目录点击跳转
本章概要
本章主要和大家一起学习
java
异常类的处理机制,深入学习
java
异常类。
掌握异常处理机制,及背后的逻辑。
1.了解异常体系,学习常见的异常类
2.知道如何处理异常,掌握
try-catch
或者
throws
的使用和区别
3.能够读懂异常代码,知道何处可能会有异常出现
java异常处理入门
二话不说,先看代码!
//异常处理入门publicclassException1{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){int m =10;int n =0;System.out.println(m/n);//分母不能为0 算数异常System.out.println("程序继续....");//异常导致程序奔溃并未执行该语句}}
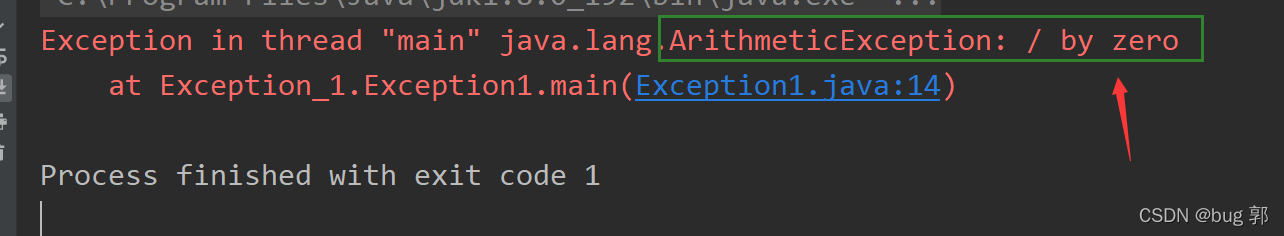 可以看到当一个代码某个语句出现异常,如果我们不做任何处理,
可以看到当一个代码某个语句出现异常,如果我们不做任何处理,
java
程序就会奔溃,导致程序中断,后面的语句无法执行!
那如果我们是一个团队在写一个项目,我们有成千上万行代码,如果应因为某一行语句出现异常,而导致整个项目奔溃,显然不合理!
我们可以采取解决方案将异常处理
捕捉异常
对异常进行捕获,保证程序可以继续运行。
用
try-catch
语句进行捕捉异常,大致细节我们后面讲到,我们先看下面代码:
//try-catch对异常捕捉publicclassException1{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){int m =10;int n =0;try{System.out.println(m/n);//分母不能为0 算数异常}catch(Exception e){//捕捉异常System.out.println(e.getMessage());//打印异常信息}System.out.println("程序继续....");//处理完异常继续执行该语句}}
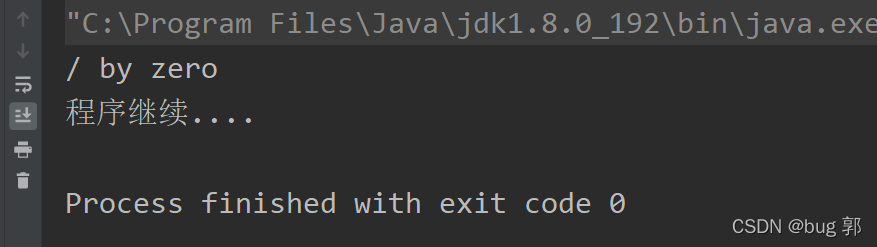
我们可以看到捕捉处理异常后程序可以正常执行!
我们再来学习一下
try-catch
语句在
IDEA
下的快捷键吧!
1.首先我们选中将会报异常的语句
2.快捷键
Ctrl+Alt+T
3.选中要进行的操作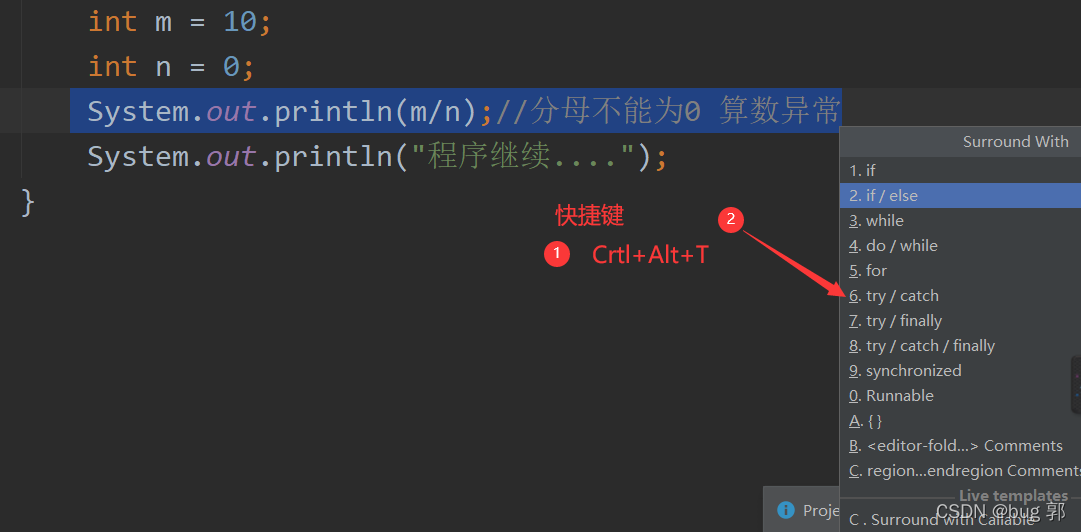
异常介绍
异常分类
java
异常分为两大类:
Error(错误)java虚拟机无法解决的重大问题,JVM系统内部错误,资源耗尽等严重情况。如:栈溢出StackOverflowError,内存不足out of memory(OOM)。Error是严重错误,会导致程序奔溃!就好比人得了绝症,没得救!Exception由编程错误或其他外界因素导致的一般性问题,可以通过针对性的代码来处理。例如:空指针访问,文件是否存在,数据库连接等等。Exception又分为两种: 1.受查(编译)异常:在编译器期间,编译器便能够查出的错误! 2.非受查(运行)异常RuntimeException:在运行期间才会报错!
异常体系图
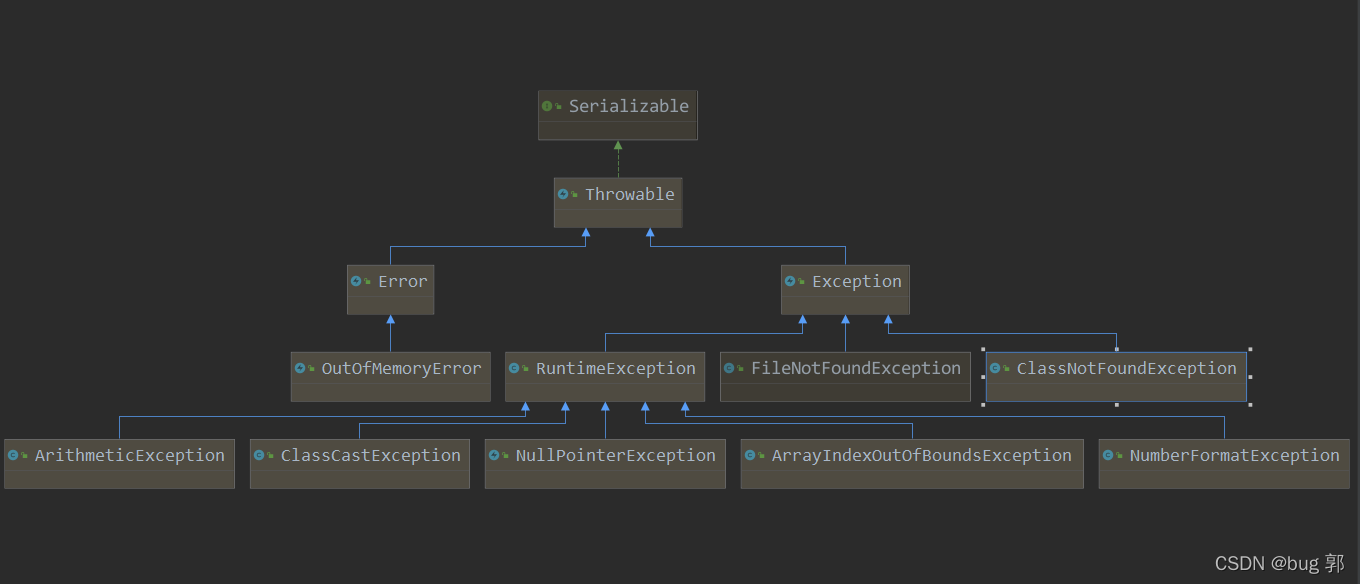 只是举例了几种常见的异常!
只是举例了几种常见的异常!
大家可以下去自行查看
异常体系图十分方便体现了继承和实现的关系!
虚线是实现接口,实线是继承父类!
**
IEDA
查看类的关系图步骤:**
1.找到一个类选中
2.鼠标右击
3.选择 4.然后再选择该类,鼠标右击查看,选择你要展现父类或者子类!
4.然后再选择该类,鼠标右击查看,选择你要展现父类或者子类!
异常体系图的小结
基本概念
java
语言中,将程序执行中出现的不正常情况称为“异常”(开发中语法错误和逻辑错误不是异常)
运行时异常
常见的运行时异常包括
NullPointerException空指针异常ArithmeticException数学运算异常ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException数组下标越界异常ClassCastException类型转换异常NumberFormatException数字格式不正确异常
常见运行时异常举例
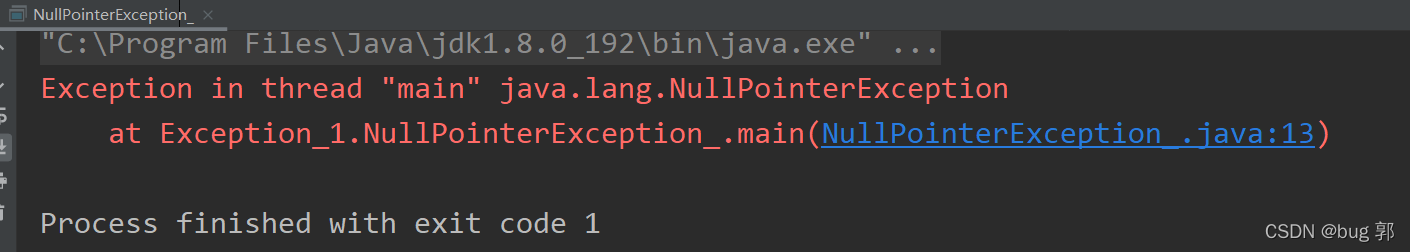
NullPointerException空指针异常
//空指针异常publicclassNullPointerException_{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){String str =null;System.out.println(str.length());//NullPointException}}
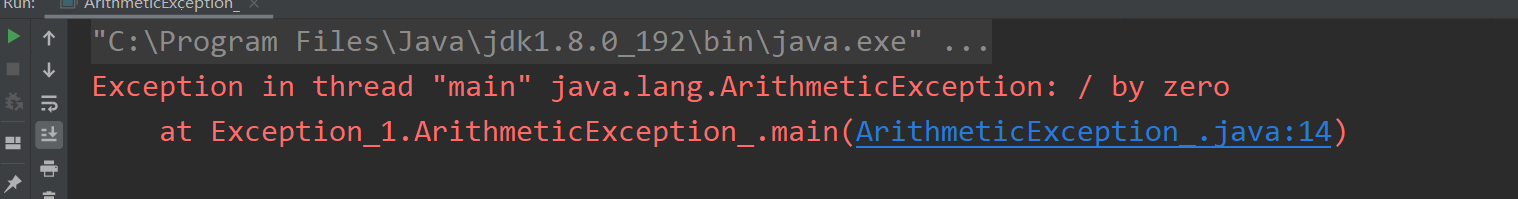
数学运算异常ArithmeticException
//数学运算异常publicclassArithmeticException_{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){int m =10;int n =0;System.out.println(m/n);//分母不能为0 算数异常}}
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException数组越界异常
//数组下标越界异常publicclassArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException_{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){int[] arr =newint[3];System.out.println(arr[4]);//arr下标[0,2]}}
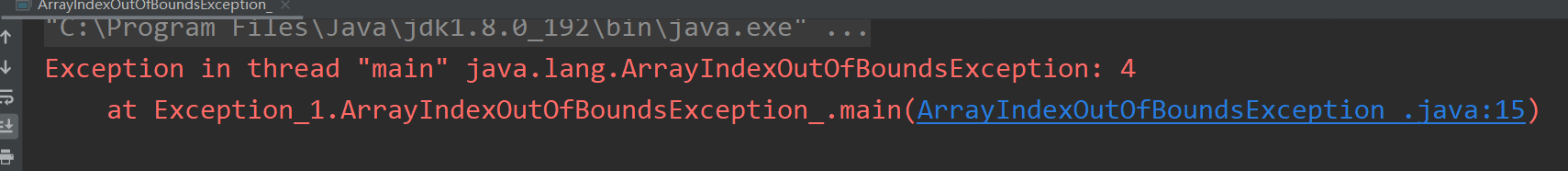
ClassCastException类型转换异常
//类型转换异常publicclassClassCastException_{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){String string ="java";Object ob = string;//上转型对象Integer integer =(Integer)ob;//类型转换异常}}
数字格式不正确异常NumberFormatException
//数字格式不正确异常publicclassNumberFormatException_{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){int a =Integer.parseInt("1aba");//将字符串转换成整型//数字格式不正确异常}}

编译异常
编译异常就是在编译期间就要处理的异常,也叫
受查异常
,就是说编译器在编译期间会进行检查,不处理该异常,就无法通过编译。
编译异常必须处理!
常见编译异常:
1.
SQLException
//操作数据库时,查询表可能发生异常
2.
IOException
//操作文件时,发生的异常
3.
FileNotFoundException
//当操作一个不存在文件时,发生的异常
4.
EOFException
//操作文件,文件到末尾,发生的异常
5.
IllegalArgumentException
//参数异常
编译异常举例
因为
bug郭
还没有学习到数据库和文件操作。我们就举一个案例来了解一下编译异常!
//操作文件,发生的编译异常publicclassIOException_{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){File file =newFile("D:\\a.txt");
file.createNewFile();//异常}}
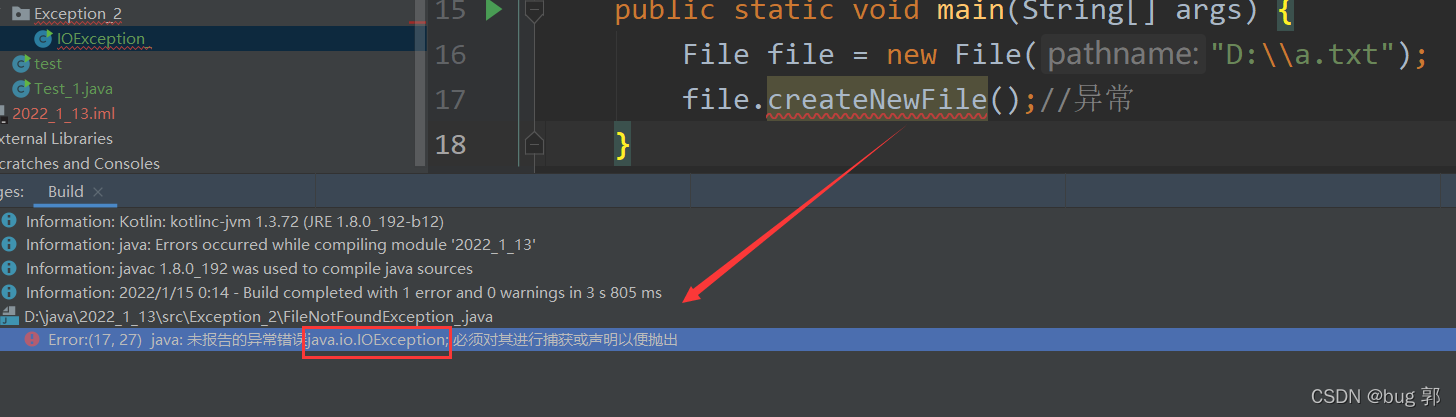 可以看到编译异常,如果我们不进行处理,代码就无法编译通过!
可以看到编译异常,如果我们不进行处理,代码就无法编译通过!
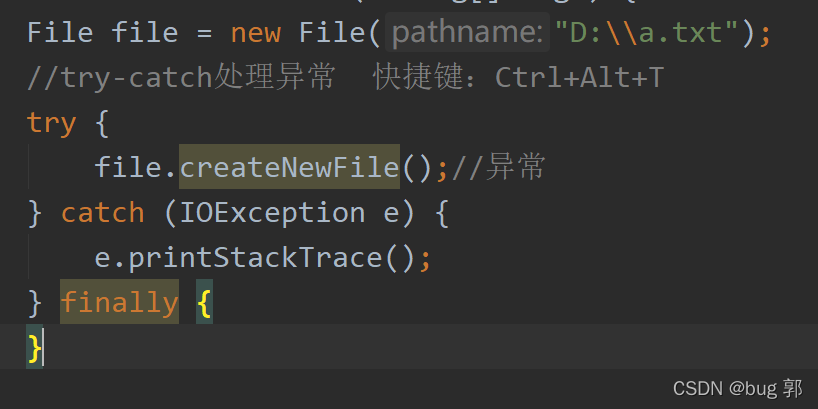
//try-catch处理异常publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){File file =newFile("D:\\a.txt");//try-catch处理异常 快捷键:Ctrl+Alt+Ttry{
file.createNewFile();//异常}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();}finally{}}
异常课堂练习
我们了解了异常,哪来看看下面代码是否会发生异常吧!
//题目一publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){String[] strings =newString[]{"java","bug","2022"};System.out.println(strings[3]);}
结果:
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
数组下标越界异常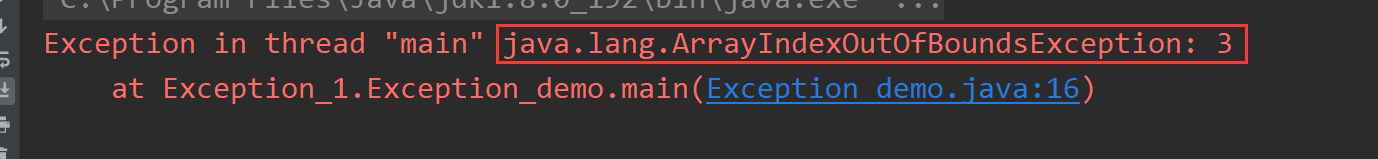
//题目二publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){String string ="java";Object ob = string;Integer integer =(Integer)ob;}
ClassCastException
类型转换异常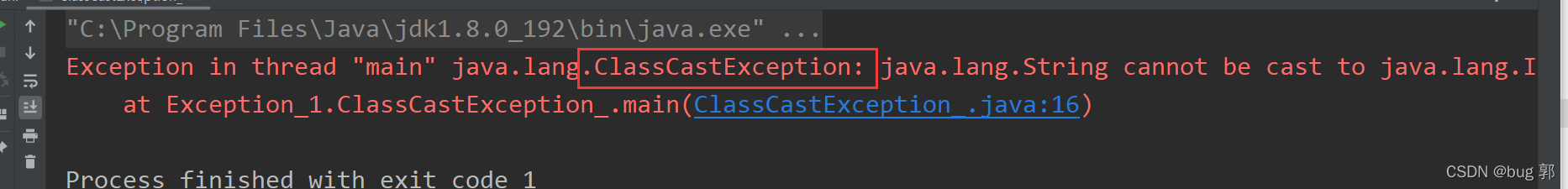
//题目三classCat{publicString name;Cat(String name){this.name = name;}}publicclass test_1 {publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){Cat cat=newCat("豆花");
cat =null;System.out.println(cat.name);}}
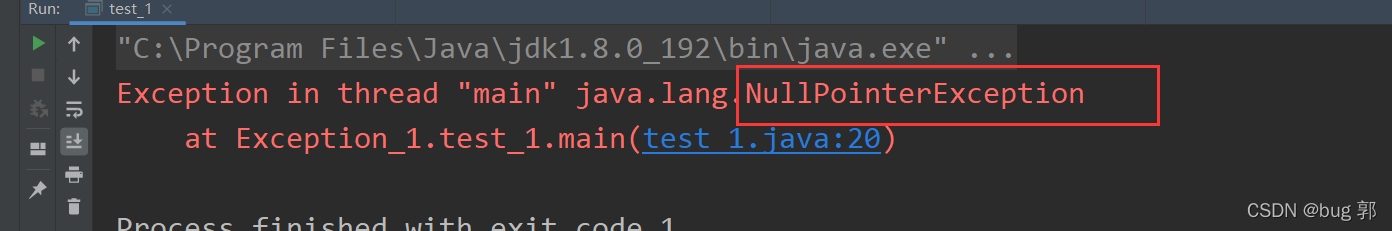
空指针异常NullPointerException
//题目四publicclassTest_1{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){int[] array =newint[]{1,3,3,4,5,6};
array =null;for(int x:
array){System.out.print(x+" ");}}}
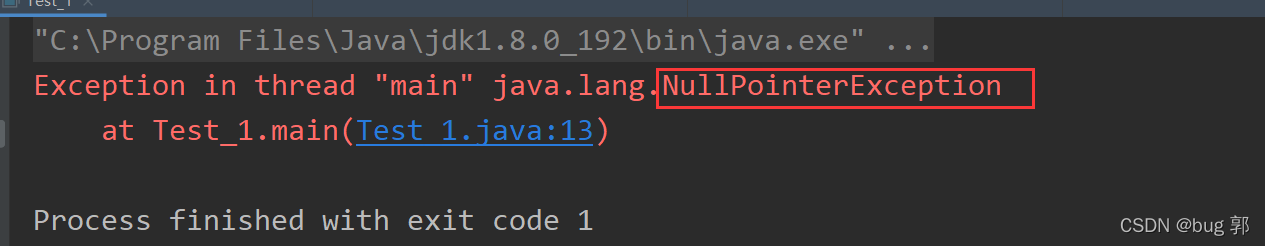
异常处理
基本介绍
异常处理就是,当异常发生时,对异常处理的方式!
异常处理方式
try-catch-finally程序员在代码中捕获发生的异常,自行处理throws将发生的异常交给调用者(方法)来处理,最顶级的处理者就是JVM
**
try-catch-finally
处理方式介绍**
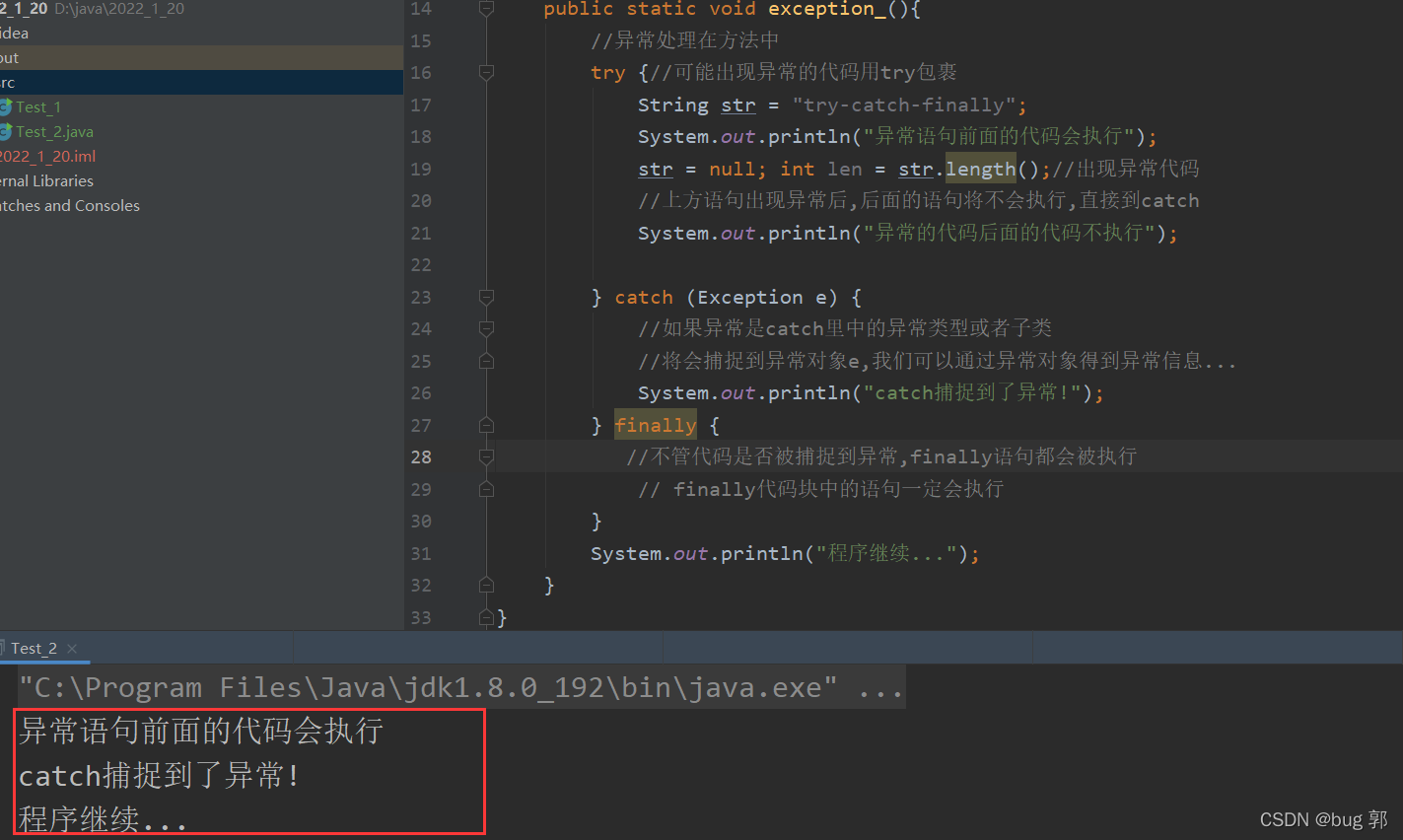
//`try-catch-finally异常处理机制介绍classException_1{publicstaticvoidexception_(){//异常处理在方法中try{//可能出现异常的代码用try包裹String str ="try-catch-finally";System.out.println("异常语句前面的代码会执行");
str =null;int len = str.length();//出现异常代码//上方语句出现异常后,后面的语句将不会执行,直接到catchSystem.out.println("异常的代码后面的代码不执行");}catch(Exception e){//如果异常是catch里中的异常类型或者子类//将会捕捉到异常对象e,我们可以通过异常对象得到异常信息...System.out.println("catch捕捉到了异常!");}finally{//不管代码是否被捕捉到异常,finally语句都会被执行// finally代码块中的语句一定会执行}System.out.println("程序继续...");}}
throws处理方式介绍
//throws机制处理异常方式publicclassTest_3{//抛出异常通常定义在 方法头部()后面 throws + 异常类型publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args)throwsNumberFormatException{f1();}publicstaticvoidf1()throwsNumberFormatException{f2();//两种选择,处理或者抛出}publicstaticvoidf2()throwsNumberFormatException{f3();//两种选择,处理或者抛出}publicstaticvoidf3()throwsNumberFormatException{f4();//两种选择,处理或者抛出}publicstaticvoidf4()throwsNumberFormatException{thrownewNumberFormatException();//出现异常,f4可选择try-catch-finally捕捉异常// 或者throws抛出给调用者}}
JVM
处理后,打印异常信息,退出程序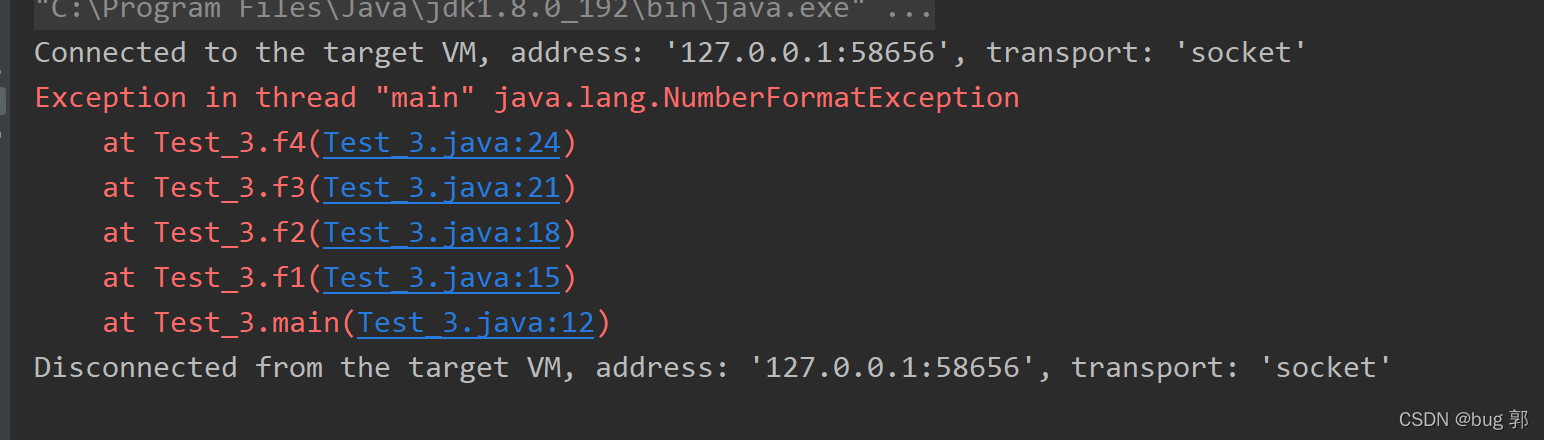
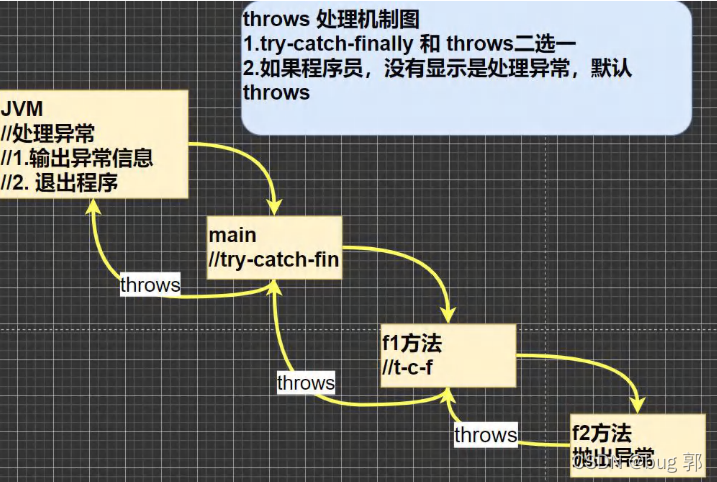
throws处理异常方式就是将异常抛出给调用者(方法),每个接收到异常的调用者(方法)都有两种处理异常的方式:
1.向上抛给他的调用者 2.try-catch-finally捕获异常如果一直向上抛给调用者,如果最后的调用者
main方法也继续抛出,那么最终会由
JVM处理该异常,并输出异常信息,最后程序中断,退出程序。
还有我们的java程序如果我们程序员不处理异常,默认
throws所以也就解释了为啥出现异常,程序便会中断,因为默认是
throws机制处理异常,然后抛给
JVM处理异常,打印异常信息,直接退出程序。
try-catch异常处理
我们刚刚介绍了
try-catch
处理异常的机制,我们现在来深入学习一下
try-catch
异常处理的一些细节!! 可以看到
可以看到
java
提供
try
和
catch
块来处理异常,
try
代码块中包含可能出错的代码,
catch
捕捉
try
块中出现的异常,如果捕捉到该异常,就在
catch
代码块中进行异常处理,打印异常等等,而
try-cath-finally
组合处理异常,
finally
代码块中不管是否捕捉到异常都将最后执行,并且一定会被执行!!也可以没有
finally
代码块,
try-catch
组合处理异常!
注意事项
我们通过下面的代码案例来学习一些
try-catch
异常处理的细节吧!
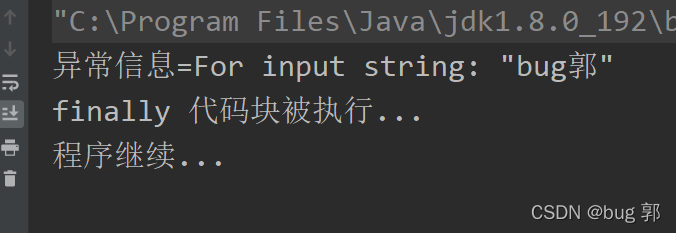
//案例一publicclassTryCatchDetail{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){//ctrl + atl + t 快捷键 try-catch-finally语句!//1. 如果异常发生了,则异常发生后面的代码不会执行,直接进入到 catch 块//2. 如果异常没有发生,则顺序执行 try 的代码块,不会进入到 catch//3. 如果希望不管是否发生异常,都执行某段代码(比如关闭连接,释放资源等)则使用如下代码- finallytry{String str ="bug郭";int a =Integer.parseInt(str);System.out.println("数字:"+ a);}catch(NumberFormatException e){System.out.println("异常信息="+ e.getMessage());}finally{System.out.println("finally 代码块被执行...");}System.out.println("程序继续...");}}
//案例二classPerson{privateString name ="jack";publicStringgetName(){return name;}}publicclassTryCatchDetail02{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){//1.如果 try 代码块有可能有多个异常//2.可以使用多个 catch 分别捕获不同的异常,相应处理//3.要求子类异常写在前面,父类异常写在后面try{Person person =newPerson();//person = null;System.out.println(person.getName());//NullPointerExceptionint n1 =10;int n2 =0;int res = n1 / n2;//ArithmeticException}catch(NullPointerException e){System.out.println("空指针异常="+ e.getMessage());}catch(ArithmeticException e){System.out.println("算术异常="+ e.getMessage());}catch(Exception e){System.out.println(e.getMessage());}finally{}}}
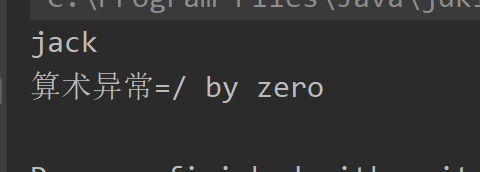
//案例三publicclassTryCatchDetail03{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){/*
可以进行 try-finally 配合使用, 这种用法相当于没有捕获异常,
因此程序会直接崩掉/退出。应用场景,就是执行一段代码,不管是否发生异常,
都必须执行某个业务逻辑
*/try{int n1 =10;int n2 =0;System.out.println(n1 / n2);}finally{System.out.println("执行了 finally..");}System.out.println("程序继续执行..");}}
 总结:
总结:
try-catch-finally异常处理可以有多种组合,try-catch(捕捉异常,不善后,程序继续运行,),try-finally(不捕捉异常,finally代码块一定会执行)- 可以有多个
catch语句,并且需要遵循异常子类在前原则,否者在前捕获到了异常,后面子类就会无法通过编译报错! - 如果有
fianlly代码块,那里面的语句一定为执行,不管是否捕捉了异常!!!
try-catch
异常处理小测试
既然已经学到这里了,那我们来巩固测试一下!读代码写结果吧!
//测试一publicclassTest_2{publicstaticintmethod(){try{String[] names =newString[3];//String[]数组if(names[1].equals("bug郭")){System.out.println(names[1]);}else{
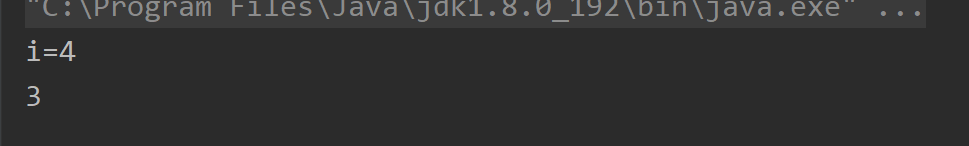
names[3]="java";}return1;}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){return2;}catch(NullPointerException e){return3;}finally{return4;}}publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){System.out.println(method());//执行结果?}}
//测试一题解publicclassTest_2{publicstaticintmethod(){try{String[] names =newString[3];//String[]数组if(names[1].equals("bug郭")){//null空指针异常names数组里的元素为null System.out.println(names[1]);}else{
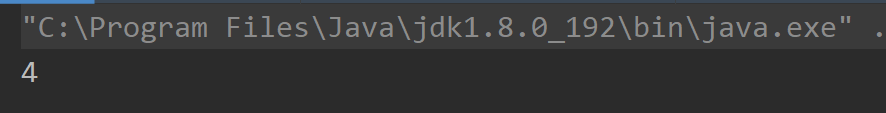
names[3]="java";}return1;}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){return2;}catch(NullPointerException e){return3;//捕捉到异常 先将3保存}finally{return4;//一定要执行 所以最后return 4!!!}}publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){System.out.println(method());//执行结果:4}}
//测试二publicclassTest_3{publicstaticintmethod(){int i =1;try{
i++;String[] names =newString[3];//String[]数组if(names[1].equals("bug郭")){//空指针System.out.println(names[1]);}else{
names[3]="java";}return1;}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){return2;}catch(NullPointerException e){return++i;}finally{return++i;}}publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){System.out.println(method());//执行结果?}}
//测试二题解publicclassTest_3{publicstaticintmethod(){int i =1;try{
i++;//i=2!String[] names =newString[3];//String[]数组if(names[1].equals("bug郭")){//空指针异常直接执行catch语句!System.out.println(names[1]);}else{
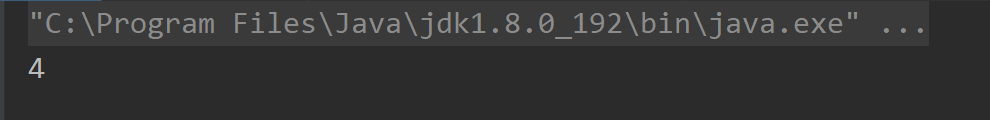
names[3]="java";}return1;}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){return2;}catch(NullPointerException e){return++i;//i = 3 并且保存了将要返回值为3 }finally{return++i;//i = 4 一定要执行,将 i = 4返回!}}publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){System.out.println(method());//执行结果:4!!!}}
//测试三publicclassTest_4{publicstaticintmethod(){int i =1;try{
i++;String[] names =newString[3];if(names[1].equals("bug郭")){System.out.println(names[1]);}else{
names[3]="java";}return1;}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){return2;}catch(NullPointerException e){return++i;}finally{++i;System.out.println("i="+i);}}publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){System.out.println(method());//执行结果?}}
//测试三题解publicclassTest_4{publicstaticintmethod(){int i =1;try{
i++;//i=2String[] names =newString[3];if(names[1].equals("bug郭")){//空指针异常System.out.println(names[1]);}else{
names[3]="java";}return1;}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){return2;}catch(NullPointerException e){return++i;//i = 3 并且用临时变量保存了该返回值3!}finally{++i;// i = 4System.out.println("i="+i);//打印 i= 4}}//最终函数返回:3publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){System.out.println(method());//执行结果:i= 4 3}}
throws异常处理
基本介绍
throws
异常处理是
java
处理异常的另一种方式,也是
JVM
的默认处理机制!
刚刚我们也已经介绍过了!
简单说就是:如果一个方法中的某处代码出现了异常,那么该方法就要进行异常异常处理!
try-catch
或者
throws
(如果不对异常进行处理那么默认也是
throws
)而
throws
处理机制就是将异常(向上一级抛)抛给方法的调用者,如果调用者都不进行异常处理,那么最终会有
JVM
处理,程序中断!
//throws异常处理细节!publicclassThrowsDetail{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){f2();}publicstaticvoidf2()/*throws ArithmeticException*/{//1.对于编译异常,程序中必须处理,比如 try-catch 或者 throws//2.对于运行时异常,程序中如果没有处理,默认就是 throws 的方式处理int n1 =10;int n2 =0;double res = n1 / n2;}publicstaticvoidf1()throwsFileNotFoundException{//这里大家思考问题 调用 f3() 报错//解答//1. 因为 f3() 方法抛出的是一个编译异常//2. 即这时,就要 f1() 必须处理这个编译异常//3. 在 f1() 中,要么 try-catch-finally ,或者继续 throws 这个编译异常f3();// 抛出异常}publicstaticvoidf3()throwsFileNotFoundException{FileInputStream fis =newFileInputStream("d://aa.txt");}publicstaticvoidf4(){//解答://1. 在 f4()中调用方法 f5() 是 OK//2. 原因是 f5() 抛出的是运行异常//3. 而 java 中,并不要求程序员显示处理,因为有默认处理机制f5();}publicstaticvoidf5()throwsArithmeticException{}}classFather{//父类publicvoidmethod()throwsRuntimeException{}}classSonextendsFather{//子类//3. 子类重写父类的方法时,对抛出异常的规定:子类重写的方法,// 所抛出的异常类型要么和父类抛出的异常一致,要么为父类抛出的异常类型的子类型//4. 在 throws 过程中,如果有方法 try-catch , 就相当于处理异常,就可以不必 throws@Overridepublicvoidmethod()throwsArithmeticException{}}
自定义异常
基本概念
当程序中出现某些“错误”,但该错误信息并没有在
Throwable
子类中描述处理,这个时候我们可以自己设计异常类,用于描述该错误信息。
自定义异常步骤
1.定义类:自定义异常类名(设计者自己编写)继承
Exception
或
RuntimeException
2.如果继承
Exception
,属于编译异常
3.如果继承
RuntimeException
,属于运行异常(一般来说,继承
RuntimeException
)
实例
客户需求:当我们接收
Person
对象年龄时,要求范围在18-120之间,否者抛出一个自定义异常,并给出提示!
//解决方案publicclassCustomException{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args)/*throws AgeException*/{int age =180;//要求范围在 18 – 120 之间,否则抛出一个自定义异常if(!(age >=18&& age <=120)){//这里我们可以通过构造器,设置信息thrownewAgeException("年龄需要在 18~120 之间");}System.out.println("你的年龄范围正确.");}}//自定义一个异常//解读//1. 一般情况下,我们自定义异常是继承 RuntimeException//2. 即把自定义异常做成 运行时异常,好处时,我们可以使用默认的处理机制//3. 即比较方便classAgeExceptionextendsRuntimeException{publicAgeException(String message){//构造器super(message);}}
throw和throws的区别
意义位置后面跟的内容throws异常处理的一种方式方法声明处异常类型throw手动生成异常对象关键字方法体中异常对象
java
异常章节学习到这里!如果对大家有所帮助,还望多多支持!如有错误多多指正!内容来自
bug郭
在B站学习韩顺平的java课程自己整理的笔记!
互关互访互相支持,一起进步!、~
版权归原作者 bug 郭 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。