Diffusion扩散模型学习2——Stable Diffusion结构解析
学习前言
用了很久的Stable Diffusion,但从来没有好好解析过它内部的结构,写个博客记录一下,嘿嘿。
源码下载地址
https://github.com/bubbliiiing/stable-diffusion
喜欢的可以点个star噢。
网络构建
一、什么是Stable Diffusion(SD)
Stable Diffusion是比较新的一个扩散模型,翻译过来是稳定扩散,虽然名字叫稳定扩散,但实际上换个seed生成的结果就完全不一样,非常不稳定哈。
Stable Diffusion最开始的应用应该是文本生成图像,即文生图,随着技术的发展Stable Diffusion不仅支持image2image图生图的生成,还支持ControlNet等各种控制方法来定制生成的图像。
Stable Diffusion基于扩散模型,所以不免包含不断去噪的过程,如果是图生图的话,还有不断加噪的过程,此时离不开DDPM那张老图,如下: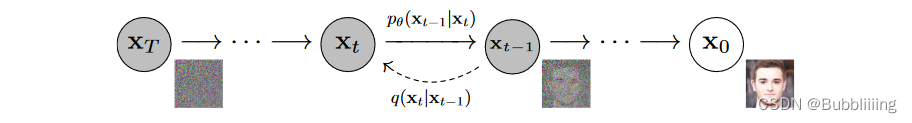
Stable Diffusion相比于DDPM,使用了DDIM采样器,使用了隐空间的扩散,另外使用了非常大的LAION-5B数据集进行预训练。
直接Finetune Stable Diffusion大多数同学应该是无法cover住成本的,不过Stable Diffusion有很多轻量Finetune的方案,比如Lora、Textual Inversion等,但这是后话。
本文主要是解析一下整个SD模型的结构组成,一次扩散,多次扩散的流程。
大模型、AIGC是当前行业的趋势,不会的话容易被淘汰,hh。
二、Stable Diffusion的组成
Stable Diffusion由四大部分组成。
1、Sampler采样器。
2、Variational Autoencoder (VAE) 变分自编码器。
3、UNet 主网络,噪声预测器。
4、CLIPEmbedder文本编码器。
每一部分都很重要,我们首先以文本生成图像为例进行解析。既然是文本生成图像,那么我们的输入也只剩下文本了,这时候没有输入图片。
三、生成流程
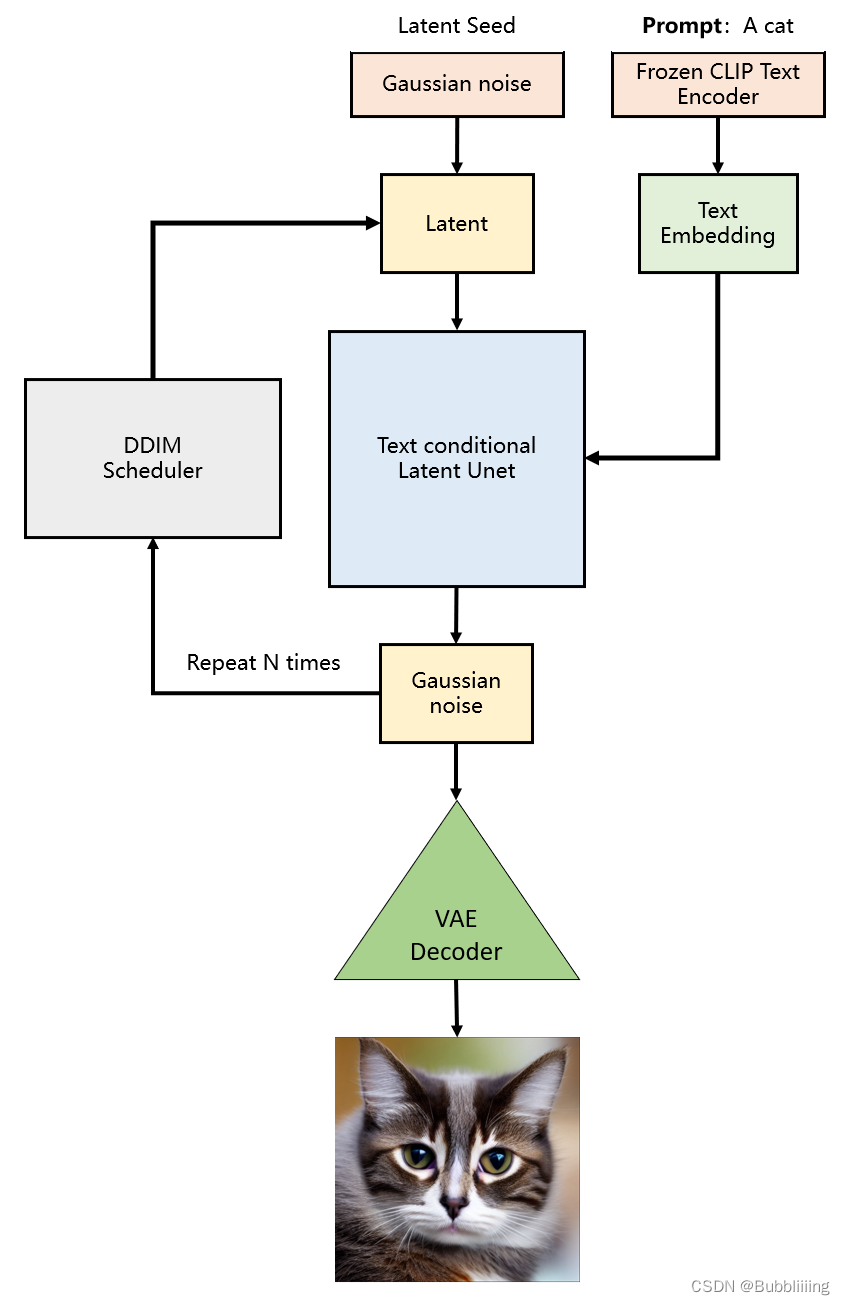
生成流程分为三个部分:
1、prompt文本编码。
2、进行若干次采样。
3、进行解码。
with torch.no_grad():if seed ==-1:
seed = random.randint(0,65535)
seed_everything(seed)# ----------------------- ## 获得编码后的prompt# ----------------------- #
cond ={"c_crossattn":[model.get_learned_conditioning([prompt +', '+ a_prompt]* num_samples)]}
un_cond ={"c_crossattn":[model.get_learned_conditioning([n_prompt]* num_samples)]}
H, W = input_shape
shape =(4, H //8, W //8)# ----------------------- ## 进行采样# ----------------------- #
samples, intermediates = ddim_sampler.sample(ddim_steps, num_samples,
shape, cond, verbose=False, eta=eta,
unconditional_guidance_scale=scale,
unconditional_conditioning=un_cond)# ----------------------- ## 进行解码# ----------------------- #
x_samples = model.decode_first_stage(samples)
x_samples =(einops.rearrange(x_samples,'b c h w -> b h w c')*127.5+127.5).cpu().numpy().clip(0,255).astype(np.uint8)
1、文本编码

文本编码的思路比较简单,直接使用CLIP的文本编码器进行编码就可以了,在代码中定义了一个FrozenCLIPEmbedder类别,使用了transformers库的CLIPTokenizer和CLIPTextModel。
在前传过程中,我们对输入进来的文本首先利用CLIPTokenizer进行编码,然后使用CLIPTextModel进行特征提取,通过FrozenCLIPEmbedder,我们可以获得一个[batch_size, 77, 768]的特征向量。
classFrozenCLIPEmbedder(AbstractEncoder):"""Uses the CLIP transformer encoder for text (from huggingface)"""
LAYERS =["last","pooled","hidden"]def__init__(self, version="openai/clip-vit-large-patch14", device="cuda", max_length=77,
freeze=True, layer="last", layer_idx=None):# clip-vit-base-patch32super().__init__()assert layer in self.LAYERS
# 定义文本的tokenizer和transformer
self.tokenizer = CLIPTokenizer.from_pretrained(version)
self.transformer = CLIPTextModel.from_pretrained(version)
self.device = device
self.max_length = max_length
# 冻结模型参数if freeze:
self.freeze()
self.layer = layer
self.layer_idx = layer_idx
if layer =="hidden":assert layer_idx isnotNoneassert0<=abs(layer_idx)<=12deffreeze(self):
self.transformer = self.transformer.eval()# self.train = disabled_trainfor param in self.parameters():
param.requires_grad =Falsedefforward(self, text):# 对输入的图片进行分词并编码,padding直接padding到77的长度。
batch_encoding = self.tokenizer(text, truncation=True, max_length=self.max_length, return_length=True,
return_overflowing_tokens=False, padding="max_length", return_tensors="pt")# 拿出input_ids然后传入transformer进行特征提取。
tokens = batch_encoding["input_ids"].to(self.device)
outputs = self.transformer(input_ids=tokens, output_hidden_states=self.layer=="hidden")# 取出所有的tokenif self.layer =="last":
z = outputs.last_hidden_state
elif self.layer =="pooled":
z = outputs.pooler_output[:,None,:]else:
z = outputs.hidden_states[self.layer_idx]return z
defencode(self, text):return self(text)
2、采样流程

a、生成初始噪声
既然输入里面只有文本,没有输入图片,那么最初始的噪声哪里来?
在这里直接搞个正态分布的噪声就可以了,简单理解就是:既然在训练的时候就是不断的给 原图 加 正态分布噪声 得到最终的噪声矩阵,那么我直接初始化一个 正态分布的噪声 作为 初始噪声 生成图片很合理吧。
在代码里面其实也是这么做的,不过因为我们是在隐空间去进行扩散的,所以我们生成的噪声也是相对于隐空间的。
在这里简单介绍一下VAE,VAE是变分自编码器,可以将输入图片进行编码,一个高宽原本为512x512x3的图片在使用VAE编码后会变成64x64x4,这个4是人为设定的,不必纠结为什么不是3。这个时候我们就使用一个简单的矩阵代替原有的512x512x3的图片了,传输与存储成本就很低。在实际要去看的时候,可以对64x64x4的矩阵进行解码,获得512x512x3的图片。
因此,如果 我们生成的噪声是相对于隐空间的,同时我们要生成一个512x512x3的图片,那么我们就要初始化一个64x64x4的隐向量,我们在隐空间扩散好后,再使用解码器就可以生成512x512x3的图像。
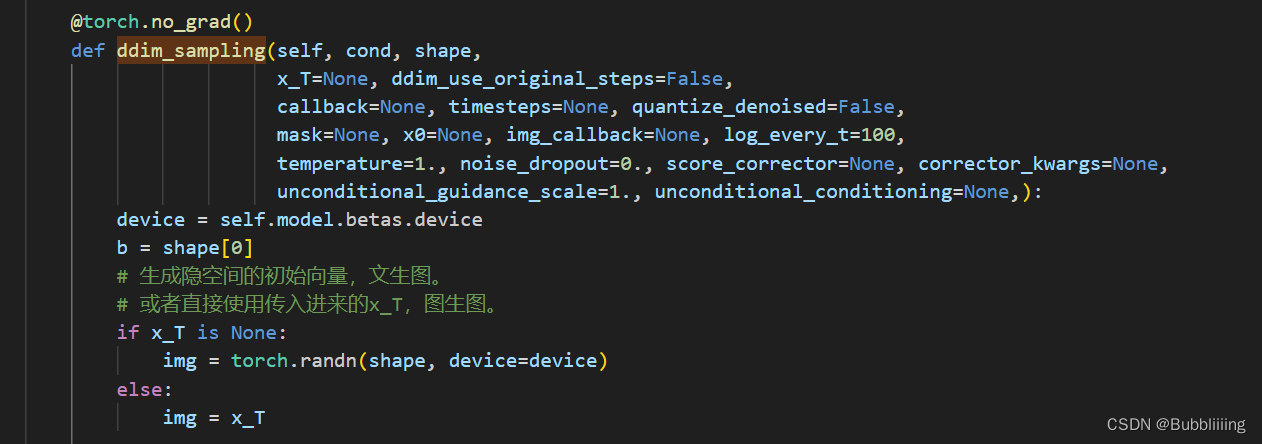
在代码中,我们确实是这么做的,初始噪声的生成代码为:
img = torch.randn(shape, device=device)
代码位于ldm.models.diffusion.ddim.py中的ddim_sampling方法中。shape是外面传进来的,大小为
[4, 64, 64]
。
b、对噪声进行N次采样
既然Stable Diffusion是一个不断扩散的过程,那么少不了不断的去噪声,那么怎么去噪声便是一个问题。
在上一步中,我们已经获得了一个img,它是一个符合正态分布的向量,我们便从它开始去噪声。
我们会对ddim_timesteps的时间步取反,因为我们现在是去噪声而非加噪声,然后对其进行一个循环,循环的代码如下:
循环中有一个mask,它的作用是用于进行局部的重建,对部分区域的隐向量进行mask,此处没用到。其它东西都是个方法或者函数,也看不出东西来。在这里面看起来最像采样过程的就是p_sample_ddim方法,我们需要进入p_sample_ddim这个方法看看。
for i, step inenumerate(iterator):# index是用来取得对应的调节参数的
index = total_steps - i -1# 将步数拓展到bs维度
ts = torch.full((b,), step, device=device, dtype=torch.long)# 用于进行局部的重建,对部分区域的隐向量进行mask。if mask isnotNone:assert x0 isnotNone
img_orig = self.model.q_sample(x0, ts)# TODO: deterministic forward pass?
img = img_orig * mask +(1.- mask)* img
# 进行采样
outs = self.p_sample_ddim(img, cond, ts, index=index, use_original_steps=ddim_use_original_steps,
quantize_denoised=quantize_denoised, temperature=temperature,
noise_dropout=noise_dropout, score_corrector=score_corrector,
corrector_kwargs=corrector_kwargs,
unconditional_guidance_scale=unconditional_guidance_scale,
unconditional_conditioning=unconditional_conditioning)
img, pred_x0 = outs
# 回调函数if callback: callback(i)if img_callback: img_callback(pred_x0, i)if index % log_every_t ==0or index == total_steps -1:
intermediates['x_inter'].append(img)
intermediates['pred_x0'].append(pred_x0)
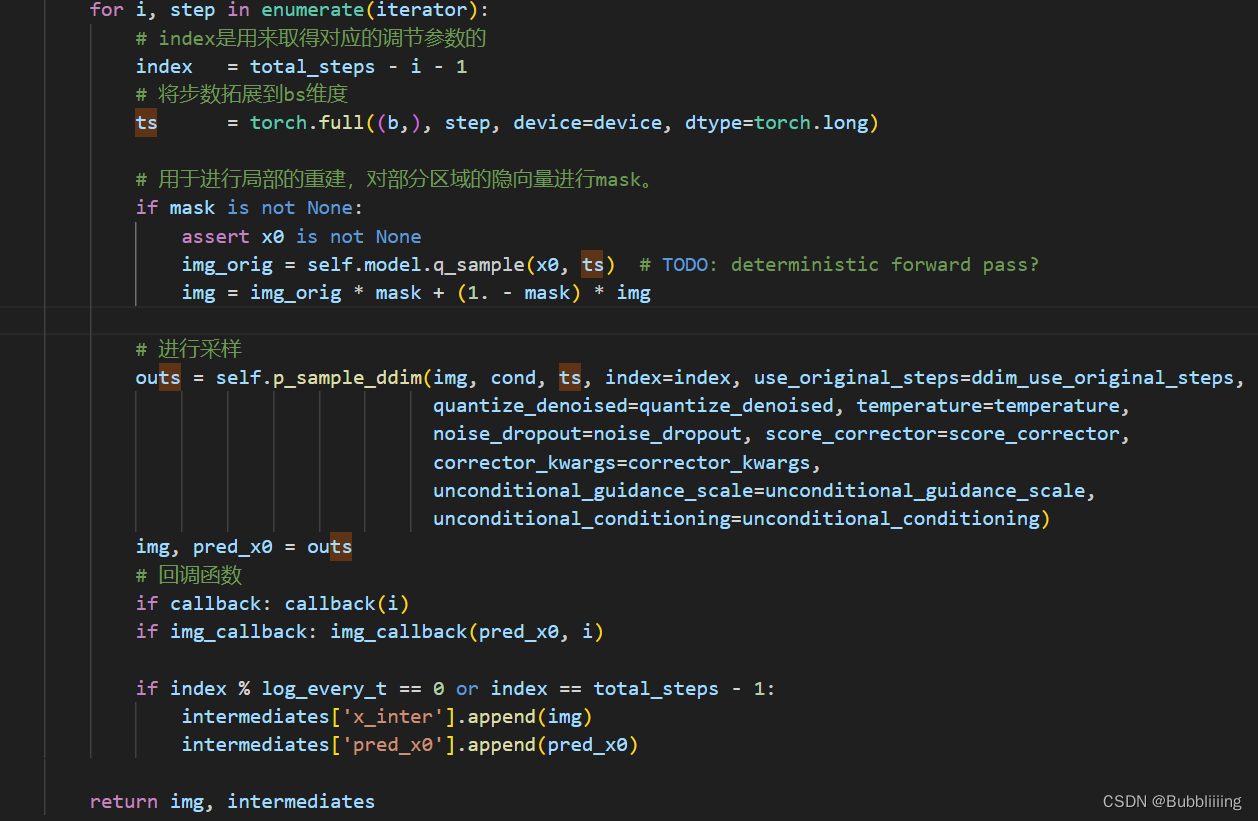
c、单次采样解析
I、预测噪声
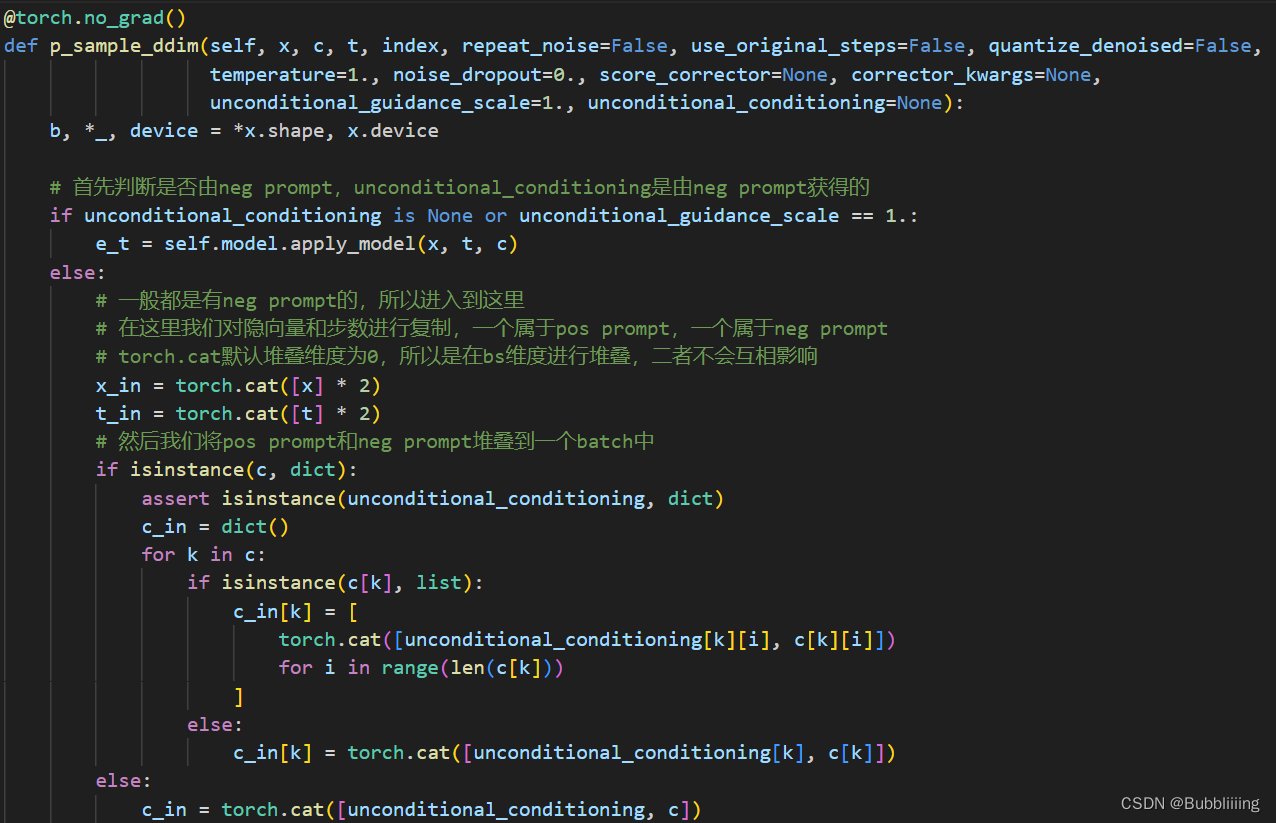
在进行单词采样前,需要首先判断是否有neg prompt,如果有,我们需要同时处理neg prompt,否则仅仅需要处理pos prompt。实际使用的时候一般都有neg prompt(效果会好一些),所以默认进入对应的处理过程。
在处理neg prompt时,我们对输入进来的隐向量和步数进行复制,一个属于pos prompt,一个属于neg prompt。torch.cat默认堆叠维度为0,所以是在batch_size维度进行堆叠,二者不会互相影响。然后我们将pos prompt和neg prompt堆叠到一个batch中,也是在batch_size维度堆叠。
# 首先判断是否由neg prompt,unconditional_conditioning是由neg prompt获得的if unconditional_conditioning isNoneor unconditional_guidance_scale ==1.:
e_t = self.model.apply_model(x, t, c)else:# 一般都是有neg prompt的,所以进入到这里# 在这里我们对隐向量和步数进行复制,一个属于pos prompt,一个属于neg prompt# torch.cat默认堆叠维度为0,所以是在bs维度进行堆叠,二者不会互相影响
x_in = torch.cat([x]*2)
t_in = torch.cat([t]*2)# 然后我们将pos prompt和neg prompt堆叠到一个batch中ifisinstance(c,dict):assertisinstance(unconditional_conditioning,dict)
c_in =dict()for k in c:ifisinstance(c[k],list):
c_in[k]=[
torch.cat([unconditional_conditioning[k][i], c[k][i]])for i inrange(len(c[k]))]else:
c_in[k]= torch.cat([unconditional_conditioning[k], c[k]])else:
c_in = torch.cat([unconditional_conditioning, c])
堆叠完后,我们将隐向量、步数和prompt条件一起传入网络中,将结果在bs维度进行使用chunk进行分割。
因为我们在堆叠时,neg prompt放在了前面。因此分割好后,前半部分
e_t_uncond
属于利用neg prompt得到的,后半部分
e_t
属于利用pos prompt得到的,我们本质上应该扩大pos prompt的影响,远离neg prompt的影响。因此,我们使用
e_t-e_t_uncond
计算二者的距离,使用scale扩大二者的距离。在e_t_uncond基础上,得到最后的隐向量。
# 堆叠完后,隐向量、步数和prompt条件一起传入网络中,将结果在bs维度进行使用chunk进行分割
e_t_uncond, e_t = self.model.apply_model(x_in, t_in, c_in).chunk(2)
e_t = e_t_uncond + unconditional_guidance_scale *(e_t - e_t_uncond)

此时获得的e_t就是通过隐向量和prompt共同获得的预测噪声啦。
II、施加噪声
获得噪声就OK了吗?显然不是的,我们还要将获得的新噪声,按照一定的比例添加到原来的原始噪声上。
这个地方我们最好结合ddim中的公式来看,我们需要获得
α
ˉ
t
\bar{\alpha}_t
αˉt、
α
ˉ
t
−
1
\bar{\alpha}_{t-1}
αˉt−1、
σ
t
\sigma_t
σt、
1
−
α
ˉ
t
\sqrt{1-\bar{\alpha}_t}
1−αˉt。


代码中,我们其实已经预先计算好了这些参数。我们只需要直接取出即可,下方的a_t也就是公式中括号外的
α
ˉ
t
\bar{\alpha}_t
αˉt,a_prev 就是公式中的
α
ˉ
t
−
1
\bar{\alpha}_{t-1}
αˉt−1,sigma_t就是公式中的
σ
t
\sigma_t
σt,sqrt_one_minus_at就是公式中的
1
−
α
ˉ
t
\sqrt{1-\bar{\alpha}_t}
1−αˉt。
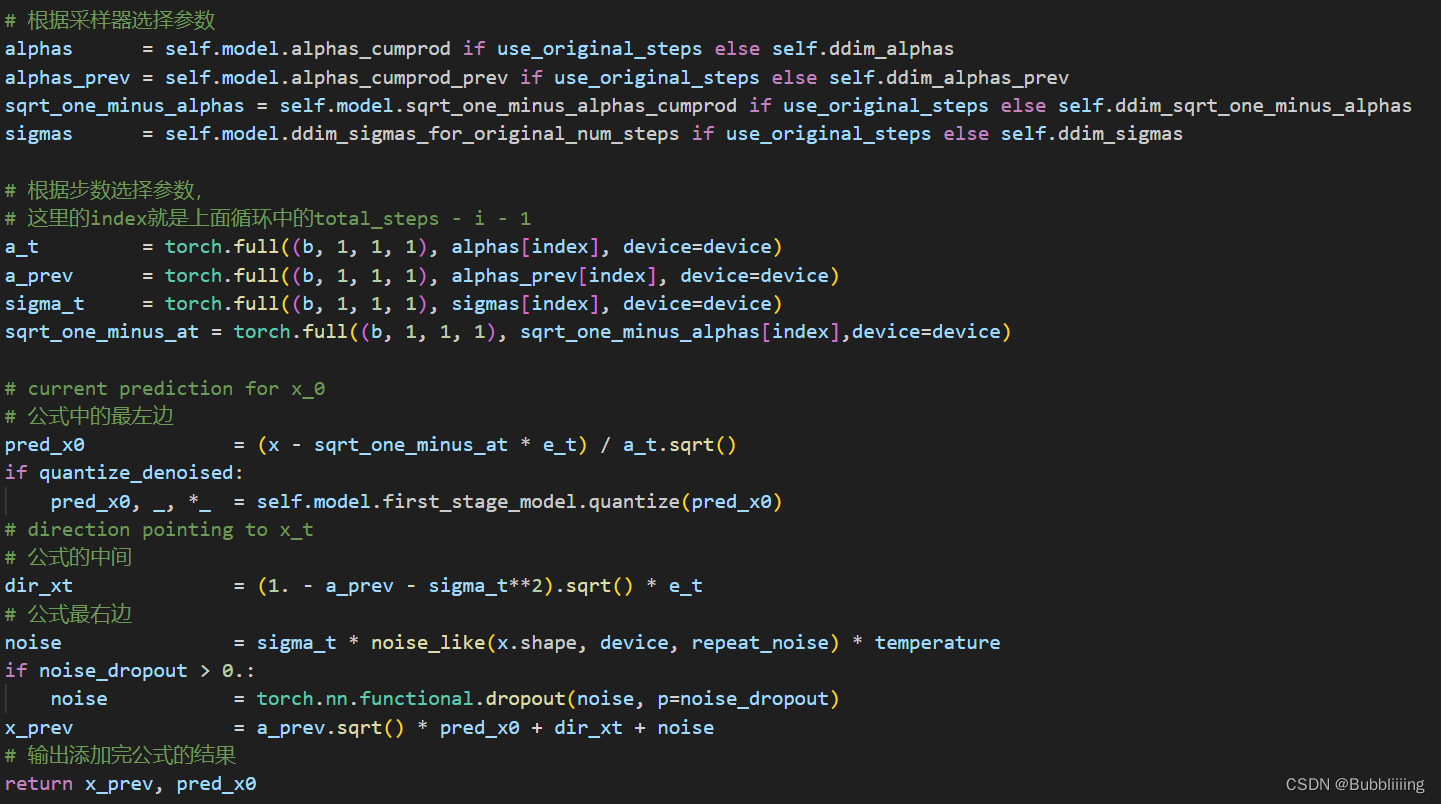
# 根据采样器选择参数
alphas = self.model.alphas_cumprod if use_original_steps else self.ddim_alphas
alphas_prev = self.model.alphas_cumprod_prev if use_original_steps else self.ddim_alphas_prev
sqrt_one_minus_alphas = self.model.sqrt_one_minus_alphas_cumprod if use_original_steps else self.ddim_sqrt_one_minus_alphas
sigmas = self.model.ddim_sigmas_for_original_num_steps if use_original_steps else self.ddim_sigmas
# 根据步数选择参数,# 这里的index就是上面循环中的total_steps - i - 1
a_t = torch.full((b,1,1,1), alphas[index], device=device)
a_prev = torch.full((b,1,1,1), alphas_prev[index], device=device)
sigma_t = torch.full((b,1,1,1), sigmas[index], device=device)
sqrt_one_minus_at = torch.full((b,1,1,1), sqrt_one_minus_alphas[index],device=device)
其实这一步我们只是把公式需要用到的系数全都拿了出来,方便后面的加减乘除。然后我们便在代码中实现上述的公式。
# current prediction for x_0# 公式中的最左边
pred_x0 =(x - sqrt_one_minus_at * e_t)/ a_t.sqrt()if quantize_denoised:
pred_x0, _,*_ = self.model.first_stage_model.quantize(pred_x0)# direction pointing to x_t# 公式的中间
dir_xt =(1.- a_prev - sigma_t**2).sqrt()* e_t
# 公式最右边
noise = sigma_t * noise_like(x.shape, device, repeat_noise)* temperature
if noise_dropout >0.:
noise = torch.nn.functional.dropout(noise, p=noise_dropout)
x_prev = a_prev.sqrt()* pred_x0 + dir_xt + noise
# 输出添加完公式的结果return x_prev, pred_x0
d、预测噪声过程中的网络结构解析
I、apply_model方法解析
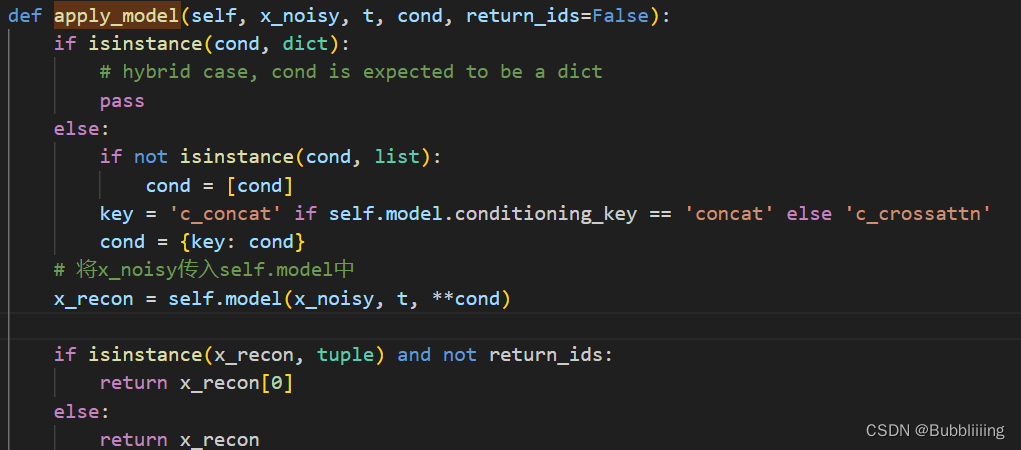
在3.a的预测噪声过程中,我们使用了model.apply_model方法进行噪声的预测,这个方法具体做了什么被隐掉了,我们看看具体做的工作。
apply_model方法在ldm.models.diffusion.ddpm.py文件中。在apply_model中,我们将x_noisy传入self.model中预测噪声。
x_recon = self.model(x_noisy, t,**cond)
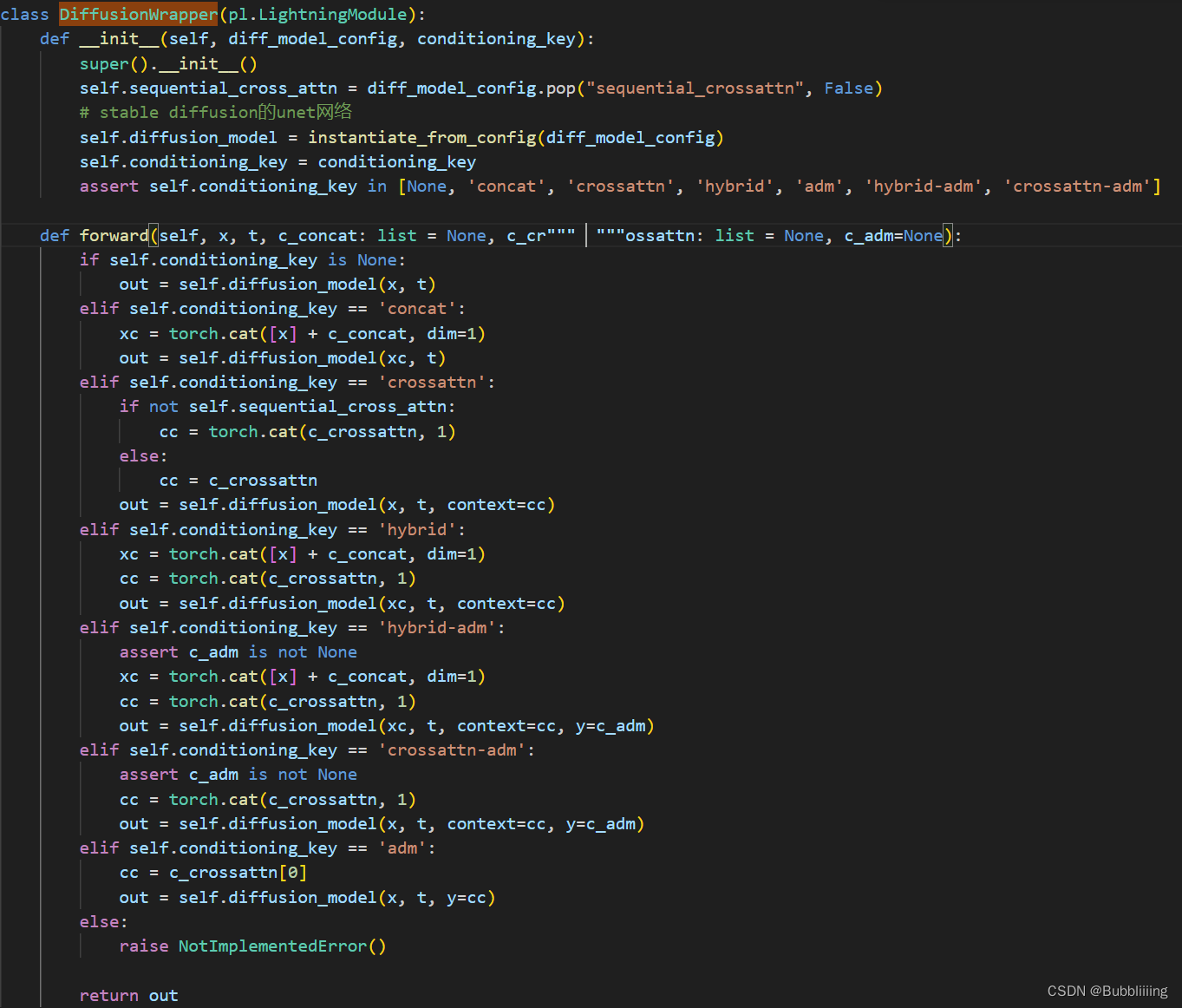
self.model是一个预先构建好的类,定义在ldm.models.diffusion.ddpm.py文件的1416行,内部包含Stable Diffusion的Unet网络,self.model的功能有点类似于包装器,根据模型选择的特征融合方式,进行文本与上文生成的噪声的融合。
c_concat代表使用堆叠的方式进行融合,c_crossattn代表使用attention的方式融合。
classDiffusionWrapper(pl.LightningModule):def__init__(self, diff_model_config, conditioning_key):super().__init__()
self.sequential_cross_attn = diff_model_config.pop("sequential_crossattn",False)# stable diffusion的unet网络
self.diffusion_model = instantiate_from_config(diff_model_config)
self.conditioning_key = conditioning_key
assert self.conditioning_key in[None,'concat','crossattn','hybrid','adm','hybrid-adm','crossattn-adm']defforward(self, x, t, c_concat:list=None, c_crossattn:list=None, c_adm=None):if self.conditioning_key isNone:
out = self.diffusion_model(x, t)elif self.conditioning_key =='concat':
xc = torch.cat([x]+ c_concat, dim=1)
out = self.diffusion_model(xc, t)elif self.conditioning_key =='crossattn':ifnot self.sequential_cross_attn:
cc = torch.cat(c_crossattn,1)else:
cc = c_crossattn
out = self.diffusion_model(x, t, context=cc)elif self.conditioning_key =='hybrid':
xc = torch.cat([x]+ c_concat, dim=1)
cc = torch.cat(c_crossattn,1)
out = self.diffusion_model(xc, t, context=cc)elif self.conditioning_key =='hybrid-adm':assert c_adm isnotNone
xc = torch.cat([x]+ c_concat, dim=1)
cc = torch.cat(c_crossattn,1)
out = self.diffusion_model(xc, t, context=cc, y=c_adm)elif self.conditioning_key =='crossattn-adm':assert c_adm isnotNone
cc = torch.cat(c_crossattn,1)
out = self.diffusion_model(x, t, context=cc, y=c_adm)elif self.conditioning_key =='adm':
cc = c_crossattn[0]
out = self.diffusion_model(x, t, y=cc)else:raise NotImplementedError()return out
代码中的self.diffusion_model便是Stable Diffusion的Unet网络,网络结构位于ldm.modules.diffusionmodules.openaimodel.py文件中的UNetModel类。
II、UNetModel模型解析
UNetModel主要做的工作是结合时间步t和文本Embedding计算这一时刻的噪声。尽管UNet的思路非常简单,但是在StableDiffusion中,UNetModel由ResBlock和Transformer模块组成,整体来讲相比于普通的UNet复杂一些。
Prompt通过Frozen CLIP Text Encoder获得Text Embedding,Timesteps通过全连接(MLP)获得Timesteps Embedding;
ResBlock用于结合时间步Timesteps Embedding,Transformer模块用于结合文本Text Embedding。
我在这里放一张大图,同学们可以看到内部shape的变化。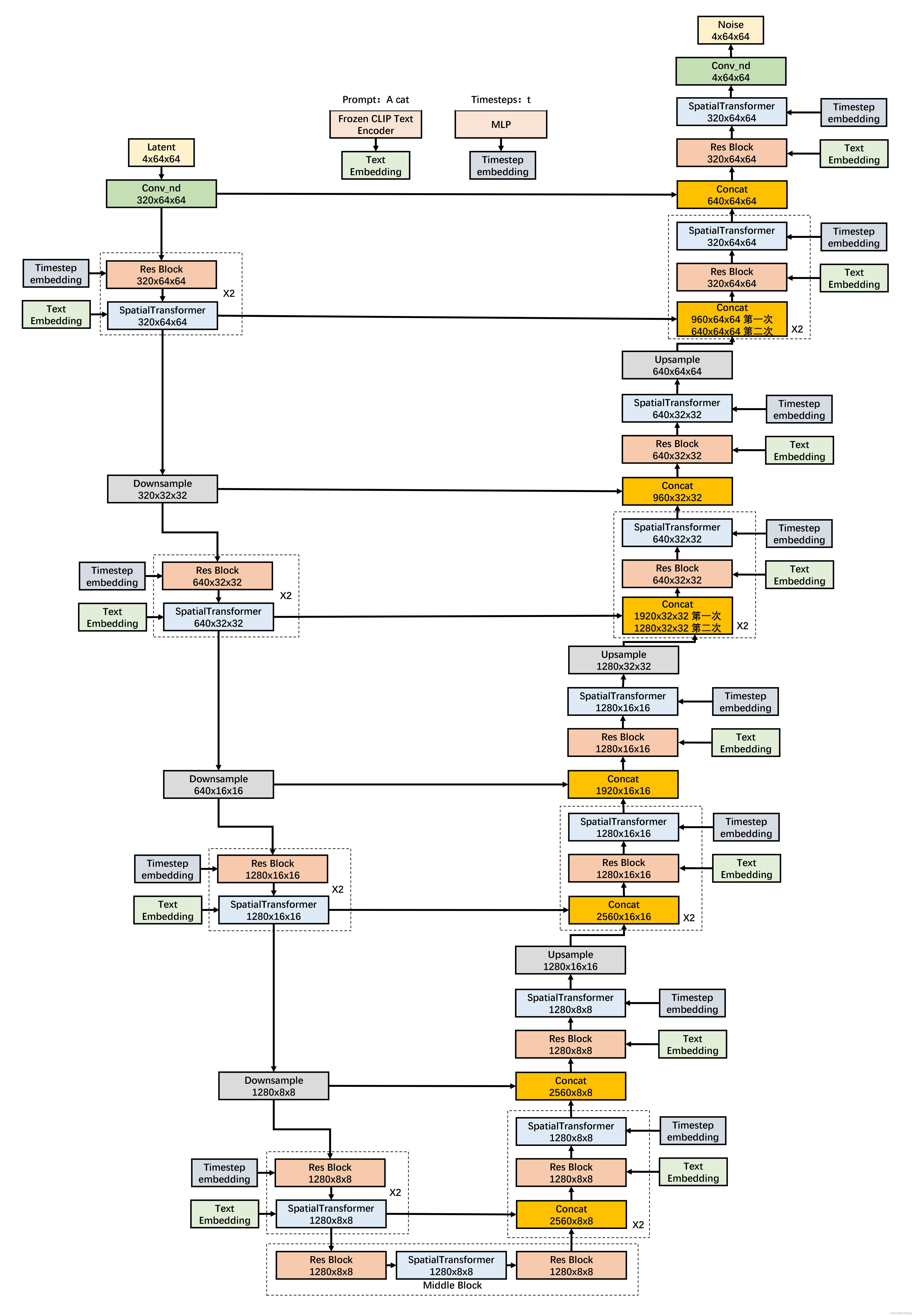
Unet代码如下所示:
classUNetModel(nn.Module):"""
The full UNet model with attention and timestep embedding.
:param in_channels: channels in the input Tensor.
:param model_channels: base channel count for the model.
:param out_channels: channels in the output Tensor.
:param num_res_blocks: number of residual blocks per downsample.
:param attention_resolutions: a collection of downsample rates at which
attention will take place. May be a set, list, or tuple.
For example, if this contains 4, then at 4x downsampling, attention
will be used.
:param dropout: the dropout probability.
:param channel_mult: channel multiplier for each level of the UNet.
:param conv_resample: if True, use learned convolutions for upsampling and
downsampling.
:param dims: determines if the signal is 1D, 2D, or 3D.
:param num_classes: if specified (as an int), then this model will be
class-conditional with `num_classes` classes.
:param use_checkpoint: use gradient checkpointing to reduce memory usage.
:param num_heads: the number of attention heads in each attention layer.
:param num_heads_channels: if specified, ignore num_heads and instead use
a fixed channel width per attention head.
:param num_heads_upsample: works with num_heads to set a different number
of heads for upsampling. Deprecated.
:param use_scale_shift_norm: use a FiLM-like conditioning mechanism.
:param resblock_updown: use residual blocks for up/downsampling.
:param use_new_attention_order: use a different attention pattern for potentially
increased efficiency.
"""def__init__(
self,
image_size,
in_channels,
model_channels,
out_channels,
num_res_blocks,
attention_resolutions,
dropout=0,
channel_mult=(1,2,4,8),
conv_resample=True,
dims=2,
num_classes=None,
use_checkpoint=False,
use_fp16=False,
num_heads=-1,
num_head_channels=-1,
num_heads_upsample=-1,
use_scale_shift_norm=False,
resblock_updown=False,
use_new_attention_order=False,
use_spatial_transformer=False,# custom transformer support
transformer_depth=1,# custom transformer support
context_dim=None,# custom transformer support
n_embed=None,# custom support for prediction of discrete ids into codebook of first stage vq model
legacy=True,):super().__init__()if use_spatial_transformer:assert context_dim isnotNone,'Fool!! You forgot to include the dimension of your cross-attention conditioning...'if context_dim isnotNone:assert use_spatial_transformer,'Fool!! You forgot to use the spatial transformer for your cross-attention conditioning...'from omegaconf.listconfig import ListConfig
iftype(context_dim)== ListConfig:
context_dim =list(context_dim)if num_heads_upsample ==-1:
num_heads_upsample = num_heads
if num_heads ==-1:assert num_head_channels !=-1,'Either num_heads or num_head_channels has to be set'if num_head_channels ==-1:assert num_heads !=-1,'Either num_heads or num_head_channels has to be set'
self.image_size = image_size
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.model_channels = model_channels
self.out_channels = out_channels
self.num_res_blocks = num_res_blocks
self.attention_resolutions = attention_resolutions
self.dropout = dropout
self.channel_mult = channel_mult
self.conv_resample = conv_resample
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.use_checkpoint = use_checkpoint
self.dtype = th.float16 if use_fp16 else th.float32
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.num_head_channels = num_head_channels
self.num_heads_upsample = num_heads_upsample
self.predict_codebook_ids = n_embed isnotNone# 用于计算当前采样时间t的embedding
time_embed_dim = model_channels *4
self.time_embed = nn.Sequential(
linear(model_channels, time_embed_dim),
nn.SiLU(),
linear(time_embed_dim, time_embed_dim),)if self.num_classes isnotNone:
self.label_emb = nn.Embedding(num_classes, time_embed_dim)# 定义输入模块的第一个卷积# TimestepEmbedSequential也可以看作一个包装器,根据层的种类进行时间或者文本的融合。
self.input_blocks = nn.ModuleList([
TimestepEmbedSequential(
conv_nd(dims, in_channels, model_channels,3, padding=1))])
self._feature_size = model_channels
input_block_chans =[model_channels]
ch = model_channels
ds =1# 对channel_mult进行循环,channel_mult一共有四个值,代表unet四个部分通道的扩张比例# [1, 2, 4, 4]for level, mult inenumerate(channel_mult):# 每个部分循环两次# 添加一个ResBlock和一个AttentionBlockfor _ inrange(num_res_blocks):# 先添加一个ResBlock# 用于对输入的噪声进行通道数的调整,并且融合t的特征
layers =[
ResBlock(
ch,
time_embed_dim,
dropout,
out_channels=mult * model_channels,
dims=dims,
use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint,
use_scale_shift_norm=use_scale_shift_norm,)]# ch便是上述ResBlock的输出通道数
ch = mult * model_channels
if ds in attention_resolutions:# num_heads=8if num_head_channels ==-1:
dim_head = ch // num_heads
else:
num_heads = ch // num_head_channels
dim_head = num_head_channels
if legacy:#num_heads = 1
dim_head = ch // num_heads if use_spatial_transformer else num_head_channels
# 使用了SpatialTransformer自注意力,加强全局特征,融合文本的特征
layers.append(
AttentionBlock(
ch,
use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint,
num_heads=num_heads,
num_head_channels=dim_head,
use_new_attention_order=use_new_attention_order,)ifnot use_spatial_transformer else SpatialTransformer(
ch, num_heads, dim_head, depth=transformer_depth, context_dim=context_dim
))
self.input_blocks.append(TimestepEmbedSequential(*layers))
self._feature_size += ch
input_block_chans.append(ch)# 如果不是四个部分中的最后一个部分,那么都要进行下采样。if level !=len(channel_mult)-1:
out_ch = ch
# 在此处进行下采样# 一般直接使用Downsample模块
self.input_blocks.append(
TimestepEmbedSequential(
ResBlock(
ch,
time_embed_dim,
dropout,
out_channels=out_ch,
dims=dims,
use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint,
use_scale_shift_norm=use_scale_shift_norm,
down=True,)if resblock_updown
else Downsample(
ch, conv_resample, dims=dims, out_channels=out_ch
)))# 为下一阶段定义参数。
ch = out_ch
input_block_chans.append(ch)
ds *=2
self._feature_size += ch
if num_head_channels ==-1:
dim_head = ch // num_heads
else:
num_heads = ch // num_head_channels
dim_head = num_head_channels
if legacy:#num_heads = 1
dim_head = ch // num_heads if use_spatial_transformer else num_head_channels
# 定义中间层# ResBlock + SpatialTransformer + ResBlock
self.middle_block = TimestepEmbedSequential(
ResBlock(
ch,
time_embed_dim,
dropout,
dims=dims,
use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint,
use_scale_shift_norm=use_scale_shift_norm,),
AttentionBlock(
ch,
use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint,
num_heads=num_heads,
num_head_channels=dim_head,
use_new_attention_order=use_new_attention_order,)ifnot use_spatial_transformer else SpatialTransformer(
ch, num_heads, dim_head, depth=transformer_depth, context_dim=context_dim
),
ResBlock(
ch,
time_embed_dim,
dropout,
dims=dims,
use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint,
use_scale_shift_norm=use_scale_shift_norm,),)
self._feature_size += ch
# 定义Unet上采样过程
self.output_blocks = nn.ModuleList([])# 循环把channel_mult反了过来for level, mult inlist(enumerate(channel_mult))[::-1]:# 上采样时每个部分循环三次for i inrange(num_res_blocks +1):
ich = input_block_chans.pop()# 首先添加ResBlock层
layers =[
ResBlock(
ch + ich,
time_embed_dim,
dropout,
out_channels=model_channels * mult,
dims=dims,
use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint,
use_scale_shift_norm=use_scale_shift_norm,)]
ch = model_channels * mult
# 然后进行SpatialTransformer自注意力if ds in attention_resolutions:if num_head_channels ==-1:
dim_head = ch // num_heads
else:
num_heads = ch // num_head_channels
dim_head = num_head_channels
if legacy:#num_heads = 1
dim_head = ch // num_heads if use_spatial_transformer else num_head_channels
layers.append(
AttentionBlock(
ch,
use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint,
num_heads=num_heads_upsample,
num_head_channels=dim_head,
use_new_attention_order=use_new_attention_order,)ifnot use_spatial_transformer else SpatialTransformer(
ch, num_heads, dim_head, depth=transformer_depth, context_dim=context_dim
))# 如果不是channel_mult循环的第一个# 且# 是num_res_blocks循环的最后一次,则进行上采样if level and i == num_res_blocks:
out_ch = ch
layers.append(
ResBlock(
ch,
time_embed_dim,
dropout,
out_channels=out_ch,
dims=dims,
use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint,
use_scale_shift_norm=use_scale_shift_norm,
up=True,)if resblock_updown
else Upsample(ch, conv_resample, dims=dims, out_channels=out_ch))
ds //=2
self.output_blocks.append(TimestepEmbedSequential(*layers))
self._feature_size += ch
# 最后在输出部分进行一次卷积
self.out = nn.Sequential(
normalization(ch),
nn.SiLU(),
zero_module(conv_nd(dims, model_channels, out_channels,3, padding=1)),)if self.predict_codebook_ids:
self.id_predictor = nn.Sequential(
normalization(ch),
conv_nd(dims, model_channels, n_embed,1),#nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1) # change to cross_entropy and produce non-normalized logits)defconvert_to_fp16(self):"""
Convert the torso of the model to float16.
"""
self.input_blocks.apply(convert_module_to_f16)
self.middle_block.apply(convert_module_to_f16)
self.output_blocks.apply(convert_module_to_f16)defconvert_to_fp32(self):"""
Convert the torso of the model to float32.
"""
self.input_blocks.apply(convert_module_to_f32)
self.middle_block.apply(convert_module_to_f32)
self.output_blocks.apply(convert_module_to_f32)defforward(self, x, timesteps=None, context=None, y=None,**kwargs):"""
Apply the model to an input batch.
:param x: an [N x C x ...] Tensor of inputs.
:param timesteps: a 1-D batch of timesteps.
:param context: conditioning plugged in via crossattn
:param y: an [N] Tensor of labels, if class-conditional.
:return: an [N x C x ...] Tensor of outputs.
"""assert(y isnotNone)==(
self.num_classes isnotNone),"must specify y if and only if the model is class-conditional"
hs =[]# 用于计算当前采样时间t的embedding
t_emb = timestep_embedding(timesteps, self.model_channels, repeat_only=False)
emb = self.time_embed(t_emb)if self.num_classes isnotNone:assert y.shape ==(x.shape[0],)
emb = emb + self.label_emb(y)# 对输入模块进行循环,进行下采样并且融合时间特征与文本特征。
h = x.type(self.dtype)for module in self.input_blocks:
h = module(h, emb, context)
hs.append(h)# 中间模块的特征提取
h = self.middle_block(h, emb, context)# 上采样模块的特征提取for module in self.output_blocks:
h = th.cat([h, hs.pop()], dim=1)
h = module(h, emb, context)
h = h.type(x.dtype)# 输出模块if self.predict_codebook_ids:return self.id_predictor(h)else:return self.out(h)
3、隐空间解码生成图片

通过上述步骤,已经可以多次采样获得结果,然后我们便可以通过隐空间解码生成图片。
隐空间解码生成图片的过程非常简单,将上文多次采样后的结果,使用decode_first_stage方法即可生成图片。
在decode_first_stage方法中,网络调用VAE对获取到的64x64x3的隐向量进行解码,获得512x512x3的图片。
@torch.no_grad()defdecode_first_stage(self, z, predict_cids=False, force_not_quantize=False):if predict_cids:if z.dim()==4:
z = torch.argmax(z.exp(), dim=1).long()
z = self.first_stage_model.quantize.get_codebook_entry(z, shape=None)
z = rearrange(z,'b h w c -> b c h w').contiguous()
z =1./ self.scale_factor * z
# 一般无需分割输入,所以直接将x_noisy传入self.model中,在下面else进行ifhasattr(self,"split_input_params"):......else:ifisinstance(self.first_stage_model, VQModelInterface):return self.first_stage_model.decode(z, force_not_quantize=predict_cids or force_not_quantize)else:return self.first_stage_model.decode(z)
文本到图像预测过程代码
整体预测代码如下:
import random
import einops
import numpy as np
import torch
import cv2
import os
from ldm_hacked import DDIMSampler
from ldm_hacked import create_model, load_state_dict, DDIMSampler
from pytorch_lightning import seed_everything
# ----------------------- ## 使用的参数# ----------------------- ## config的地址
config_path ="model_data/sd_v15.yaml"# 模型的地址
model_path ="model_data/v1-5-pruned-emaonly.safetensors"# 生成的图像大小为input_shape
input_shape =[512,512]# 一次生成几张图像
num_samples =2# 采样的步数
ddim_steps =20# 采样的种子,为-1的话则随机。
seed =12345# eta
eta =0# 提示词
prompt ="a cat"# 正面提示词
a_prompt ="best quality, extremely detailed"# 负面提示词
n_prompt ="longbody, lowres, bad anatomy, bad hands, missing fingers, extra digit, fewer digits, cropped, worst quality, low quality"# 正负扩大倍数
scale =9# save_path
save_path ="imgs/outputs_imgs"# ----------------------- ## 创建模型# ----------------------- #
model = create_model(config_path).cpu()
model.load_state_dict(load_state_dict(model_path, location='cuda'), strict=False)
model = model.cuda()
ddim_sampler = DDIMSampler(model)with torch.no_grad():if seed ==-1:
seed = random.randint(0,65535)
seed_everything(seed)# ----------------------- ## 获得编码后的prompt# ----------------------- #
cond ={"c_crossattn":[model.get_learned_conditioning([prompt +', '+ a_prompt]* num_samples)]}
un_cond ={"c_crossattn":[model.get_learned_conditioning([n_prompt]* num_samples)]}
H, W = input_shape
shape =(4, H //8, W //8)# ----------------------- ## 进行采样# ----------------------- #
samples, intermediates = ddim_sampler.sample(ddim_steps, num_samples,
shape, cond, verbose=False, eta=eta,
unconditional_guidance_scale=scale,
unconditional_conditioning=un_cond)# ----------------------- ## 进行解码# ----------------------- #
x_samples = model.decode_first_stage(samples)
x_samples =(einops.rearrange(x_samples,'b c h w -> b h w c')*127.5+127.5).cpu().numpy().clip(0,255).astype(np.uint8)# ----------------------- ## 保存图片# ----------------------- #ifnot os.path.exists(save_path):
os.makedirs(save_path)for index, image inenumerate(x_samples):
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(save_path,str(index)+".jpg"), cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
版权归原作者 Bubbliiiing 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。