🍓个人主页:个人主页
🍒系列专栏:SSM框架
💬推荐一款模拟面试、刷题神器,从基础到大厂面试题👉点击跳转刷题网站进行注册学习
1.查询一个实体类对象
/**
根据用户id查询用户信息
@param id
@return
*/
User getUserById(@Param("id") int id);
<select id="getUserById" resultType="User">
select * from t_user where id=#{id};
</select>
@Test
public void test() {
SqlSessionUtils sqlSessionUtils = new SqlSessionUtils();
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionUtils.getSqlSession();
SelectMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(SelectMapper.class);
User user = mapper.getUserById(2);
System.out.println(user);
}
表:
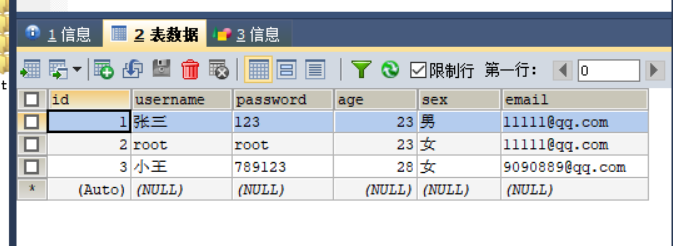
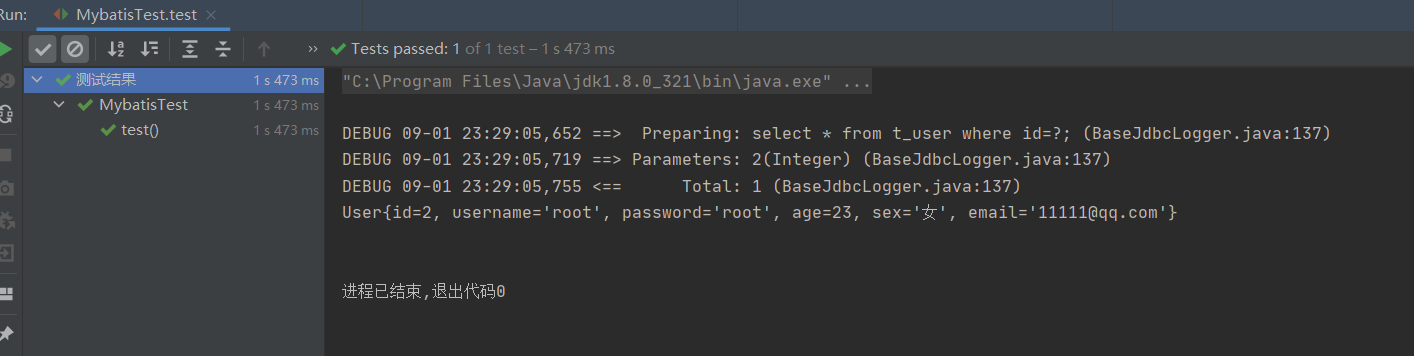
** 查询结果:**
**假如,我把后面的条件删除,会发生什么情况呢? **
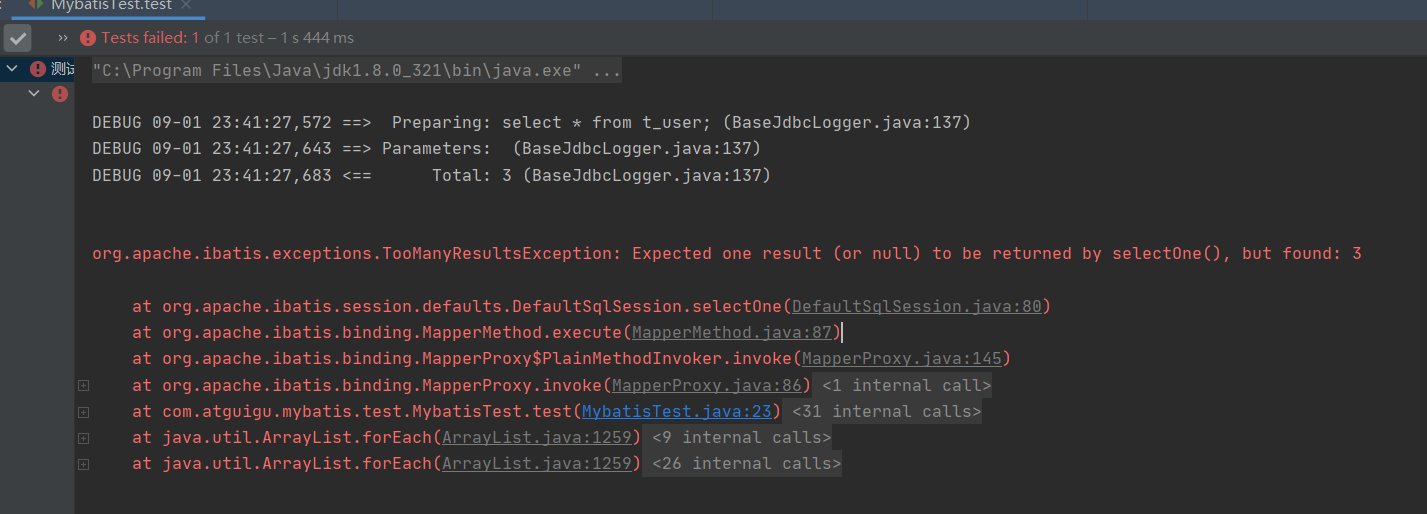
org.apache.ibatis.exceptions.TooManyResultsException: Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: 3
**当查询的数据为多条时,不能使用实体类作为返回值,否则会抛出异常 **
TooManyResultsException;但是若查询的数据只有一条,可以使用实体类或集合作为返回值
*2.查询一个list*集合 **
/**
查询所有用户信息
@return
*/
List<User> getUserList();
<select id="getAllUser" resultType="User">
select * from t_user;
</select>
测试类:
@Test
public void test2(){
SqlSessionUtils sqlSessionUtils = new SqlSessionUtils();
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionUtils.getSqlSession();
SelectMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(SelectMapper.class);
List<User> allUser = mapper.getAllUser();
allUser.forEach(System.out::println);
}
** 查询结果:**
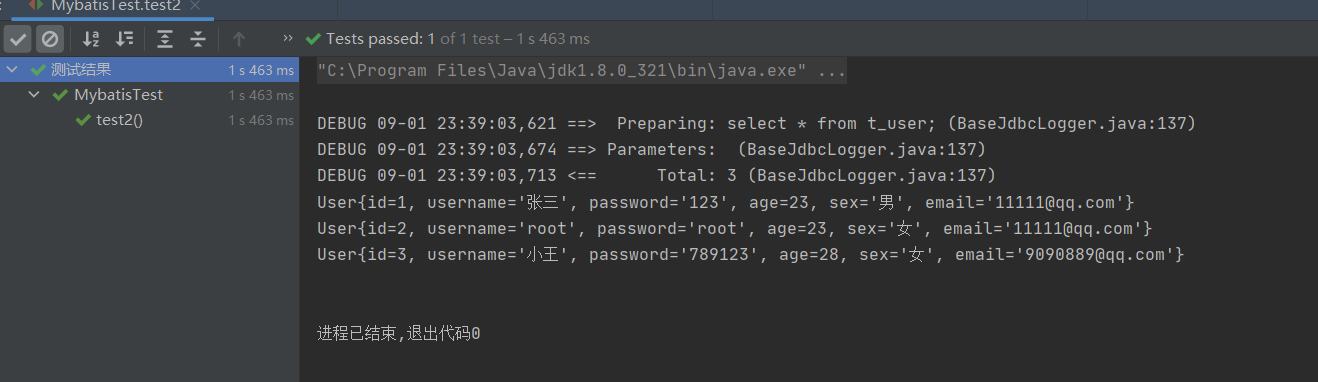
3.查询单个数据
/**
查询用户的总记录数
@return
在MyBatis中,对于Java中常用的类型都设置了类型别名
例如: java.lang.Integer-->int|integer
例如: int-->_int|_integer
例如: Map-->map,List-->list
*/
int getCount();
<select id="getCount" resultType="java.lang.Integer">
select count(id) from t_user;
</select>
测试类:
@Test
public void test3(){
SqlSessionUtils sqlSessionUtils = new SqlSessionUtils();
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionUtils.getSqlSession();
SelectMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(SelectMapper.class);
Integer count = mapper.getCount();
System.out.println(count);
}
表:
查询结果:
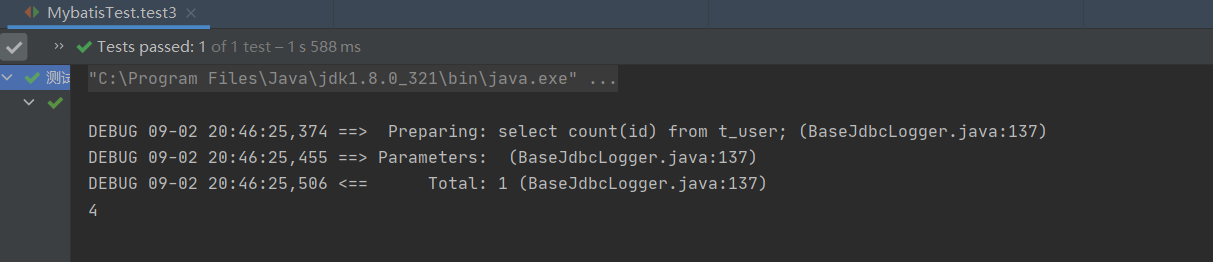
4.查询一条数据为map集合
/**
根据用户id查询用户信息为map集合
@param id
@return
*/
Map<String, Object> getUserToMap(@Param("id") int id);
<!--Map<String, Object> getUserToMap(@Param("id") int id);-->
<select id="getUserToMap" resultType="map">
select * from t_user where id = #{id}
</select>
测试类:
@Test
public void test4(){
SqlSessionUtils sqlSessionUtils = new SqlSessionUtils();
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionUtils.getSqlSession();
SelectMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(SelectMapper.class);
Map<String, Object> map = mapper.getUserToMap(4);
System.out.println(map);
}
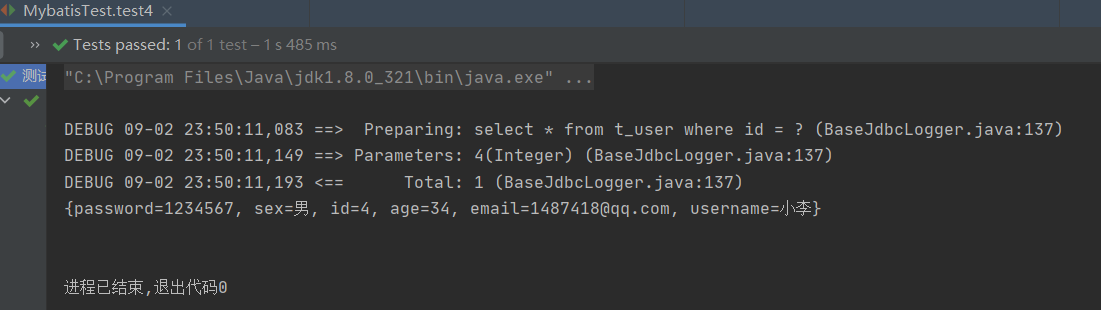
*5.查询多条数据为map*集合
**①方式一 **
/**
查询所有用户信息为map集合
@return
将表中的数据以map集合的方式查询,一条数据对应一个map;若有多条数据,就会产生多个map集合,此
时可以将这些map放在一个list集合中获取
*/
List<Map<String, Object>> getAllUserToMap();
<!--Map<String, Object> getAllUserToMap();-->
<select id="getAllUserToMap" resultType="map">
select * from t_user
</select>
测试类:
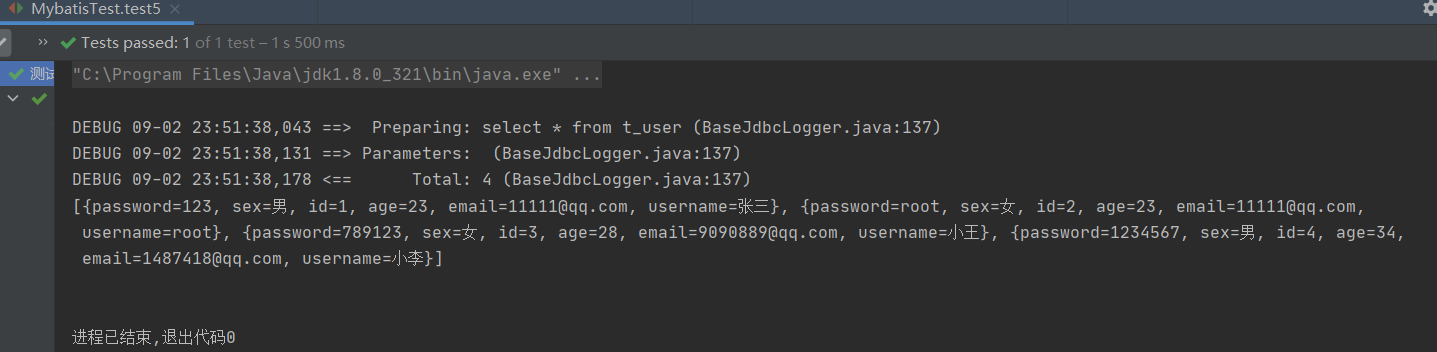
@Test
public void test5(){
SqlSessionUtils sqlSessionUtils = new SqlSessionUtils();
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionUtils.getSqlSession();
SelectMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(SelectMapper.class);
List<Map<String, Object>> allUserToMap = mapper.getAllUserToMap();
System.out.println(allUserToMap);
}
②方式二
/**
查询所有用户信息为map集合
@return
将表中的数据以map集合的方式查询,一条数据对应一个map;若有多条数据,就会产生多个map集合,并
且最终要以一个map的方式返回数据,此时需要通过@MapKey注解设置map集合的键,值是每条数据所对应的
map集合
*/
@MapKey("id")
Map<String, Object> getAllUserToMap();
<select id="getAllUserToMap" resultType="map">
select * from t_user
</select>
测试类:
@Test
public void test6(){
SqlSessionUtils sqlSessionUtils = new SqlSessionUtils();
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionUtils.getSqlSession();
SelectMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(SelectMapper.class);
Map<String, Object> allUserToMap = mapper.getAllUserToMap();
System.out.println(allUserToMap);
}
运行结果:
{1={password=123, sex=男, id=1, age=23, email=11111@qq.com, username=张三},
2={password=root, sex=女, id=2, age=23, email=11111@qq.com, username=root},
3={password=789123, sex=女, id=3, age=28, email=9090889@qq.com, username=小王}, 4={password=1234567, sex=男, id=4, age=34, email=1487418@qq.com, username=小李}}
版权归原作者 热爱编程的小白白 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。