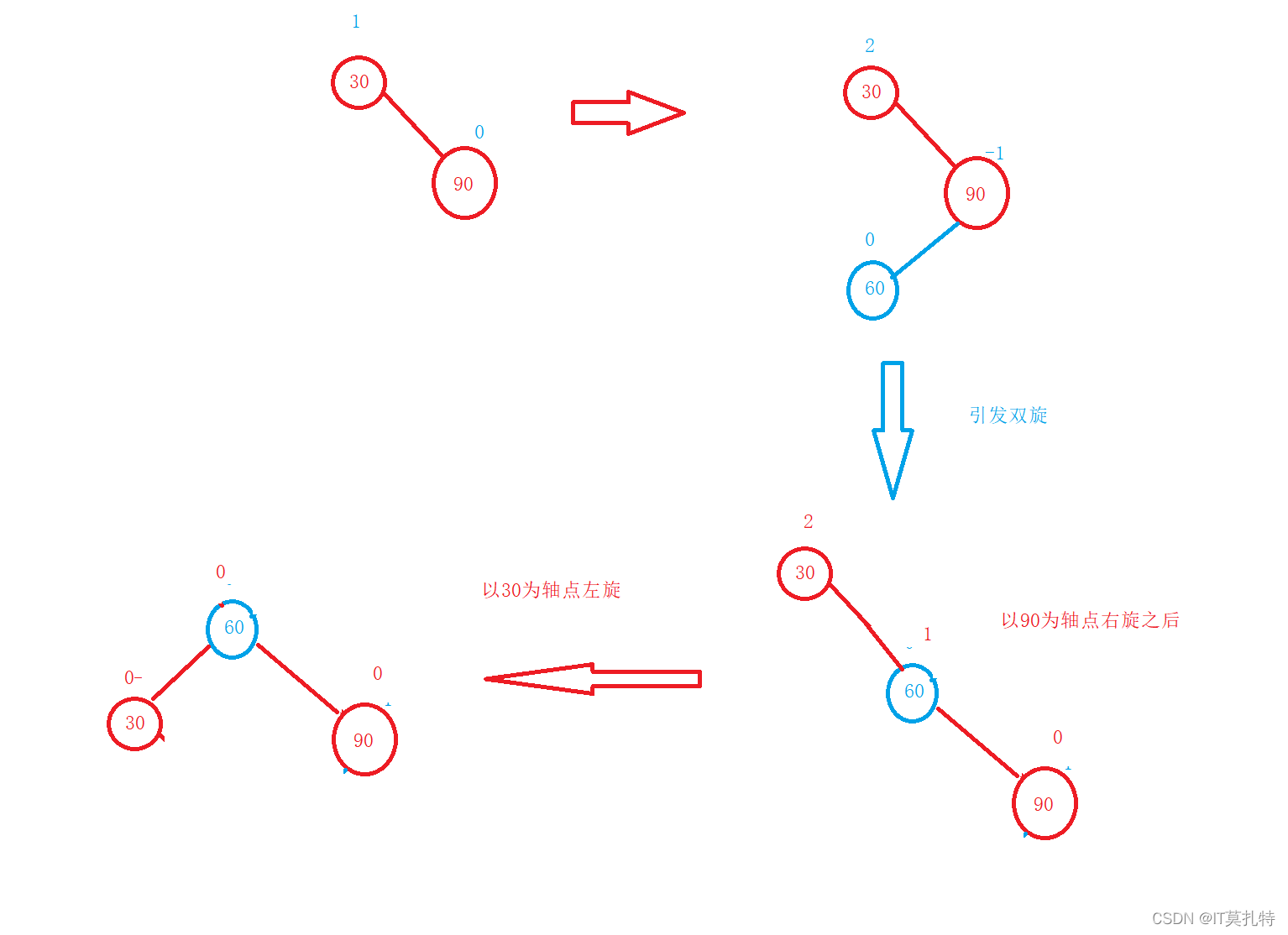
左右双旋
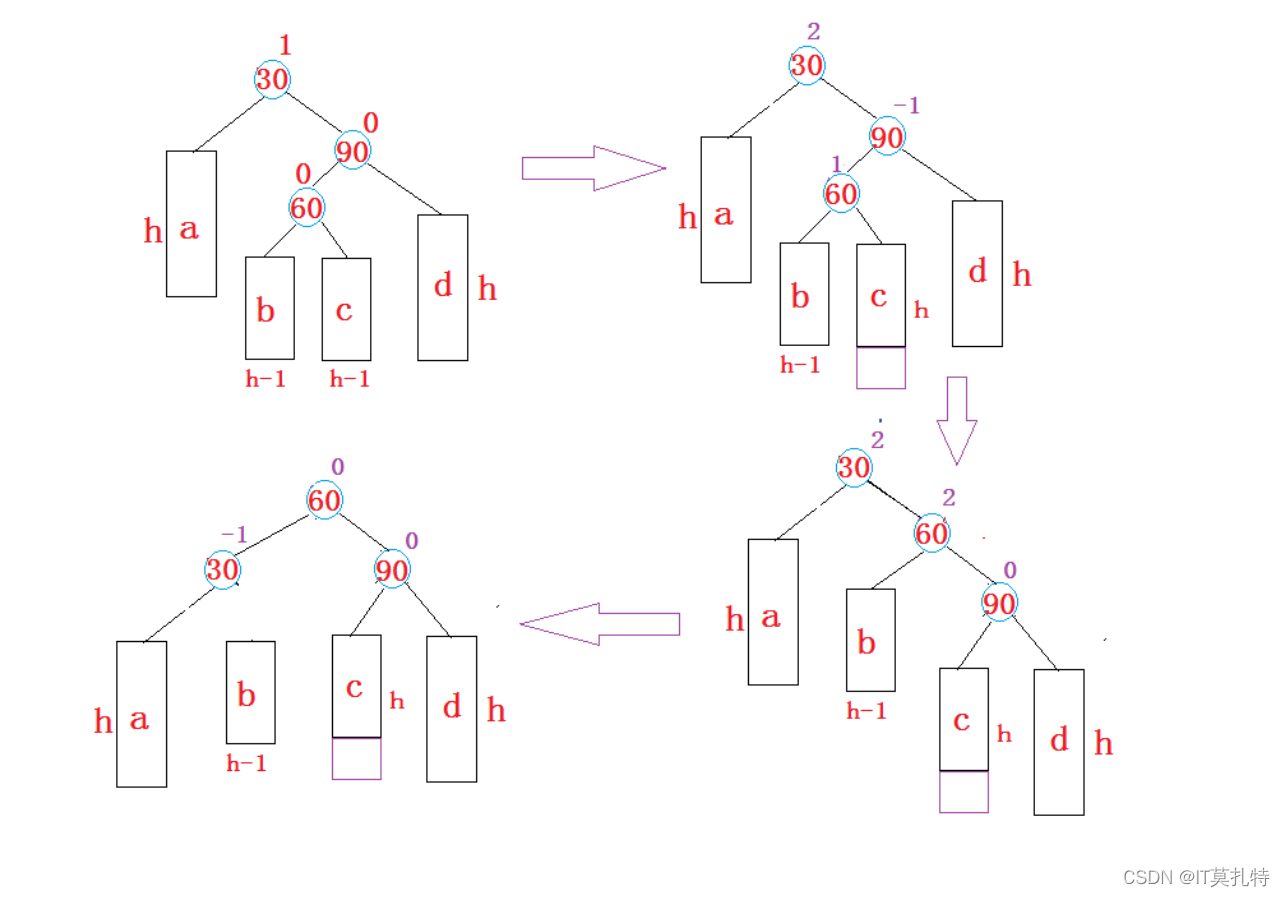
新节点插入较高左子树的右侧—左右:先左单旋再右单旋
1、新增结点在b或c都会影响左右子树的高度,从而引发双旋
h > 0情况一: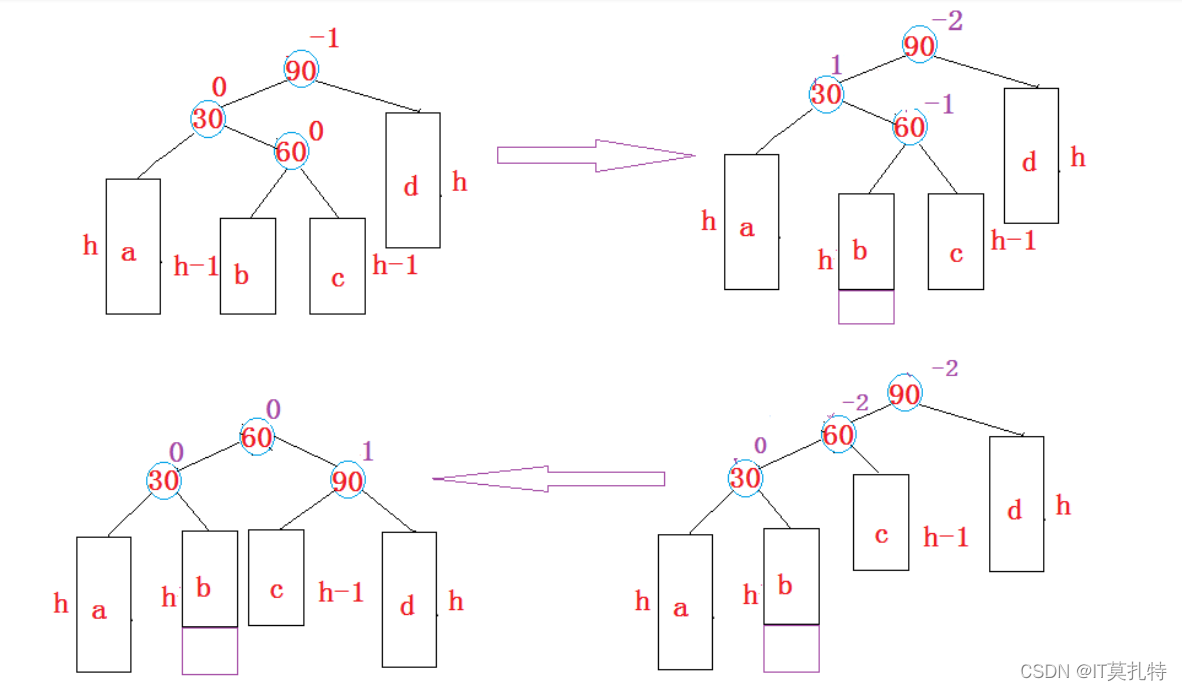
h > 0,情况二: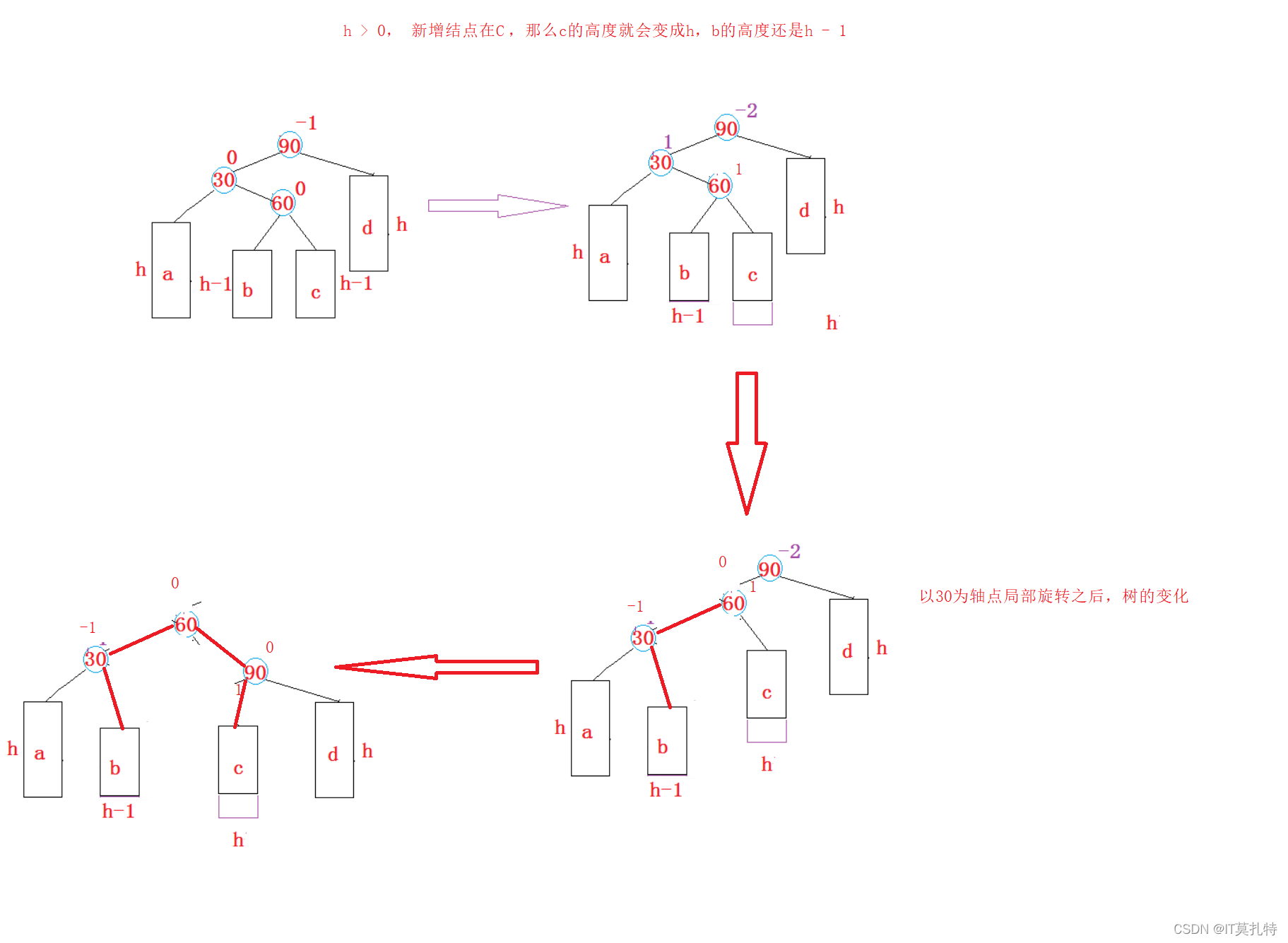
h == 0情况三:
//左右旋转voidRotateLR(Node* parent){
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;int bf = subLR->_bf;RotateL(parent->_left);RotateR(parent);if(bf ==-1)//h > 0,新增结点在b{
parent->_bf =1;
subLR->_bf =0;
subL->_bf =0;}elseif(bf ==1)//h > 0,新增结点在c{
subL->_bf =-1;
subLR->_bf =0;
parent->_bf =0;}elseif(bf ==0)//h = 0{
parent->_bf =0;
subLR->_bf =0;
subL->_bf =0;}}
右左双旋
右左双旋跟左右双旋的情况基本是类似的,这里就不列举多种情况了
新节点插入较高右子树的左侧—右左:先右单旋再左单旋
//右左旋转voidRotateRL(Node* parent){
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;int bf = subRL->_bf;RotateR(parent->_right);RotateL(parent);if(bf ==-1)//h > 0,新增结点在b{
parent->_bf =0;
subR->_bf =1;
subRL->_bf =0;}elseif(bf ==1)//h > 0,新增结点在c{
parent->_bf =-1;
subR->_bf =0;
subRL->_bf =0;}elseif(bf ==0)//h = 0{
subR->_bf =0;
subRL->_bf =0;
parent->_bf =0;}}
查找
Node*Find(const K& key){
Node* cur = _root;while(cur){if(key > cur->_Kv.first) cur = cur->_right;//左子树elseif(key < cur->_Kv.first) cur = cur->_left;//右子树elsereturn cur;}}
其他接口
判断是不是平衡二叉树
intheight(Node* root)//求高度{return!root ?0:max(height(root->_left),height(root->_right))+1;}void_Inorder(Node* root)//中序遍历 {if(!root)return;_Inorder(root->_left);printf("%d : %d\n",root->_Kv.first, root->_Kv.second);_Inorder(root->_right);}//判断是不是平衡二叉树boolIsAVLTree(){return_IsAVLTree(_root);}bool_IsAVLTree(Node* root){if(!root)returntrue;int left =height(root->_left);int right =height(root->_right);//检查平衡因子 if(right - left != root->_bf){printf("错误的平衡因子 %d :%d\n", root->_Kv.first, root->_Kv.second);returnfalse;}return(abs(right - left)<2)&&_IsAVLTree(root->_left)&&_IsAVLTree(root->_right);}
析构函数
//析构函数~AVLTree(){Destroy(_root);
_root =nullptr;}voidDestroy(Node *root)//后序销毁结点{if(!root)return;Destroy(root->_left);Destroy(root->_right);delete root;}
拷贝构造
Node*copy(Node* cp){if(!cp)returnnullptr;
Node* newnode =newNode(cp->_Kv);
newnode->_left =copy(cp->_left);
newnode->_right =copy(cp->_right);return newnode;}//拷贝构造AVLTree(const AVLTree<K, V>& job){if(&job !=this)
_root =copy(job._root);}
拷贝赋值
voidoperator=(AVLTree<K, V> tmp){if(&tmp !=this)swap(tmp._root,this->_root);}
重载operator[ ]
V&operator[](const K& key){return(Insert(make_pair(key,V())).first)->_Kv.second;}
AVL树的完整实现代码博主已经放在 git.

版权归原作者 IT莫扎特 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。