文章目录
一、框架概述
1.1、三层架构
三层架构包含的三层:
界面层:和用户打交道的,接收用户的请求参数,显示处理结果的。对应的包是controller包。
业务逻辑层:接收了界面层传递的数据,计算逻辑,调用数据库,获取数据。对应的包是service包。
数据访问层:就是访问数据库,执行对数据的查询,修改,删除等等。对应的包是dao包。
三层的处理请求的交互:
用户使用界面层–> 业务逻辑层—>数据访问层(持久层)–>数据库(mysql)
如图: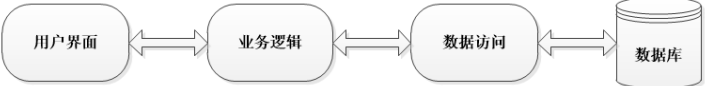
为什么使用三层:
1、结构清晰、耦合度低,各层分工明确;
2、可维护性高、可扩展行高;
3、有利于各层逻辑的复用。
1.2、什么是框架
框架(Framework)是整个或部分系统的可重用设计,表现为一组抽象构件及构件实例间交互的方法;框架是可被应用开发者定制的应用骨架、模板。
简单的说,框架其实是半成品软件,就是一组组件,供你使用完成你自己的系统。框架是安全的,可复用的,不断升级的软件。
1.3、MyBatis框架
一个框架,早期叫做ibatis,代码在GitHub。
MyBatis是MyBatis SQL Mapper Framework for Java(sql映射框架)
(1)sql mapper:sql映射
可以把数据库表中的一行数据,映射为一个java对象。一行数据可以看作是一个java对象。操作这个对象就相当于操作表中的数据.
(2)Data Access Object(DAOs):数据访问,对数据库执行增删改查。
1.3.1、使用JDBC的缺陷
1、代码比较多,开发效率低
2、需要关注Connection,Statement、ResultSet对象创建和销毁
3、对ResultSet查询的结果,需要自己封装为List
4、重复的代码比较多
1.3.2、MyBatis解决的主要问题
减轻使用JDBC的复杂性,不用编写重复的创建Connection,Statement;不用编写关闭资源代码。直接使用java对象,表示结果数据。
1.3.3、MyBatis提供的功能
1、 提供了创建Connection ,Statement, ResultSet的能力 ,不用开发人员创建这些对象了;
2. 提供了执行sql语句的能力, 不用你执行sql;
3. 提供了循环sql, 把sql的结果转为java对象, List集合的能力;
4. 提供了关闭资源的能力,不用你关闭Connection, Statement, ResultSet。
开发人员做的是:提供sql语句。
MyBatis是一个sql映射框架,提供的数据库的操作能力,增强的JDBC,使用MyBatis让开发人员集中精神写sql就可以了,不必关心Connection ,Statement, ResultSet的创建,销毁,sql的执行。
二、MyBatis使用传统Dao开发方式
2.1、编写Student实体类
publicclassStudent{//定义属性,目前要求是属性名和列名一致privateint id;privateString name;privateString email;privateint age;//构造方法、set、get、toString
2.2、编写StudentDao接口
publicinterfaceStudentDao{//查询student表中所有数据List<Student>selectStudents();//向student表中插入数据,参数student表示向数据库表中插入的数据//返回值int表示执行insert操作后影响数据库的行数intinsertStudents(Student student);}
2.3、编写Dao接口Mapper映射文件StudentDao.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPEmapperPUBLIC"-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"><mappernamespace="com.dao.StudentDao"><!--
select:表示查询操作
id:你要执行的sql语法的唯一标识,mybatis会使用这个id的值来找到要执行的sql语句
可以自定义,但是前要求使用接口中的方法名称
resultType:表示结果类型的,是sql语句执行后得到ResultSet,遍历这个ResultSet得到java对象的类型
值写的是类型的全限定名称
--><selectid="selectStudents"resultType="com.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student order by id
</select><insertid="insertStudents">
insert into student values(#{id},#{name},#{email},#{age})
</insert></mapper>
2.4、创建MyBatis主配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPEconfigurationPUBLIC"-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"><configuration><settings><settingname="logImpl"value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/></settings><!--环境配置:数据库的连接信息
default:必须和某个environment的id值一样
告诉mybatis使用哪个数据库的连接信息。也就是访问哪个数据库
--><environmentsdefault="mydev"><!--environment : 一个数据库信息的配置,环境
id:一个唯一值,自定义,表示环境的名称
--><environmentid="mydev"><!--transactionManager:mybatis的事务类型
type:JDBC(表示使用jdbc中的Connection对象的commit,rollback做事务处理)--><transactionManagertype="JDBC"/><!-- dataSource:表示数据源,连接数据库的
type:表示数据源的类型,POOLED表示使用连接池--><dataSourcetype="POOLED"><!--driver,url,username,password是固定的,不能自定义--><propertyname="driver"value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/><propertyname="url"value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm"/><propertyname="username"value="root"/><propertyname="password"value="6269131.x"/></dataSource></environment></environments><!--sql映射文件的位置--><mappers><!--一个mapper标签它指定一个文件的位置。
从类路径开始的路径信息。 target/clasess(类路径)--><mapperresource="com/dao/StudentDao.xml"/></mappers></configuration>
配置日志功能:在mybatis.xml文件加入日志配置,可以在控制台输出执行是sql语句和参数
<settings><settingname="logImpl"value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/></settings>
2.5、创建工具类(MyBatisUtils类)
publicclassMybatisUtil{privatestaticSqlSessionFactory factory =null;static{//1、定义mybatis主配置文件的名称,从类路径的根开始String config ="mybatis.xml";try{InputStream in =Resources.getResourceAsStream(config);//创建SqlSessionFactory对象,使用SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
factory =newSqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in);}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();}}//获取SqlSession对象publicstaticSqlSessiongetSqlSession(){SqlSession sqlSession =null;if(factory !=null){
sqlSession = factory.openSession();}return sqlSession;}}
2.6、创建Dao接口的实现类
publicclassStudentDaoImplimplementsStudentDao{publicList<Student>selectStudents(){//获取SqlSession对象SqlSession sqlSession =MybatisUtil.getSqlSession();String sqlId ="com.dao.StudentDao.selectStudents";List<Student> studentList = sqlSession.selectList(sqlId);
sqlSession.close();return studentList;}publicintinsertStudents(Student student){SqlSession sqlSession =MybatisUtil.getSqlSession();String sqlId ="com.dao.StudentDao.insertStudents";int nums = sqlSession.insert(sqlId,student);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();return nums;}}
2.7、创建测试类
publicclassTestMybatis{@TestpublicvoidselectTest(){StudentDao dao =newStudentDaoImpl();List<Student> students = dao.selectStudents();for(Student stu : students){System.out.println(stu);}}@TestpublicvoidinsertTest(){StudentDao dao =newStudentDaoImpl();Student student =newStudent(1017,"张三","[email protected]",40);int nums = dao.insertStudents(student);System.out.println(nums);}}
2.8、主要类介绍
(1)、Resources:mybatis中的一个类,负责读取主配置文件,返回不同类型的IO流对象。
InputStream in = Resources.getResourceAsStream(“mybatis.xml”);
(2)、SqlSessionFactoryBuilder : 创建SqlSessionFactory对象。
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder()
SqlSessionFactory factory = builder.build(in);
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder对象在创建完工厂对象后,即可被销毁。
(3)、SqlSessionFactory接口
重量级对象, 程序创建一个对象耗时比较长,使用资源比较多。
在整个项目中,有一个就够用了。
SqlSessionFactory:接口,接口实现类: DefaultSqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory作用: 获取SqlSession对象。SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();
openSession()方法说明:
1. openSession() :无参数的, 获取是非自动提交事务的SqlSession对象
2. openSession(boolean): openSession(true) 获取自动提交事务的SqlSession.
openSession(false) 非自动提交事务的SqlSession对象
(4)、SqlSession接口:定义了操作数据的方法 例如 selectList() ,insert(),update(), delete(), commit(), rollback()。
SqlSession接口的实现类DefaultSqlSession。
SqlSession对象不是线程安全的,需要在方法内部使用,在执行sql语句前,使用openSession()获取SqlSession对象。在执行完sql语句后,需要关闭它,执行SqlSession.close(),这样才能保证它的使用是线程安全的。
三、MyBatis实现Dao的动态代理
3.1Dao的动态代理
使用SqlSession.getMapper(dao接口.class)获取dao接口的对象。
这样就不需要Dao接口的实现类
publicclassMybatisTest{@Test/**
* 使用Mybatis的动态代理机制,使用sqlSession.getMapper(dao接口)
* getMapper能获取dao接口对应的实现类对象
*/publicvoidselectTest(){SqlSession sqlSession =MybatisUtil.getSqlSession();StudentDao dao = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentDao.class);//com.sun.proxy.$Proxy9: jdk的动态代理System.out.println(dao.getClass().getName());//调用dao的方法执行数据库的操作List<Student> students = dao.selectStudents();for(Student stu : students){System.out.println(stu);}}@TestpublicvoidinsertTest(){SqlSession sqlSession =MybatisUtil.getSqlSession();StudentDao dao = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentDao.class);Student student =newStudent(1032,"李四","[email protected]",21);int nums = dao.insertStudents(student);
sqlSession.commit();System.out.println(nums);}}
3.2、深入理解参数
MyBatis传递参数:从java代码中把数据传入到mapper文件的sql语句中。
3.2.1、parameterType
parameterType:写在mapper文件中的一个属性。表示dao接口中方法的参数的数据类型。
parameterType它的值是java数据类型的全限定名称或者是mybatis定义的别名
eg:parameterType = “int”
parameterType = “java.lang.Integer”
注意:parameterType不是强制的,mybatis通过反射机制能够发现接口参数的数据类型。所以可以没有,一般我们也不写。
eg:
例如StudentDao接口
public Student selectStudentById(Integer id)
<selectid="selectStudentById"parameterType="java.lang.Integer"resultType="com.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student where id = #{studentId}
</select>
3.2.2、一个简单类型的参数
简单类型:mybatis把java的基本数据类型和String都叫简单数据类型。
在mapper文件获取简单类型的一个参数的值,使用#{任意字符}
例如StudentDao接口
public Student selectStudentById(int id)
mapper:
<selectid="selectStudentById"resultType="com.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student where id = #{studentId}
</select>
3.2.3、多个参数,使用@Param命名参数
当Dao接口方法有多个参数,需要通过名称使用参数。在方法形参前面加入@Param(“自定义参数名”),mapper文件使用#{自定义参数名}。
接口方法:
List selectMultiParam(@Param(“myName”) String name,@Param(“myAge”) int age);
mapper:
<selectid="selectMultiParam"resultType="com.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student where name = #{myName} or age = #{myAge}
</select>
3.2.4、多个参数-使用java对象
使用java对象传递参数,java的属性值就是sql需要的参数值。每一个属性就是一个参数。
语法格式:#{属性名,javaType=java中数据类型名称,jdbcType=数据库数据类型名称} 这是最为完整的方式。但是javaType、jdbcType的值mybatis通过反射机制可以获取,一般不需要设置。常用格式:#{属性名}
接口方法:
List selectMultiStudent(Student student);
mapper:
<selectid="selectMultiStudent"resultType="com.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student where
name = #{name} or age = #{age}
</select>
或者为:
<selectid="selectMultiStudent"resultType="com.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student where name = #{name,javaType=java.lang.String,jdbcType=VARCHAR}
or age = #{age,javaType=java.lang.Integer,jdbcType=INTEGER}
</select>
3.2.5、多个参数-按位置
参数位置从0开始,引用参数语法==#{arg位置}==,第一个参数是#{arg0},第二个参数是#{arg1}
注意:mybatis-3.3版本和之前的版使用#{0},#{1}方式,从mybatis-3.4开始使用#{arg0}方式。
接口方法:
List selectMultiPosition(String name,int age);
mapper:
<!--多个参数使用位置--><selectid="selectMultiPosition"resultType="com.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student where
name = #{arg0} or age = #{arg1}
</select>
3.2.6、多个参数-使用Map
Map集合可以存储多个值,使用Map向mapper文件一次传入多个参数,Map集合使用String的key,Object类型的值存储参数。mapper文件使用==#{key}==引用参数值。
比如:
HashMap<String,Object> map =newHashMap<>();
map.put("name","zhangsan");
map.put("age",20);
接口方法:
List selectMultiMap(Map<String,Object> map);
mapper文件:
<!--多个参数使用Map,使用语法:#{map的key}--><selectid="selectMultiMap"resultType="com.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student where
name = #{name} or age = #{age}
</select>
3.2.7、# 和 $
#:占位符,告诉mybatis使用实际的参数值代替。并使用PrepareStatement对象执行sql语句,#{…}代替sql语句的 “ ?”。这样做更安全、通常也是首选做法。
例如:
select id,name, email,age from student where id=#{studentId}
#的结果:select id,name, email,age from student where id=?
$:字符串替换,告诉mybatis使用 $ 包含的“字符串”替换所在位置。使用Statement把sql语句和${}的内容连接起来,主要用在替换表名、列名,不同列排序等操作。
例如:
select id,name, email,age from student where id=${studentId}
$的结果:select id,name, email,age from student where id=1001
相当于:String sql=“select id,name, email,age from student where id=” + “1001”;
#和$的区别:
1、#使用?在sql语句中做占位的,使用PrepareStatement执行sql,效率高
2、#能够避免sql注入,更安全
3、$不使用占位符,是字符串连接的方法,使用Statement对象执行sql,效率低
4、$有sql注入的风险,缺乏安全性
5、$可以替换表名或者列名
3.3、MyBatis的输出结果
3.3.1、resultType
resultType:执行sql得到ResultSet转换的类型,使用类型的完全限定名或者别名。注意如果返回的是集合,那应该设置为集合包含的类型,而不是集合本身。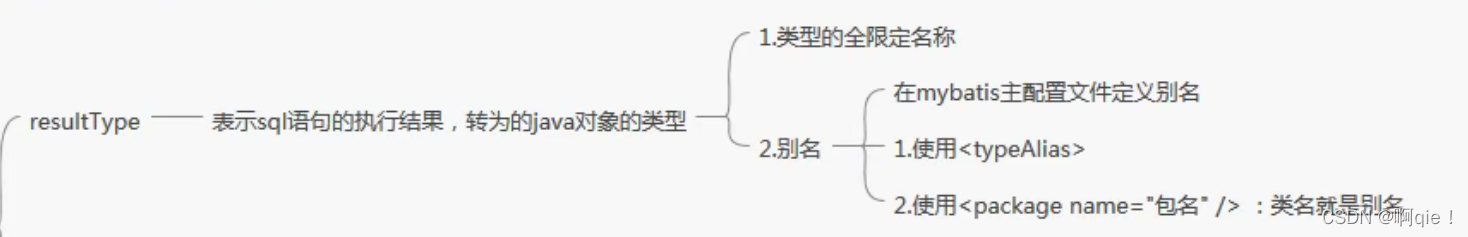
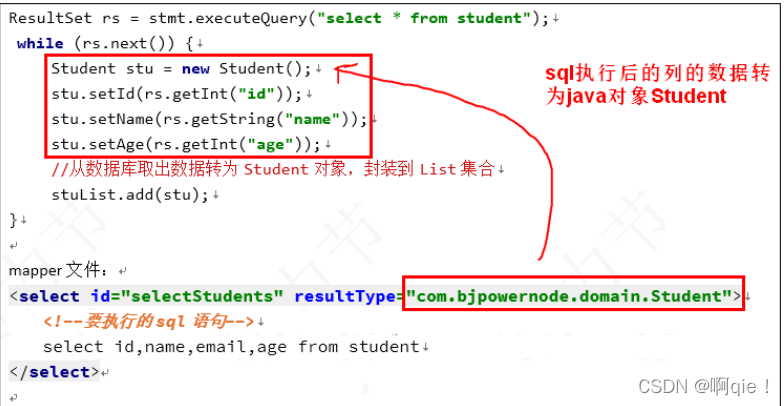
1、简单类型
接口方法:int countStudent();
mapper文件:
<selectid="countStudent"resultType="java.lang.Integer">
select count(*) from student
</select>
2、对象类型
接口方法:List<Student> selectStudent( int id);
mapper文件:
<selectid="selectStudent"resultType="com.domain.Student">
select id,name from student where id = #{id}
</select>
框架的处理:使用构造方法创建对象,调用setXXX给属性赋值。
Student student = new Student();
注意:Dao接口方法的返回值是集合类型,需要指定集合中的类型,不是集合本身。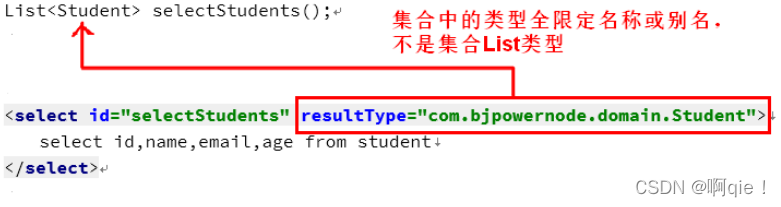
3、Map
sql的查询结果作为Map的key和value。推荐使用Map<Object,Object>.
注意:Map作为接口返回值,sql语句的查询结果最多只能有一条记录,大于一条记录是错误。
接口方法:Map<Object,Object> selectMapById(int id);
mapper文件:
<!--返回Map (用的少)
1、列名是Map的key,列值是Map的value
2、最多只能返回一行记录,多一行是错误的
--><selectid="selectMapById"resultType="java.util.HashMap">
select id,name,email,age from student where id = #{id}
</select>
测试方法:
@TestpublicvoidtestSelectMapById(){SqlSession sqlSession =MybatisUtil.getSqlSession();StudentDao dao = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentDao.class);Map<Object,Object> map = dao.selectMapById(1017);System.out.println(map);}
3.3.2、resultMap
resultMap可以自定义sql的结果和java对象属性的映射关系。更灵活的把列值赋值给指定属性。
常用在列名和java对象属性名不一样的情况。
使用方式:
1、先定义resultMap,指定列名和属性的对应关系。
2、在<select>标签中把resultType替换为resultMap。
接口方法:List<MyStudent> selectMyStudent();
mapper文件:
<!--列名和属性名不一致的第一种方式:使用resultMap
1、先定义resultMap
2、在select标签中引用1定义的resultMap
--><!--定义resultMap
id:自定义名称,表示你定义的这个resultMap
type:javaleix的全限定名称
--><resultMapid="MyStudentMap"type="com.domain.MyStudent"><!--列名和java属性的关系--><!--主键列,使用id标签
column:列名
property:java对象的属性名
--><idcolumn="id"property="stuId"/><!--非主键字段使用result--><resultcolumn="name"property="stuName"/><resultcolumn="email"property="stuEmail"/><resultcolumn="age"property="stuAge"/></resultMap><selectid="selectMyStudent"resultMap="MyStudentMap">
select id,name,email,age from student
</select>
3.3.3、实体类属性名和列名不同的处理方式
(1)、使用列别名和<resultType>
<!--
resultType的默认原则是: 同名的列值赋给同名的属性,使用列别名(java属性名)
--><selectid="selectMyStudentDiffProperty"resultType="com.domain.MyStudent">
select id as stuId,name as stuName,email as stuEmali,age as stuAge from student
</select>
(2)、使用<resultMap> (推荐使用)
注意:resultMap和resultType不要一起用,二选一
3.3.4、模糊 like
使用like进行模糊查询的第一种方式 : 在java代码中指定like的内容。
<selectid="selectLikeOne"resultType="com.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student where name like #{name}
</select>
测试程序:
@TestpublicvoidtestSelectLikeOne(){SqlSession sqlSession =MybatisUtil.getSqlSession();StudentDao dao = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentDao.class);String name ="%杨%";List<Student> students = dao.selectLikeOne(name);for(Student stu : students){System.out.println("student = "+ stu);}
sqlSession.close();}
使用like进行模糊查询的第二种方式:在mapper文件中拼接like的内容。
<selectid="selectLikeTwo"resultType="com.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student where name like "%" #{name} "%"
</select>
测试程序:
@TestpublicvoidtestSelectLikeTwo(){SqlSession sqlSession =MybatisUtil.getSqlSession();StudentDao dao = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentDao.class);String name ="杨";List<Student> students = dao.selectLikeTwo(name);for(Student stu : students){System.out.println("student = "+ stu);}
sqlSession.close();}
四、动态SQL
在mapper的动态SQL中若出现大于号、小于号。大于等于号,小于等于号等符号,最好将其转为实体符号,否则,XML可能会出现解析出错问题。
特别是对于小于号(<),在XML
z红是绝不能出现的。否则解析mapper文件会出错。
实体符号表:
4.1、if标签
对于该标签的执行,当test的值为true时,会将其包含的SQL片段拼接到其所在的SQL语句中。
语法:<if test=“条件”> sql语句的部分 </if>
mapper文件:
<selectid="selectStudentIf"resultType="com.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student where true
<iftest="name != null and name != ''">
name = #{name}
</if><iftest="age > 0">
or age > #{age}
</if></select>
4.2、where标签
<if/>标签中存在一个麻烦的地方,需要在where后手工添加1=1的子句。因为,若where后的所有<if/>条件均为false,而where后若没有1=1子句,则sql中就会剩下一个空的where,sql出错。所以在where后需要添加永为真子句1=1,以防这种情况发生。但当数据量很大的时候,会严重影响查询效率。
使用<where/>标签,在有查询条件时,可以自动添上where子句,没有查询条件时,不会添加where子句。注意:第一个<if/>标签中的sql片段,可以不包含and,不过写上也不会出错,系统会将多余的and去掉。但其它<if/>中sql片断的and,必须要求写上,否则sql语句将拼接出错。
<selectid="selectStudentWhere"resultType="com.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student
<where><iftest="name != null and name != ''">
name = #{name}
</if><iftest="age > 0">
or age = #{age}
</if></where></select>
4.3、foreach标签
<foreach/>标签用于实现对于数组与集合的遍历。
collection:表示要遍历的集合类型,list,array等
open、close、separator为对遍历内容的SQL拼接。
语法: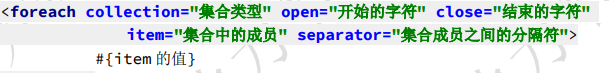
遍历简单类型:
mapper文件:
<selectid="selectStudentForOne"resultType="com.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student where id in
<foreachcollection="list"item="myid"open="("close=")"separator=",">
#{myid}
</foreach></select>
测试程序:
@TestpublicvoidselectStudentForOne(){SqlSession sqlSession =MybatisUtil.getSqlSession();StudentDao dao = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentDao.class);List<Integer> list =newArrayList<>();
list.add(1032);
list.add(1017);
list.add(1001);List<Student> students = dao.selectStudentForOne(list);for(Student stu : students){System.out.println("student= "+ stu);}
sqlSession.close();}
遍历对象类型:
mapper文件:
<selectid="selectStudentForTwo"resultType="com.domain.Student">
select id,name,email,age from student where id in
<foreachcollection="list"item="student"open="("close=")"separator=",">
#{student.id}
</foreach></select>
测试程序:
@TestpublicvoidselectStudentForTwo(){SqlSession sqlSession =MybatisUtil.getSqlSession();StudentDao dao = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentDao.class);List<Student> stuList =newArrayList<>();Student s1 =newStudent();
s1.setId(1001);
stuList.add(s1);
s1 =newStudent();
s1.setId(1017);
stuList.add(s1);List<Student> students = dao.selectStudentForTwo(stuList);for(Student stu : students){System.out.println("student= "+ stu);}
sqlSession.close();}
4.4、代码片段
<sql/>标签用于定义SQL片段,以便其他SQL标签复用。而其他标签使用该SQL片段,需要使用<include/>子标签。该<sql/>标签可以定义SQL语句中的任何部分,所以子标签可以放在动态SQL的任何位置。
mapper文件:
<sqlid="studentSql">
select id,name,email,age from student
</sql><selectid="selectStudentForTwo"resultType="com.domain.Student"><includerefid="studentSql"/>
where id in
<foreachcollection="list"item="student"open="("close=")"separator=",">
#{student.id}
</foreach></select>
4.5、总结

五、MyBatis主配置文件
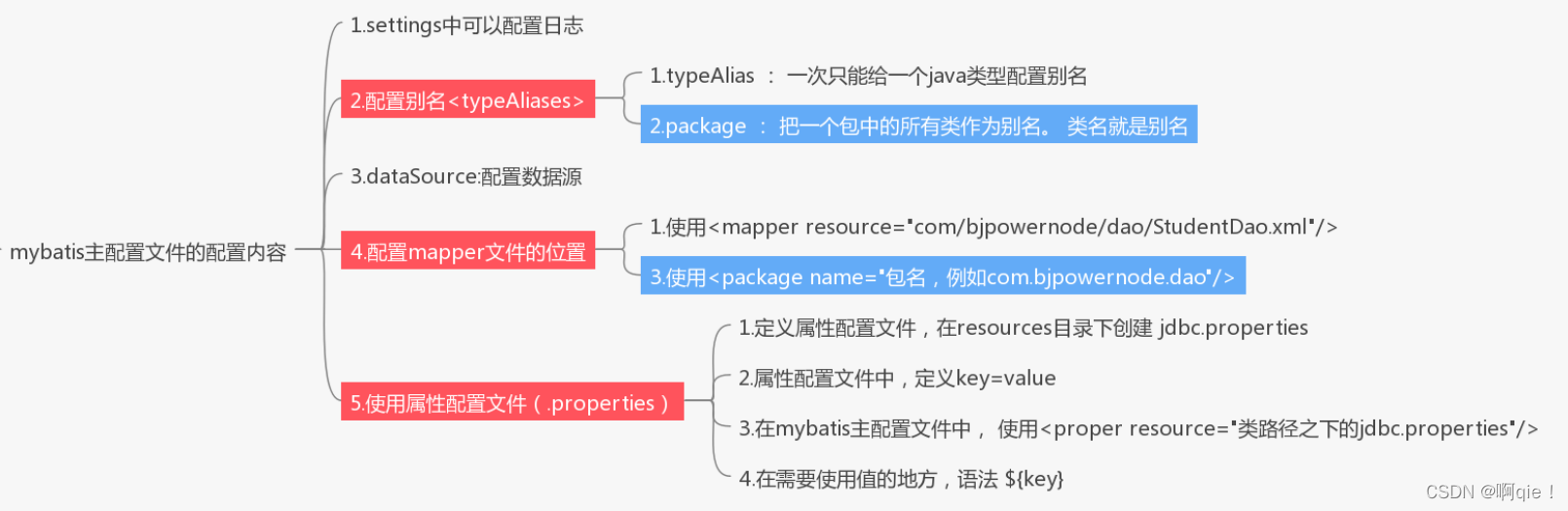
1、数据库的属性配置文件:把数据库连接信息放到一个单独的文件中。和mybatis主配置文件分开。目的是便于修改,保存,处理多个数据库的信息。
1)在resource目录中定义一个属性配置文件,xxx.properties。在属性配置文件中,定义数据,格式是key=value
key:一般使用 . 做多级目录的。
2)在mybatis的主配置文件,使用<property>指定文件的位置,在需要使用值的地方,$(key)
2、mapper文件,使用package指定路径
<mappers><packagename="com.dao"/></mappers>
name:xml文件(mapper文件)所在的包名,这个包中所有xml文件一次都能加载给mybatis
使用package的要求:
1、mapper文件名称需要和接口名称一样,区分大小写的一样
2、mapper文件和dao接口需要在同一目录
六、MyBatis扩展
基于PageHelper的分页
1)maven坐标
<!--pageHelper的依赖--><!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.github.pagehelper/pagehelper --><dependency><groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId><artifactId>pagehelper</artifactId><version>5.1.0</version></dependency>
2)加入plugin配置:
<!--在<environments>之前加入--><plugins><plugininterceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor"/></plugins>
3)PageHelper对象
查询语句之前调用PageHelper.startPage静态方法。
在你需要进行分页的Mybatis查询方法前调用PageHelper.startPage静态方法即可,紧跟在这个方法后的第一个MyBatis查询方法会被进行分页。
@TestpublicvoidtestSelectAllByPageHelper(){SqlSession sqlSession =MybatisUtil.getSqlSession();StudentDao dao = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentDao.class);PageHelper.startPage(2,3);List<Student> students = dao.selectAll();for(Student stu : students){System.out.println("student= "+ stu);}
sqlSession.close();}
版权归原作者 啊qie! 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。