
深入理解RabbitMQ交换机的原理与应用
引言
在当今的分布式系统和微服务架构中,消息中间件扮演着至关重要的角色。RabbitMQ作为一个功能强大的消息中间件,其交换机是其中核心的组件之一。本文将深入探讨RabbitMQ交换机的原理和应用,帮助读者更好地理解和应用消息队列技术。
1. RabbitMQ交换机简介介绍
1.1 什么是RabbitMQ?
RabbitMQ是一个开源的消息代理软件,它遵循AMQP(高级消息队列协议)标准,用于在分布式系统中存储和转发消息。作为消息中间件,RabbitMQ扮演着消息传递和消息队列的角色,允许应用程序之间进行异步通信。
1.1.1 消息中间件的作用
消息中间件的作用在于解耦消息的发送者和接收者,实现异步通信,提高系统的可伸缩性和弹性。它可以协调不同服务之间的通信,确保消息的可靠传递,并提供消息的持久化、路由和传输等功能。
1.1.2 RabbitMQ的特点和优势
RabbitMQ具有高可靠性、灵活的路由、消息持久化、集群和分布式部署支持等特点。它的优势在于支持多种消息传递模式,如点对点、发布/订阅和路由等,同时提供了丰富的插件和管理工具。
1.2 RabbitMQ的基本概念
1.2.1 队列
队列是消息的容器,用于存储消息直到消费者准备接收它们。消息可以被一个或多个消费者订阅。
1.2.2 交换机
交换机是消息的分发中心,它接收来自生产者的消息,并将它们路由到一个或多个队列。
1.2.3 路由键
路由键是生产者在将消息发送到交换机时附加的关键字,交换机根据路由键将消息路由到一个或多个队列。
1.3 交换机的作用和分类
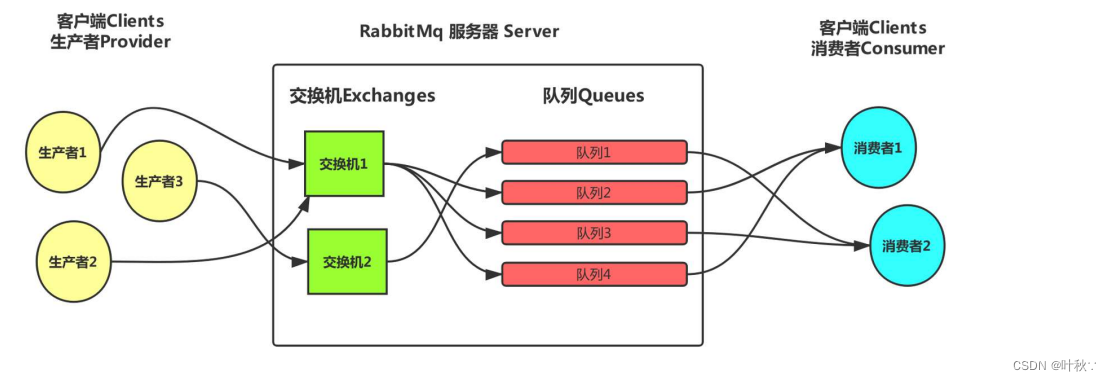
交换机负责接收来自生产者的消息,并将它们路由到一个或多个队列。RabbitMQ提供了不同类型的交换机,包括直连交换机、扇出交换机、主题交换机和头交换机。
1.3.1 直连交换机(direct exchange)
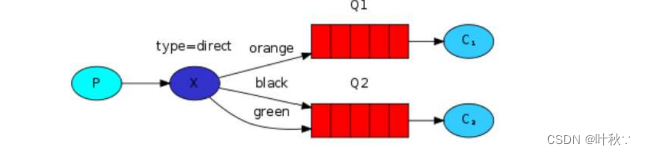
直连交换机根据消息的路由键将消息路由到特定的队列。它是最简单的交换机类型,路由键与队列绑定的路由键完全匹配时,消息才会被路由到相应的队列。
1.3.2 扇出交换机(fanout exchange)
扇出交换机会将消息路由到与之绑定的所有队列,忽略消息的路由键。这种模式适合广播消息给多个消费者的场景。
1.3.3 主题交换机(topic exchange)
主题交换机根据消息的路由键和通配符将消息路由到一个或多个队列。它提供了更灵活的路由规则,可以根据路由键的模式进行匹配。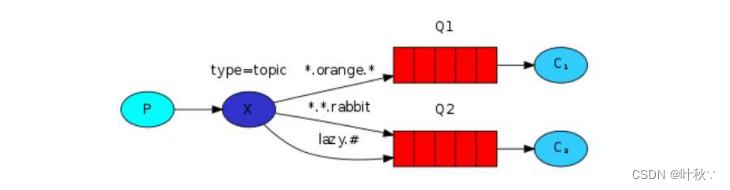
1.3.4 头交换机(headers exchange)
头交换机使用消息的属性(headers)来进行匹配,而不是路由键。这种交换机类型提供了更复杂的匹配规则,可以根据消息的属性进行匹配和路由。
1.3.5 死信交换机

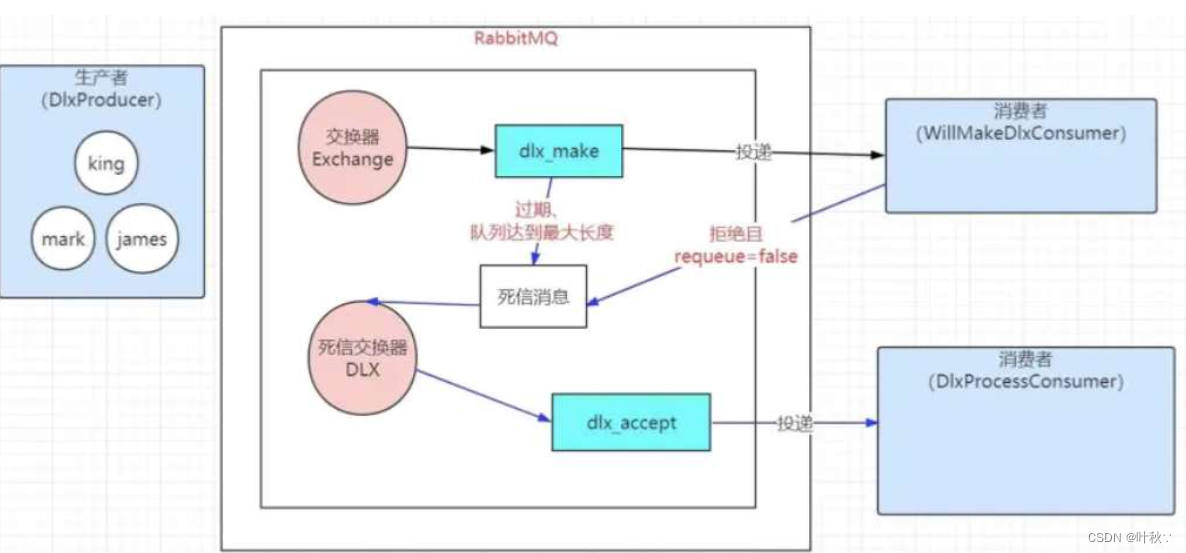
2. RabbitMQ交换机应用
2.1直连交换机实践
创建好队列与交换机,并且绑定
@BeanpublicQueuequeue1(){returnnewQueue("queue1");}@BeanpublicQueuequeue2(){returnnewQueue("queue2");}@BeanpublicDirectExchangedrectexchange(){returnnewDirectExchange("drectexchange");}@BeanpublicBindingbingding1(){returnBindingBuilder.bind(queue1()).to(drectexchange()).with("a");}@BeanpublicBindingbingding2(){returnBindingBuilder.bind(queue2()).to(drectexchange()).with("b");}
生产者方法
@RequestMapping("/send3")publicStringsend3(){//向消息队列发送消息
amqpTemplate.convertAndSend("drectexchange","a","hello");return"哈哈;";}
消费者监听
packagecom.example.consumer;importlombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;importorg.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;importorg.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;importorg.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component@SuppressWarnings("all")@Slf4j@RabbitListener(queues ="queue1")publicclassReceiverQ1{@RabbitHandlerpublicvoidprocess(String msg){
log.warn("Q1接收到:"+ msg);}}
packagecom.example.consumer;importlombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;importorg.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;importorg.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;importorg.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component@SuppressWarnings("all")@Slf4j@RabbitListener(queues ="queue2")publicclassReceiverQ2{@RabbitHandlerpublicvoidprocess(String msg){
log.warn("Q2接收到:"+ msg);}}
运行一遍send3方法
2.2 主题交换机实践
前提准备,打开RabbitMQ服务,参考 构建高可用消息队列系统 01
进入实战
创建好队列与交换机,并且绑定
@BeanpublicTopicExchangetopicExchange(){returnnewTopicExchange("topicExchange");}@BeanpublicBindingbingding3(){returnBindingBuilder.bind(queue1()).to(topicExchange()).with("*.*.a");}@BeanpublicBindingbingding4(){returnBindingBuilder.bind(queue2()).to(topicExchange()).with("*.*.b");}@BeanpublicBindingbingding5(){returnBindingBuilder.bind(queue1()).to(topicExchange()).with("mq.#");}@BeanpublicBindingbingding6(){returnBindingBuilder.bind(queue2()).to(topicExchange()).with("mq.#");}
生产者方法
@RequestMapping("/send4")publicStringsend4(String rex){//向消息队列发送消息
amqpTemplate.convertAndSend("topicExchange",rex,"hello");return"哈哈;";}
消费者监听在直连交换机上有
测试1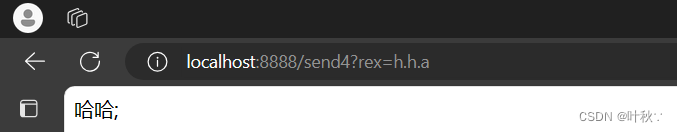

测试2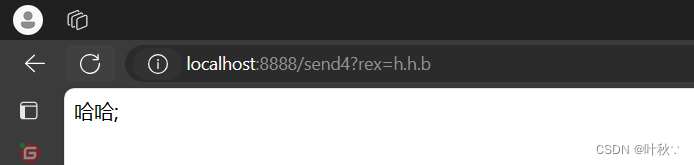

测试3
mq打头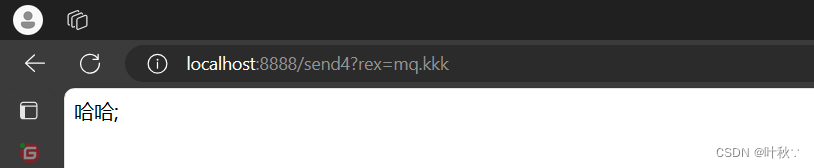

2.3 扇形交换机实践
创建好队列与交换机,并且绑定
@BeanpublicFanoutExchangefanoutExchange(){returnnewFanoutExchange("fanoutExchange");}@BeanpublicBindingbingding7(){returnBindingBuilder.bind(queue1()).to(fanoutExchange());}@BeanpublicBindingbingding8(){returnBindingBuilder.bind(queue2()).to(fanoutExchange());}
生产者方法
生产者调用convertAndSend时第二个参数必须要有,可以给null值,否则报错
@RequestMapping("/send5")publicStringsend5(){//向消息队列发送消息
amqpTemplate.convertAndSend("fanoutExchange","","hello");return"哈哈;";}
消费者监听在直连交换机上有
测试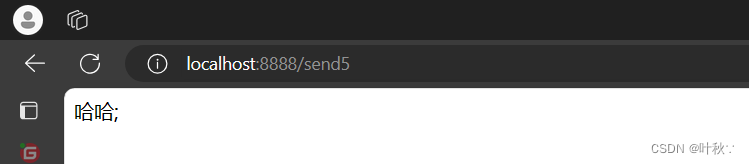

总结
RabbitMQ交换机作为消息中间件的核心组件,其灵活的路由规则和丰富的特性为分布式系统和微服务架构提供了强大的消息通信支持。通过深理解RabbitMQ交换机的原理和应用,可以更好地设计和构建可靠的消息传递系统,为复杂的应用场景提供稳定高效的消息通信机制。
版权归原作者 叶秋∵ 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。