我们用three.js可以绘制出各种酷炫的画面,但是当我们想要一个更加真实的物理效果的话,这个时候我们就需要一个物理的库,接下来我们就讲解一下今天要学习的canon,它可以给我们提供一个更加真实的物理效果,像物体的张力、摩擦力、拉伸、反弹等等各种真实的物理效果。该库都能够有一个非常好的模拟。
PS:目前博主在一家互联网公司工作,该公司的编码风格是vue+tsx,所以接下来的项目以该编码风格进行举例,详细了解参考我之前的文章:地址 。
canon基本使用
Cannon 是一种轻量级的 JavaScript 3D 物理引擎,用于实现虚拟世界中的物理模拟和交互。它提供了一套强大的功能,能够处理刚体碰撞、力学模拟、约束系统等物理效果,使开发者能够在 Web 应用程序和游戏中实现逼真的物理行为。
Cannon的官网:地址 ,提供了一系列关于物理运动在three世界的实现,实现案例 的效果非常直观,展示了物理运动的魅力,如下:

接下来我们在three.js的vue项目中使用Cannon,终端执行如下命令安装,具体参考:官网
npm i cannon-es
接下来我们通过tsx风格语法撰写three基础项目实现:
import { defineComponent } from "vue";
import * as THREE from 'three'
import { OrbitControls } from 'three/examples/jsm/controls/OrbitControls.js'
import * as CANNON from 'cannon-es'
import './index.scss'
import { div } from "three/examples/jsm/nodes/Nodes.js";
export default defineComponent({
setup() {
// 初始化物理世界
const world = new CANNON.World()
// 初始化物理世界的重力
world.gravity.set(0, -9.82, 0)
// 初始化3D世界
const scene = new THREE.Scene()
// 初始化相机
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(75, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 0.1, 1000)
camera.position.z = 3
// 初始化渲染器
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({ antialias: true })
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight)
document.body.appendChild(renderer.domElement)
// 初始化控制器
const controls = new OrbitControls(camera, renderer.domElement)
controls.enableDamping = true
// 渲染
let clock = new THREE.Clock()
const animate = () => {
let delta = clock.getDelta()
controls.update()
renderer.render(scene, camera)
requestAnimationFrame(animate)
}
animate()
return () => {
<div></div>
}
}
})
接下来我们需要给场景添加一些物体,如下:
// 创建一个物理球体,半径为0.5
const sphereShape = new CANNON.Sphere(0.5)
// 创建一个刚体
const sphereBody = new CANNON.Body({
mass: 1,
shape: sphereShape,
position: new CANNON.Vec3(0, 5, 0)
})
// 将刚体添加到物理世界中
world.addBody(sphereBody)
// 物理世界创建的东西不显示,所以我们要再通过three.js再创建一个球
const sphereGeometry = new THREE.SphereGeometry(0.5, 32, 32) // 创建一个几何体
const sphereMaterial = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0x00ff00 }) // 创建一个球体材质
const shpereMesh = new THREE.Mesh(sphereGeometry, sphereMaterial) // 创建一个球体网格
// 将网格添加到3D场景中
scene.add(shpereMesh)
打开控制台,可以看到我们的球体已经显示出来了:
接下来我们要把物理世界的球体给到我们three渲染出来的球体,让两者开始关联起来。在每一帧中,根据物理引擎模拟的结果来更新 Three.js 场景中球体网格的位置和旋转状态,从而实现了基于物理引擎的球体模拟效果,如下:
得到的结果如下:

基础碰撞使用
上面我们实现了一个物体的自由下落,接下来我们实现物体与平面的碰撞效果。如下添加平面:
// 创建一个物理世界的平面
const planeShape = new CANNON.Plane()
// 创建一个刚体
const planeBody = new CANNON.Body({
mass: 0, // 设置质量为0,不受碰撞的影响
shape: planeShape,
position: new CANNON.Vec3(0, 0, 0)
})
// 设置刚体旋转(设置旋转X轴)
planeBody.quaternion.setFromAxisAngle(new CANNON.Vec3(1, 0, 0), -Math.PI / 2)
// 将刚体添加到物理世界当中
world.addBody(planeBody)
// 物理世界创建的东西不显示,所以我们要再通过three.js再创建一个平面
const planeGeometry = new THREE.PlaneGeometry(10, 10) // 因为渲染的东西不是无限衍生,这里给10x10
// 创建一个平面材质
const planeMaterial = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0xffff00 })
// 创建一个平面网格
const planeMesh = new THREE.Mesh(planeGeometry, planeMaterial)
// 旋转平面90度让其平铺
planeMesh.rotation.x = -Math.PI / 2
// 将网格添加到3D场景当中
scene.add(planeMesh)
当然除了我们设置平面质量为0之外,我们也可以设置平面为静态效果,也不受碰撞影响:

最终得到的效果如下:

那我们让物理世界和渲染世界的平面倾斜度加上0.1,小球是否会滑落而掉下去呢?测试一下:
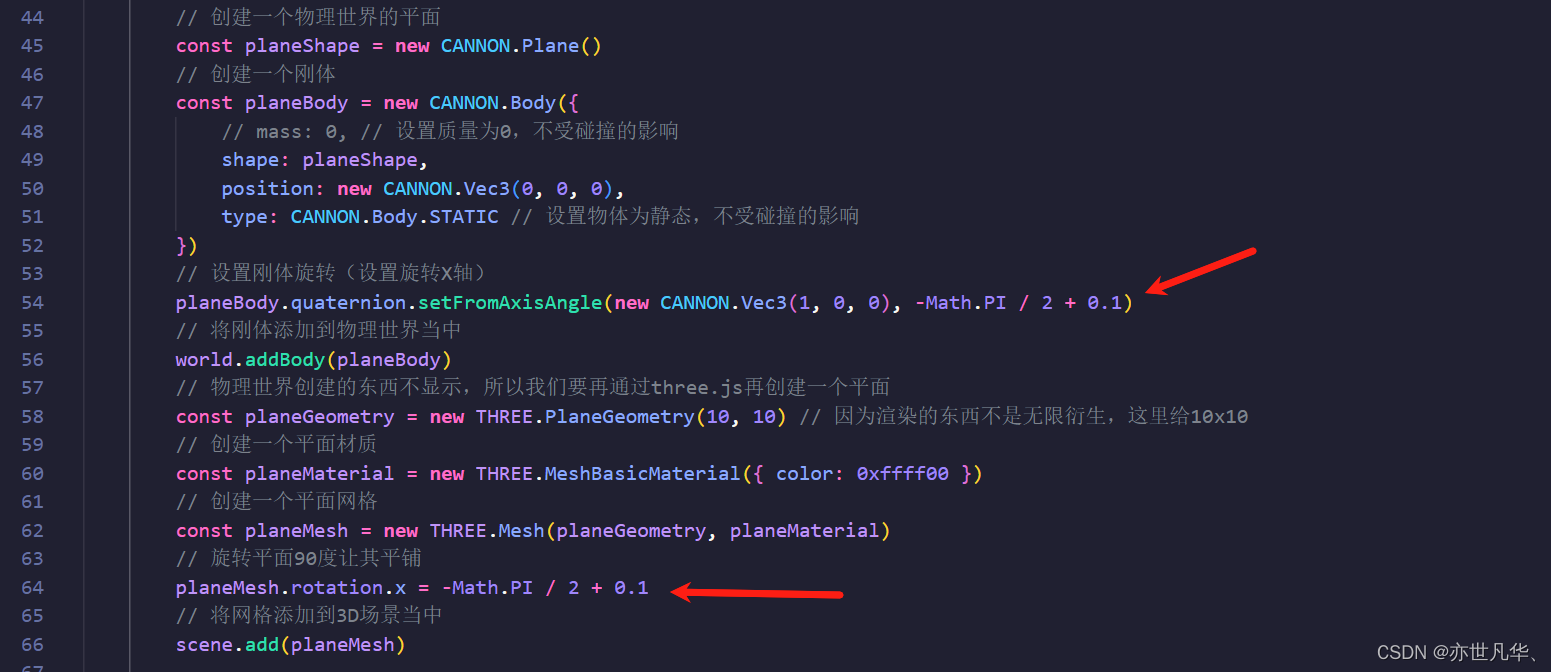
得到的效果如下,可见小球是不会掉落下去的,因为物理世界的平面是无限衍生的,即使渲染世界的平面有限,小球仍然会走物理世界的规律,如下:

如果我们想在物理世界有一个有限大的平面的话, 我们可以通过构建一个立方体,然后把立方体压扁形成一个平面来使用,因为立方体已经有高度了,所以我们也不需要在旋转90度了,稍微给点倾斜度0.1即可,代码如下:

得到的效果如下,可见到我们的小球已经实现了掉落的效果:

上面两标题的案例代码如下:
import { defineComponent } from "vue";
import * as THREE from 'three'
import { OrbitControls } from 'three/examples/jsm/controls/OrbitControls.js'
import * as CANNON from 'cannon-es'
import './index.scss'
export default defineComponent({
setup() {
// 初始化物理世界
const world = new CANNON.World()
// 初始化物理世界的重力
world.gravity.set(0, -9.82, 0)
// 初始化3D世界
const scene = new THREE.Scene()
// 初始化相机
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(75, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 0.1, 1000)
camera.position.z = 3
// 初始化渲染器
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({ antialias: true })
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight)
document.body.appendChild(renderer.domElement)
// 初始化控制器
const controls = new OrbitControls(camera, renderer.domElement)
controls.enableDamping = true
// 创建一个物理球体,半径为0.5
const sphereShape = new CANNON.Sphere(0.5)
// 创建一个刚体
const sphereBody = new CANNON.Body({
mass: 1,
shape: sphereShape,
position: new CANNON.Vec3(0, 5, 0)
})
// 将刚体添加到物理世界中
world.addBody(sphereBody)
// 物理世界创建的东西不显示,所以我们要再通过three.js再创建一个球
const sphereGeometry = new THREE.SphereGeometry(0.5, 32, 32) // 创建一个几何体
const sphereMaterial = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0x00ff00 }) // 创建一个球体材质
const shpereMesh = new THREE.Mesh(sphereGeometry, sphereMaterial) // 创建一个球体网格
// 将网格添加到3D场景中
scene.add(shpereMesh)
// 创建一个物理世界的平面
// const planeShape = new CANNON.Plane()
const planeShape = new CANNON.Box(new CANNON.Vec3(5, 0.1, 5))
// 创建一个刚体
const planeBody = new CANNON.Body({
// mass: 0, // 设置质量为0,不受碰撞的影响
shape: planeShape,
position: new CANNON.Vec3(0, 0, 0),
type: CANNON.Body.STATIC // 设置物体为静态,不受碰撞的影响
})
// 设置刚体旋转(设置旋转X轴)
planeBody.quaternion.setFromAxisAngle(new CANNON.Vec3(1, 0, 0), 0.1)
// 将刚体添加到物理世界当中
world.addBody(planeBody)
// 物理世界创建的东西不显示,所以我们要再通过three.js再创建一个平面
// const planeGeometry = new THREE.PlaneGeometry(10, 10) // 因为渲染的东西不是无限衍生,这里给10x10
const planeGeometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(10, 0.2, 10)
// 创建一个平面材质
const planeMaterial = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0xffff00 })
// 创建一个平面网格
const planeMesh = new THREE.Mesh(planeGeometry, planeMaterial)
// 旋转平面90度让其平铺
planeMesh.rotation.x = 0.1
// 将网格添加到3D场景当中
scene.add(planeMesh)
// 渲染
let clock = new THREE.Clock()
const animate = () => {
// 获取了两次渲染之间的时间差,通常用于控制动画和物理模拟。
let delta = clock.getDelta()
// 使用时间差来推进物理世界的模拟
world.step(delta)
// 更新球体网格的位置和旋转
// 将物理引擎中球体的位置赋值给 Three.js 中球体网格(shpereMesh)的位置,从而将物理模拟的结果更新到可视化场景中。
shpereMesh.position.copy(sphereBody.position)
// 将物理引擎中球体的旋转状态赋值给 Three.js 中球体网格(shpereMesh)的旋转状态,确保网格的旋转与物理模拟一致。
shpereMesh.quaternion.copy(sphereBody.quaternion)
controls.update()
renderer.render(scene, camera)
requestAnimationFrame(animate)
}
animate()
return () => {
<div></div>
}
}
})
材质与摩擦系数设置
cannon的材质可以模拟我们现实生活当中的物理的效果,比如说我们可以设置它的摩擦系数,弹性系数来实现我们这个物体的滑动的有摩擦的效果。借助上面的案例,我们将球体换成立方体,因为要创建多个立方体,这里我们设置一个变量用于存储
// 创建网格数组
let phyMeshes: any[] = [] // 物理世界
let meshes: any[] = [] // 渲染世界
// 创建物理立方体
const boxShape = new CANNON.Box(new CANNON.Vec3(0.5, 0.5, 0.5))
// 设置立方体的材质
const boxMaterialCon = new CANNON.Material("boxMaterial")
// 创建一个刚体
const boxBody = new CANNON.Body({
shape: boxShape,
position: new CANNON.Vec3(0, 15, 0),
mass: 1,
material: boxMaterialCon
})
// 将刚体添加到物理世界当中
world.addBody(boxBody)
phyMeshes.push(boxBody)
// 创建立方体几何体
const boxGeometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(1, 1, 1)
// 创建立方体材质
const boxMaterial = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0x00ff00 })
// 创建立方体网格
const boxMesh = new THREE.Mesh(boxGeometry, boxMaterial)
// 将网格添加到3D场景当中
scene.add(boxMesh)
meshes.push(boxMesh)
在渲染函数处,我们变量数组来推进物理世界模拟:

最终得到是效果如下:

接下来我们添加第二个物体,将第二个物体的摩擦系数设置为0,第一个物体和平面的摩擦系数设置为0.7,代码如下:
// 创建网格数组
let phyMeshes: any[] = [] // 物理世界
let meshes: any[] = [] // 渲染世界
// 创建物理立方体
const boxShape = new CANNON.Box(new CANNON.Vec3(0.5, 0.5, 0.5))
// 设置立方体的材质
const boxMaterialCon = new CANNON.Material("boxMaterial")
boxMaterialCon.friction = 0.7
// 创建一个刚体
const boxBody = new CANNON.Body({
shape: boxShape,
position: new CANNON.Vec3(0, 15, 0),
mass: 1,
material: boxMaterialCon
})
// 将刚体添加到物理世界当中
world.addBody(boxBody)
phyMeshes.push(boxBody)
// 创建立方体几何体
const boxGeometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(1, 1, 1)
// 创建立方体材质
const boxMaterial = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0x00ff00 })
// 创建立方体网格
const boxMesh = new THREE.Mesh(boxGeometry, boxMaterial)
// 将网格添加到3D场景当中
scene.add(boxMesh)
meshes.push(boxMesh)
// 创建第二个物理立方体(使用第一个物理立方体的内容,材质不同)
const boxSlipperyMaterial = new CANNON.Material("boxSlipperyMaterial")
boxSlipperyMaterial.friction = 0 // 摩擦系数为0
// 创建刚体
const boxBody2 = new CANNON.Body({
shape: boxShape,
position: new CANNON.Vec3(1, 5, 0), // 区别于第一个物体,位置改变一下
mass: 1,
material: boxSlipperyMaterial
})
// 将刚体添加到物理世界当中
world.addBody(boxBody2)
phyMeshes.push(boxBody2)
// 创建立方体几何体(使用第一个物体的内容)
const boxMesh2 = new THREE.Mesh(boxGeometry, boxMaterial)
// 将网格添加到3D场景当中
scene.add(boxMesh2)
meshes.push(boxMesh2)
// 创建一个物理世界的平面
// const planeShape = new CANNON.Plane()
const planeShape = new CANNON.Box(new CANNON.Vec3(5, 0.1, 5))
// 创建一个刚体
const planeBody = new CANNON.Body({
// mass: 0, // 设置质量为0,不受碰撞的影响
shape: planeShape,
position: new CANNON.Vec3(0, 0, 0),
type: CANNON.Body.STATIC, // 设置物体为静态,不受碰撞的影响
material: boxMaterialCon
})
// 设置刚体旋转(设置旋转X轴)
planeBody.quaternion.setFromAxisAngle(new CANNON.Vec3(1, 0, 0), 0.1)
// 将刚体添加到物理世界当中
world.addBody(planeBody)
// 物理世界创建的东西不显示,所以我们要再通过three.js再创建一个平面
// const planeGeometry = new THREE.PlaneGeometry(10, 10) // 因为渲染的东西不是无限衍生,这里给10x10
const planeGeometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(10, 0.2, 10)
// 创建一个平面材质
const planeMaterial = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0xffff00 })
// 创建一个平面网格
const planeMesh = new THREE.Mesh(planeGeometry, planeMaterial)
// 旋转平面90度让其平铺
planeMesh.rotation.x = 0.1
// 将网格添加到3D场景当中
scene.add(planeMesh)
最终得到的效果如下,可以看到我们设置的第二个物体因为很光滑,所以很容易就滑落下去:

弹性与接触材质设置
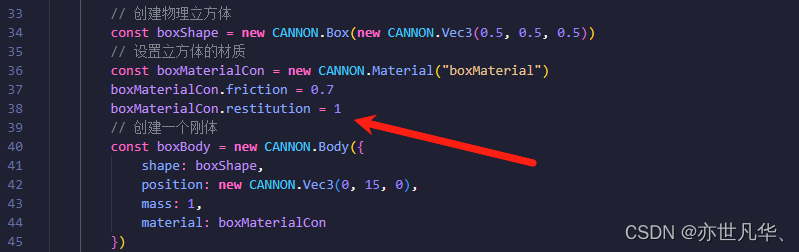
上文我们介绍了摩擦效果的操作,接下来我们继续开始讲解物体的弹性操作,我们根据上文的代码,再创建第三个立方体,然后给该立方体添加弹性系数
// 创建第三个物理立方体(使用第一个物理立方体的内容,材质不同)
const boxBouncyMaterial = new CANNON.Material("boxBouncyMaterial")
boxBouncyMaterial.friction = 0.1
boxBouncyMaterial.restitution = 1 // 设置弹性系数为1
// 创建刚体
const boxBody3 = new CANNON.Body({
shape: boxShape,
mass: 1,
position: new CANNON.Vec3(2, 5, 3),
material: boxBouncyMaterial
})
// 将刚体添加到物理世界当中
world.addBody(boxBody3)
phyMeshes.push(boxBody3)
// 创建几何体(使用第一个立方体的内容以及材质)
const boxMesh3 = new THREE.Mesh(boxGeometry, boxMaterial) // 添加网格
// 将网格添加到3D场景当中
scene.add(boxMesh3)
meshes.push(boxMesh3)
给立方体设置弹性系数之后,如果我们想让弹性效果奏效的话,我们也需要给平面网格设置相同的弹性系数,因为平面网格使用的材质是第一个立方体的材质,所以我们只要给第一个立方体设置弹性系数即可,如下:
最终得到的效果如下,可以看到设置高度高的物体,从高处下落反弹的效果是很直观的:

当然我们也没有必要单独设置一下立方体和平面的弹性和摩擦系数,我们也可以通过接触材质的系数设置两个材质之间的一个弹性和摩擦系数,来实现相应的效果,如下:
// 创建第三个物理立方体(使用第一个物理立方体的内容,材质不同)
const boxBouncyMaterial = new CANNON.Material("boxBouncyMaterial")
// boxBouncyMaterial.friction = 0.1
// boxBouncyMaterial.restitution = 1 // 设置弹性系数为1
// 创建刚体
const boxBody3 = new CANNON.Body({
shape: boxShape,
mass: 1,
position: new CANNON.Vec3(2, 5, 3),
material: boxBouncyMaterial
})
// 将刚体添加到物理世界当中
world.addBody(boxBody3)
phyMeshes.push(boxBody3)
// 创建几何体(使用第一个立方体的内容以及材质)
const boxMesh3 = new THREE.Mesh(boxGeometry, boxMaterial) // 添加网格
// 将网格添加到3D场景当中
scene.add(boxMesh3)
meshes.push(boxMesh3)
// 定义接触材质
const material3toplane = new CANNON.ContactMaterial(
boxMaterialCon,
boxBouncyMaterial,
{
friction: 0,
restitution: 1
}
)
// 将接触材质添加到物理世界当中
world.addContactMaterial(material3toplane)
最终呈现的效果依然很明显:

碰撞与碰撞组
Cannon中的碰撞指的是游戏开发中物体之间的相互作用,通常包括物体之间的碰撞检测和碰撞响应两个部分。碰撞检测用于判断物体是否发生了碰撞,而碰撞响应则是在发生碰撞时对物体进行相应的处理,比如改变物体的速度、方向等。如下我们设置代码来实现:
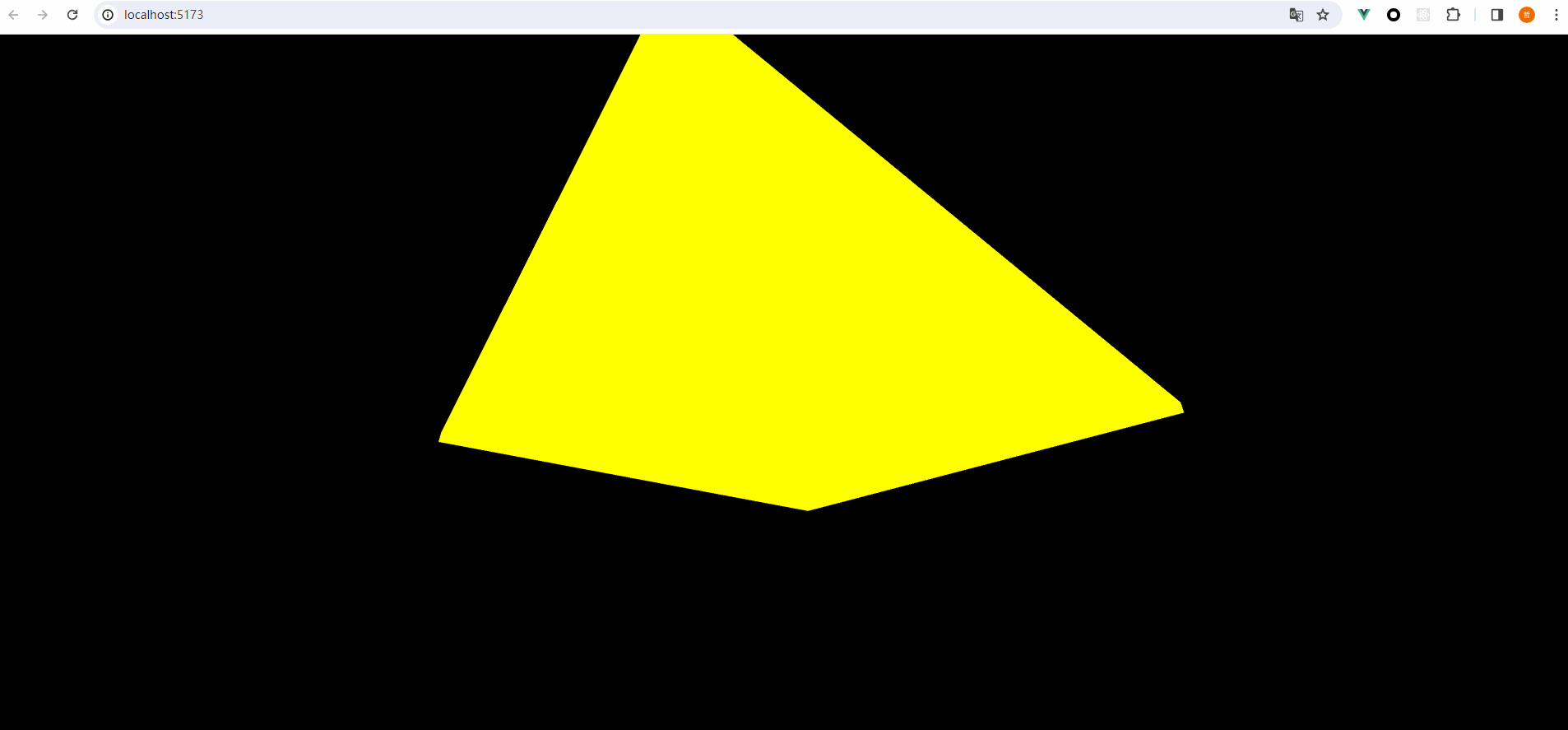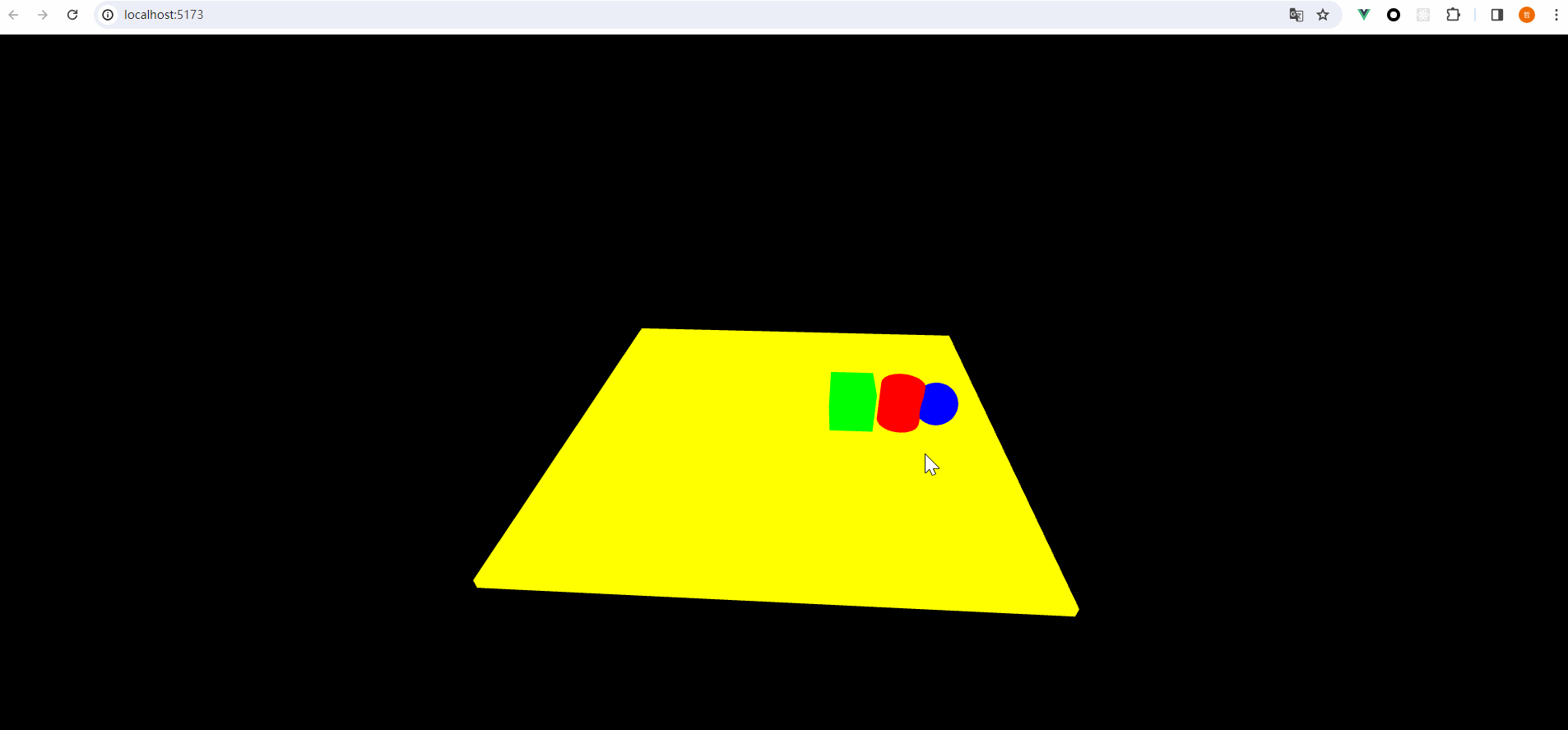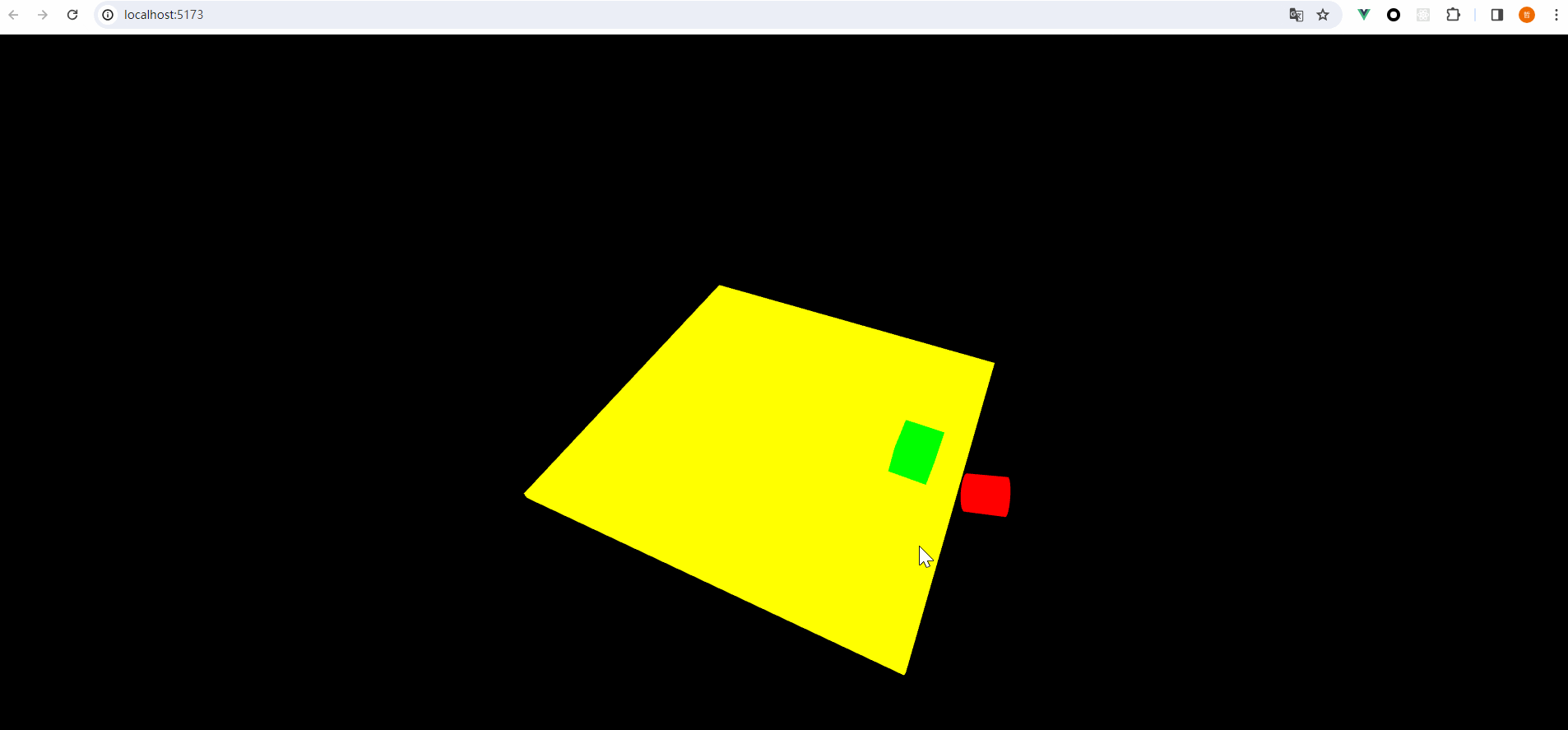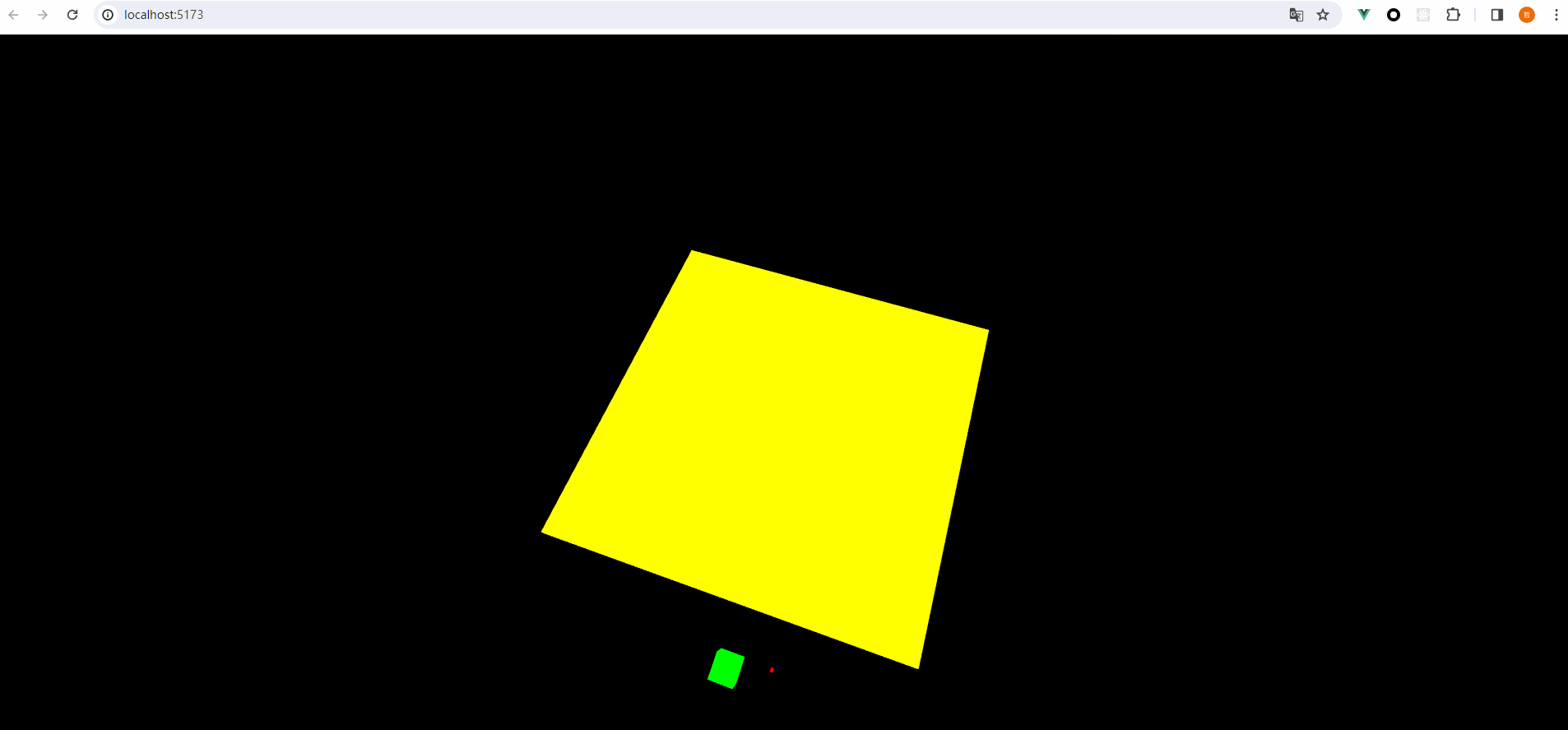
依次创建立方体、球体、圆柱体到场景当中,举例代码如下:

接下来我们给创建到场景的立方体添加一个初速度使其运动来碰撞另外两个物体,如下:

这里给出完整的代码来给大家进行学习:
import { defineComponent } from "vue";
import * as THREE from 'three'
import { OrbitControls } from 'three/examples/jsm/controls/OrbitControls.js'
import * as CANNON from 'cannon-es'
import './index.scss'
export default defineComponent({
setup() {
// 初始化物理世界
const world = new CANNON.World()
// 初始化物理世界的重力
world.gravity.set(0, -9.82, 0)
// 初始化3D世界
const scene = new THREE.Scene()
// 初始化相机
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(75, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 0.1, 1000)
camera.position.z = 8
camera.position.y = 5
camera.position.x = 2
// 初始化渲染器
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({ antialias: true })
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight)
document.body.appendChild(renderer.domElement)
// 初始化控制器
const controls = new OrbitControls(camera, renderer.domElement)
controls.enableDamping = true
// 创建网格数组
let phyMeshes: any[] = [] // 物理世界
let meshes: any[] = [] // 渲染世界
// 创建物理立方体
const boxShape = new CANNON.Box(new CANNON.Vec3(0.5, 0.5, 0.5))
// 设置立方体的材质
const boxMaterialCon = new CANNON.Material("boxMaterial")
boxMaterialCon.friction = 0
// 创建一个刚体
const boxBody = new CANNON.Body({
shape: boxShape,
position: new CANNON.Vec3(2, 0.8, 0),
mass: 1,
material: boxMaterialCon
})
// 将刚体添加到物理世界当中
world.addBody(boxBody)
phyMeshes.push(boxBody)
// 创建立方体几何体
const boxGeometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(1, 1, 1)
// 创建立方体材质
const boxMaterial = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0x00ff00 })
// 创建立方体网格
const boxMesh = new THREE.Mesh(boxGeometry, boxMaterial)
// 将网格添加到3D场景当中
scene.add(boxMesh)
meshes.push(boxMesh)
// 创建物理球
const spereShape = new CANNON.Sphere(0.5)
// 创建一个刚体
const sphereBody = new CANNON.Body({
shape: spereShape,
position: new CANNON.Vec3(0, 0.8, 0),
mass: 1,
material: boxMaterialCon
})
// 将刚体添加到物理世界当中
world.addBody(sphereBody)
phyMeshes.push(sphereBody)
// 创建球的几何体
const sphereGeometry = new THREE.SphereGeometry(0.5, 32, 32)
// 创建球的材质
const sphereMaterial = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0x0000ff })
// 创建球网格
const sphereMesh = new THREE.Mesh(sphereGeometry, sphereMaterial)
// 将网格添加到3D场景当中
scene.add(sphereMesh)
meshes.push(sphereMesh)
// 创建物理圆柱体
const cylinderShape = new CANNON.Cylinder(0.5, 0.5, 1, 32)
// 创建一个刚体
const cylinderBody = new CANNON.Body({
shape: cylinderShape,
position: new CANNON.Vec3(-2, 0.8, 0),
mass: 1,
material: boxMaterialCon
})
// 将刚体添加到物理世界当中
world.addBody(cylinderBody)
phyMeshes.push(cylinderBody)
// 创建圆柱体几何体
const cylinderGeometry = new THREE.CylinderGeometry(0.5 ,0.5, 1, 32)
// 创建圆柱体材质
const cylinderMaterial = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0xff0000 })
// 创建圆柱体网格
const cylinderMesh = new THREE.Mesh(cylinderGeometry, cylinderMaterial)
// 将网格添加到3D场景当中
scene.add(cylinderMesh)
meshes.push(cylinderMesh)
// 创建一个物理世界的平面
// const planeShape = new CANNON.Plane()
const planeShape = new CANNON.Box(new CANNON.Vec3(5, 0.1, 5))
// 创建一个刚体
const planeBody = new CANNON.Body({
// mass: 0, // 设置质量为0,不受碰撞的影响
shape: planeShape,
position: new CANNON.Vec3(0, 0, 0),
type: CANNON.Body.STATIC, // 设置物体为静态,不受碰撞的影响
material: boxMaterialCon
})
// 设置刚体旋转(设置旋转X轴)
// planeBody.quaternion.setFromAxisAngle(new CANNON.Vec3(1, 0, 0), 0.1)
// 将刚体添加到物理世界当中
world.addBody(planeBody)
// 物理世界创建的东西不显示,所以我们要再通过three.js再创建一个平面
// const planeGeometry = new THREE.PlaneGeometry(10, 10) // 因为渲染的东西不是无限衍生,这里给10x10
const planeGeometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(10, 0.2, 10)
// 创建一个平面材质
const planeMaterial = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0xffff00 })
// 创建一个平面网格
const planeMesh = new THREE.Mesh(planeGeometry, planeMaterial)
// 旋转平面90度让其平铺
// planeMesh.rotation.x = 0.1
// 将网格添加到3D场景当中
scene.add(planeMesh)
// 设置立方体的初始速度
boxBody.velocity.set(-2, 0, 0)
// 渲染
let clock = new THREE.Clock()
const animate = () => {
// 获取了两次渲染之间的时间差,通常用于控制动画和物理模拟。
let delta = clock.getDelta()
world.step(delta)
// 使用时间差来推进物理世界的模拟
for(let i = 0; i < phyMeshes.length; i++) {
meshes[i].position.copy(phyMeshes[i].position)
meshes[i].quaternion.copy(phyMeshes[i].quaternion)
}
controls.update()
renderer.render(scene, camera)
requestAnimationFrame(animate)
}
animate()
return () => {
<div></div>
}
}
})
接下来实现碰撞组,碰撞组是为了更高效地管理和处理碰撞而引入的概念。通过将具有相似碰撞特性的物体分组,可以在碰撞检测和碰撞响应时只考虑同一组内的物体之间的碰撞,从而减少不必要的计算量,提高游戏的性能和效率。代码如下:
我们设置立方体为组1,然后碰撞掩码就是能够和谁发生碰撞,我们设置立方体可以和所有物体碰撞:

在球体的分组当中,我们设置碰撞掩码如下,可以看到我们的球不能碰撞圆柱体:

最终呈现的效果如下:
给出案例的完整代码供大家学习:
import { defineComponent } from "vue";
import * as THREE from 'three'
import { OrbitControls } from 'three/examples/jsm/controls/OrbitControls.js'
import * as CANNON from 'cannon-es'
import './index.scss'
export default defineComponent({
setup() {
// 初始化物理世界
const world = new CANNON.World()
// 初始化物理世界的重力
world.gravity.set(0, -9.82, 0)
// 初始化3D世界
const scene = new THREE.Scene()
// 初始化相机
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(75, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 0.1, 1000)
camera.position.z = 8
camera.position.y = 5
camera.position.x = 2
// 初始化渲染器
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({ antialias: true })
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight)
document.body.appendChild(renderer.domElement)
// 初始化控制器
const controls = new OrbitControls(camera, renderer.domElement)
controls.enableDamping = true
// 创建网格数组
let phyMeshes: any[] = [] // 物理世界
let meshes: any[] = [] // 渲染世界
// 设置碰撞组,数值要用2的幂
const GROUP1 = 1 // 分组立方体
const GROUP2 = 2 // 分组球体
const GROUP3 = 4 // 分组圆柱体
const GROUP4 = 8 // 分组平面
// 创建物理立方体
const boxShape = new CANNON.Box(new CANNON.Vec3(0.5, 0.5, 0.5))
// 设置立方体的材质
const boxMaterialCon = new CANNON.Material("boxMaterial")
boxMaterialCon.friction = 0
// 创建一个刚体
const boxBody = new CANNON.Body({
shape: boxShape,
position: new CANNON.Vec3(2, 0.8, 0),
mass: 1,
material: boxMaterialCon,
collisionFilterGroup: GROUP1, // 设置碰撞组
collisionFilterMask: GROUP2 | GROUP3 | GROUP4, // 碰撞掩码,可以和二组和三、四组碰撞
})
// 将刚体添加到物理世界当中
world.addBody(boxBody)
phyMeshes.push(boxBody)
// 创建立方体几何体
const boxGeometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(1, 1, 1)
// 创建立方体材质
const boxMaterial = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0x00ff00 })
// 创建立方体网格
const boxMesh = new THREE.Mesh(boxGeometry, boxMaterial)
// 将网格添加到3D场景当中
scene.add(boxMesh)
meshes.push(boxMesh)
// 创建物理球
const spereShape = new CANNON.Sphere(0.5)
// 创建一个刚体
const sphereBody = new CANNON.Body({
shape: spereShape,
position: new CANNON.Vec3(0, 0.8, 0),
mass: 1,
material: boxMaterialCon,
collisionFilterGroup: GROUP2, // 设置碰撞组
collisionFilterMask: GROUP1 | GROUP4, // 碰撞掩码,可以和一、四组碰撞
})
// 将刚体添加到物理世界当中
world.addBody(sphereBody)
phyMeshes.push(sphereBody)
// 创建球的几何体
const sphereGeometry = new THREE.SphereGeometry(0.5, 32, 32)
// 创建球的材质
const sphereMaterial = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0x0000ff })
// 创建球网格
const sphereMesh = new THREE.Mesh(sphereGeometry, sphereMaterial)
// 将网格添加到3D场景当中
scene.add(sphereMesh)
meshes.push(sphereMesh)
// 创建物理圆柱体
const cylinderShape = new CANNON.Cylinder(0.5, 0.5, 1, 32)
// 创建一个刚体
const cylinderBody = new CANNON.Body({
shape: cylinderShape,
position: new CANNON.Vec3(-2, 0.8, 0),
mass: 1,
material: boxMaterialCon,
collisionFilterGroup: GROUP3, // 设置碰撞组
collisionFilterMask: GROUP1 | GROUP4, // 碰撞掩码,可以和一、四组碰撞
})
// 将刚体添加到物理世界当中
world.addBody(cylinderBody)
phyMeshes.push(cylinderBody)
// 创建圆柱体几何体
const cylinderGeometry = new THREE.CylinderGeometry(0.5 ,0.5, 1, 32)
// 创建圆柱体材质
const cylinderMaterial = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0xff0000 })
// 创建圆柱体网格
const cylinderMesh = new THREE.Mesh(cylinderGeometry, cylinderMaterial)
// 将网格添加到3D场景当中
scene.add(cylinderMesh)
meshes.push(cylinderMesh)
// 创建一个物理世界的平面
// const planeShape = new CANNON.Plane()
const planeShape = new CANNON.Box(new CANNON.Vec3(5, 0.1, 5))
// 创建一个刚体
const planeBody = new CANNON.Body({
// mass: 0, // 设置质量为0,不受碰撞的影响
shape: planeShape,
position: new CANNON.Vec3(0, 0.1, 0),
type: CANNON.Body.STATIC, // 设置物体为静态,不受碰撞的影响
material: boxMaterialCon,
collisionFilterGroup: GROUP4, // 设置碰撞组
collisionFilterMask: GROUP1 | GROUP2 | GROUP3, // 碰撞掩码,可以和一组、二组和三组碰撞
})
// 设置刚体旋转(设置旋转X轴)
// planeBody.quaternion.setFromAxisAngle(new CANNON.Vec3(1, 0, 0), 0.1)
// 将刚体添加到物理世界当中
world.addBody(planeBody)
// 物理世界创建的东西不显示,所以我们要再通过three.js再创建一个平面
// const planeGeometry = new THREE.PlaneGeometry(10, 10) // 因为渲染的东西不是无限衍生,这里给10x10
const planeGeometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(10, 0.2, 10)
// 创建一个平面材质
const planeMaterial = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0xffff00 })
// 创建一个平面网格
const planeMesh = new THREE.Mesh(planeGeometry, planeMaterial)
// 旋转平面90度让其平铺
// planeMesh.rotation.x = 0.1
// 将网格添加到3D场景当中
scene.add(planeMesh)
// 设置立方体的初始速度
boxBody.velocity.set(-2, 0, 0)
// 渲染
let clock = new THREE.Clock()
const animate = () => {
// 获取了两次渲染之间的时间差,通常用于控制动画和物理模拟。
let delta = clock.getDelta()
world.step(delta)
// 使用时间差来推进物理世界的模拟
for(let i = 0; i < phyMeshes.length; i++) {
meshes[i].position.copy(phyMeshes[i].position)
meshes[i].quaternion.copy(phyMeshes[i].quaternion)
}
controls.update()
renderer.render(scene, camera)
requestAnimationFrame(animate)
}
animate()
return () => {
<div></div>
}
}
})
本篇文章对canon的学习暂时结束,下篇文章将对canon更加深入讲解!!!
版权归原作者 亦世凡华、 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。