
🔎这里是【秒懂·云原生】,关注我学习云原生不迷路
👍如果对你有帮助,给博主一个免费的点赞以示鼓励
欢迎各位🔎点赞👍评论收藏⭐️
👀专栏介绍
【秒懂·云原生】 目前主要更新微服务,一起学习一起进步。
👀本期介绍
主要介绍Spring Cloud —— 配置绑定和配置属性校验
文章目录
配置绑定
所谓“配置绑定”就是把配置文件中的值与 JavaBean 中对应的属性进行绑定。通常,我们会把一些配置信息(例如,数据库配置)放在配置文件中,然后通过 Java 代码去读取该配置文件,并且把配置文件中指定的配置封装到 JavaBean(实体类) 中。
SpringBoot 提供了以下 2 种方式进行配置绑定:
- 使用 @ConfigurationProperties 注解
- 使用 @Value 注解
先建立数据配置文件
application.yml
sb:port:8086username:'abc \n hello'#字符串 password:6564321#字符串 birthday: 2011/12/23 #日期 books:#map jsp:36html:78spring:78books2:{jsp:56,spring:65,mybatis:98}#map 行内 person:#javabean name: abc
age:23person2:{name: lily,age:36}#javabean行内 hobby:#数组 - jsp
- hibernate
- spring
- mybatis
list:# list集合 -32-65-98set:#set 集合 - hello
- world
hobby2:[23,45,56]#数组 list set 行内 mapList:# 数组 list set 里存map -jsp:36hibernate:58-html:65css:98js:65-{vue:36,react:98}
@ConfigurationProperties
通过 Spring Boot 提供的 @ConfigurationProperties 注解,可以将全局配置文件中的配置数据绑定到 JavaBean 中。
DbConfig.java
@Configuration@ConfigurationProperties(prefix ="sb")publicclassDbConfig{String username;String password;Date birthday;Map books;Person person;Map books2;Person person2;String[] hobby;List list;Set set ;int[] hobby2;List<Map> mapList;/************省略geter/seter方法*************/}
只有在容器中的组件,才会拥有 SpringBoot 提供的强大功能。如
果我们想要使用 @ConfigurationProperties 注解进行配置绑定,
那么首先就要保证该对 JavaBean 对象在 IoC 容器中,所以需要用
到 @Configuration 注解来添加组件到容器中。
JavaBean 上使用了注解 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “sb”)
,它表示将这个 JavaBean 中的所有属性与配置文件中以“sb”为前
缀的配置进行绑定。
@Value
@Value的作用是通过注解将常量、配置文件中的值、其他bean的属性值注入到变量中,作为变量的初始值。 @Value的值有两类:
① ${property : default_value }
② #{ obj.property? :default_value }
第一个注入的是外部配置文件对应的property,第二个则是SpEL表达式对应的内容。
default_value,就是前面的值为空时的默认值。注意二者的不同,#{}里面那个obj代表对象。
也就是说@Value注解有两种用法,一种是@Value(“${}”)和@Value(“#{}”),搞清楚分类后我们一一来分析。
第一种 @Value(“${}”)
controller层代码:
@RestController@RequestMapping("/test")publicclassValueController{@AutowiredprivateCarpollingService carpollingService;@GetMapping("/getValue")publicStringgetValue(){return carpollingService.getValue();}}
配置类代码:
@ConfigurationpublicclassCarpollingServiceImpl{@Value("${db.port}")privateString port;@OverridepublicStringgetValue(){return port;}}
第二种@Value(“#{}”)
注意: #{}是不能以第一种方式来进行取值,否则会报错
前面已经说了,#{}里面包含的是obj,所以需要配合bean来使用,现在创建一个UserBean,并且给某个字段加上@Value(“#{}”)注解(按自己的需求任意添加注解)
UserBean类代码:
@Data@Component//添加component注解,使其注册进容器,交由容器进行管理publicclassUserBean{privateString name="张三";}
controller层代码:
@RestController@RequestMapping("/test")publicclassValueController{@AutowiredCarpollingServiceImpl carpollingService;@GetMapping("/getValue")publicStringgetValue(){return carpollingService.getValue();}}
配置类代码:
@ConfigurationpublicclassCarpollingServiceImpl{@Value("#{userBean.name}")privateString port;publicStringgetValue(){return port;}}

@PropertySource
如果将所有的配置都集中到 application.properties 或 application.yml
中,那么这个配置文件会十分的臃肿且难以维护,因此我们通常会将与Spring Boot 无关的配置(例如自定义配置)提取出来,写在一个单独的配置文件中,并在对应的 JavaBean 上使用 @PropertySource 注解指向该配置文件。
我们也可以自定义配置文件,例如新建 db.properties ,配置内容如下:
pro.username=admin
pro.password=123456
pro.birthday=2000/12/01
pro.age=23
pro.books={jsp:36,html:360,spring:65}
pro.hobby=23,34
pro.list=sprig,myatis
pro.set=34,45,56
配置类:
@Component@PropertySource("classpath:db.properties")@DatapublicclassUser{@Value("${pro.username}")String username;@Value("${pro.password}")String password;@Value("${pro.birthday}")Date birthday;}
注: 该注解只能引用properties文件
配置属性校验
自定义配置文件时,可以使用@Validated注解对注入的值进行一些简单的校验,示例代码:
Testconfig.java
@Validated@Configuration@ConfigurationProperties(prefix ="sb")publicclassTestconfig{@Max(value =123)privateString password;publicStringgetPassword(){return password;}publicvoidsetPassword(String password){this.password = password;}}
测试
@AutowiredTestconfig testconfig;@Testvoida(){System.out.println(testconfig.getPassword());}
抛出错误,最大值不能超过123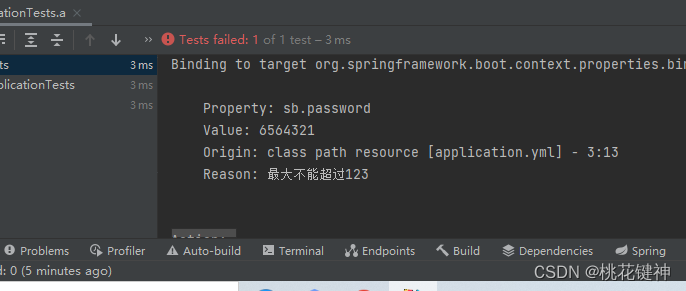
@Max(value = 123)注解会对注入的值进行校验,如果不是小于123的将会报错抛出
其它常见注解:
@AssertFalse 校验false
@AssertTrue 校验true
@DecimalMax(value=,inclusive=) 小于等于value,inclusive=true,
是小于等于
@DecimalMin(value=,inclusive=) 与上类似
@Max(value=) 小于等于value
@Min(value=) 大于等于value
@NotNull 检查Null
@Past 检查日期
@Pattern(regex=,flag=) 正则
@Size(min=, max=) 字符串,集合,map限制大小
@Validate 对po实体类进行校验
上述的这些注解位于javax.validation.constraints包下, SpringBoot 2.3.0以后maven引用:
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId></dependency>
@Value 与 @ConfigurationProperties对比
@Value 和 @ConfigurationProperties 注解都能读取配置文件中的属性值并绑定到 JavaBean 中,但两者存在以下不同。
1. 使用位置不同
- @ConfigurationProperties:标注在 JavaBean 的类名上;
- @Value:标注在 JavaBean 的属性上。
2. 功能不同
- @ConfigurationProperties:用于批量绑定配置文件中的配置;
- @Value:只能一个一个的指定需要绑定的配置。
3. 松散绑定支持不同
@ConfigurationProperties:支持松散绑定(松散语法),例如实体类Person 中有一个属性为 firstName,那么配置文件中的属性名支持以下写法:
- person.firstName
- person.first-name
- person.first_name
- PERSON_FIRST_NAME
@Vaule:不支持松散绑定。
4. SpEL 支持不同
- @ConfigurationProperties:不支持 SpEL 表达式;
- @Value:支持 SpEL 表达式。
5. 复杂类型封装
- @ConfigurationProperties:支持所有类型数据的封装,例如 Map、 List、Set、以及对象等;
- @Value:支持基本数据类型的封装,例如字符串、布尔值、整数等类型, 对集合Map list set配置有要求
6.属性校验
- @Value不支持属性校验
- @ConfigurationProperties 支持属性校验
7. 应用场景不同
@Value 和 @ConfigurationProperties 两个注解之间,并没有明显的优劣之分,它们只是适合的应用场景不同而已。
- 若只是获取配置文件中的某项值,则推荐使用 @Value 注解;
- 若专门编写了一个 JavaBean 来和配置文件进行映射,则建议使用 @ConfigurationProperties 注解。
我们在选用时,根据实际应用场景选择合适的注解能达到事半功倍的效
果。
结束语🏆🏆🏆
🔥推荐一款模拟面试、刷题神器网站
点击注册即可
牛客刷题网
1、算法篇(398题):面试必刷100题、算法入门、面试高频榜单
2、SQL篇(82题):快速入门、SQL必知必会、SQL进阶挑战、面试真题
3、大厂笔试真题:字节跳动、美团、百度、腾讯…
版权归原作者 桃花键神 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。