概述
在我们实际的应用程序开发过程种,常常会使用Excel中的数据,或者是将数据写入到Excel中去。就是Excel文件解析(导入)或者生成(导出)。
POI
Apache POI是用jAVA编写的免费工具,提供了JAVA程序对Office格式档案进行读写功能的API开源类。
其中的XSSF是对Excel格式文件的读写功能
在下载完整的Jar包并装载后就可使用。
注意:XSSF往往是读写数据量少的情况下使用,如果数据量大建议使用别的方法。在后面介绍了几种这样的方法。
**
XSSF解析EXcel文件
**在使用过程中Workbook接口代表了一个Excel文件,而在他的实现类里面,XSSFWorkbook是用来创建或解析Excel文件的。
创建Excel文件
创建输出流:
```java
Workbook workBook =newXSSFWorkbook();FileOutputStream out =newFileOutputStream("D:\\附件5\\test.xlsx"))
workbook.write(out);
out.close();
workbook.close;
如上就创建出了一个Excel文件对象。
而一个标准的Excel文件是由Sheet,Row,Cell
分别是工作簿,行,单元格。
这里把他们每一个都封装成对象。
如果要确切的在某个单元格中写入一个值,那么我们应该如下操作。
try(Workbook workBook =newXSSFWorkbook();FileOutputStream out =newFileOutputStream("D:\\附件5\\test.xlsx")){//利用workBook.createSheet()方法创造一个sheet对象Sheet sheet=workBook.createSheet();//利用Sheet.createRow()方法创造一个Row对象Row row = sheet.createRow(0);//利用Row.createSheet()方法创造一个Cell对象Cell cell = row.createCell(0);//使用Cell.setCellvalue()方法给这个单元格设置一个值
cell.setCellValue(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
workBook.write(out);}catch(IOException e){// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();}
显然如果我们需要给多个单元格设置值只需要:
Cell cell1= row.createCell(1);
cell1.setCellValue(Math.random());Cell cell2= row.createCell(2);
cell2.setCellValue(LocalDateTime.now());
如果要写入很多数据如下使用for循环即可
for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){String name =list.get(i);Row row =sheet.createRow(i+1);Cell cell0=row.createCell(0);
cell0.setCellValue(String.valueOf(i+1));Cell cell1=row.createCell(1);
cell1.setCellValue(name);Cell cell2=row.createCell(2);
cell2.setCellValue(newDate());Cell cell3=row.createCell(3);
cell3.setCellValue((int)(Math.random()*1000000));}
设置单元格样式
// 创建单元格样式DataFormat dataFormat = workbook.createDataFormat();Short formatCode = dataFormat.getFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");CellStyle cellStyle = workbook.createCellStyle();
cellStyle.setDataFormat(formatCode);// 为当前行创建单元格Cell cell1 = row.createCell(1);
cell1.setCellStyle(cellStyle);// 设置单元格样式
cell1.setCellValue(newDate());// 保存当前日期时间至本单元格
设置单元格对齐
// 创建单元格样式CellStyle cellStyle = workbook.createCellStyle();//设置单元格的水平对齐类型。 此时水平居中
cellStyle.setAlignment(HorizontalAlignment.CENTER);// 设置单元格的垂直对齐类型。 此时垂直靠底边
cellStyle.setVerticalAlignment(VerticalAlignment.BOTTOM);
完成模式:
try(FileInputStream in =newFileInputStream("C:\\Users\\AAA\\Desktop\\zero\\text.xlsx");Workbook workbook =newXSSFWorkbook(in);FileOutputStream out =newFileOutputStream("C:\\Users\\AAA\\Desktop\\zero\\text.xlsx")){Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet();//获取格式编码DataFormat dataFormat=workbook.createDataFormat();short dateFormatCode = dataFormat.getFormat("YYYY-MM-dd HH:MM:ss");short monyeFormatCode = dataFormat.getFormat("¥#,###");//创建日期格式对象CellStyle dateCellStyle = workbook.createCellStyle();
dateCellStyle.setDataFormat(dateFormatCode);//创建货币格式对象CellStyle monyeCellStyle = workbook.createCellStyle();
monyeCellStyle.setDataFormat(monyeFormatCode);for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){String name =list.get(i);Row row =sheet.createRow(i+1);Cell cell0=row.createCell(0);
cell0.setCellValue(String.valueOf(i+1));Cell cell1=row.createCell(1);
cell1.setCellValue(name);Cell cell2=row.createCell(2);
cell2.setCellStyle(dateCellStyle);
cell2.setCellValue(newDate());Cell cell3=row.createCell(3);
cell3.setCellStyle(monyeCellStyle);
cell3.setCellValue((int)(Math.random()*1000000));}
workbook.write(out);}catch(IOException e){// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();}
**
对超大Excel文件的读写
**
POI适合小的Excel文件的写入,而大型的Excel文件推荐使用EasyExcel
EasyExcel是alibaba开源的jar包,可以去相关网站下载。
**
EasyExcel写入
**
首先需要准备一个实体类如订单实体类
publicclassOrder{@ExcelProperty("订单编号")privateString orderId;// 订单编号@ExcelProperty("支付金额")@NumberFormat("¥#,###")privateDouble payment;// 支付金额@ExcelProperty(value ="创建日期",converter =LocalDateTimeConverter.class)privateLocalDateTime creationTime;// 创建时间publicOrder(){this.orderId =LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyyMMddhhmmss"))+ UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0,5);this.payment =Math.random()*10000;this.creationTime =LocalDateTime.now();}publicStringgetOrderId(){return orderId;}publicvoidsetOrderId(String orderId){this.orderId = orderId;}publicDoublegetPayment(){return payment;}publicvoidsetPayment(Double payment){this.payment = payment;}publicLocalDateTimegetCreationTime(){return creationTime;}publicvoidsetCreationTime(LocalDateTime creationTime){this.creationTime = creationTime;}@OverridepublicStringtoString(){return"Order [orderId="+ orderId +", payment="+ payment +", creationTime="+ creationTime +"]";}}
准备一个Converter转换类(因为他兼容了LocalDateTime日期时间类)在EasyExcel中并不支持LocalDateTime,但是监视器类Converter可以传入LocalDareTime类
这样我们只需要利用匿名类的模式重写部分方法就可以使用它
写入一百万行数据
publicclassDemo{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){// 写入100wEasyExcel.write("c:\\test\\run\\easy.xlsx",Order.class).sheet("订单列表").doWrite(data());}// 创建100w条订单数据privatestaticList<Order>data(){List<Order> list =newArrayList<Order>();for(int i =0; i <1000000; i++){
list.add(newOrder());}return list;}}
读取数据
EasyExcel.read("c:\\test\\run\\easy.xlsx",Order.class,newAnalysisEventListener<Order>(){@Overridepublicvoidinvoke(Order order,AnalysisContext arg1){// 读取每条数据
orderList.add(order);}@OverridepublicvoidinvokeHeadMap(Map<Integer,String> headMap,AnalysisContext context){// 读取到列头System.out.println(headMap);}@OverridepublicvoiddoAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext arg0){// 读取完毕System.out.println("END");}}).sheet().doRead();
如果要使用POI来写入数据就需要使用POI的SXXSSFWorkbook进行写入,他是通过设SXXSSFWorkbook的构造参数来设置每次在内存中保持的行数,当写入的行数达到这个值的说话,就将这些数据输出到磁盘上。而之前的XXSSFWorkbook没有设置这个参数,只能每次把所有的值都一口气放在内存中,在处理超大数据量的时候会形成 CUP和内存的占用过高。
使用SXSSFWorkbook:
try(Workbook workbook =newSXSSFWorkbook(100);FileOutputStream fos =newFileOutputStream("c:\\test\\temp.xlsx")){Sheet sheet1 = workbook.createSheet();for(int i =0; i <=1000000; i++){Row row = sheet1.createRow(i);Cell cell0 = row.createCell(0);
cell0.setCellValue(UUID.randomUUID().toString());Cell cell1 = row.createCell(1);
cell1.setCellValue(newDate());}
workbook.write(fos);}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();}
我们可以对比使用EasyExcel和SXSSFworkbook两者的运行时间来更直观的感受他们两个的性能差异。
在我电脑的环境条件下处理1000000(一百万万行数据)
CPU: i5-9300H CPU @ 2.40GHz 2.40 GHz
内存:16.0 GB
使用POI
内存和CPU的占用情况

运行时间是9.887秒
 blog.csdnimg.cn/a3923b3a0bf341cb8089486e29312084.png)
blog.csdnimg.cn/a3923b3a0bf341cb8089486e29312084.png)
在easyExcel下需要的时间是7.959秒
CPU使用情况: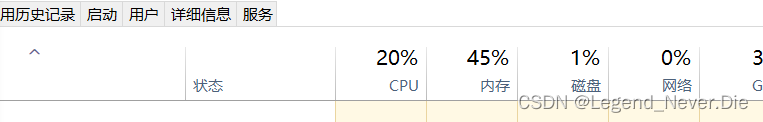
对比可以看见使用EasyExcel
EasyExcel比POI提升了很多效率。对比使用EasyExcel与POI的在处理大量的数据的时候推荐使用EasyExcel。
版权归原作者 Legend_Never.Die 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。