前言
Hive-3.1.2版本支持6种join语法。分别是:inner join(内连接)、left join(左连接)、right join(右连接)、full outer join(全外连接)、left semi join(左半开连接)、cross join(交叉连接,也叫做笛卡尔乘积)。
一、Hive的Join连接
数据准备: 有两张表studentInfo、studentScore
create table if not exists studentInfo
(
user_id int comment '学生id',
name string comment '学生姓名',
gender string comment '学生性别'
)
comment '学生信息表';
INSERT overwrite table studentInfo
VALUES (1, '吱吱', '男'),
(2, '格格', '男'),
(3, '纷纷', '女'),
(4, '嘻嘻', '女'),
(5, '安娜', '女');
create table if not exists studentScore
(
user_id int comment '学生id',
subject string comment '学科',
score int comment '分数'
)
comment '学生分数表';
INSERT overwrite table studentScore
VALUES (1, '生物', 78),
(2, '生物', 88),
(3, '生物', 34),
(4, '数学', 98),
(null, '数学', 64);
1.1 inner join 内连接
内连接是最常见的一种连接,其中inner可以省略:inner join == join ; 只有进行连接的两个表中都存在与连接条件相匹配的数据才会被留下来。

select
t1.user_id,
t1.name,
t1.gender,
t2.subject,
t2.score
from studentInfo t1
inner join studentScore t2 on t1.user_id = t2.user_id
1.2 left join 左外连接
join时以左表的全部数据为准,右边与之关联;左表数据全部返回,右表关联上的显示返回,关联不上的显示null返回。

select
t1.user_id,
t1.name,
t1.gender,
t2.user_id,
t2.subject,
t2.score
from studentInfo t1
left join studentScore t2
on t1.user_id = t2.user_id;
1.3 right join 右外连接
join时以右表的全部数据为准,左边与之关联;右表数据全部返回,左表关联上的显示返回,关联不上的显示null返回。

select
t2.user_id,
t2.subject,
t2.score,
t1.user_id,
t1.name,
t1.gender
from studentInfo t1
right join studentScore t2
on t1.user_id = t2.user_id;
1.4 full join 满外连接
包含左、右两个表的全部行,不管另外一边的表中是否存在与它们匹配的行;在功能上等价于对这两个数据集合分别进行左外连接和右外连接,然后再使用消去重复行的操作将上述两个结果集合并为一个结果集。**full join 本质等价于 left join union right join; **

select
t1.user_id,
t1.name,
t1.gender,
t2.user_id,
t2.subject,
t2.score
from studentInfo t1
full join studentScore t2
on t1.user_id = t2.user_id;

**ps:full join 本质等价于 left join union right join; **
select
t1.user_id,
t1.name,
t1.gender,
t2.user_id,
t2.subject,
t2.score
from studentInfo t1
full join studentScore t2
on t1.user_id = t2.user_id;
----- 等价于下述代码
select
t1.user_id as t1_user_id ,
t1.name,
t1.gender,
t2.user_id as t2_user_id,
t2.subject,
t2.score
from studentInfo t1
left join studentScore t2
on t1.user_id = t2.user_id
union
select
t1.user_id as t1_user_id ,
t1.name,
t1.gender,
t2.user_id as t2_user_id,
t2.subject,
t2.score
from studentInfo t1
right join studentScore t2
on t1.user_id = t2.user_id
1.5 多表连接
注意:连接 n 个表,至少需要 n-1 个连接条件。例如:连接三个表,至少需要两个连接
条件。join on使用的key有几组就会被转化为几个MR任务,使用相
同的key来连接,则只会被转化为1个MR任务。
1.6 cross join 交叉连接
交叉连接cross join,将会返回被连接的两个表的**笛卡尔积**,返回结果的行数等于**两个表行数的乘积 N*M**。对于大表来说,cross join慎用(笛卡尔积可能会造成**数据膨胀**)
在SQL标准中定义的cross join就是无条件的inner join。返回两个表的笛卡尔积,无需指定关联 键。
在HiveSQL语法中,cross join 后面可以跟where子句进行过滤,或者on条件过滤。
---举例:
select
t1.user_id as t1_user_id ,
t1.name,
t1.gender,
t2.user_id as t2_user_id,
t2.subject,
t2.score
from studentInfo t1, studentScore t2
--- 等价于:
select
t1.user_id as t1_user_id ,
t1.name,
t1.gender,
t2.user_id as t2_user_id,
t2.subject,
t2.score
from studentInfo t1
join studentScore t2
---等价于:
select
t1.user_id as t1_user_id ,
t1.name,
t1.gender,
t2.user_id as t2_user_id,
t2.subject,
t2.score
from studentInfo t1
cross join studentScore t2
1.7 join on和where条件区别
两者之间的区别见文章:
Hive中left join 中的where 和 on的区别-CSDN博客文章浏览阅读1.2k次,点赞21次,收藏23次。Hive中left join 中的where 和 on的区别https://blog.csdn.net/SHWAITME/article/details/135892183?ops_request_misc=%257B%2522request%255Fid%2522%253A%2522170780016016800197016026%2522%252C%2522scm%2522%253A%252220140713.130102334.pc%255Fblog.%2522%257D&request_id=170780016016800197016026&biz_id=0&utm_medium=distribute.pc_search_result.none-task-blog-2~blog~first_rank_ecpm_v1~rank_v31_ecpm-1-135892183-null-null.nonecase&utm_term=where&spm=1018.2226.3001.4450
1.8 join中不能有null
- group by字段为null,会导致结果不正确(null值也会参与group by 分组)
group by column1
- join字段为null会导致结果不正确(例如:下述 t2.b字段是null值)
t1 left join t2 on t1.a=t2.a and t1.b=t2.b
1.9 join操作导致数据膨胀
select *
from a
left join b
on a.id = b.id
如果主表a的id是唯一的,副表b的id有重复值,非唯一,那当on a.id = b.id 时,就会导致**数据膨胀(一条变多条)**。因此两表或多表join的时候,需保证**join的字段唯一性**,否则会出现一对多的数据膨胀现象。
二、Hive的谓词下推
2.1 谓词下推概念
在不影响结果的情况下,尽量将过滤条件提前执行。谓词下推后,过滤条件在map端执行,减少了map端的输出,降低了数据在集群上传输的量,提升任务性能。
在hive生成的物理执行计划中,有一个配置项用于管理谓词下推是否开启。
set hive.optimize.ppd=true; 默认是true
** 疑问:如果hive谓词下推的功能与join同时存在,那下推功能可以在哪些场景下生效**?
2.2 谓词下推场景分析
数据准备:以上述两张表studentInfo、studentScore为例
查看谓词下推是否开启:
set hive.optimize.ppd;

(1) inner join 内连接
- 对左表where过滤
explain
select
t1.user_id as t1_user_id,
t1.name,
t1.gender,
t2.user_id as t2_user_id,
t2.subject,
t2.score
from studentInfo t1
inner join studentScore t2 on t1.user_id = t2.user_id
where t1.user_id >2
explain查看执行计划,在对t2表进行scan后,优先对t1表进行filter,过滤t1.user_id >2,即**谓词下推生效。**

- 对右表where过滤
explain
select
t1.user_id as t1_user_id,
t1.name,
t1.gender,
t2.user_id as t2_user_id,
t2.subject,
t2.score
from studentInfo t1
inner join studentScore t2 on t1.user_id = t2.user_id
where t2.user_id is not null
explain查看执行计划,在对t2表进行scan后,优先进行filter,过滤t2.user_id is not null,即**谓词下推生效。**

- 对左表on过滤
explain
select
t1.user_id as t1_user_id,
t1.name,
t1.gender,
t2.user_id as t2_user_id,
t2.subject,
t2.score
from studentInfo t1
inner join studentScore t2 on t1.user_id = t2.user_id and t1.user_id >2
explain查看执行计划,在对t2表进行scan后,优先对t1表进行filter,过滤t1.user_id >2,即**谓词下推生效。**

- 对右表on过滤
explain
select
t1.user_id as t1_user_id,
t1.name,
t1.gender,
t2.user_id as t2_user_id,
t2.subject,
t2.score
from studentInfo t1
inner join studentScore t2 on t1.user_id = t2.user_id and t2.user_id is not null
explain查看执行计划,在对t2表进行scan后,优先进行filter,过滤t2.user_id is not null,即**谓词下推生效。**
(2) left join(right join 同理)
- 对左表where过滤
explain
select
t1.user_id,
t1.name,
t1.gender,
t2.user_id,
t2.subject,
t2.score
from studentInfo t1
left join studentScore t2
on t1.user_id = t2.user_id
where t1.user_id >2;
explain查看执行计划,在对t2表进行scan后,优先对t1表进行filter,过滤t1.user_id >2,即**谓词下推生效。**

- 对右表where过滤
explain
select
t1.user_id,
t1.name,
t1.gender,
t2.user_id,
t2.subject,
t2.score
from studentInfo t1
left join studentScore t2
on t1.user_id = t2.user_id
where t2.user_id is not null;
explain查看执行计划,在对t2表进行scan后,优先进行filter,过滤t2.user_id is not null,即**谓词下推生效。** 

- 对左表on过滤
explain
select
t1.user_id as t1_user_id,
t1.name,
t1.gender,
t2.user_id as t2_user_id,
t2.subject,
t2.score
from studentInfo t1
left join studentScore t2
on t1.user_id = t2.user_id and t1.user_id >2
explain查看执行计划,在对t2表进行scan后,在对t1表未进行filter,即**谓词下推不生效**。


- 对右表on过滤
explain
select
t1.user_id as t1_user_id,
t1.name,
t1.gender,
t2.user_id as t2_user_id,
t2.subject,
t2.score
from studentInfo t1
left join studentScore t2
on t1.user_id = t2.user_id and t2.user_id is not null;
explain查看执行计划,在对t2表进行scan后,优先进行filter,过滤t2.user_id is not null,即**谓词下推生效。**

(3) full join
- 对左表where过滤
explain
select
t1.user_id as t1_user_id,
t1.name,
t1.gender,
t2.user_id as t2_user_id,
t2.subject,
t2.score
from studentInfo t1
full join studentScore t2
on t1.user_id = t2.user_id
where t1.user_id >2 ;
explain查看执行计划,在对t2表进行scan后,优先对t1表进行filter,过滤t1.user_id >2,即**谓词下推生效。**


- 对右表where过滤
explain
select
t1.user_id as t1_user_id,
t1.name,
t1.gender,
t2.user_id as t2_user_id,
t2.subject,
t2.score
from studentInfo t1
full join studentScore t2
on t1.user_id = t2.user_id
where t2.user_id is not null
explain查看执行计划,在对t1 表进行scan后,优先进行filter,过滤t2.user_id is not null,即**谓词下推生效。**

- 对左表on过滤
explain
select
t1.user_id as t1_user_id,
t1.name,
t1.gender,
t2.user_id as t2_user_id,
t2.subject,
t2.score
from studentInfo t1
full join studentScore t2
on t1.user_id = t2.user_id and t1.user_id >2;
explain查看执行计划,在对t1表进行scan后,未对t1表进行filter,即**谓词下推不生效**。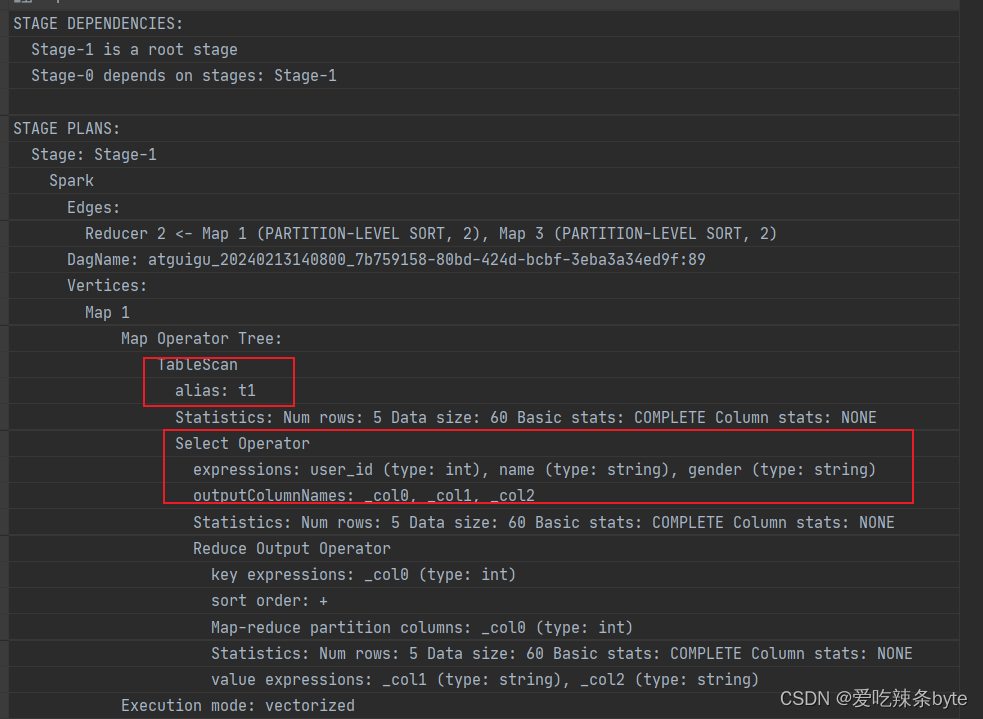

- 对右表on过滤
explain
select
t1.user_id as t1_user_id,
t1.name,
t1.gender,
t2.user_id as t2_user_id,
t2.subject,
t2.score
from studentInfo t1
full join studentScore t2
on t1.user_id = t2.user_id and t2.user_id is not null;
explain查看执行计划,在对t1表进行scan后,未对t2表未进行filter,即**谓词下推不生效**。


总结:
hive中谓词下推的各种场景下的生效情况如下表:
inner joinleft joinright join****full join左表右表左表右表左表右表左表右表where条件√√√√√√√√on条件√√×√√×××
三、Hive Join的数据倾斜
待补充
参考文章:
Hive的Join操作_hive join-CSDN博客
《Hive用户指南》- Hive的连接join与排序_hive 对主表排序后连接查询能保持顺序吗-CSDN博客
Hive 中的join和谓词下推_hive谓词下推-CSDN博客
版权归原作者 吵吵叭火 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。








