1.引言
我们上次介绍了神经网络主要功能之一预测,本篇大部分内容与回归相似,有看不懂的点可以看看我回归 Regression ,今天介绍一下神经网络的另一种功能:分类。
2.网络搭建
2.1 准备工作
还是先引用我们所需要的库,和回归所需的一样。
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
n_data = torch.ones(2000, 2)
x0 = torch.normal(2*n_data, 1) # class0 x data (tensor), shape=(100, 2)
y0 = torch.zeros(2000) # class0 y data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
x1 = torch.normal(-2*n_data, 1) # class1 x data (tensor), shape=(100, 2)
y1 = torch.ones(2000) # class1 y data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
x = torch.cat((x0, x1), 0).type(torch.FloatTensor) # shape (200, 2) FloatTensor = 32-bit floating
y = torch.cat((y0, y1), ).type(torch.LongTensor) # shape (200,) LongTensor = 64-bit integer
然后我们生成一些二维数据来代表许多不同的点,我们就是要对这些点进行分类。
2.2 搭建网络
主体部分和回归没有什么区别,只是需要修改几个小部分就行了:因为我们的点是二维数据所以输入层有两个神经元,最终结果也是二维数据所以输出层也有两个神经元,损失函数我们选取交叉熵(CrossEntropy)。
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self,n_feature,n_hidden,n_output):
super(Net,self).__init__()
self.hidden=torch.nn.Linear(n_feature,n_hidden)
self.predict=torch.nn.Linear(n_hidden,n_output)
def forward(self,x):
x=F.relu(self.hidden(x))
x=self.predict(x)
return x
net=Net(2,20,2)
print(net)
optimizer=torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(),lr=0.001)
loss_func=torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
2.3 训练网络
训练网络与回归一样,就不赘述了。
for t in range(200):
out = net(x)
loss = loss_func(out, y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
最后效果是这样的:
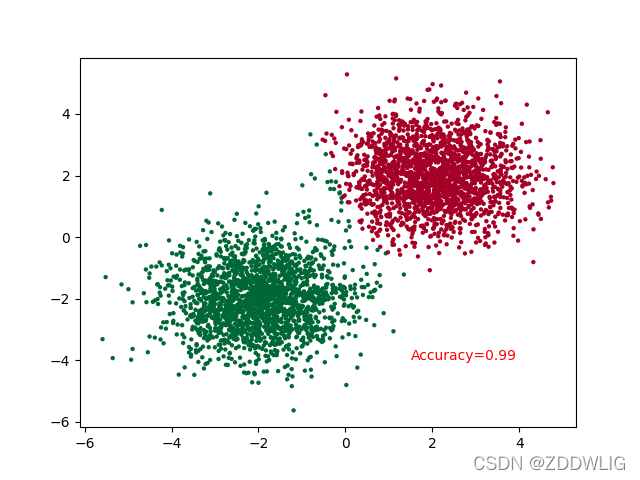
3.完整代码
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
n_data = torch.ones(2000, 2)
x0 = torch.normal(2*n_data, 1) # class0 x data (tensor), shape=(100, 2)
y0 = torch.zeros(2000) # class0 y data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
x1 = torch.normal(-2*n_data, 1) # class1 x data (tensor), shape=(100, 2)
y1 = torch.ones(2000) # class1 y data (tensor), shape=(100, 1)
x = torch.cat((x0, x1), 0).type(torch.FloatTensor) # shape (200, 2) FloatTensor = 32-bit floating
y = torch.cat((y0, y1), ).type(torch.LongTensor) # shape (200,) LongTensor = 64-bit integer
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self,n_feature,n_hidden,n_output):
super(Net,self).__init__()
self.hidden=torch.nn.Linear(n_feature,n_hidden)
self.predict=torch.nn.Linear(n_hidden,n_output)
def forward(self,x):
x=F.relu(self.hidden(x))
x=self.predict(x)
return x
net=Net(2,20,2)
print(net)
optimizer=torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(),lr=0.001)
loss_func=torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
plt.ion()
for t in range(200):
out = net(x)
loss = loss_func(out, y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if t % 2 == 0:
# plot and show learning process
plt.cla()
prediction = torch.max(out, 1)[1]
pred_y = prediction.data.numpy()
target_y = y.data.numpy()
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy()[:, 0], x.data.numpy()[:, 1], c=pred_y, s=10, lw=0, cmap='RdYlGn')
accuracy = float((pred_y == target_y).astype(int).sum()) / float(target_y.size)
plt.text(1.5, -4, 'Accuracy=%.2f' % accuracy, fontdict={'size': 10, 'color': 'red'})
plt.pause(0.1)
plt.ioff()
plt.show()
版权归原作者 ZDDWLIG 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。