陈老老老板
说明:工作了,学习一些新的技术栈和工作中遇到的问题,边学习边总结,各位一起加油。需要注意的地方都标红了,还有资源的分享. 一起加油。
本文是介绍Elasticsearch用法与SpringBoot整合
1.ES简介
注:公司中大部分也是对于管理日志信息使用es,我们也是,这里做简单的教学,之后会有更加完整的ES学习介绍。
说明:
ES(Elasticsearch)Elasticsearch是一个基于Lucene的搜索服务器。它提供了一个分布式多用户能力的全文搜索引擎,基于RESTful web接口。Elasticsearch是用Java语言开发的,并作为Apache许可条款下的开放源码发布,是一种流行的企业级搜索引擎。Elasticsearch用于云计算中,能够达到实时搜索,稳定,可靠,快速,安装使用方便 。
其实记住是一个分布式全文搜索引擎,重点是全文搜索。
全文搜索:这里解释一下全文索引比如用户要搜索一个文章,以Java为关键字进行搜索,不管是书名中还是文章的标题,文章的作者名字,文章的摘要,只要是包含java关键字就会作为查询结果返回给用户查看,这就使用了全文搜索技术。
搜索的条件不再是仅用于对某一个字段进行比对与查找,而是在一条数据中使用搜索条件去比对表中更多的字段,只要能匹配上就作为查询结果,而ES技术就是一种可以实现上述效果的技术。
2.全文搜索实现过程:倒排索引
ES设计了一种全新的思想,来实现全文搜索。具体操作过程如下:
(1)进行分词
将被查询的字段的数据全部文本信息进行查分,分成若干个词
- 例如“我不想上班”就会被拆分成三个词,分别是“我”、“不想”、“上班”,此过程专业术语叫做分词。(根据分词的策略不同,分出的效果是不一样的,不同的分词策略称为分词器(ik)。)
(2)存储对应id
将分词得到的结果存储起来,对应每条数据的id
- 例如id为1的数据中名称这一项的值是“我不想上班”,那么分词结束后,就会出现“我”对应id为1,“不想”对应id为1,“上班”对应id为1
- 例如id为2的数据中名称这一项的值是“上班真的快乐“,那么分词结束后,就会出现“上班”对应id为2,“真的”对应id为2,“快乐”对应id为2
- 按照上述形式可以对所有文档进行分词。需要注意分词的过程不是仅对一个字段进行,而是对每一个参与查询的字段都执行,最终结果汇总到一个表格中此时就会出现如下对应结果:分词结果关键字对应id我1不想1上班1,2真的2快乐2
(3)通过id查询结果
当进行查询时,如果输入“上班”作为查询条件,可以通过上述表格数据进行比对,得到id值1,2,然后根据id值就可以得到查询的结果数据了。
注:全文搜索中的分词结果关键字查询后得到的并不是整条的数据,而是数据的id,要想获得具体数据还要再次查询,这种分词结果关键字叫做倒排索引。
3.安装
(1)下载ES
windows版安装包下载地址:https://www.elastic.co/cn/downloads/elasticsearch
(2)解压缩
下载的安装包是解压缩就能使用的zip文件,解压缩完毕后会得到如下文件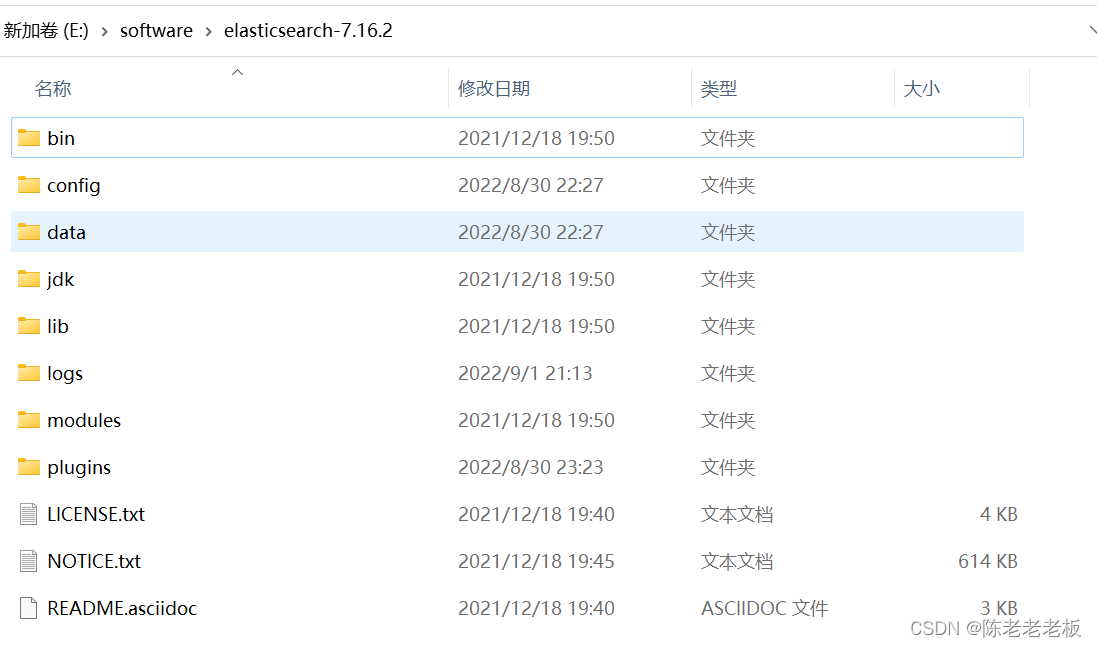
- bin目录:包含所有的可执行命令
- config目录:包含ES服务器使用的配置文件
- jdk目录:此目录中包含了一个完整的jdk工具包,版本17,当ES升级时,使用最新版本的jdk确保不会出现版本支持性不足的问题
- lib目录:包含ES运行的依赖jar文件
- logs目录:包含ES运行后产生的所有日志文件
- modules目录:包含ES软件中所有的功能模块,也是一个一个的jar包。和jar目录不同,jar目录是ES运行期间依赖的jar包,modules是ES软件自己的功能jar包
- plugins目录:包含ES软件安装的插件,默认为空
(3)启动服务器
进入bin目录,再进入命令窗口,输入以下命令:
elasticsearch.bat
双击elasticsearch.bat文件即可启动ES服务器,默认服务端口9200。通过浏览器访问http://localhost:9200看到如下信息视为ES服务器正常启动
{
"name" : "CZBK-**********",
"cluster_name" : "elasticsearch",
"cluster_uuid" : "j137DSswTPG8U4Yb-0T1Mg",
"version" : {
"number" : "7.16.2",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "zip",
"build_hash" : "2b937c44140b6559905130a8650c64dbd0879cfb",
"build_date" : "2021-12-18T19:42:46.604893745Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "8.10.1",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "6.8.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "6.0.0-beta1"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}

(4)基本操作
ES中保存要查询的数据,只不过格式和数据库存储数据格式不同。在ES中我们要先创建倒排索引(这个索引的功能又点类似于数据库的表),然后将数据添加到倒排索引中,添加的数据称为文档。所以要进行ES的操作要先创建索引,再添加文档,这样才能进行后续的查询操作。
要操作ES可以通过Rest风格的请求来进行,也就是说发送一个请求就可以执行一个操作。比如新建索引,删除索引这些操作都可以使用发送请求的形式来进行。
(1)创建索引
- user是索引名称,注意是put请求
PUT请求 http://localhost:9200/user发送请求后,看到如下信息即索引创建成功{"acknowledged":true,"shards_acknowledged":true,"index":"books"}
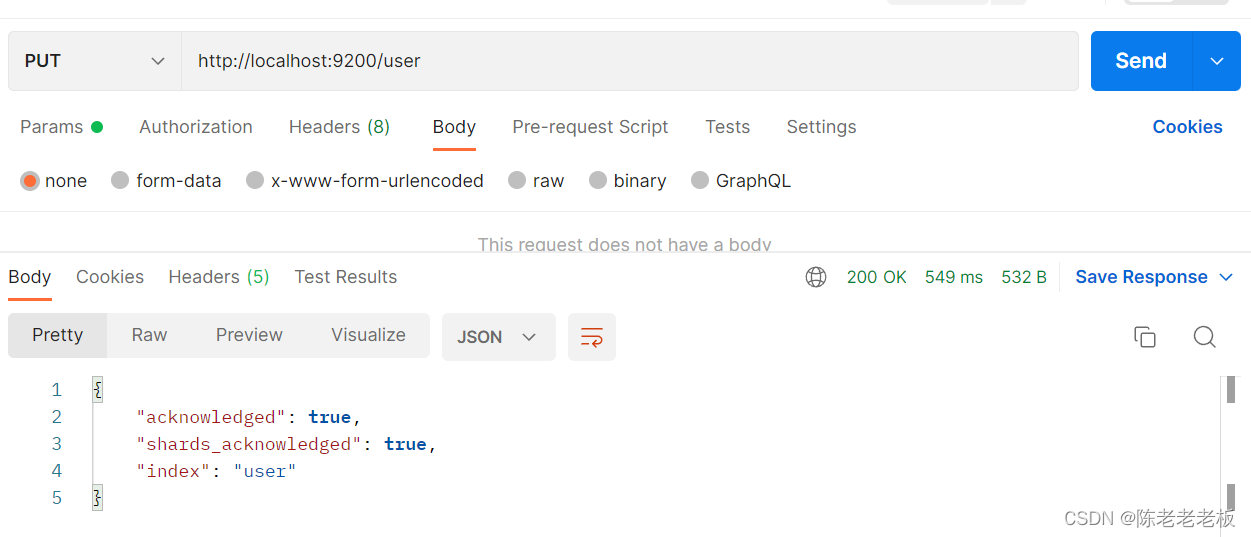
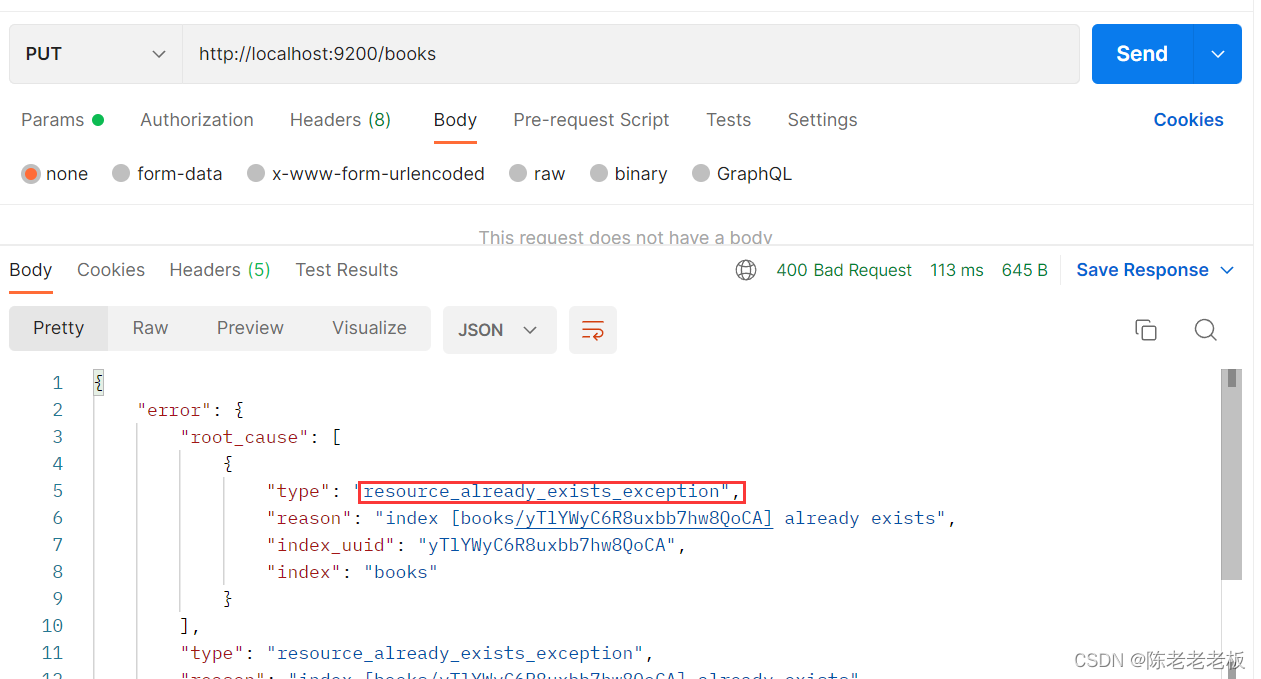
注: 重复创建已经存在的索引会出现错误信息,reason属性中描述错误原因。
{"error":{"root_cause":[{"type":"resource_already_exists_exception","reason":"index [books/VgC_XMVAQmedaiBNSgO2-w] already exists","index_uuid":"VgC_XMVAQmedaiBNSgO2-w","index":"books"}],"type":"resource_already_exists_exception","reason":"index [books/VgC_XMVAQmedaiBNSgO2-w] already exists", # books索引已经存在
"index_uuid":"VgC_XMVAQmedaiBNSgO2-w","index":"book"},"status":400}
(2)查询索引
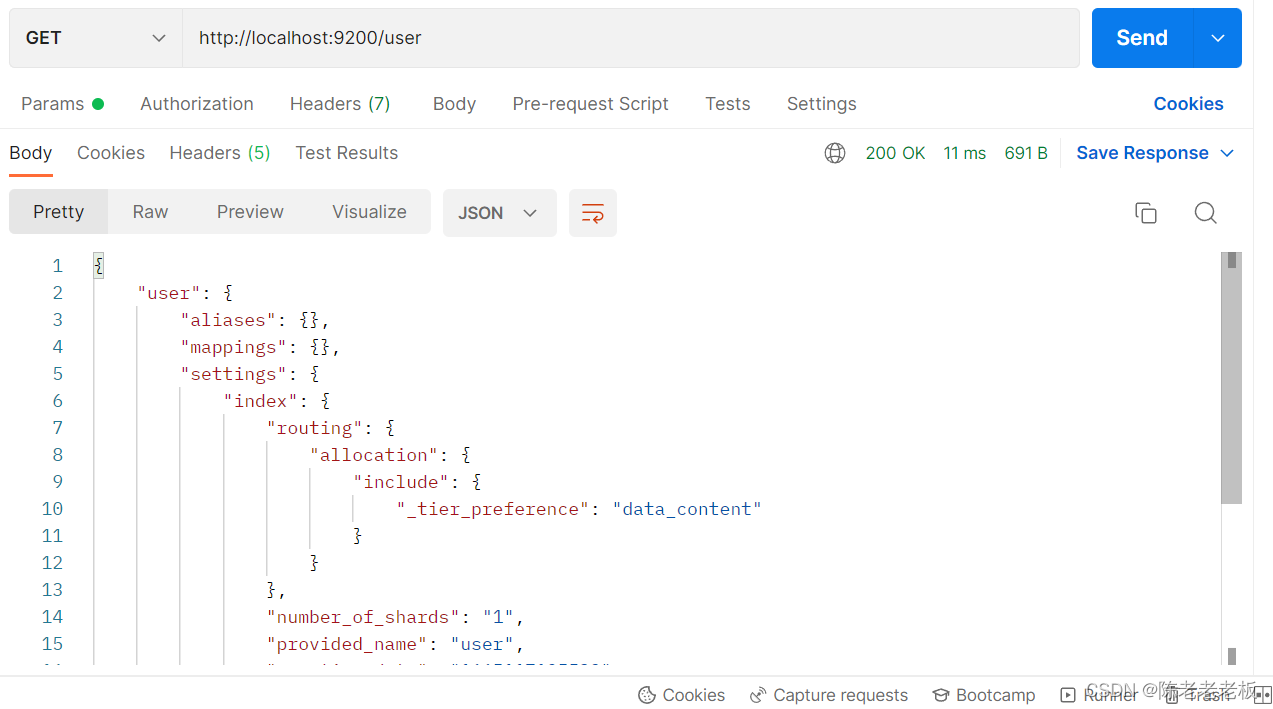
GET请求 http://localhost:9200/user
查询索引得到索引相关信息,如下
{"book":{"aliases":{},"mappings":{},"settings":{"index":{"routing":{"allocation":{"include":{"_tier_preference":"data_content"}}},"number_of_shards":"1","provided_name":"books","creation_date":"1645768584849","number_of_replicas":"1","uuid":"VgC_XMVAQmedaiBNSgO2-w","version":{"created":"7160299"}}}}}
注: 如果查询了不存在的索引,会返回错误信息。
{"error":{"root_cause":[{"type":"index_not_found_exception","reason":"no such index [book]","resource.type":"index_or_alias","resource.id":"book","index_uuid":"_na_","index":"book"}],"type":"index_not_found_exception","reason":"no such index [book]", # 没有book索引
"resource.type":"index_or_alias","resource.id":"book","index_uuid":"_na_","index":"book"},"status":404}

(3)删除索引
DELETE请求 http://localhost:9200/books
删除所有后,给出删除结果
{"acknowledged":true}

注: 如果重复删除,会给出错误信息,同样在reason属性中描述具体的错误原因
{
"error": {
"root_cause": [
{
"type": "index_not_found_exception",
"reason": "no such index [books]",
"resource.type": "index_or_alias",
"resource.id": "book",
"index_uuid": "_na_",
"index": "book"
}
],
"type": "index_not_found_exception",
"reason": "no such index [books]", # 没有books索引
"resource.type": "index_or_alias",
"resource.id": "book",
"index_uuid": "_na_",
"index": "book"
},
"status": 404
}

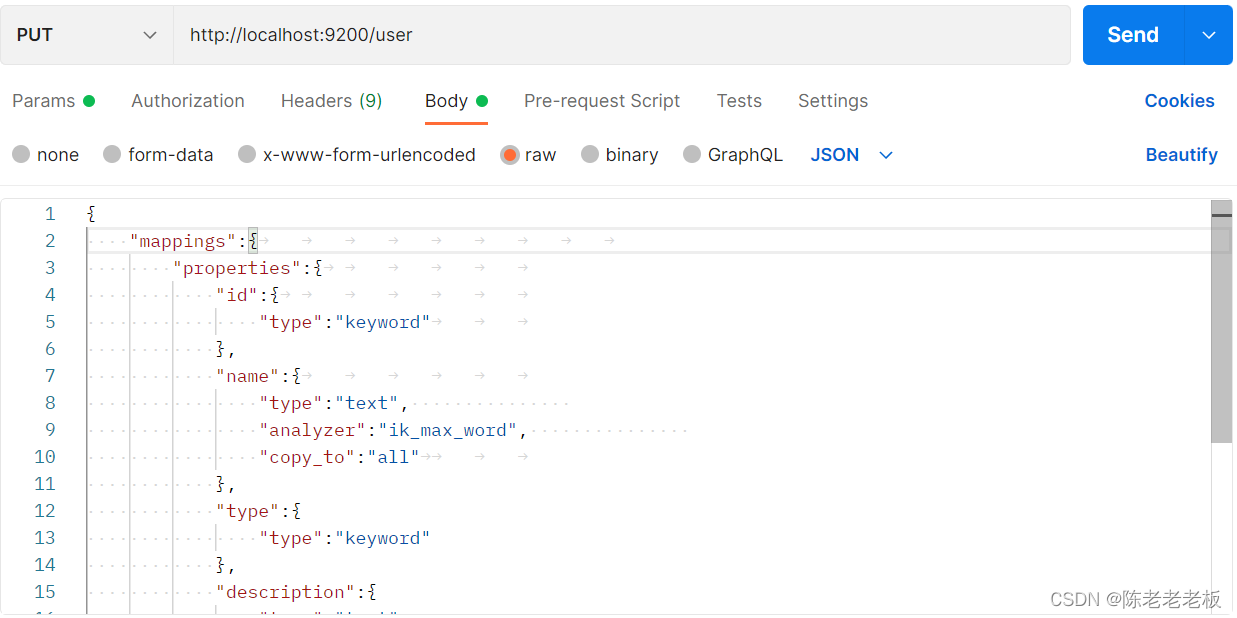
(4)创建索引并指定分词器
前面创建的索引是未指定分词器的,可以在创建索引时添加请求参数,设置分词器。目前国内较为流行的分词器是IK分词器,使用前先在下对应的分词器,然后使用。
IK分词器下载地址:https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik/releases
分词器下载后解压到ES安装目录的plugins目录中即可,安装分词器后需要重新启动ES服务器。
使用IK分词器创建索引格式:(要把注释删掉否则报错)
PUT请求 http://localhost:9200/books
请求参数如下(注意是json格式的参数)
{"mappings":{ #定义mappings属性,替换创建索引时对应的mappings属性
"properties":{ #定义索引中包含的属性设置
"id":{ #设置索引中包含id属性
"type":"keyword" #当前属性可以被直接搜索
},"name":{ #设置索引中包含name属性
"type":"text", #当前属性是文本信息,参与分词
"analyzer":"ik_max_word", #使用IK分词器进行分词
"copy_to":"all" #分词结果拷贝到all属性中
},"type":{"type":"keyword"},"description":{"type":"text","analyzer":"ik_max_word","copy_to":"all"},"all":{ #定义属性,用来描述多个字段的分词结果集合,当前属性可以参与查询
"type":"text","analyzer":"ik_max_word"}}}}
创建完毕后返回结果和不使用分词器创建索引的结果是一样的。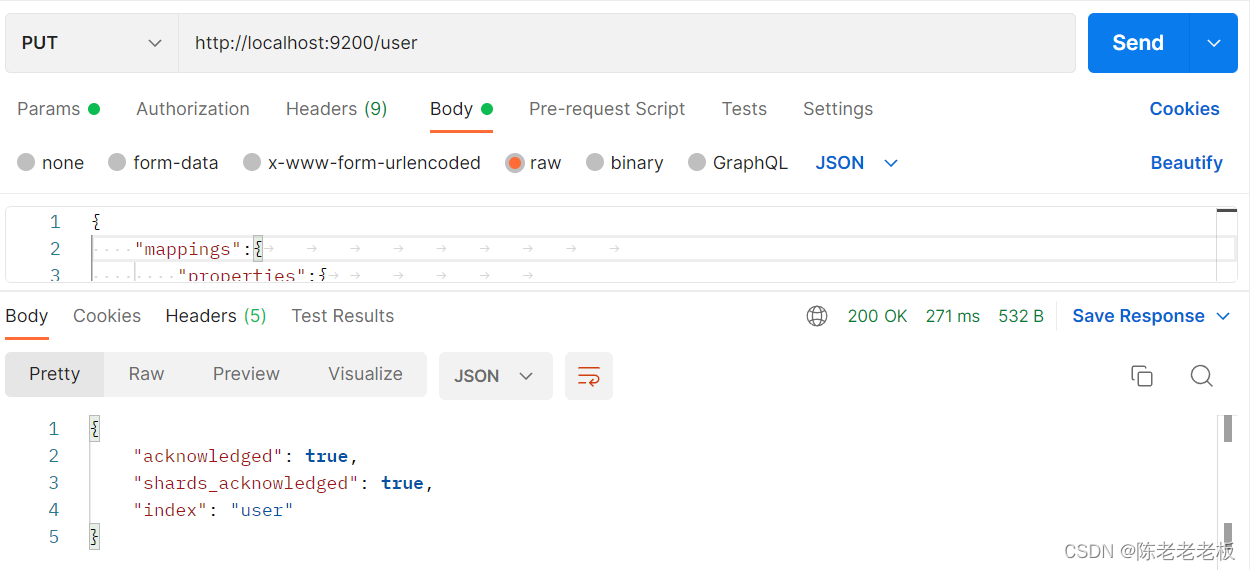
此时可以通过查看索引信息观察到添加的请求参数mappings已经进入到了索引属性中
{"user":{"aliases":{},"mappings":{ #mappings属性已经被替换
"properties":{"all":{"type":"text","analyzer":"ik_max_word"},"description":{"type":"text","copy_to":["all"],"analyzer":"ik_max_word"},"id":{"type":"keyword"},"name":{"type":"text","copy_to":["all"],"analyzer":"ik_max_word"},"type":{"type":"keyword"}}},"settings":{"index":{"routing":{"allocation":{"include":{"_tier_preference":"data_content"}}},"number_of_shards":"1","provided_name":"books","creation_date":"1645769809521","number_of_replicas":"1","uuid":"DohYKvr_SZO4KRGmbZYmTQ","version":{"created":"7160299"}}}}}
目前我们已经有了索引了,但是索引中还没有数据,所以要先添加数据,ES中称数据为文档,下面进行文档操作。
a.添加文档,有三种方式
POST请求 http://localhost:9200/user/_doc #使用系统生成id
POST请求 http://localhost:9200/user/_create/1 #使用指定id
POST请求 http://localhost:9200/user/_doc/1 #使用指定id,不存在创建,存在更新(版本递增)
文档通过请求参数传递,数据格式json
{"name":"cllb","type":"bozhu","description":"xihuan java"}

b.查询文档
这里注意请求时要把参数调整为none,否则会报错。
GET请求 http://localhost:9200/user/_doc/1 #查询单个文档
GET请求 http://localhost:9200/user/_search #查询全部文档

c.条件查询
GET请求 http://localhost:9200/user/_search?q=name:cllb # q=查询属性名:查询属性值

d.修改文档(全量更新)
PUT请求 http://localhost:9200/user/_doc/1
文档通过请求参数传递,数据格式json
{"name":"ccc","type":"bb","description":"123"}

e.修改文档(部分更新)
POST请求 http://localhost:9200/user/_update/1
文档通过请求参数传递,数据格式json
{"doc":{ #部分更新并不是对原始文档进行更新,而是对原始文档对象中的doc属性中的指定属性更新
"name":"springboot" #仅更新提供的属性值,未提供的属性值不参与更新操作
}}

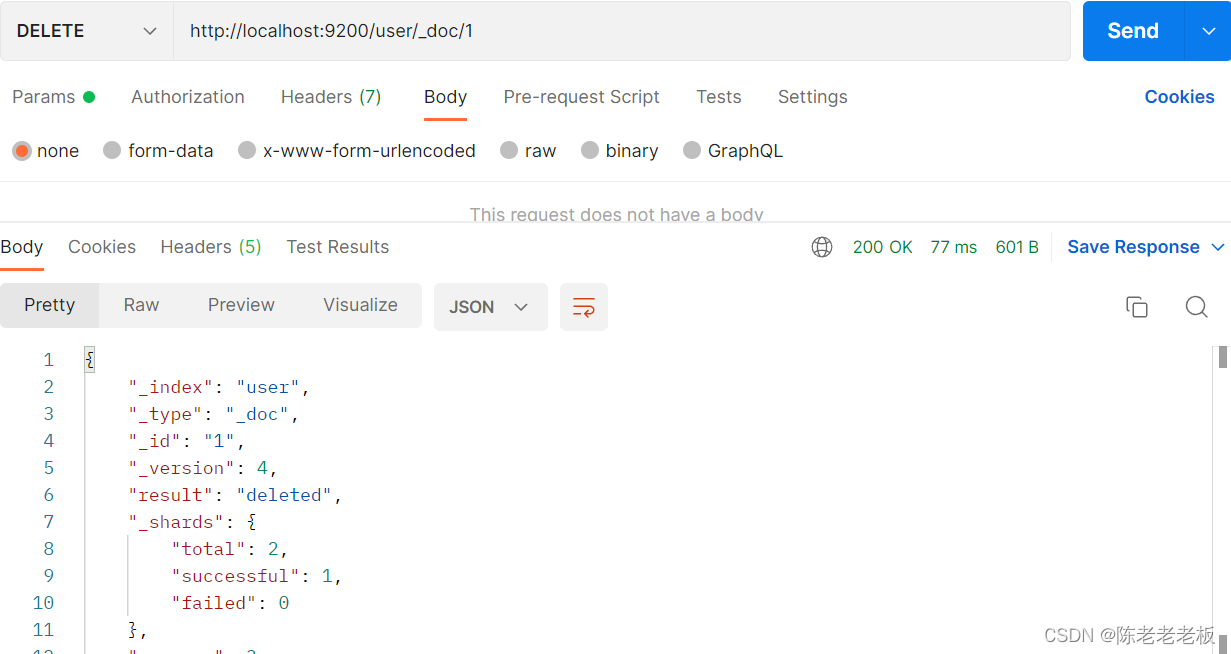
f.删除文档
DELETE请求 http://localhost:9200/books/_doc/1
4. 整合(早期低级版)
其实和整合Redis,MongoDB,ES都是一样的。
下面就开始springboot整合ES,操作步骤如下:
(1):导入springboot整合ES的starter坐标
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId></dependency>
(2):进行基础配置
spring:elasticsearch:rest:uris: http://localhost:9200
配置ES服务器地址,端口9200
(3):使用springboot整合ES的专用客户端接口ElasticsearchRestTemplate来进行操作
@SpringBootTestclassSpringboot18EsApplicationTests{@AutowiredprivateElasticsearchRestTemplate template;}
(4)连接pojo层
packagecom.test;importorg.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.Document;importjava.lang.annotation.Documented;@Document(indexName ="user")publicclassUser{privateInteger id;privateString name;privateString type;privateString description;publicUser(Integer id,String name,String type,String description){this.id = id;this.name = name;this.type = type;this.description = description;}publicUser(){}publicIntegergetId(){return id;}publicvoidsetId(Integer id){this.id = id;}publicStringgetName(){return name;}publicvoidsetName(String name){this.name = name;}publicStringgetType(){return type;}publicvoidsetType(String type){this.type = type;}publicStringgetDescription(){return description;}publicvoidsetDescription(String description){this.description = description;}@OverridepublicStringtoString(){return"Book{"+"id="+ id +", name='"+ name +'\''+", type='"+ type +'\''+", description='"+ description +'\''+'}';}}
(5)连接dao层
packagecom.test;importorg.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchSecurityException;importorg.springframework.data.elasticsearch.repository.ElasticsearchRepository;publicinterfaceEsresposityextendsElasticsearchRepository<User,Integer>{}
注: 上述这是ES早期的操作方式,使用的客户端被称为Low Level Client,因为这种操作方式在性能方面略显不足。
于是ES开发了全新的客户端操作方式,称为High Level Client。
高级别客户端与ES版本同步更新,但是springboot最初整合ES的时候使用的是低级别客户端,所以企业开发需要更换成高级别的客户端模式。
5.整合(最新高级版)
下面使用高级别客户端方式进行springboot整合ES,操作步骤如下:
(1)导入springboot整合ES高级别客户端的坐标
此种形式目前没有对应的starter,需要去找。
<dependency><groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId><artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId></dependency>
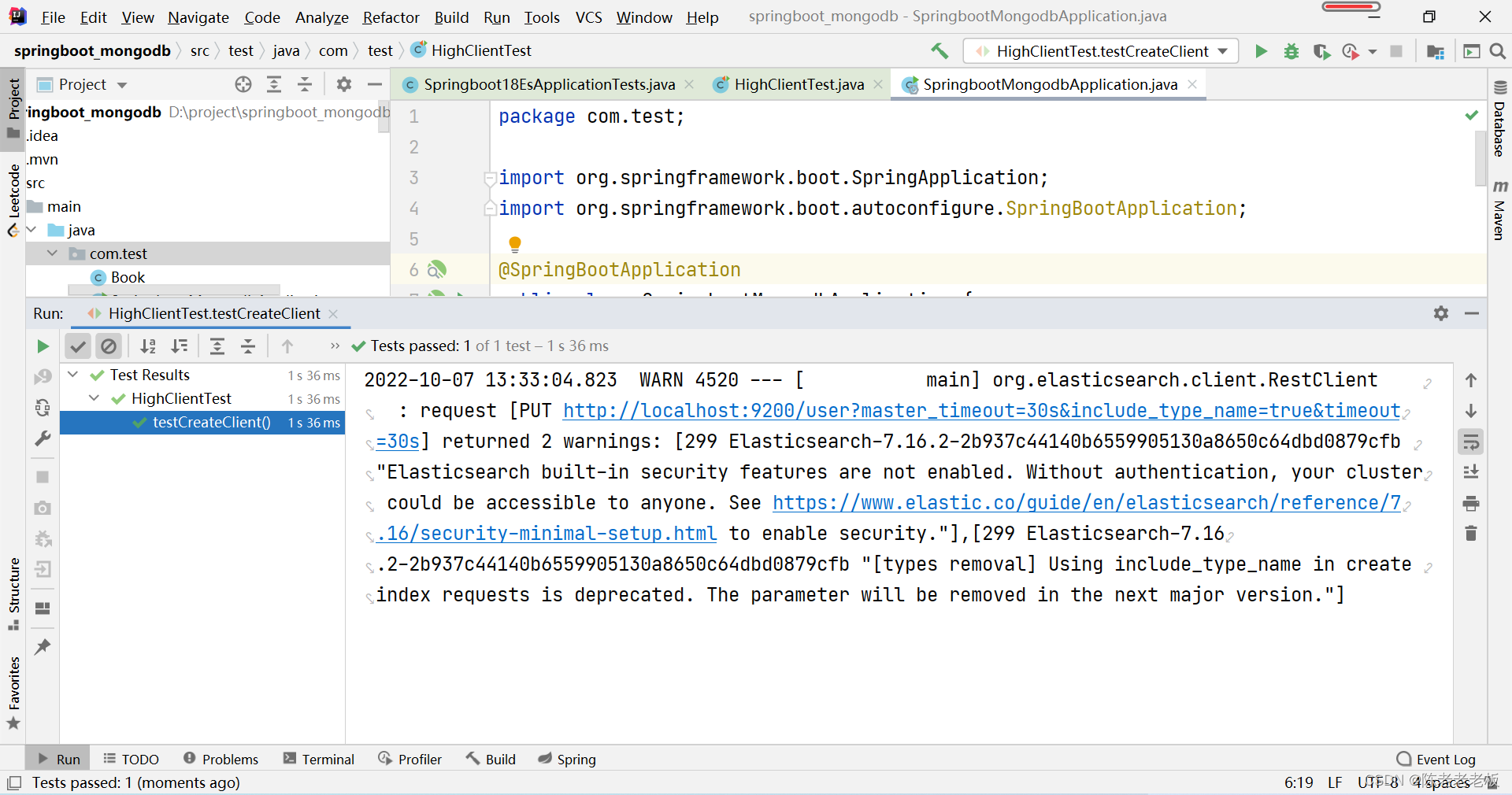
(2)使用编程的形式设置连接的ES服务器,并获取客户端对象
@SpringBootTestclassHighClientTest{privateRestHighLevelClient client;@TestvoidtestCreateClient()throwsIOException{HttpHost host =HttpHost.create("http://localhost:9200");RestClientBuilder builder =RestClient.builder(host);
client =newRestHighLevelClient(builder);
client.close();}}
注: 记得客户端使用完毕需要手工关闭。配置ES服务器地址与端口9200,由于当前客户端是手工维护的,因此不能通过自动装配的形式加载对象。
(3)使用客户端对象操作ES
例如创建索引:(这里需要先执行上面的删除索引操作,否则会报错)
@SpringBootTestclassHighClientTest{privateRestHighLevelClient client;@TestvoidtestCreateIndex()throwsIOException{HttpHost host =HttpHost.create("http://localhost:9200");RestClientBuilder builder =RestClient.builder(host);
client =newRestHighLevelClient(builder);CreateIndexRequest request =newCreateIndexRequest("user");
client.indices().create(request,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
client.close();}}
注:第一步永远是获取RestHighLevelClient对象,创建索引的对象是CreateIndexRequest,其他操作也会有自己专用的Request对象。最后一步永远是关闭该对象的连接。可以得出以下结论,进行方法提取。
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot18EsApplicationTests {
@BeforeEach //在测试类中每个操作运行前运行的方法
void setUp() {
HttpHost host = HttpHost.create("http://localhost:9200");
RestClientBuilder builder = RestClient.builder(host);
client = new RestHighLevelClient(builder);
}
@AfterEach //在测试类中每个操作运行后运行的方法
void tearDown() throws IOException {
client.close();
}
private RestHighLevelClient client;
@Test
void testCreateIndex() throws IOException {
CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("book");
client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
}
现在的书写简化了很多,也更合理。下面使用上述模式将所有的ES操作执行一遍,测试结果
创建索引(IK分词器):
@TestvoidtestCreateIndexByIK()throwsIOException{CreateIndexRequest request =newCreateIndexRequest("books");String json ="{\n"+" \"mappings\":{\n"+" \"properties\":{\n"+" \"id\":{\n"+" \"type\":\"keyword\"\n"+" },\n"+" \"name\":{\n"+" \"type\":\"text\",\n"+" \"analyzer\":\"ik_max_word\",\n"+" \"copy_to\":\"all\"\n"+" },\n"+" \"type\":{\n"+" \"type\":\"keyword\"\n"+" },\n"+" \"description\":{\n"+" \"type\":\"text\",\n"+" \"analyzer\":\"ik_max_word\",\n"+" \"copy_to\":\"all\"\n"+" },\n"+" \"all\":{\n"+" \"type\":\"text\",\n"+" \"analyzer\":\"ik_max_word\"\n"+" }\n"+" }\n"+" }\n"+"}";//设置请求中的参数
request.source(json,XContentType.JSON);
client.indices().create(request,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);}
注:IK分词器是通过请求参数的形式进行设置的,设置请求参数使用request对象中的source方法进行设置,至于参数是什么,取决于你的操作种类。当请求中需要参数时,均可使用当前形式进行参数设置。
添加文档:
@Test//添加文档voidtestCreateDoc()throwsIOException{User user = userDao.selectById(1);IndexRequest request =newIndexRequest("user").id(book.getId().toString());String json = JSON.toJSONString(book);
request.source(json,XContentType.JSON);
client.index(request,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);}
添加文档使用的请求对象是IndexRequest,与创建索引使用的请求对象不同。
批量添加文档:
@Test//批量添加文档voidtestCreateDocAll()throwsIOException{List<User> userList = userDao.selectList(null);BulkRequest bulk =newBulkRequest();for(User user : userList){IndexRequest request =newIndexRequest("user").id(user.getId().toString());String json = JSON.toJSONString(book);
request.source(json,XContentType.JSON);
bulk.add(request);}
client.bulk(bulk,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);}
注:批量做时,先创建一个BulkRequest的对象,可以将该对象理解为是一个保存request对象的容器,将所有的请求都初始化好后,添加到BulkRequest对象中,再使用BulkRequest对象的bulk方法,一次性执行完毕。
按id查询文档:
@Test//按id查询voidtestGet()throwsIOException{GetRequest request =newGetRequest("user","1");GetResponse response = client.get(request,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);String json = response.getSourceAsString();System.out.println(json);}
根据id查询文档使用的请求对象是GetRequest。
按条件查询文档:
@Test//按条件查询voidtestSearch()throwsIOException{SearchRequest request =newSearchRequest("user");SearchSourceBuilder builder =newSearchSourceBuilder();
builder.query(QueryBuilders.termQuery("all","spring"));
request.source(builder);SearchResponse response = client.search(request,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);SearchHits hits = response.getHits();for(SearchHit hit : hits){String source = hit.getSourceAsString();//System.out.println(source);Book book = JSON.parseObject(source,Book.class);System.out.println(book);}}
注:按条件查询文档使用的请求对象是SearchRequest,查询时调用SearchRequest对象的termQuery方法,需要给出查询属性名,此处支持使用合并字段,也就是前面定义索引属性时添加的all属性。
**总结:ES是为了查询速度快,之后会有更细致的有关ES的博客。希望对您有帮助,感谢阅读
结束语:裸体一旦成为艺术,便是最圣洁的。道德一旦沦为虚伪,便是最下流的。
勇敢去做你认为正确的事,不要被世俗的流言蜚语所困扰。**
版权归原作者 陈老老老板 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。