基于flink jdbc方言(dialect)里不同Statement何时、如何被调用的思考。
前言:在修改flink-connector-jdbc源码时,观察到jdbc有方言的实现,在 JdbcDialect.class 里存在insert/update和upsert两种更新语义,所以研究下何种情况执行insert/update,何种情况执行upsert。如有任何错误,欢迎大家指正。
flink jdbc插入模式主要分为两类:
1、Append-Only
仅追加流,简单来讲,不管数据重不重复,只是往里添加。
2、Upsert
更新插入流,即更新或者插入,一般要求 sink 端数据库需要唯一的键值。例如 Mysql 的 INSERT INTO ... ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE ...语法。
一、jdbc方言
既然 flink sql 可以适配多种数据库,所以在 jdbc 方言方面肯定会有不同的适配,flink 适配的interface就是 JdbcDialect.class
JdbcDialect.class
/** Handle the SQL dialect of jdbc driver. */
@Internal
public interface JdbcDialect extends Serializable {
/**
* Get the name of jdbc dialect.
*
* @return the dialect name.
*/
String dialectName();
/**
* Check if this dialect instance can handle a certain jdbc url.
*
* @param url the jdbc url.
* @return True if the dialect can be applied on the given jdbc url.
*/
boolean canHandle(String url);
/**
* Get converter that convert jdbc object and Flink internal object each other.
*
* @param rowType the given row type
* @return a row converter for the database
*/
JdbcRowConverter getRowConverter(RowType rowType);
/**
* Get limit clause to limit the number of emitted row from the jdbc source.
*
* @param limit number of row to emit. The value of the parameter should be non-negative.
* @return the limit clause.
*/
String getLimitClause(long limit);
/**
* Check if this dialect instance support a specific data type in table schema.
*
* @param schema the table schema.
* @exception ValidationException in case of the table schema contains unsupported type.
*/
default void validate(TableSchema schema) throws ValidationException {}
/**
* @return the default driver class name, if user not configure the driver class name, then will
* use this one.
*/
default Optional<String> defaultDriverName() {
return Optional.empty();
}
/**
* Quotes the identifier. This is used to put quotes around the identifier in case the column
* name is a reserved keyword, or in case it contains characters that require quotes (e.g.
* space). Default using double quotes {@code "} to quote.
*/
default String quoteIdentifier(String identifier) {
return "\"" + identifier + "\"";
}
/**
* Get dialect upsert statement, the database has its own upsert syntax, such as Mysql using
* DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE, and PostgresSQL using ON CONFLICT... DO UPDATE SET..
*
* @return None if dialect does not support upsert statement, the writer will degrade to the use
* of select + update/insert, this performance is poor.
*/
default Optional<String> getUpsertStatement(
String tableName, String[] fieldNames, String[] uniqueKeyFields) {
return Optional.empty();
}
/** Get row exists statement by condition fields. Default use SELECT. */
default String getRowExistsStatement(String tableName, String[] conditionFields) {
String fieldExpressions =
Arrays.stream(conditionFields)
.map(f -> format("%s = :%s", quoteIdentifier(f), f))
.collect(Collectors.joining(" AND "));
return "SELECT 1 FROM " + quoteIdentifier(tableName) + " WHERE " + fieldExpressions;
}
/** Get insert into statement. */
default String getInsertIntoStatement(String tableName, String[] fieldNames) {
String columns =
Arrays.stream(fieldNames)
.map(this::quoteIdentifier)
.collect(Collectors.joining(", "));
String placeholders =
Arrays.stream(fieldNames).map(f -> ":" + f).collect(Collectors.joining(", "));
return "INSERT INTO "
+ quoteIdentifier(tableName)
+ "("
+ columns
+ ")"
+ " VALUES ("
+ placeholders
+ ")";
}
/**
* Get update one row statement by condition fields, default not use limit 1, because limit 1 is
* a sql dialect.
*/
default String getUpdateStatement(
String tableName, String[] fieldNames, String[] conditionFields) {
String setClause =
Arrays.stream(fieldNames)
.map(f -> format("%s = :%s", quoteIdentifier(f), f))
.collect(Collectors.joining(", "));
String conditionClause =
Arrays.stream(conditionFields)
.map(f -> format("%s = :%s", quoteIdentifier(f), f))
.collect(Collectors.joining(" AND "));
return "UPDATE "
+ quoteIdentifier(tableName)
+ " SET "
+ setClause
+ " WHERE "
+ conditionClause;
}
/**
* Get delete one row statement by condition fields, default not use limit 1, because limit 1 is
* a sql dialect.
*/
default String getDeleteStatement(String tableName, String[] conditionFields) {
String conditionClause =
Arrays.stream(conditionFields)
.map(f -> format("%s = :%s", quoteIdentifier(f), f))
.collect(Collectors.joining(" AND "));
return "DELETE FROM " + quoteIdentifier(tableName) + " WHERE " + conditionClause;
}
/** Get select fields statement by condition fields. Default use SELECT. */
default String getSelectFromStatement(
String tableName, String[] selectFields, String[] conditionFields) {
String selectExpressions =
Arrays.stream(selectFields)
.map(this::quoteIdentifier)
.collect(Collectors.joining(", "));
String fieldExpressions =
Arrays.stream(conditionFields)
.map(f -> format("%s = :%s", quoteIdentifier(f), f))
.collect(Collectors.joining(" AND "));
return "SELECT "
+ selectExpressions
+ " FROM "
+ tableName
+ (conditionFields.length > 0 ? " WHERE " + fieldExpressions : "");
}
}
本次主要关注两类方法
1、Append-Only:getInsertIntoStatement()
2、Upsert:getUpsertStatement()、getRowExistsStatement()
二、Insert/Upsert分析
在查看getUpsertStatement()调用方时,会发现有两个使用的地方:
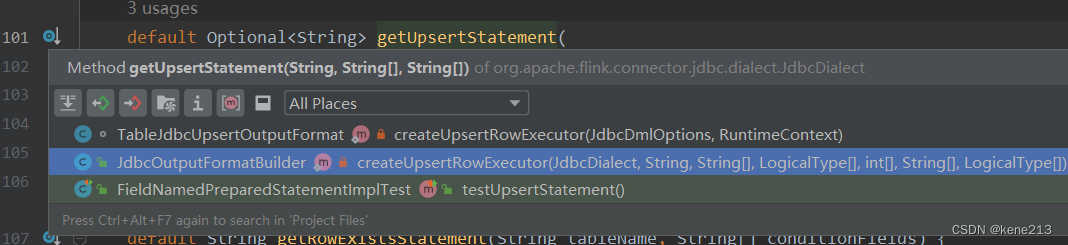
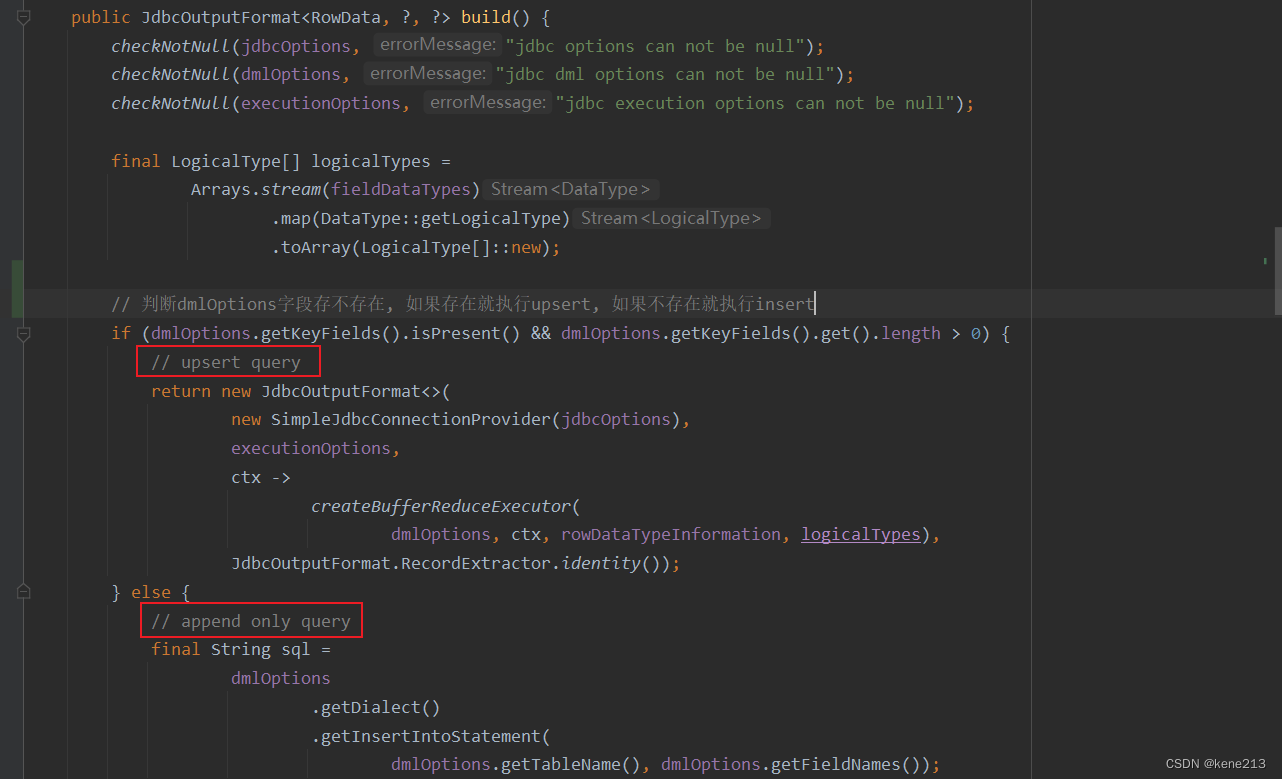
主要查看 JdbcOutputFormatBuilder 类时,最终继续在本类内查找调用方,最终唯一会找到 build():
现在只需要知道 dmlOptions 是什么,在讨论 JdbcDmlOptions 之前,我们先思考一下,在 Flink 官网介绍 Upsert SQL 时有这么一个关键点,就是增加主键的声明:
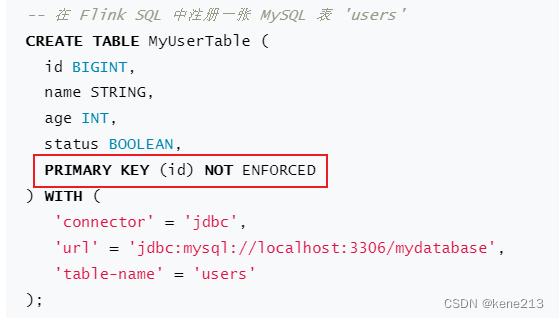
所以在执行 flink sql 时debug验证了此猜想,JdbcDmlOptions 在此就是主键定义,也就是定义了主键的时候会执行 Upsert 语义。
三、Upsert 分析
对于不用数据库,Flink 官网也给出了不同幂等性SQL的实现(即 getUpsertStatement() 方法的实现):
JDBC | Apache Flink

此外,在上述介绍 Upsert 方法时,还提到了一个 getRowExistsStatement():
/** Get row exists statement by condition fields. Default use SELECT. */
default String getRowExistsStatement(String tableName, String[] conditionFields) {
String fieldExpressions =
Arrays.stream(conditionFields)
.map(f -> format("%s = :%s", quoteIdentifier(f), f))
.collect(Collectors.joining(" AND "));
return "SELECT 1 FROM " + quoteIdentifier(tableName) + " WHERE " + fieldExpressions;
}
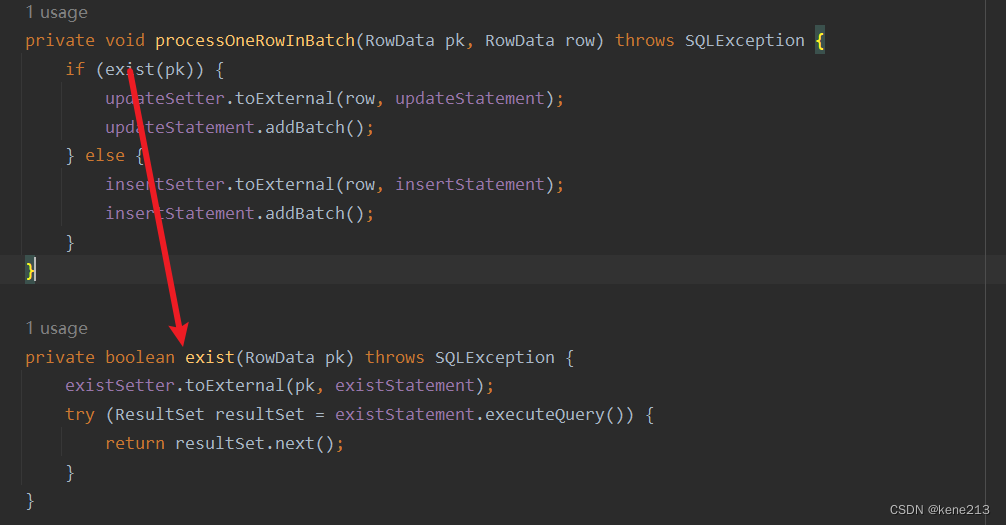
不是在所有的数据库里面都有实现幂等写入的SQL语法(例如ClickHouse),所以 Fink 还提供了另一种实现,即先查询一遍该行数据是否存在,再根据存在与否执行 Insert 或者 Update。如果 getUpdateStatement() 获取为 Empty (默认未实现),则执行 orElseGet() 获取 InsertOrUpdate方式:
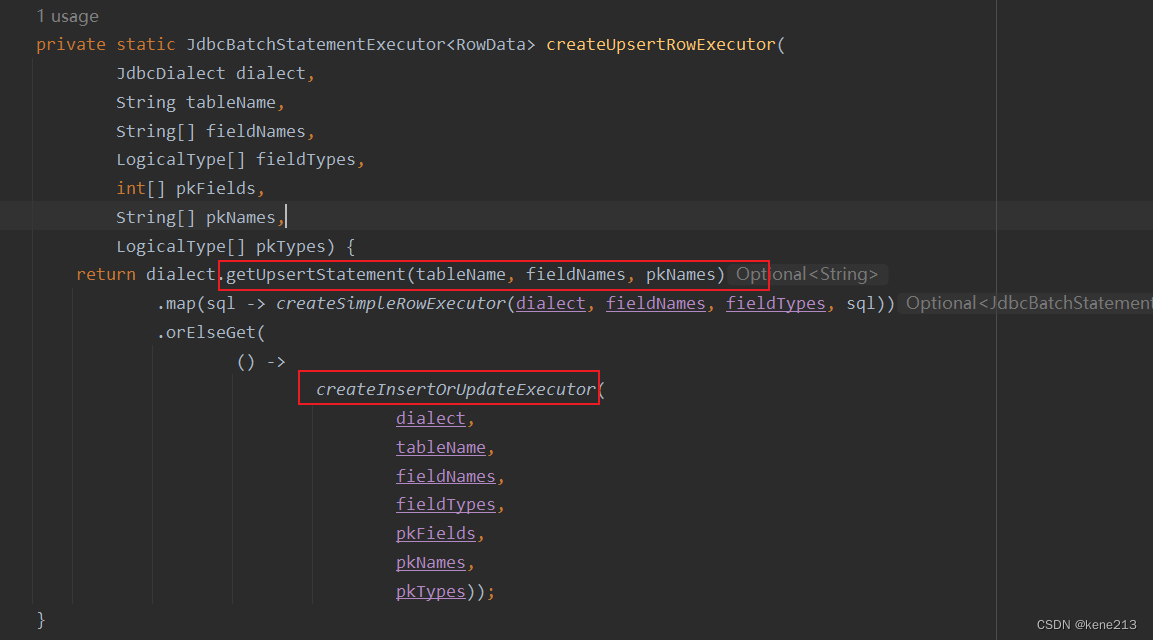
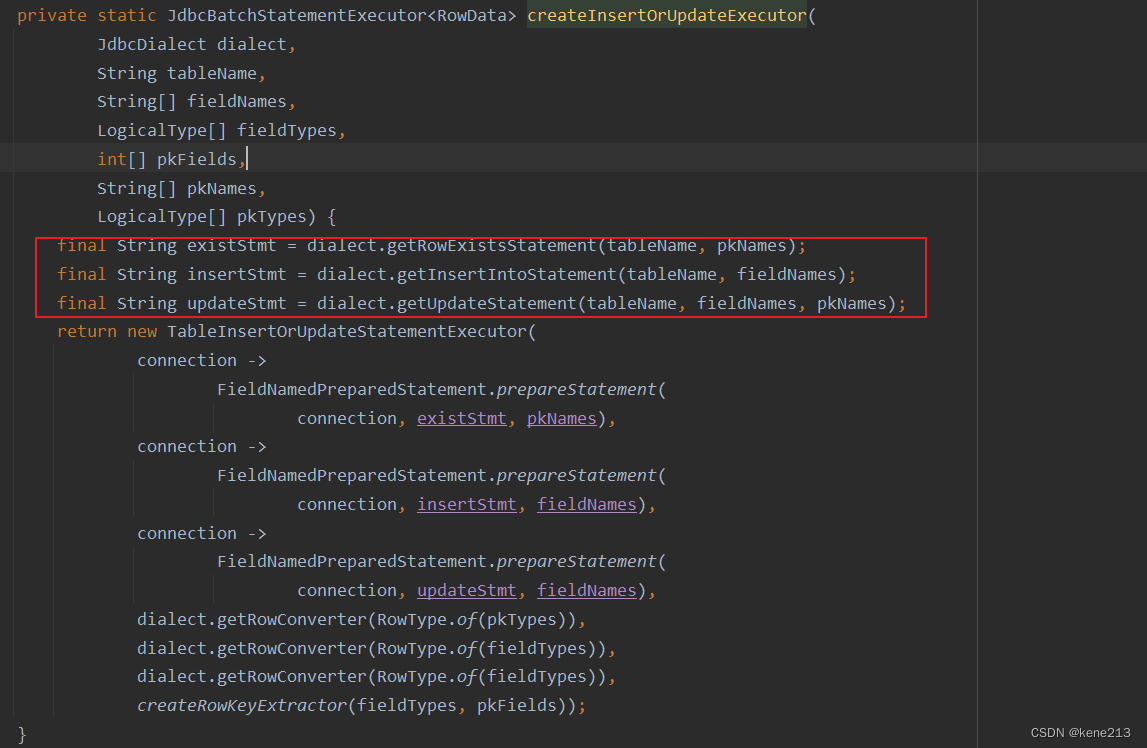
createInsertOrUpdateExecutor() 方法会获取三个SQL,其中包含 getRowExistsStatement(),后续再处理每一条数据时,都会先判断该条数据是否存在,存在则更新,不存在则插入:
四、结论
每条数据执行时,都会根据 DML SQL 判断是否声明了主键,有主键则执行 Upsert 语义,无主键则执行 Append-Only 语义。
其中 Upsert 又根据具体数据库方言的实现分为两种,支持幂等写入则为一次 SQL 执行,不支持幂等写入则为两次 SQL 执行(先查询存不存在,再根据存在与否更新或插入)。
版权归原作者 kene213 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。