🖥️ NodeJS专栏:Node.js从入门到精通
🖥️ 蓝桥杯真题解析:蓝桥杯Web国赛真题解析
🧧 加入社区领红包:海底烧烤店ai(从前端到全栈)
🧑💼个人简介:即将大三的学生,一个不甘平庸的平凡人🍬
👉 你的一键三连是我更新的最大动力❤️!🏆分享博主自用牛客网🏆:一个非常全面的面试刷题求职网站,真的超级好用🍬
文章目录
前言
最近博主一直在牛客网刷题巩固基础知识,快来和我一起冲关升级吧!点击进入牛客网
这一节我们去学习
NodeJs
的内置模块:
http
、
url
、
querystring
,并使用它们来搭建我们的
node
后端服务器,正式迈入后端开发!
这篇文章内容比较多,篇幅较长,建议先收藏再观看🍬
Node系列专栏开始更新了,关注博主,订阅专栏,学习Node不迷路!
一、创建服务器
http
是
node
的内置模块,我们可以直接引入它进行使用,
http
这个模块内有一个
createServer
方法,这个方法可以帮助我们快速创建一个服务器:
// 引入http模块const http =require("http");// 创建服务器
http.createServer((req, res)=>{// req:接受浏览器传的参数// res:返回渲染的内容}).listen(3000,()=>{// 服务器端口号为3000
console.log("服务器启动啦!");});
另一种写法(推荐写法):
const http =require("http");// 创建服务器const server = http.createServer();
server.on("request",(req, res)=>{// req:接受浏览器传的参数// res:返回渲染的内容});
server.listen(3000,()=>{// 服务器端口号为3000
console.log("服务器启动啦!");});
createServer
方法返回一个服务器对象,对象内有一个
listen
方法,可以设置服务器启动的端口号和启动成功的回调内容
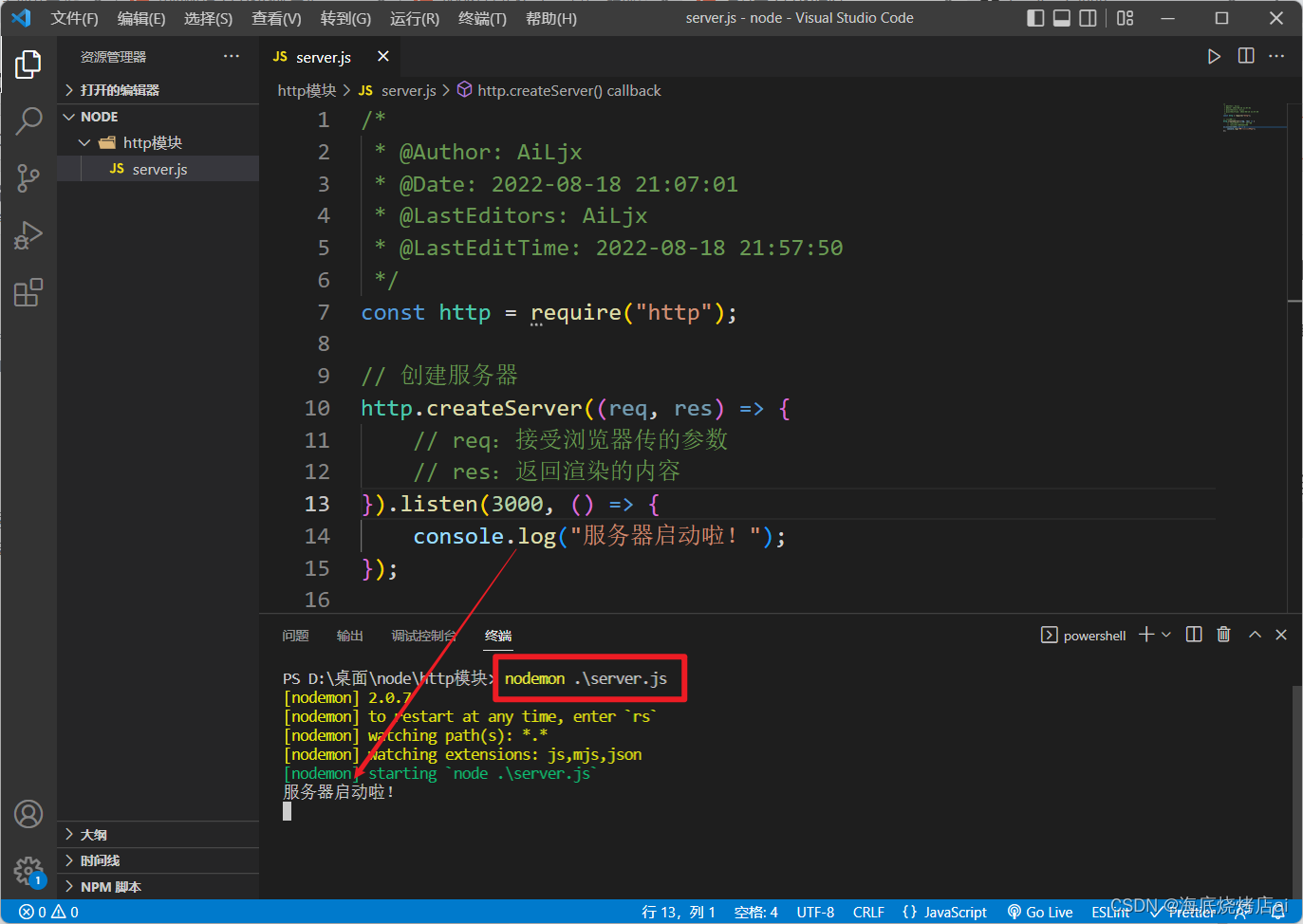
通过
nodemon
运行这个文件(
nodemon
可以在我们修改文件后帮助我们自动重启服务器),控制台打印出了我们在
listen
中设置的回调内容,说明服务器启动成功了
我们直接在浏览器访问
http://localhost:3000/
时会发现浏览器一直在转圈圈加载
注意: 直接在浏览器地址栏里访问服务器接口,相当于是使用
get请求访问服务器接口(并且没有跨域限制)
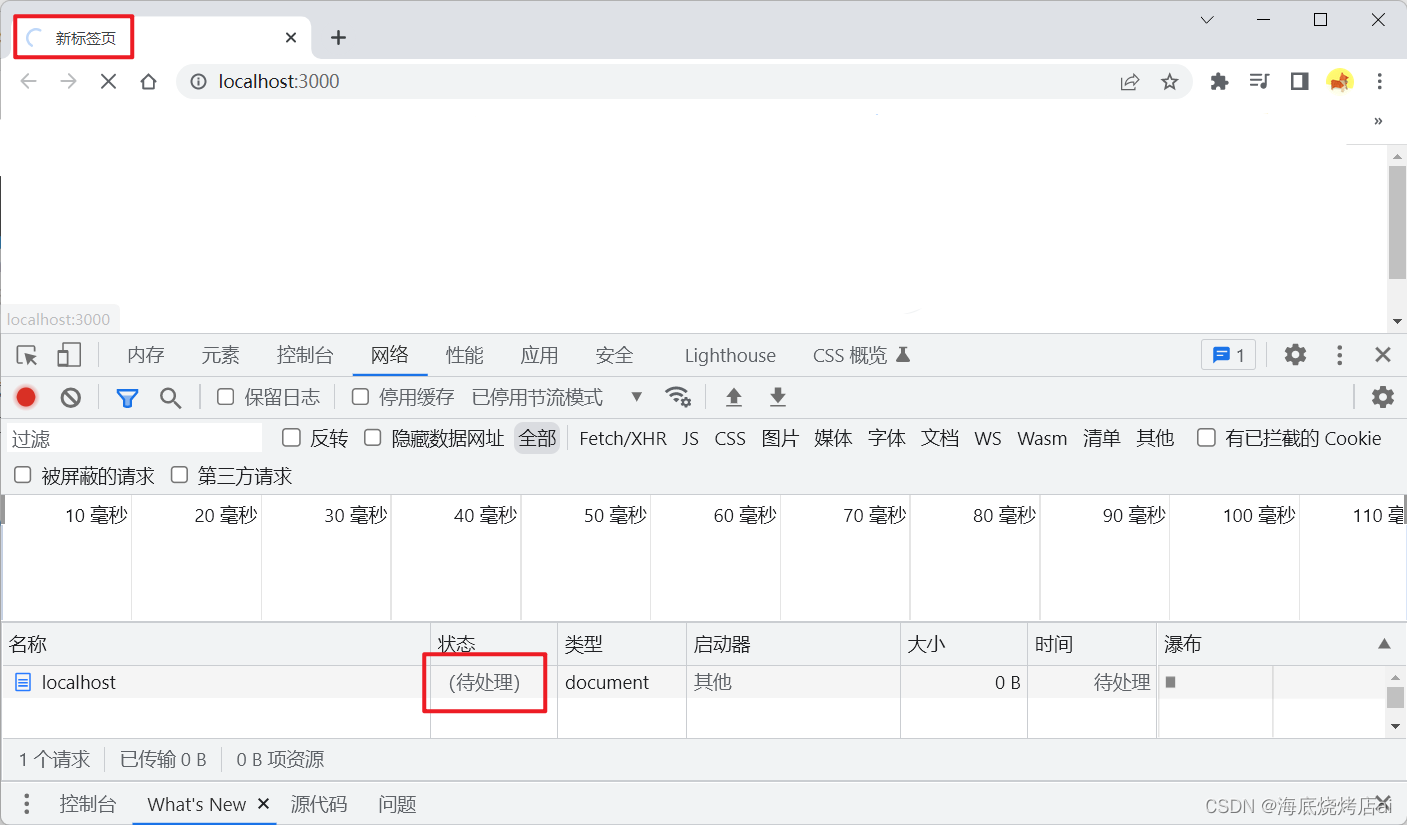
这是因为我们并没有在我们创建的
node
服务器中返回任何内容
二、返回响应数据
我们可以通过我们定义的
res
(
response
对象)参数向客户端发送响应内容:
const http =require("http");// 创建服务器
http.createServer((req, res)=>{// req:接受浏览器传的参数// res:返回渲染的内容// 传递数据
res.write("hello world");
res.write("Ailjx");
res.end();}).listen(3000,()=>{
console.log("服务器启动啦!");});
write方法传递内容,可以调用多次write传递多条内容,内容必须是字符串格式- 最后必须调用
end方法告诉请求的调用者我们响应结束了 - 也可以直接在
end方法内传递内容,效果与使用write方法相同,但end方法只能调用一次
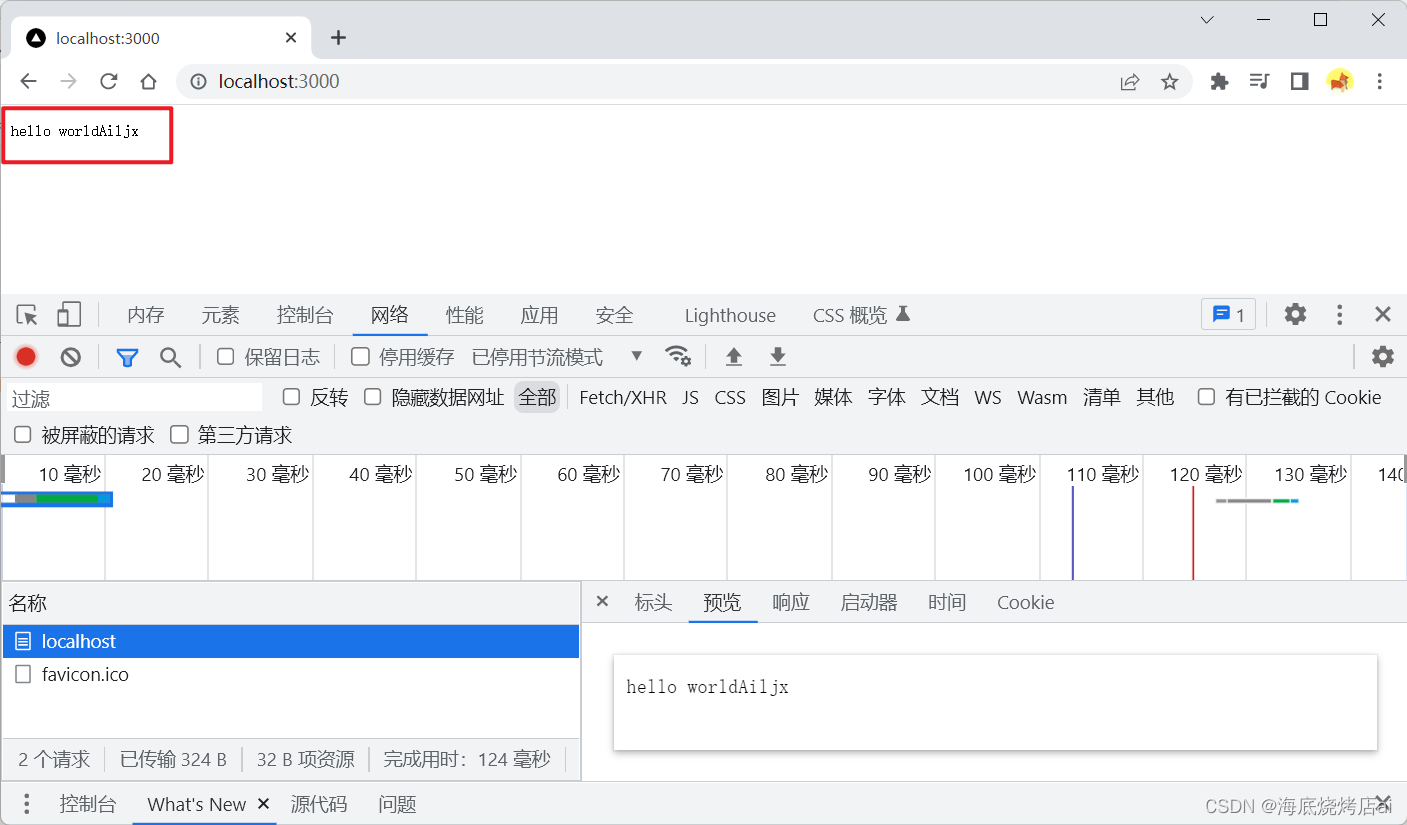
运行上述代码,我们直接在浏览器调用服务器接口:
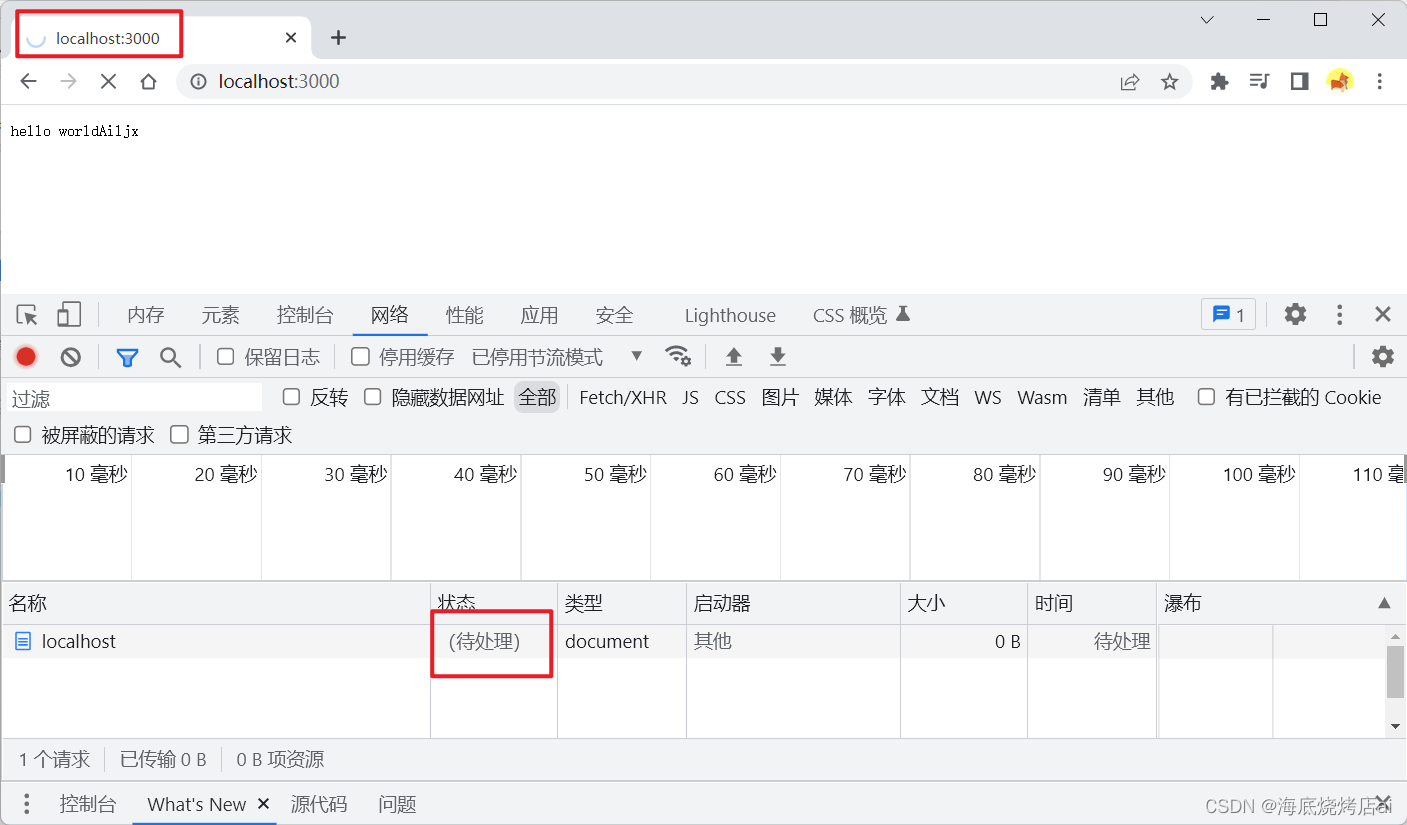
如果服务器中不调用
end
方法,浏览器会收不到服务器传递的响应结束的信号,便会一直加载请求:
返回复杂对象数据
可以传递复杂对象数据,但必须是字符串(
JSON
)的格式:
const http =require("http");// 创建服务器
http.createServer((req, res)=>{// end方法也可以传递内容,效果与write相同
res.end("{name:{me:'Ailjx'}}");// 或者res.end(JSON.stringify({ name: { me: "Ailjx" } }));}).listen(3000,()=>{
console.log("服务器启动啦!");});
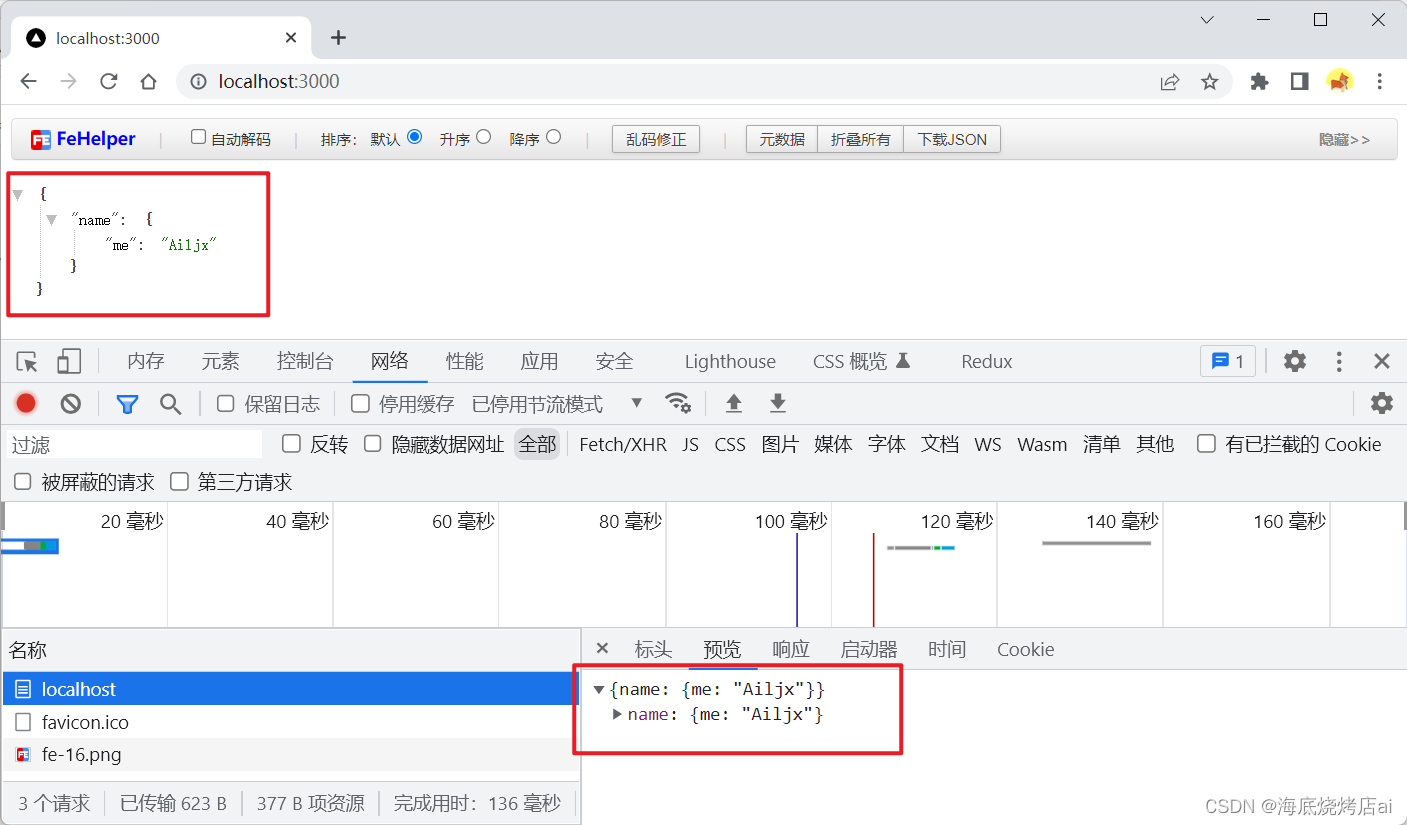
上面浏览器显示的数据被格式化了,是因为我在浏览器中安装了FeHelper(前端助手)插件,能够自动格式化JSON数据,点击查看博主推荐的浏览器插件
返回html文档数据
const http =require("http");// 创建服务器
http.createServer((req, res)=>{// 传递html内容
res.end(`
<h1>我是Ailjx,你好!</h1>
`);}).listen(3000,()=>{
console.log("服务器启动啦!");});

这时发现我们传递的中文乱码了,我们可以在响应头的
Content-Type
中指定
utf-8
的字符集来解析中文,下面会讲到
三、设置响应头和状态码
我们可以使用
response
对象的
writeHead
方法来同时设置状态码和响应头信息:
const http =require("http");// 创建服务器
http.createServer((req, res)=>{// 设置相应头,第一参数为状态码,第二个参数为响应头配置,第二个参数可不填
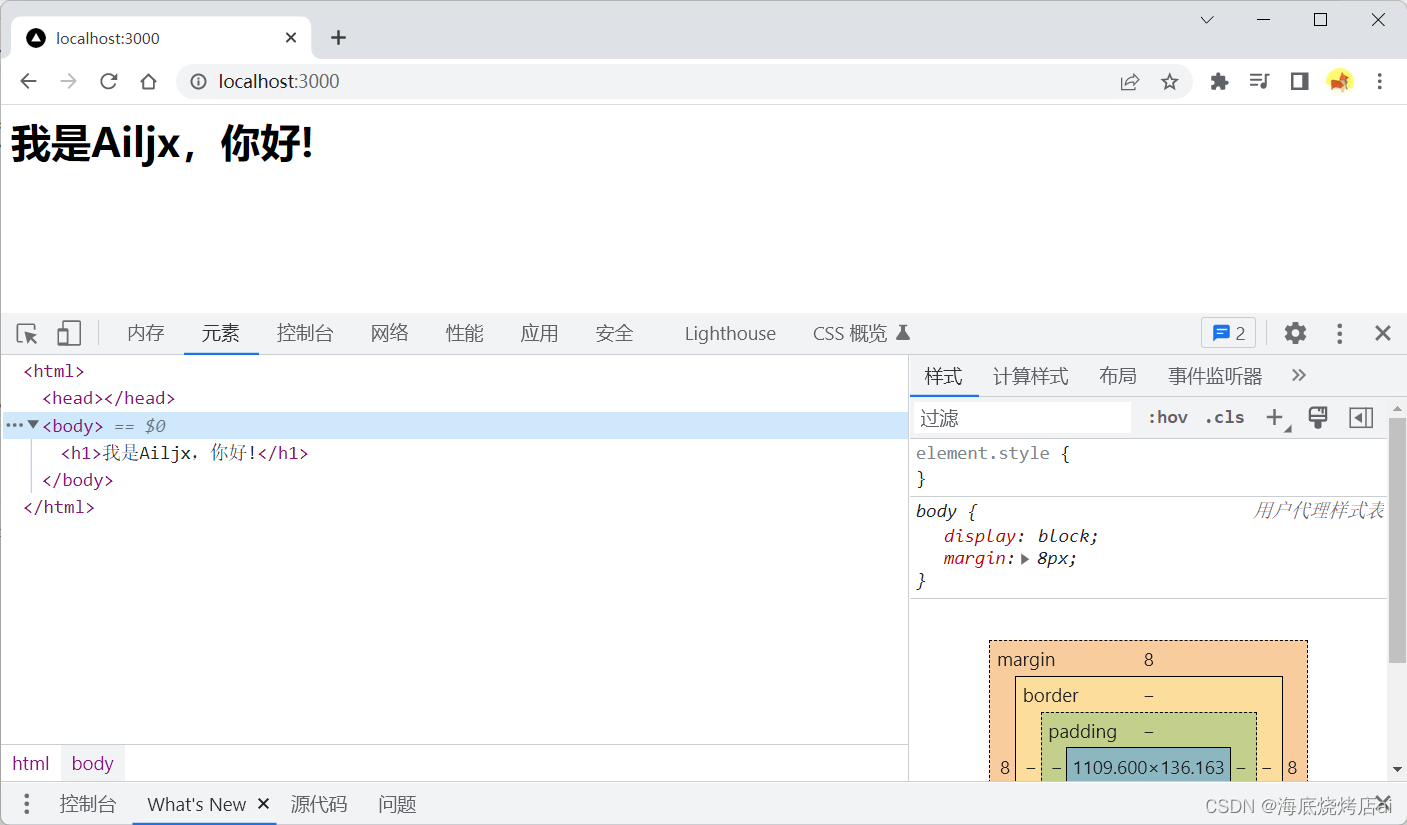
res.writeHead(200,{"Content-Type":"text/html;charset=utf-8"});// 传递html内容
res.end(`
<h1>我是Ailjx,你好!</h1>
`);// 直接在end中传递,效果与write方法相同}).listen(3000,()=>{
console.log("服务器启动啦!");});
我们也可以使用
setHeader
单独设置响应头信息,
statusCode
单独设置状态码:
const http =require("http");// 创建服务器
http.createServer((req, res)=>{// 设置相应头信息
res.setHeader("Content-Type","text/html;charset=utf-8");// 设置状态码
res.statusCode =200;// 传递html内容
res.end(`
<h1>我是Ailjx,你好!</h1>
`);// 直接在end中传递,效果与write方法相同}).listen(3000,()=>{
console.log("服务器启动啦!");});
四、实现路由接口
上面我们已经成功创建了一个服务器,并能够使用
res
参数中的
write
或
end
方法向调用者发送内容,但发送的这些内容是不会随着我们请求的路径而变化的:
const http =require("http");// 创建服务器const server = http.createServer();
server.on("request",(req, res)=>{
res.end("Ailjx");});
server.listen(3000);
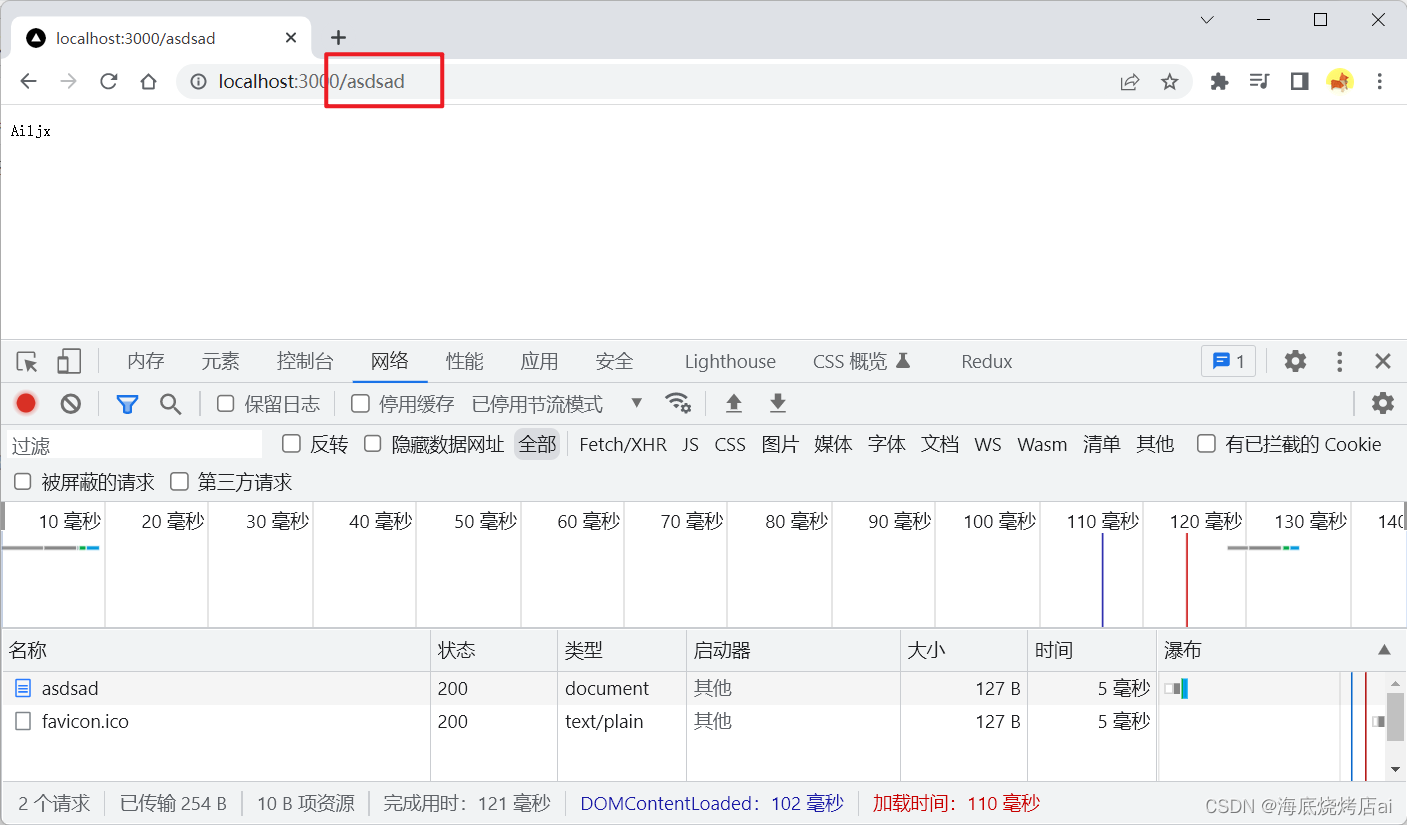
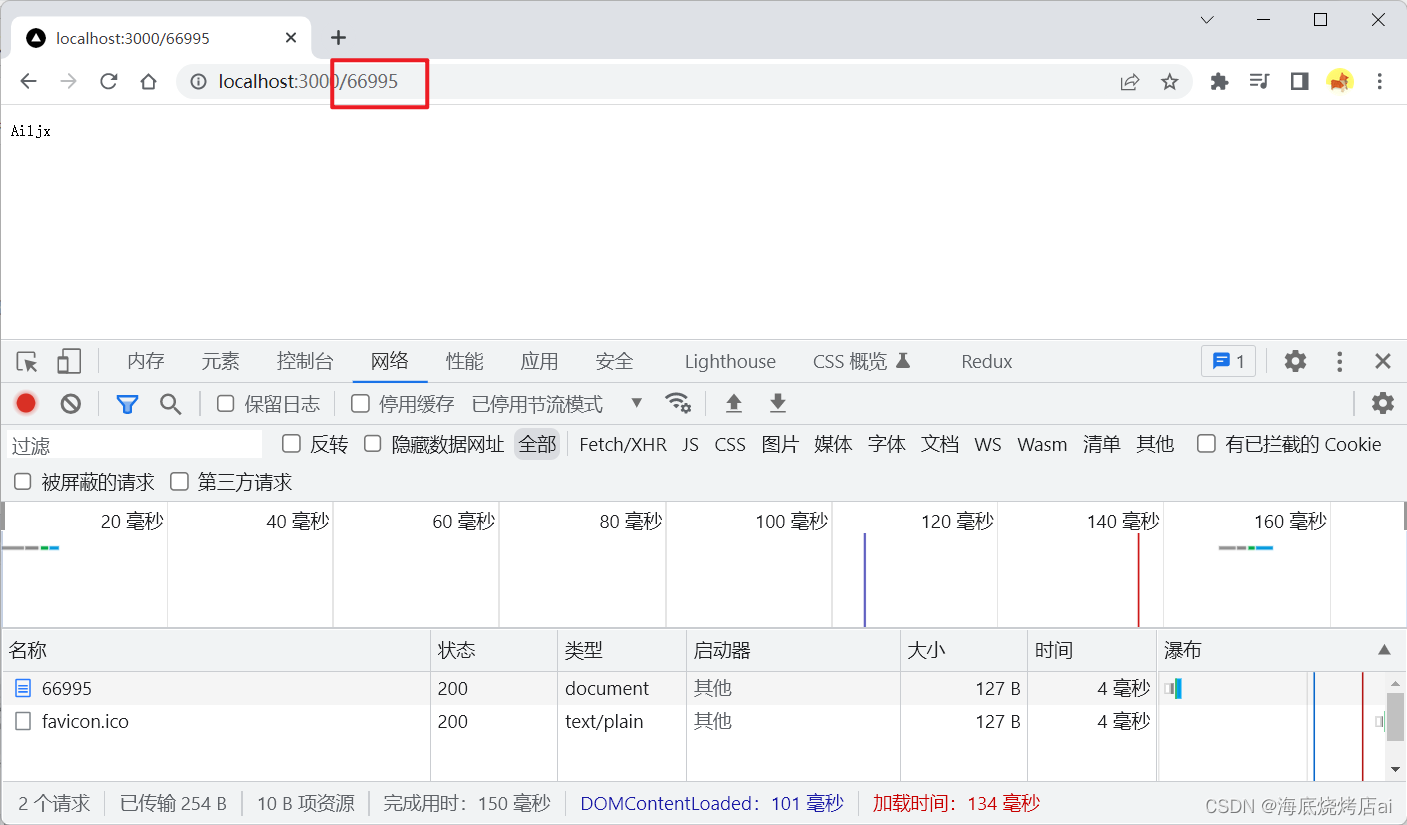
可以看到,我们请求(访问)不同路径,服务器返回的数据都是一样的,而我们在实际开发中往往是需要不同的路径有不同的数据
这时我们就可以利用我们创建服务器时定义的
req
参数(
request
对象)来获取用户请求的路径从而判断需要返回哪些数据:
const http =require("http");// 创建服务器const server = http.createServer();
server.on("request",(req, res)=>{// req.url拿到用户请求的路径
console.log(req.url);
res.end();});
server.listen(3000);
运行代码,之后在浏览器访问调用一下http://localhost:3000/list,控制台会打印出:
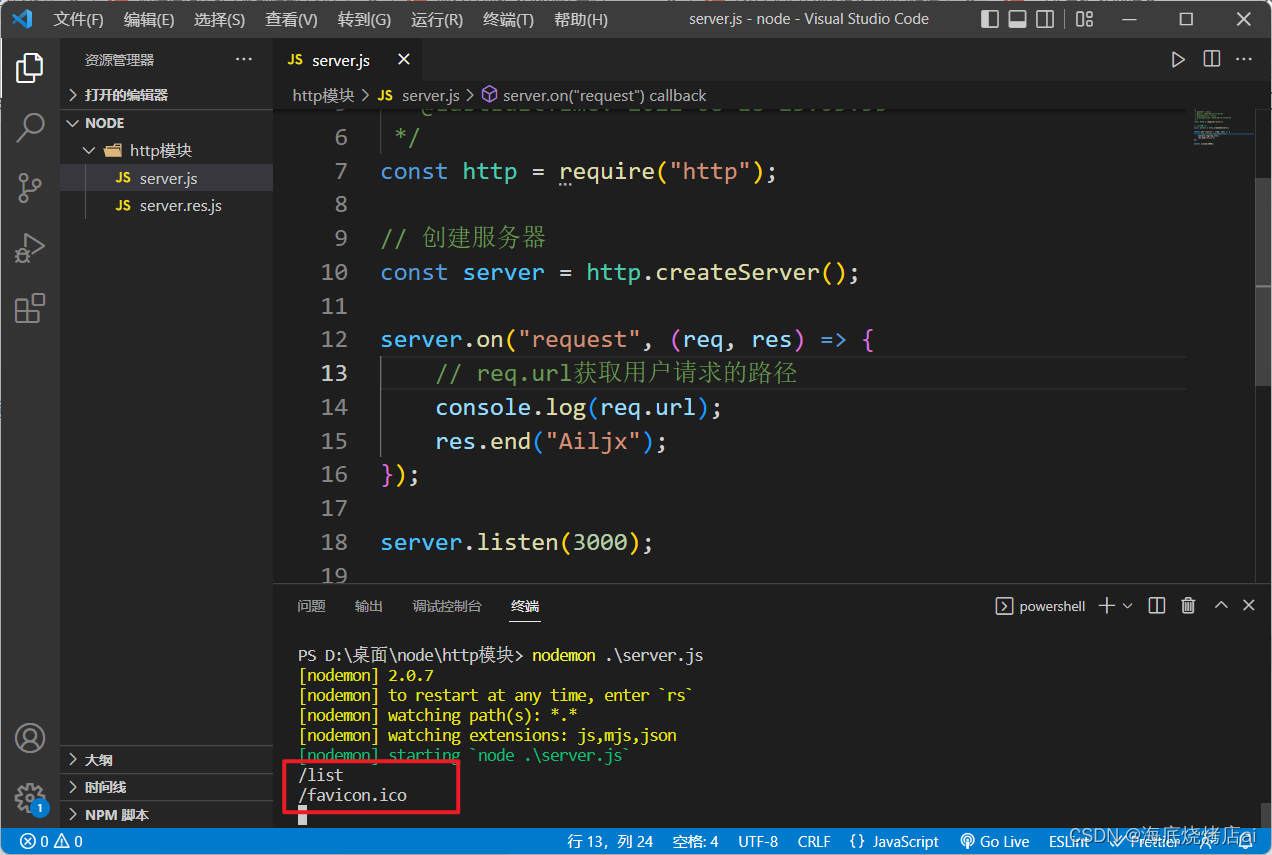
可以看到我们访问的
/list
路径确实被打印出来了,但怎么还打印了一个
/favicon.ico
呢?
这其实是浏览器在访问一个域名时会自动访问该域名下的
/favicon.ico
静态文件,来作为网页标签栏的小图标,所以我们的服务器才会打印出
/favicon.ico
如果是普通的
ajax
调用接口是不会出现这种情况的,这里我们是为了方便,直接使用浏览器访问接口来进行演示,所以才出现这种请求,我们可以简单做一下处理:
const http =require("http");// 创建服务器const server = http.createServer();
server.on("request",(req, res)=>{// req.url获取用户请求的路径if(req.url ==="/favicon.ico"){// 读取本地图标return;}
console.log(req.url);
res.end("Ailjx");});
server.listen(3000);
这样当服务器收到
/favicon.ico
请求时就能直接跳过不对其进行处理
创建简易路由应用
现在,我们开始实现一个简易的路由应用,我们先创建两个模块:
renderContent.js
用来根据用户请求路径来返回对应的内容:
functionrenderContent(url){switch(url){case"/api/home":return`
{
page:'首页'
}
`;case"/api/about":return`
{
page:'关于页'
}
`;default:return"404";}}
exports.renderContent = renderContent;
renderStatus.js
用来根据用户请求的路径来返回对应的响应状态码:
functionrenderStatus(url){const arr =["/api/home","/api/about"];return arr.includes(url)?200:404;}
module.exports ={
renderStatus,};
之后在我们的服务器文件
server.js
中调用这两个模块:
const http =require("http");const{ renderContent }=require("./module/renderContent");const{ renderStatus }=require("./module/renderStatus");// 创建服务器const server = http.createServer();
server.on("request",(req, res)=>{// req.url获取用户请求的路径if(req.url ==="/favicon.ico"){return;}// 响应头
res.writeHead(renderStatus(req.url),{// 标志返回JSON数据 "Content-Type":"application/json",});// 返回的内容
res.end(renderContent(req.url));});
server.listen(3000);
之后启动服务器,在浏览器调用接口查看效果:
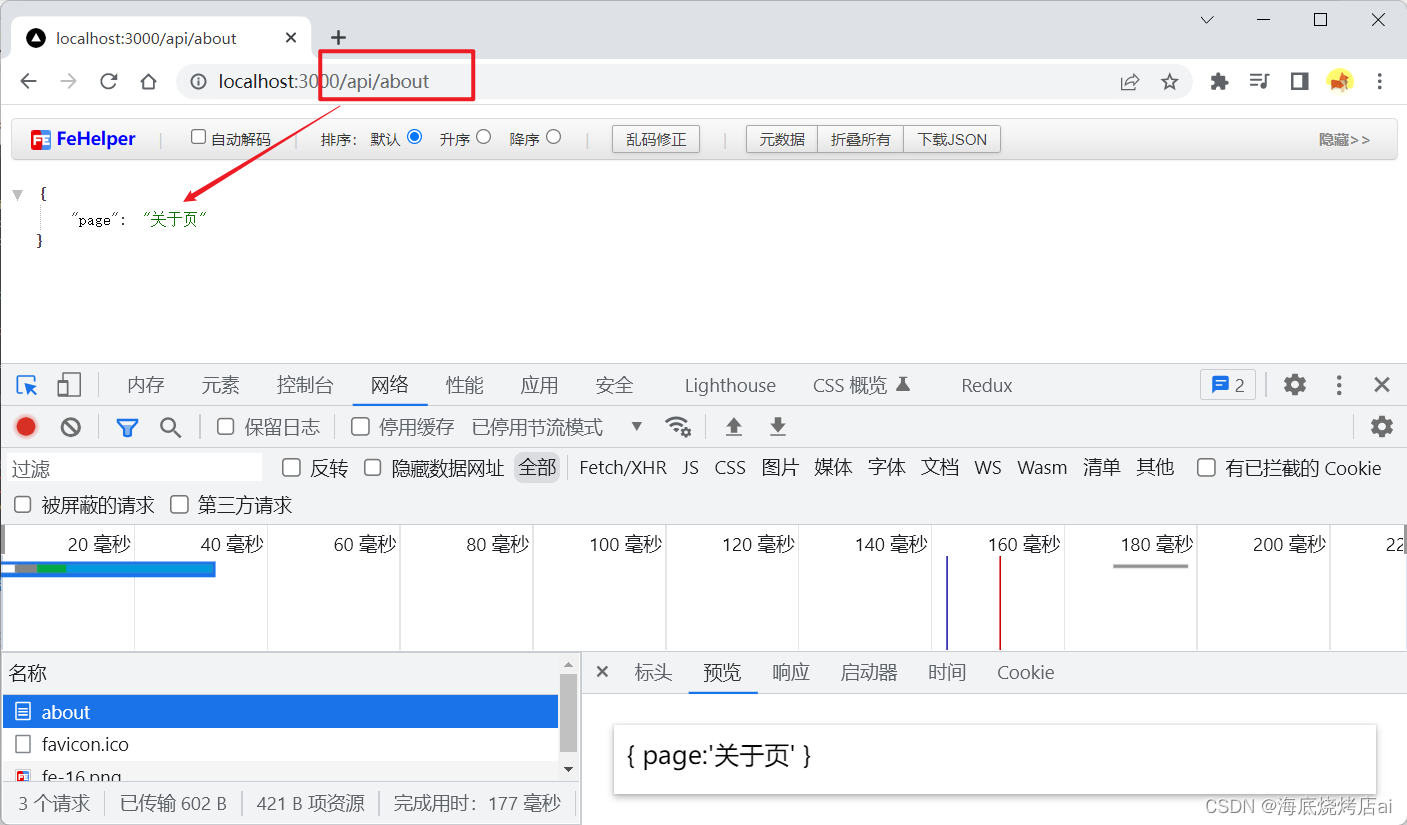
五、处理URL
在上面我们通过判断
req.url
来实现了简易的路由接口应用,但当用户调用带有url参数的接口时,这就会出现问题:
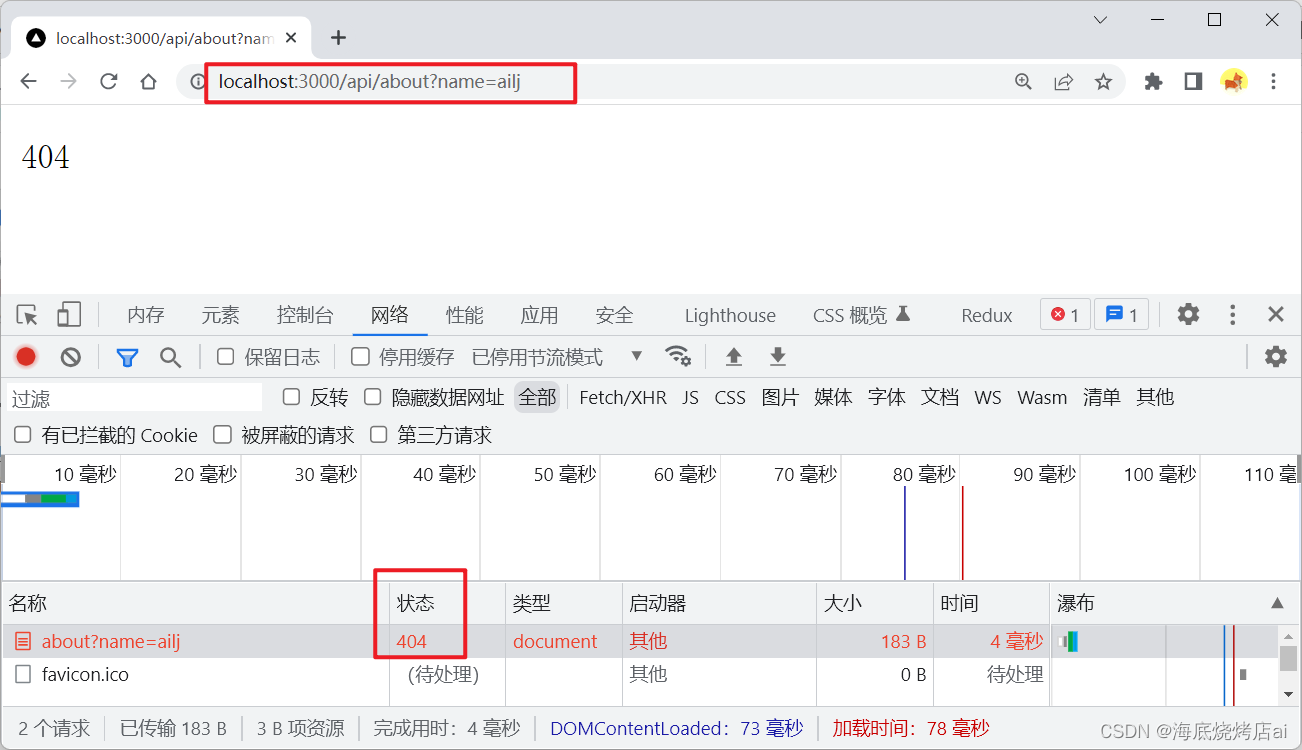
这是因为这时
req.url
为
/api/about?name=ailj
而并不是
/api/about
,我们可以手动的对这个字符串进行处理来获得正确的路由路径,也可以使用
node.js
的内置模块
url
来处理
URL格式转换
修改上面的
server.js
文件:
const http =require("http");const url =require("url");const{ renderContent }=require("./module/renderContent");const{ renderStatus }=require("./module/renderStatus");// 创建服务器const server = http.createServer();
server.on("request",(req, res)=>{// req.url获取用户请求的路径if(req.url ==="/favicon.ico"){return;}// 新版使用全局的URL构造函数// 传两个参数用法const myUrl =newURL(req.url,"http://127.0.0.1:3000").pathname;// 传一个参数用法// const myUrl = new URL("http://127.0.0.1:3000" + req.url).pathname;
console.log(newURL(req.url,"http://127.0.0.1:3000"));
res.writeHead(renderStatus(myUrl),{"Content-Type":"application/json",});
res.end(renderContent(myUrl));});
server.listen(3000,()=>{// 服务器端口号为3000
console.log("服务器启动啦!");});
全局的构造函数UR可以将完整的 **
url
地址转换成
url
对象(WHATWG URL标准的对象)**
我们可以对其传递两个参数,第一个是用户请求的路径(路由),第二个参数是地址的根域名(我们这里是本地启动的服务器,根域名为
http://127.0.0.1:3000)
也可以直接传递一个参数,该参数是带有域名的完整
url地址
当我们访问
http://localhost:3000/api/about?name=ailjx
时
server.js
会打印出:
URL{href:'http://127.0.0.1:3000/api/about?name=ailjx',origin:'http://127.0.0.1:3000',protocol:'http:',username:'',password:'',host:'127.0.0.1:3000',hostname:'127.0.0.1',port:'3000',pathname:'/api/about',search:'?name=ailjx',searchParams: URLSearchParams {'name'=>'ailjx'},hash:''}
上面
Url
对象里
searchParams
是
url
的参数部分,是一个迭代器对象(URLSearchParams对象):
// searchParams对象是一个迭代器对象const query =newURL(req.url,"http://127.0.0.1:3000").searchParams;// 使用get方法获取指定的值
console.log(query.get("name"));// ailjx
点击查看URLSearchParams对象的更多方法
我们还可以从组成部分构造
URL
并获取构造的字符串:
const myURL =newURL("https://www.baidu.com");
myURL.port ="443";
myURL.pathname ="/ad/index.html";
myURL.search ="?id=8&name=mouse";
myURL.hash ="#tag=110";// 获取构造的 URL 字符串,请使用href属性访问器
console.log(myURL.href);// https://www.baidu.com/ad/index.html?id=8&name=mouse#tag=110
或者:
const pathname ='/a/b/c';const search ='?d=e';const hash ='#fgh';const myURL =newURL(`https://example.org${pathname}${search}${hash}`);
console.log(myURL.href);
使用
url.format
方法可以自定义序列化
url
字符串,format方法接收两个参数:
new URL返回的一个WHATWG URL格式的对象- 配置对象: -
fragment:序列化的网址字符串是否包含片段,默认为true-auth:序列化的网址字符串是否包含用户名和密码,默认为true-unicode:是否将出现在URL字符串的主机组件中的Unicode字符直接编码而不是Punycode编码,默认是false-search:序列化的网址字符串是否包含搜索查询(参数),默认为true
const myURL =newURL("https://username:password@URL路径序列化测试?name=ailjx#foo");
console.log(
url.format(myURL,{fragment:false,// 不显示片段(#foo)unicode:true,// 不转化Unicode字符(中文字符)auth:false,// 不包含用户名和密码(username:password)search:false,// 不显示参数(?name=ailjx)}));// 打印结果: 'https://url路径序列化测试/'
- 旧版Node使用parse和format处理URL:> 注意:旧版的>
> parse>> 方法官方表示已弃用,>> format>> 方法在新版中使用方式有所更改const http =require("http");const url =require("url");const{ renderContent }=require("./module/renderContent");const{ renderStatus }=require("./module/renderStatus");// 创建服务器const server = http.createServer();server.on("request",(req, res)=>{// req.url获取用户请求的路径if(req.url ==="/favicon.ico"){return;} console.log(url.parse(req.url));const myUrl = url.parse(req.url).pathname; res.writeHead(renderStatus(myUrl),{"Content-Type":"application/json",}); res.end(renderContent(myUrl));});server.listen(3000,()=>{// 服务器端口号为3000 console.log("服务器启动啦!");});``````url模块的parse方法可以将完整的url地址转换成url对象,如当我们访问http://localhost:3000/api/about?name=ailjx时server.js会打印出:Url {protocol:null,slashes:null,auth:null,host:null,port:null,hostname:null,hash:null,search:'?name=ailjx',query:'name=ailjx',pathname:'/api/about',path:'/api/about?name=ailjx',href:'/api/about?name=ailjx'}上面Url对象里query是url的参数部分,默认是字符串的格式,可以给parse方法传递第二个参数,将其转换成对象格式:url.parse(req.url,true)``````Url {protocol:null,slashes:null,auth:null,host:null,port:null,hostname:null,hash:null,search:'?name=ailjx',query:[Object:null prototype]{name:'ailjx'},pathname:'/api/about',path:'/api/about?name=ailjx',href:'/api/about?name=ailjx'}这时通过url.parse(req.url, true).query.name就可以拿到ailjx这个参数与parse方法相反的有一个format方法,它能将一个url对象转换成url地址 :const url =require("url");const urlObject ={protocol:"https:",slashes:true,auth:null,host:"www.baidu.com:443",port:"443",hostname:"www.baidu.com",hash:"#tag=110",search:"?id=8&name=mouse",query:{id:"8",name:"mouse"},pathname:"/ad/index.html",path:"/ad/index.html?id=8&name=mouse",};const parsedObj = url.format(urlObject);console.log(parsedObj);// https://www.baidu.com:443/ad/index.html?id=8&name=mouse#tag=110
URL路径拼接
URL
构造函数,传递两个字符串路径时能够实现路径的拼接:
let myURL =newURL('http://Example.com/','https://example.org/');// http://example.com/
myURL =newURL('https://Example.com/','https://example.org/');// https://example.com/
myURL =newURL('foo://Example.com/','https://example.org/');// foo://Example.com/
myURL =newURL('http:Example.com/','https://example.org/');// http://example.com/
myURL =newURL('https:Example.com/','https://example.org/');// https://example.org/Example.com/
myURL =newURL('foo:Example.com/','https://example.org/');// foo:Example.com/
- 旧版Node使用resolve方法拼接路径:> 注意:旧版node的>
> resolve>> 方法官方表示已弃用const url =require('url')var a = url.resolve("/one/two/three","four");// /one/two/four// var a = url.resolve("/one/two/three/", "four"); // /one/two/three/four// var a = url.resolve("/one/two/three", "/four"); // /four// var a = url.resolve("/one/two/three/", "/four"); // /fourvar b = url.resolve("http://example.com/","/one");// var b = url.resolve("http://example.com/", "one");// var b = url.resolve("http://example.com", "one");// var b = url.resolve("http://example.com", "/one");// 以上b的结果都是:http://example.com/onevar c = url.resolve("http://example.com/one","two");// var c = url.resolve("http://example.com/one", "/two");// var c = url.resolve("http://example.com/one/", "/two");// var c = url.resolve("http://example.com/one/a/b", "/two");// 以上c的结果都是:http://example.com/twovar d = url.resolve("http://example.com/one/","two");// http://example.com/one/twovar e = url.resolve("http://example.com/one/aaa","http://example.com/one/two");// var e = url.resolve("/one/aaa", "http://example.com/one/two");// 以上e的结果都是:http://example.com/one/two``````resolve方法并不是简单的将两个路径直接拼接在一起,而是具有它自己的一些拼接规则:- 如果第二个路径(接收的第二个参数)开头前带/,则将直接用第二个路径替代第一个路径的路由部分(不会替代第一个路径的根域名,如上面的最后一个变量c所示:/two替代了/one/a/b)- 如果第二个路径开头前不带/,第一个路径结尾处不带/,则第二个路径将会替代第一个路径的最后一个路由,如上边的第一个变量a和第一个变量c- 如果第二个路径开头前不带/,第一个路径结尾处带/,则直接将第二个路径拼接在第一个路径后面,如上边的第变量d和第二个变量a- 如果第二个路径包含根域名(http://xxx),则直接以第二个路径为主(第一个路径失效)
处理URL路径参数
注意:
querystring方法官方表示已弃用
NodeJS
有一个内置模块
querystring
,它里面的
parse
和
stringify
方法可以帮助我们快速处理
URL
上的形如
id=8&name=mouse
的参数:
const querystring =require("querystring");var qs ="id=8&name=Ailjx";// parse:路径将参数转化为对象var parsed = querystring.parse(qs);
console.log(parsed.id, parsed.name);// 8 Ailjxvar qo ={x:3,y:4,};//stringify:将对象转化为路径参数var parsed = querystring.stringify(qo);
console.log(parsed);// x=3&y=4
querystring
中还有一对能够转义特殊字符的方法:
escape
/
unescape
:
const querystring =require("querystring");var str ='ns"--';// escape:将特殊字符转义var escaped = querystring.escape(str);
console.log(escaped);//ns%22--// unescape:恢复转义的特殊字符
console.log(querystring.unescape(escaped));// ns"--
对于特殊字符的转义在一些特殊情况下特别重要,例如我们通过用户传递的参数来向
mysql
数据库查询数据,我们为了防止用户传递的参数与
sql
语句发送冲突,就可以对该参数进行转义,以防止
sql
注入
例如有一条含有用户传递的
param
参数的
sql
语句:
let sql =`select * from users where name = "${param}" and del_status=1`
上面的
sql
语句在正常情况下是只能查询到一条数据,如:
// let param = 'Ailjx' ,对应的sql语句如下:select*from users where name ="Ailjx"and del_status=1
但当
param
与
sql
语句冲突时:
// let param = 'ns"--',对应的sql语句如下:select*from tb_nature where nature ="ns"-- " and del_status=1
可以看到
del_status
被参数中的
--
注释掉了,失去了作用,这时这条
sql
能查询到多条数据,这就是
sql
注入的危害,也就是我们需要转义特殊字符的原因
正确转换文件路径
url
模块针对转换文件路径提供了单独的
fileURLToPath
和
pathToFileURL
方法,它们不仅能正确进行文件路径的转换而且能自动适配不同的操作系统
fileURLToPath
该方法能够正确将文件网址
url
转换成文件路径:
const{ fileURLToPath }=require("url");
console.log(newURL("file:///C:/path/").pathname);// 获得错误路径:/C:/path/
console.log(fileURLToPath("file:///C:/path/"));// 获得正确路径:C:\path\ (Windows)
console.log(newURL("file://nas/foo.txt").pathname);// 获得错误路径:/foo.txt
console.log(fileURLToPath("file://nas/foo.txt"));// 获得正确路径: \\nas\foo.txt (Windows)
console.log(newURL("file://c://你好.txt").pathname);// 获得错误路径:/c://%E4%BD%A0%E5%A5%BD.txt
console.log(fileURLToPath("file://c://你好.txt"));// 获得正确路径: c:\\你好.txt (Windows)
pathToFileURL
方法,能够将文件路径转换成文件网址
url
对象:
const{ pathToFileURL }=require("url");
console.log(newURL("/foo#1","file:").href);// 错误: file:///foo#1
console.log(pathToFileURL("/foo#1").href);// 正确: file:///D:/foo%231
console.log(newURL("/some/path%.c","file:").href);// 错误: file:///some/path%.c
console.log(pathToFileURL("/some/path%.c").href);// 正确: file:///D:/some/path%25.c
转换为Options Url对象
urlToHttpOptions
方法可以将
new URL
返回的
WHATWG URL
对象转换成
http.request()
或
https.request()
需要的
Options Url
对象
http.request()和
https.request()在下面会讲到
const{ urlToHttpOptions }=require("url");const myURL =newURL('https://a:b@測試?abc#foo');
console.log(urlToHttpOptions(myURL));/*
{
protocol: 'https:',
hostname: 'xn--g6w251d',
hash: '#foo',
search: '?abc',
pathname: '/',
path: '/?abc',
href: 'https://a:b@xn--g6w251d/?abc#foo',
auth: 'a:b'
}
*/
六、跨域处理
在不做处理的情况下,前后端交互会出现
CORS
跨域的问题,如:
定义一个简单的服务器:
server.js
const http =require("http");const url =require("url");const server = http.createServer();
server.on("request",(req, res)=>{const urlObj = url.parse(req.url,true);switch(urlObj.pathname){case"/api/user":// 模拟数据const userinfo ={name:"Ailjx",};
res.end(JSON.stringify(userinfo));break;default:
res.end("404");break;}});
server.listen(3000,()=>{
console.log("服务器启动啦!");});
可以看到上面我们定义的服务器并没有设置跨域,我们直接在
html
文件内请求该服务器的接口:
index.html
<body><div>jsonp接口测试</div><script>fetch('http://localhost:3000/api/user').then(res=> res.json()).then(res=> console.log(res))</script></body>
打开该
html
文件,可以看到果然出现了
CORS
跨域的报错
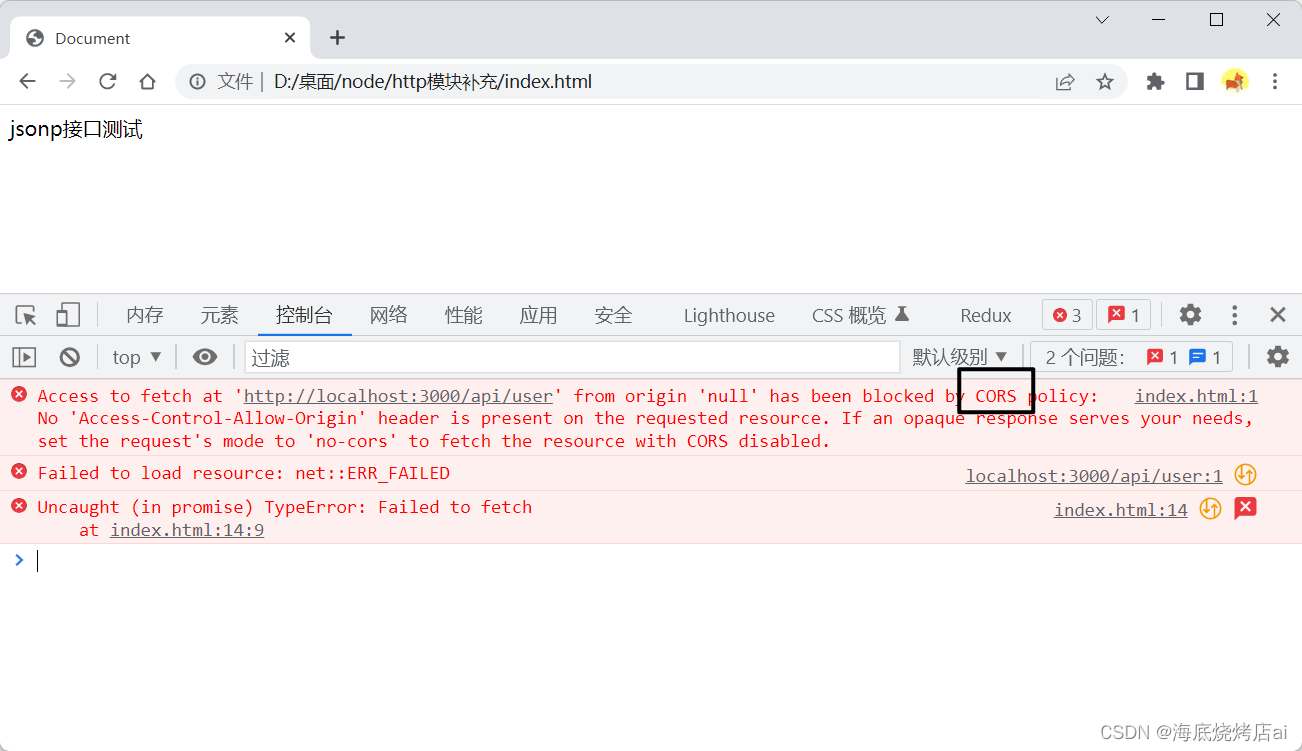
这种问题有多种解决方案:
- 后端设置响应头来允许前端访问服务器(只需要后端进行修改)
- 前后端使用
jsonp方式进行交互(前后端都需要进行相应修改) - 前端配置代理(只需要前端进行修改,这在像
vue,react等这些框架中经常使用)
后端设置跨域
后端可以直接在响应头里设置跨域,而前端不需要做额外的操作
我们下载一个
vscode
的
Live Server
插件,用于在线运行
html
文件:
右键
html
文件选择
Open with Live Server
:
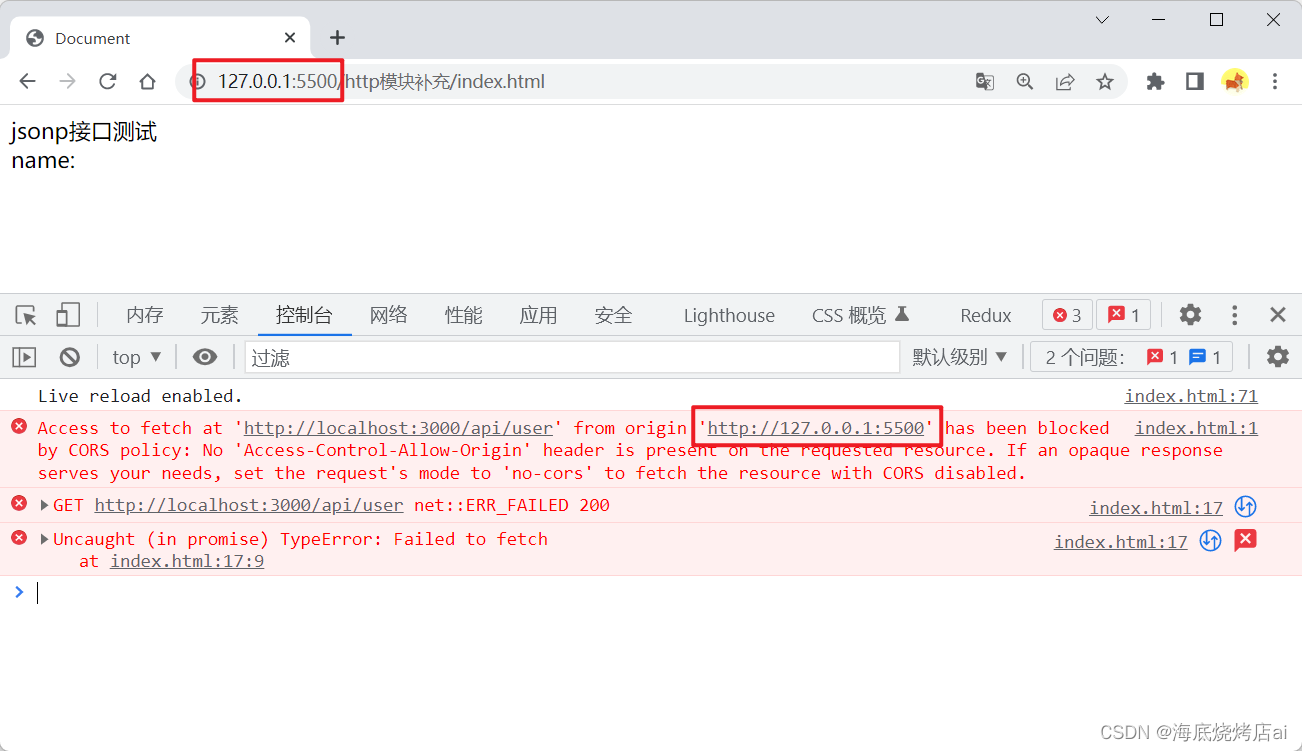
打开后发现前端
html
的在线运行地址为
http://127.0.0.1:5500
,我们在后端返回数据的响应头里允许该地址访问即可:
修改一下上边的
server.js
const http =require("http");const url =require("url");const server = http.createServer();
server.on("request",(req, res)=>{const urlObj = url.parse(req.url,true);
res.writeHead(200,{"content-type":"application/json;charset=utf-8",// 设置跨域允许http://127.0.0.1:5500访问"Access-Control-Allow-Origin":"http://127.0.0.1:5500",// "Access-Control-Allow-Origin": "*", 也可以使用'*',代表允许所有地址访问});switch(urlObj.pathname){case"/api/user":// 模拟数据const userinfo ={name:"Ailjx",};
res.end(JSON.stringify(userinfo));break;default:
res.end("404");break;}});
server.listen(3000,()=>{
console.log("服务器启动啦!");});
这时前端就能正常调用该接口了:
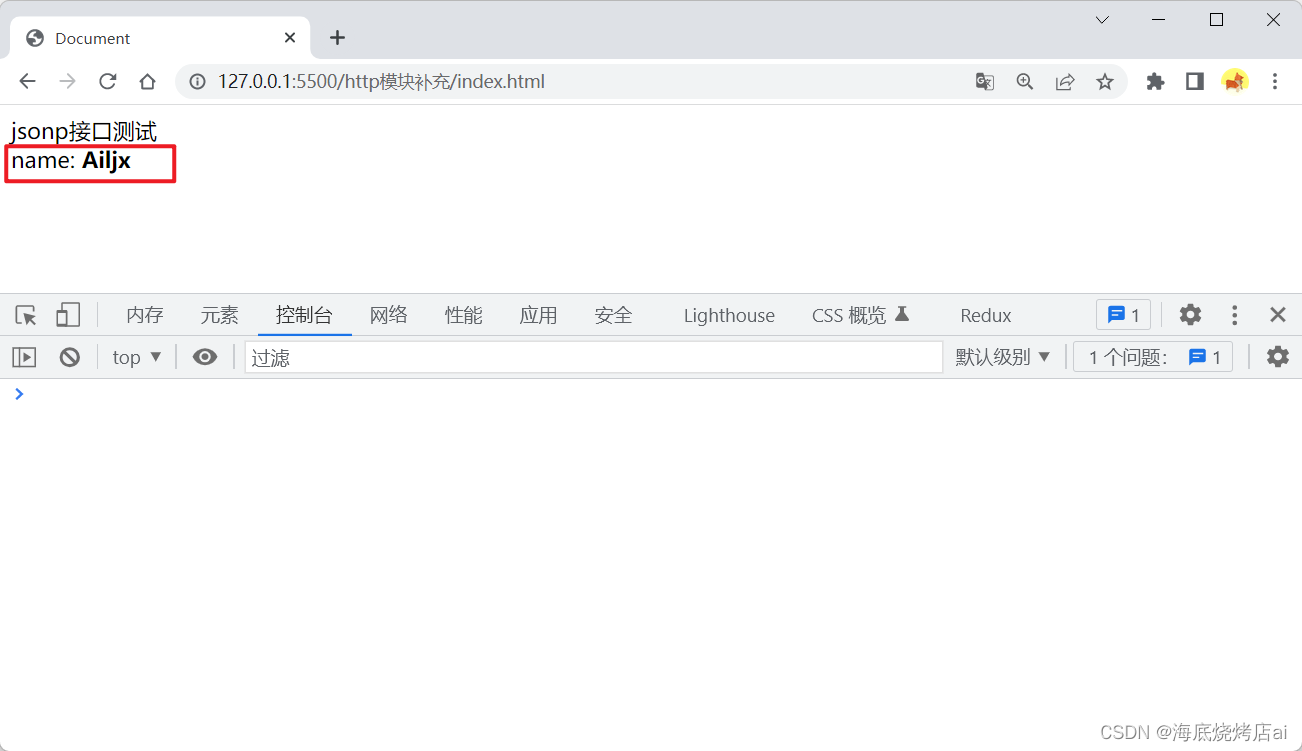
jsonp接口
我们知道
html
的
script
标签可以引入
js
文件,并且重要的是使用
script
标签引入
js
没有跨域的要求,所以我们可以在
script
标签的
src
属性中调用我们的接口来获取后端返回的数据
前端处理:
<body><div>jsonp接口测试</div><div>name:<b id="myName"></b></div><script>// 定义一个接收后端返回数据的函数functiongetUser(params){const myName = document.getElementById('myName')// 可以做一些操作
myName.innerText = params.name
}// 创建一个script标签const myScript = document.createElement('script')// script标签的src内调用接口,需要将我们定义的接收数据的函数名传递给后端
myScript.src ='http://localhost:3000/api/user?cb=getUser'// 向文档内插入该script标签
document.body.appendChild(myScript)</script></body>
或者直接用
script
调用后端接口:
<body><div>jsonp接口测试</div><div>
name: <bid="myName"></b></div><script>// // 定义一个接收后端返回数据的函数functiongetUser(params){const myName = document.getElementById('myName')
myName.innerText = params.name
}</script><!-- 调用后端接口 --><scriptsrc="http://localhost:3000/api/user?cb=getUser"></script></body>
后端处理:
const http =require("http");const url =require("url");const server = http.createServer();
server.on("request",(req, res)=>{const urlObj = url.parse(req.url,true);switch(urlObj.pathname){case"/api/user":// 模拟数据const userinfo ={name:"Ailjx",};// urlObj.query.cb是前端传递的接收数据的函数名称// 返回给前端一个函数调用
res.end(`${urlObj.query.cb}(${JSON.stringify(userinfo)})`);break;default:
res.end("404");break;}});
server.listen(3000,()=>{
console.log("服务器启动啦!");});
可以看到使用
jsonp
的原理就是在
script
标签中调用后端接口,因为
script
标签内的
js
代码是立即执行的
所以我们需要提前定义一个接收后端参数的处理函数,然后将该函数名传递给后端,后端根据这个函数名返回给前端一个该函数的调用并将需要给前端的数据作为该函数的参数
上述代码的最终效果如下:
<script>// 定义一个接收后端返回数据的函数functiongetUser(params){const myName = document.getElementById('myName')
myName.innerText = params.name
}</script><!-- <script src="http://localhost:3000/api/user?cb=getUser"></script>的效果如下 --><script>getUser({name:"Ailjx",})</script>
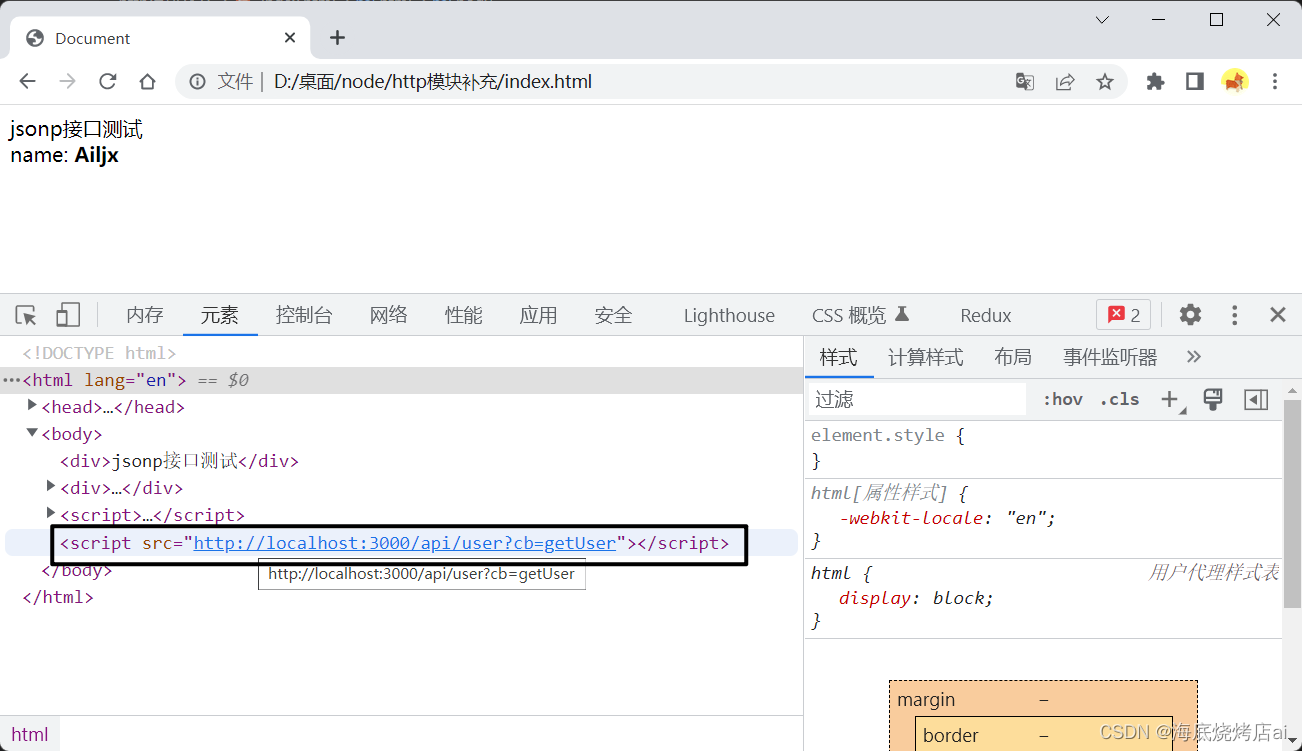
七、Node作为中间层使用
上面我们使用
node
搭建了后端服务器,使其作为服务端运行,但其实
node
还能当作客户端反过来去调用其它服务端的接口,这使得
node
成为了一个中间层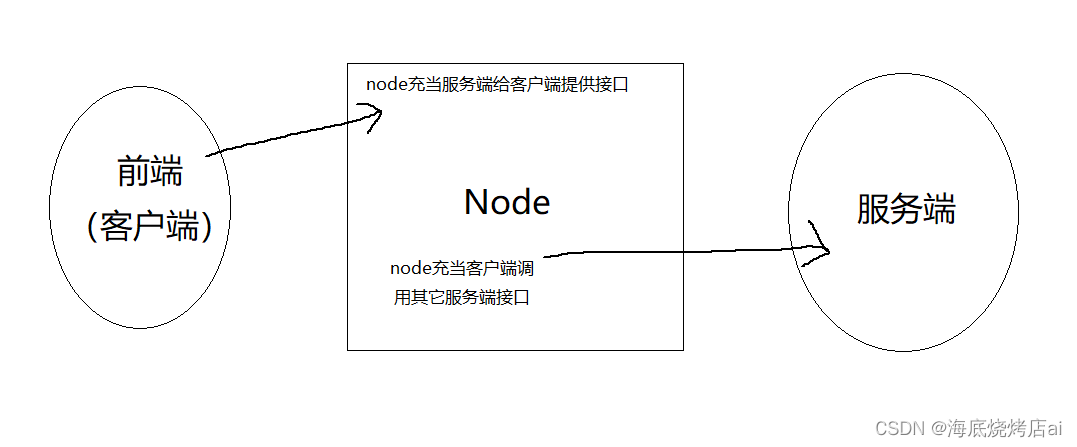
因为跨域只是浏览器的限制,服务端之间的通信并不存在跨域的问题,这样我们就能借助
node
去调用第三方具有跨域限制的接口,这是**将
node
作为中间层的一个非常实用的功能**
模拟get请求(转发跨域数据)
在猫眼电影网上随便找了一个带有跨域的接口,我们直接调用时会报
CORS
跨域问题:
<h1>使用node模拟get请求</h1><script>fetch('https://i.maoyan.com/api/mmdb/movie/v3/list/hot.json?ct=%E8%A5%BF%E5%8D%8E&ci=936&channelId=4').then(res=> res.json()).then(res=>{
console.log(res);})</script>
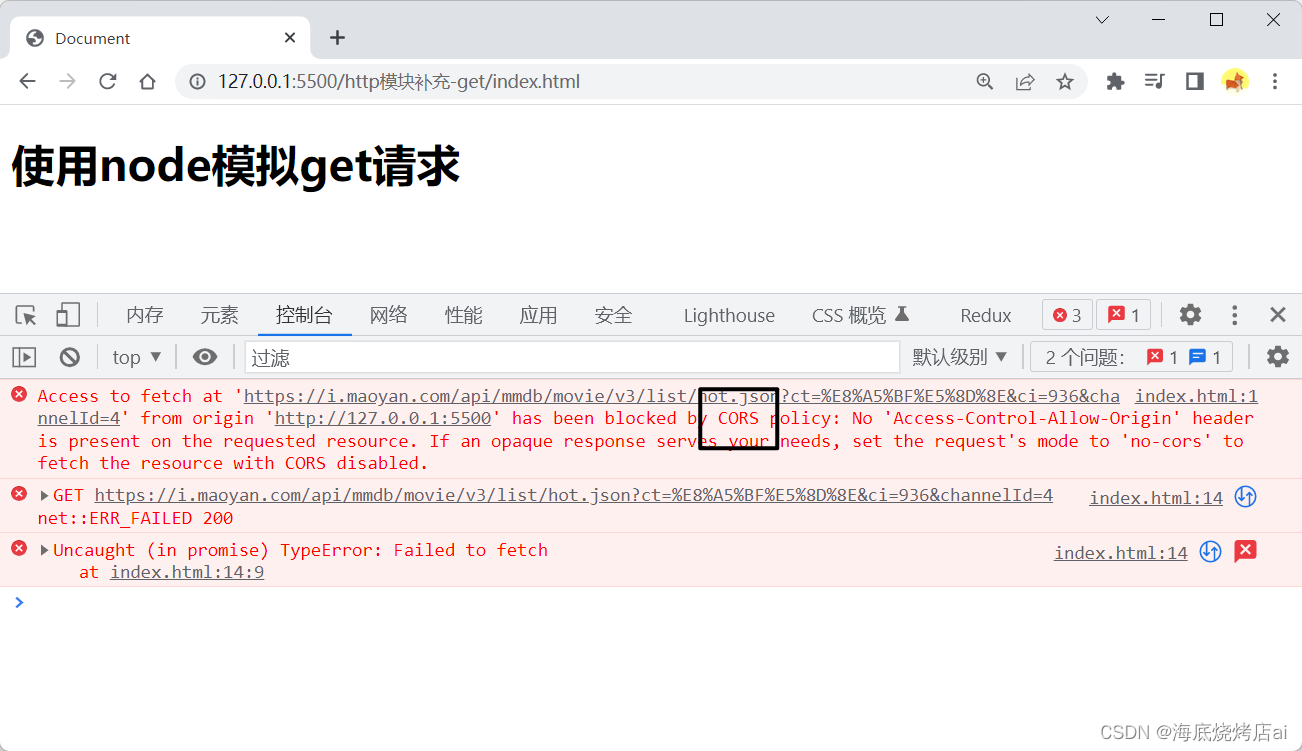
这时我们可以利用
node
帮我们去请求这个接口的数据:
const http =require("http");const https =require("https");// http和https的区别仅在于一个是http协议一个是https协议const url =require("url");const server = http.createServer();
server.on("request",(req, res)=>{const urlObj = url.parse(req.url,true);
res.writeHead(200,{"content-type":"application/json;charset=utf-8","Access-Control-Allow-Origin":"http://127.0.0.1:5500",});switch(urlObj.pathname){case"/api/maoyan":// 我们定义的httpget方法:使node充当客户端去猫眼的接口获取数据httpget((data)=> res.end(data));break;default:
res.end("404");break;}});
server.listen(3000,()=>{
console.log("服务器启动啦!");});functionhttpget(cb){// 定义一个存放数据的变量let data ="";// 因为猫眼的接口是https协议的,所以我们需要引入https// http和https都具有一个get方法能够发起get请求,区别是一个是http协议,一个是https协议// http get方法第一个参数为接口地址,第二个参数为回调函数
https.get("https://i.maoyan.com/api/mmdb/movie/v3/list/hot.json?ct=%E8%A5%BF%E5%8D%8E&ci=936&channelId=4",(res)=>{// http get方法获取的数据是一点点返回的,并不是直接返回全部// 监听data,当有数据返回时就会被调用
res.on("data",(chunk)=>{// 收集数据
data += chunk;});// 监听end,数据返回完毕后调用
res.on("end",()=>{cb(data);});});}
之后我们调用我们
node
的接口即可:
<h1>使用node模拟get请求</h1><script>fetch('http://localhost:3000/api/maoyan').then(res=> res.json()).then(res=>{
console.log(res);})</script>
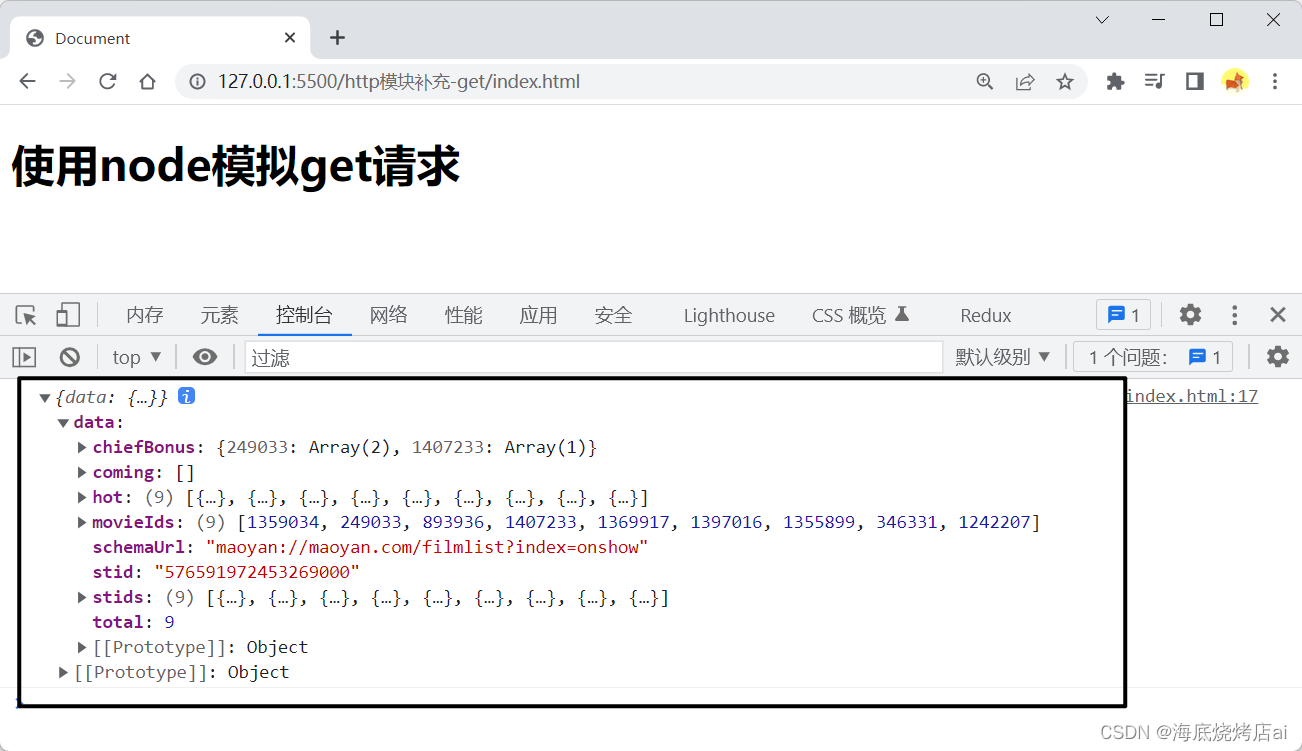
这里
node
即作为服务端给我们提供接口
/api/maoyan
,又充当了一下客户端去调用猫眼的接口,这样我们就绕过了猫眼的跨域限制获取了它的数据
模拟post请求(服务器提交)
使用
node
模拟
post
请求需要使用
http
或
https
的
request
方法来进行请求的配置,稍微有点麻烦:
http和
https模块的区别仅在于一个是
http协议一个是
https协议
const http =require("http");const https =require("https");const url =require("url");const server = http.createServer();
server.on("request",(req, res)=>{const urlObj = url.parse(req.url,true);
res.writeHead(200,{"content-type":"application/json;charset=utf-8","Access-Control-Allow-Origin":"http://127.0.0.1:5500",});switch(urlObj.pathname){case"/api/xiaomiyoumin":// httpPost方法:使node充当客户端去小米有品的post接口获取数据httpPost((data)=> res.end(data));break;default:
res.end("404");break;}});
server.listen(3000,()=>{
console.log("服务器启动啦!");});functionhttpPost(cb){// 定义一个存放数据的变量let data ="";// 这是小米有品的一个post接口:"https://m.xiaomiyoupin.com/mtop/market/search/placeHolder"// 这个接口调用时需要传“[{}, { baseParam: { ypClient: 1 } }]”这样一个参数才能返回数据// 配置Options Url请求对象const options ={// 域名hostname:"m.xiaomiyoupin.com",// 接口端口号,443代表https,80代表httpport:"443",// 路径path:"/mtop/market/search/placeHolder",// 请求方式method:"POST",// 请求头Headers:{// 表示接收json数据"Content-Type":"application/json",},};// http request方法第一个参数为请求对象,第二个参数为回调函数,request方法返回一个值(),在该值内通过调用write向post请求传递数据const req = https.request(options,(res)=>{// 监听data,当有数据返回时就会被调用
res.on("data",(chunk)=>{// 收集数据
data += chunk;});// 监听end,数据返回完毕后调用
res.on("end",()=>{cb(data);});});// 发送post的参数// req.write(JSON.stringify([{}, { baseParam: { ypClient: 1 } }]));// 这里的使用与我们server服务器中的req参数使用方式差不多,不要忘记最后调用end方法,并且也可以直接在end方法内传递数据
req.end(JSON.stringify([{},{baseParam:{ypClient:1}}]));}
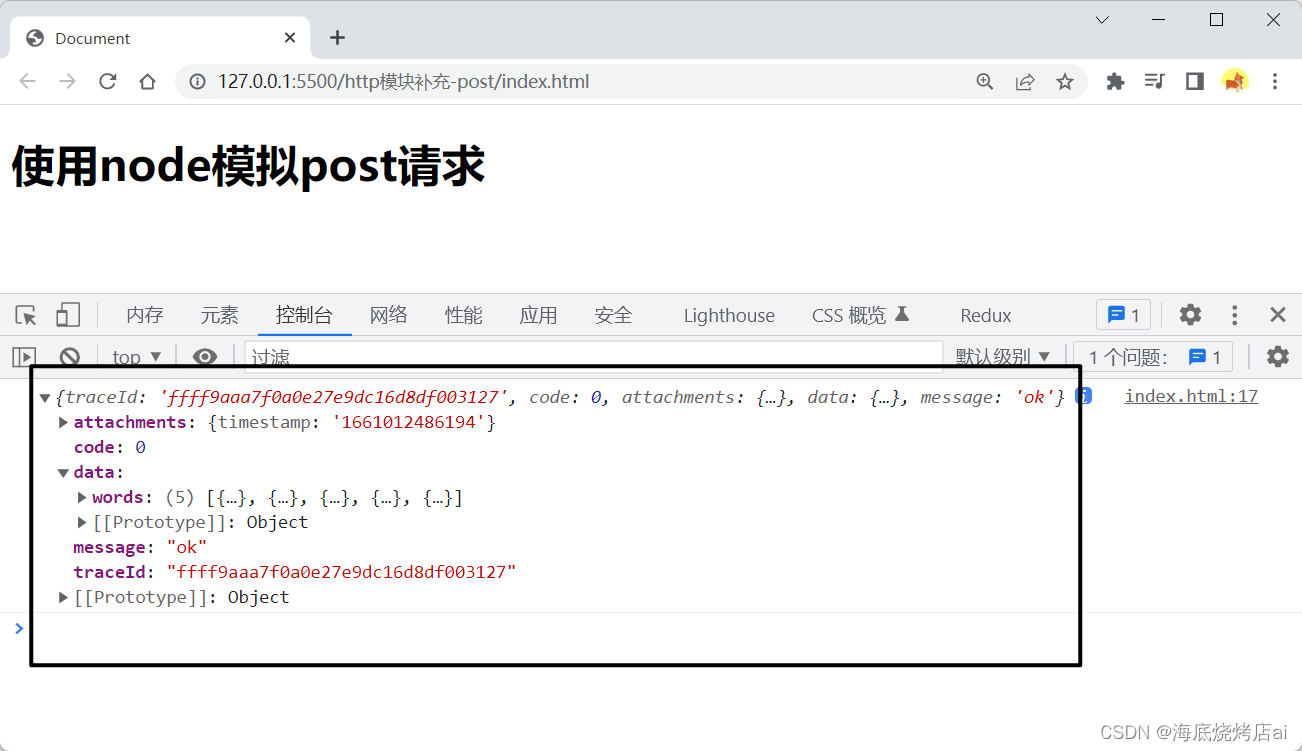
<body><h1>使用node模拟post请求</h1><script>fetch('http://localhost:3000/api/xiaomiyoumin').then(res=> res.json()).then(res=>{
console.log(res);})</script></body>
八、使用Node实现爬虫
我们使用
node
的一个
cheerio
包也可以实现爬虫功能,如我们爬取猫眼移动端
https://i.maoyan.com
首页的一些数据:
我们在一个文件夹内打开终端,先生成
package.json
文件:
npm init
安装
cheerio
:
npm i cheerio
文件夹内创建我们的服务器文件
server.js
:
const https =require("https");const http =require("http");const cheerio =require("cheerio");
http.createServer((request, response)=>{
response.writeHead(200,{"content-type":"application/json;charset=utf-8",});const options ={hostname:"i.maoyan.com",port:443,path:"/",method:"GET",};// 获取页面数据const req = https.request(options,(res)=>{let data ="";
res.on("data",(chunk)=>{
data += chunk;});
res.on("end",()=>{
response.end(data);});});
req.end();}).listen(3000);
上面演示了使用
https.request方法配置
get请求(接口为:https://i.maoyan.com)的写法,你也可以直接使用
https.get进行调用
通过浏览器调用我们的服务器:
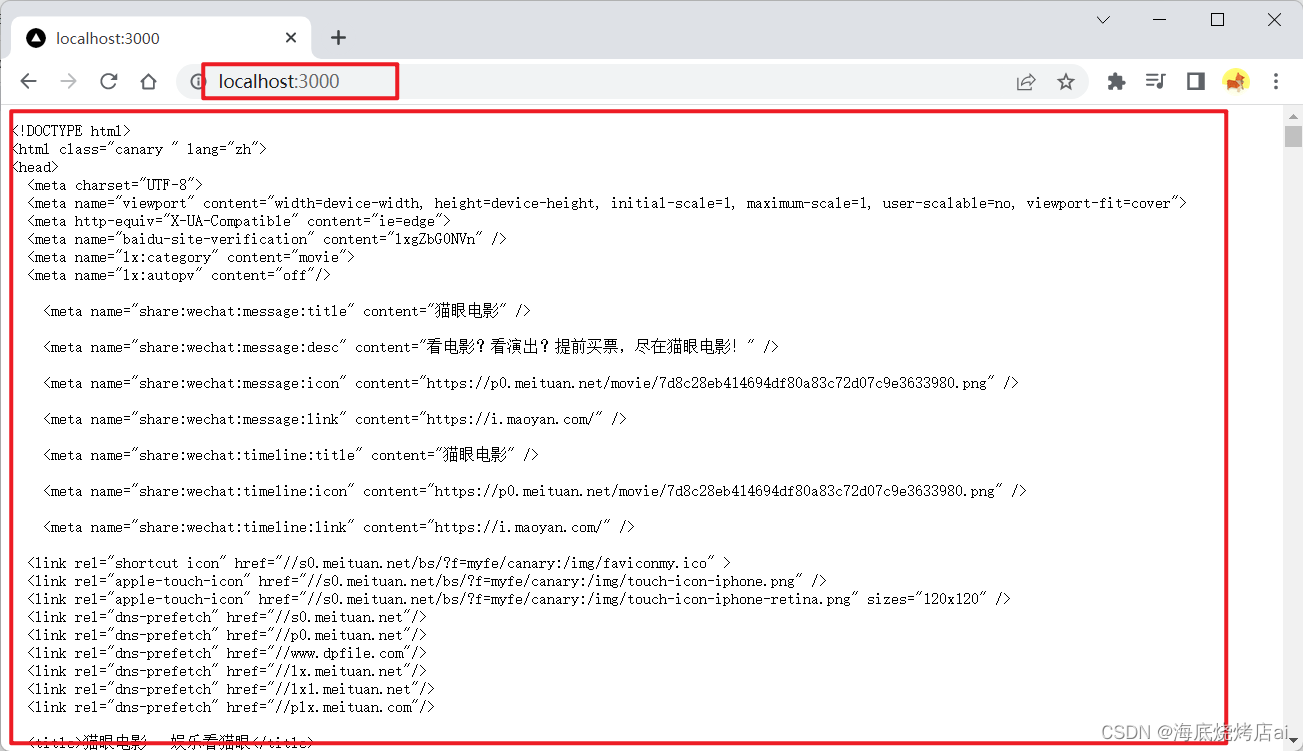
可以看到我们成功获取了猫眼移动端首页的
html
文档,我们需要的数据都在文档中了,之后我们只需将我们需要的数据提取出来,这里就将用到
cheerio
:
const https =require("https");const http =require("http");const cheerio =require("cheerio");
http.createServer((request, response)=>{
response.writeHead(200,{"content-type":"application/json;charset=utf-8",});const options ={hostname:"i.maoyan.com",port:443,path:"/",method:"GET",};// 获取页面数据const req = https.request(options,(res)=>{let data ="";
res.on("data",(chunk)=>{
data += chunk;});
res.on("end",()=>{// 处理页面数据filterData(data);});});functionfilterData(data){let $ = cheerio.load(data);// 获取class="column content"的元素let $movieList =$(".column.content");// console.log($movieList);let movies =[];
$movieList.each((index, value)=>{
movies.push({// 获取class为movie-title下的class为title的元素的文本值title:$(value).find(".movie-title .title").text(),detail:$(value).find(".detail .actor").text(),});});
response.end(JSON.stringify(movies));}
req.end();}).listen(3000);
cheerio.load接收
html文档字符串,它返回一个对象,该对象与
jQuery相似,我们可以对其使用
jQuery的语法进行操作
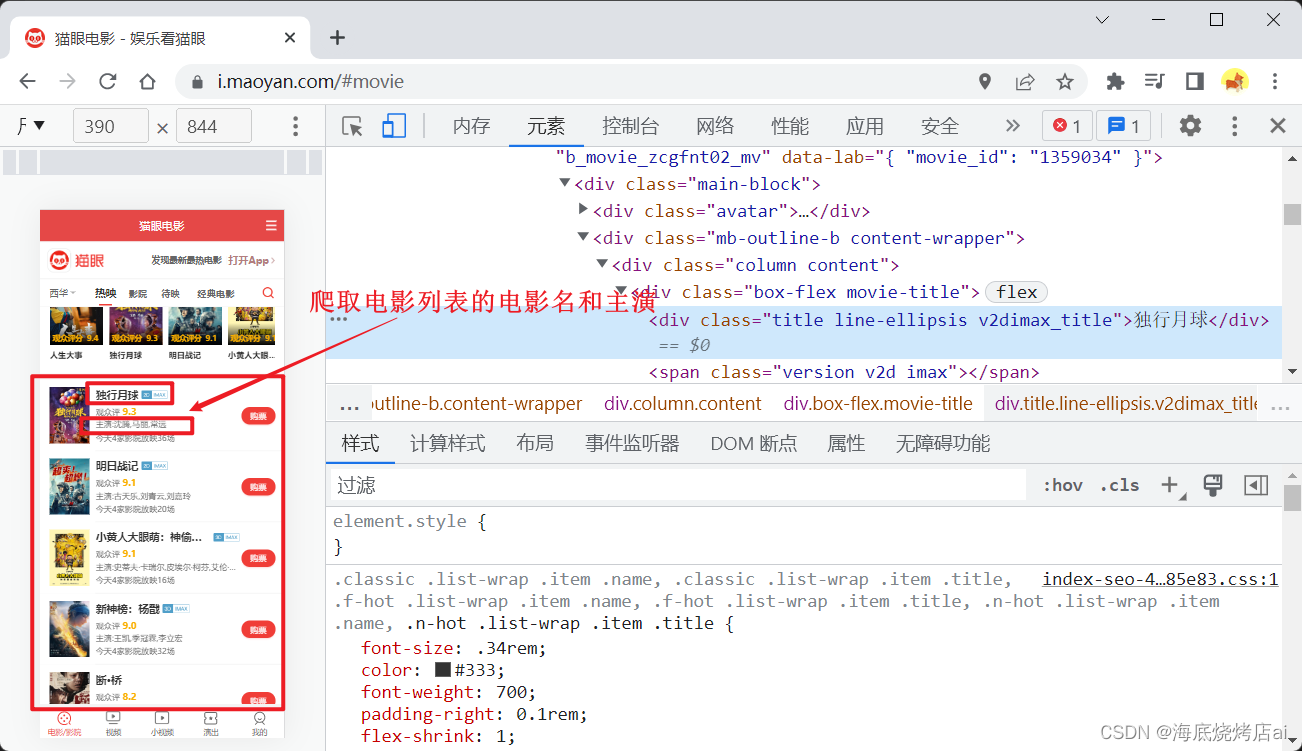
上面使用的
class
类名都是在猫眼首页文档的对应类名,如:
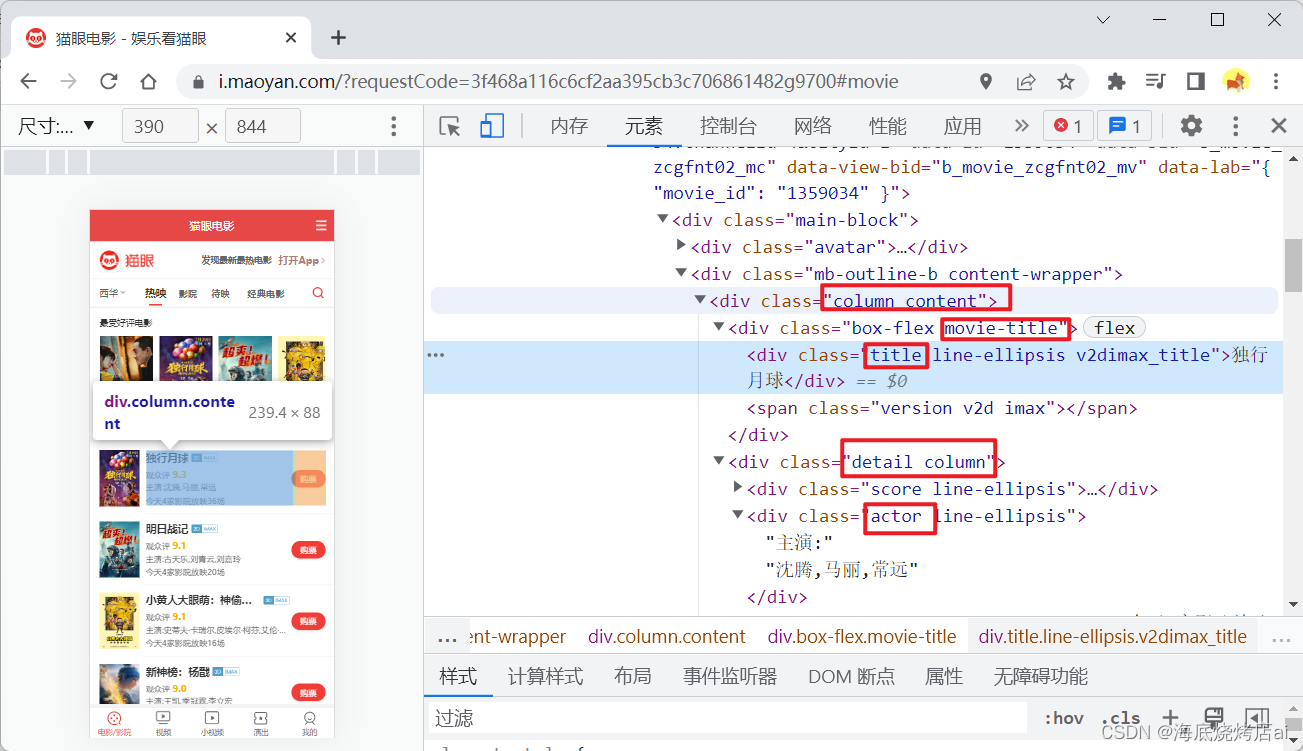
重新访问一下我们的服务器:

可以看到我们已经爬虫成功!
结语
这篇文章内容比较多,博主也是连续写了几天时间才算完成,篇幅太长了,这里就不再多说了
如果本篇文章对你有所帮助,还请客官一件四连!❤️
基础不牢,地动山摇! 快来和博主一起来牛客网刷题巩固基础知识吧!
版权归原作者 海底烧烤店ai 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。