文章目录
一、线程通信(了解)
- 概念
线程通信就是线程间相互发送数据,线程间共享一个资源即可实现线程通信
- 常见方式
通过共享一个数据的方式实现
根据共享数据的情况决定自己该怎么做,以及通知其他线程怎么做
- 场景
生产者与消费者模型:生产者线程负责生产数据,消费者线程负责消费生产者产生的数据
- 要求
生产者线程生产完数据后唤醒消费者,然后等待自己,消费者消费完该数据后唤醒生产者,然后等待自己
方法名解释
void wait()
当前线程等待,直到另一个线程调用notify() 或 notifyAll()唤醒自己
void notify()
唤醒正在等待对象监视器(锁对象)的单个线程
void notifyAll()
唤醒正在等待对象监视器(锁对象)的所有线程
二、线程池(重点)
- 概述
可以复用线程的技术
1、获得线程池对象
用ExecutorService实现类ThreadPoolExecutor自创建一个线程池对象
用Executors(线程池的工具类)调用方法返回不同特点的线程池对象
publicThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,//核心线程数int maximumPoolSize,//最大线程数long keepAliveTime,//线程空闲时间TimeUnit unit,//时间单位BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,//任务队列ThreadFactory threadFactory,//线程工厂RejectedExecutionHandler handler//拒绝策略)
参数名解释
corePoolSize
指定线程池的线程数量(核心线程),不能小于0
maximumPoolSize
指定线程池可支持的最大线程数,最大数量 >= 核心线程数量
keepAliveTime
指定临时线程的最大存活时间 ,不能小于0
unit
指定存活时间的单位(秒、分、时、天)
workQueue
指定任务队列 ,不能为null
threadFactory
指定用哪个线程工厂创建线程,不能为null
handler
指定线程忙,任务满的时候,新任务来了怎么办,不能为null
TimeUnit.DAYS;//天TimeUnit.HOURS;//小时TimeUnit.MINUTES;//分钟TimeUnit.SECONDS;//秒TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS;//毫秒TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS;//微妙TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS;//纳秒
2、线程池处理Runnable
ExecutorService方法解释
void execute(Runnable command)
执行任务/命令,没有返回值,一般用来执行 Runnable 任务
Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task)
执行任务,返回未来任务对象获取线程结果,一般拿来执行 Callable 任务
void shutdown()
等任务执行完毕后关闭线程池
List<Runnable> shutdownNow()
立刻关闭,停止正在执行的任务,并返回队列中未执行的任务4种策略解释
ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy
丢弃任务并抛出RejectedExecutionException异常。是默认的策略
ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy
丢弃任务,但是不抛出异常 这是不推荐的做法
ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy
抛弃队列中等待最久的任务 然后把当前任务加入队列中
ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy
由主线程负责调用任务的run()方法从而绕过线程池直接执行
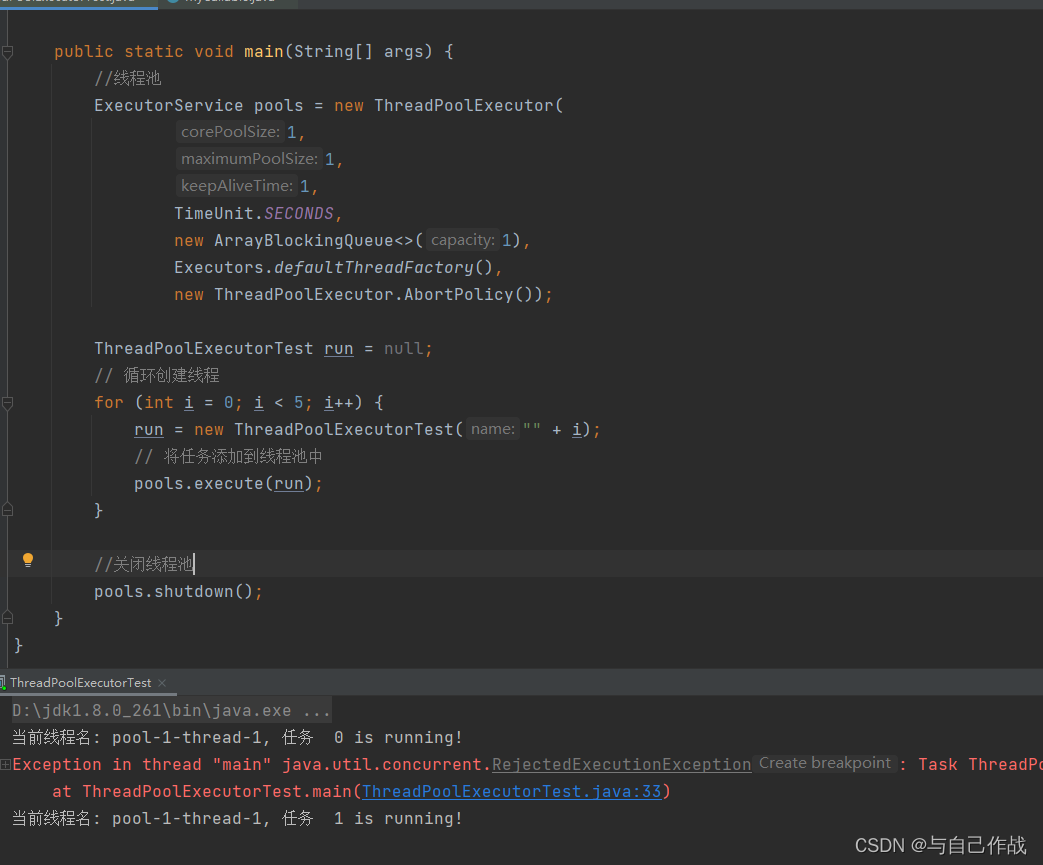
1)AbortPolicy实战
当运行任务数超过核心数时,会报RejectedExecutionException错误
importjava.util.concurrent.*;publicclassThreadPoolExecutorTestimplementsRunnable{privateString name;publicThreadPoolExecutorTest(String name){this.name = name;}@Overridepublicvoidrun(){try{System.out.println("当前线程名: "+Thread.currentThread().getName()+", 任务 "+ name +" is running!");Thread.sleep(200);}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();}}publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){//线程池ExecutorService pools =newThreadPoolExecutor(1,1,1,TimeUnit.SECONDS,newArrayBlockingQueue<>(1),Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),newThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());ThreadPoolExecutorTest run =null;// 循环创建线程for(int i =0; i <5; i++){
run =newThreadPoolExecutorTest(""+ i);// 将任务添加到线程池中
pools.execute(run);}//关闭线程池
pools.shutdown();}}
2)DiscardPolicy实战
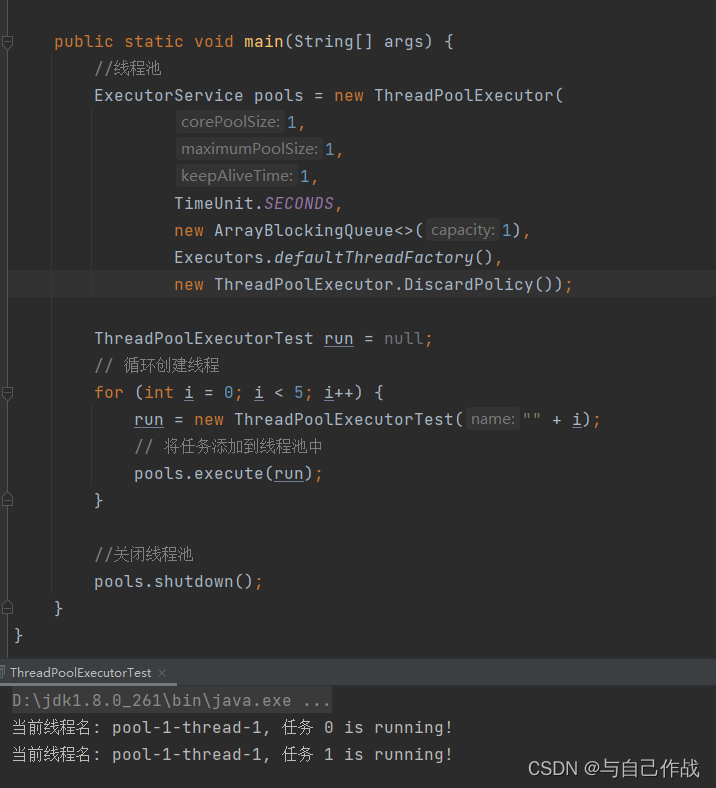
importjava.util.concurrent.*;publicclassThreadPoolExecutorTestimplementsRunnable{privateString name;publicThreadPoolExecutorTest(String name){this.name = name;}@Overridepublicvoidrun(){try{System.out.println("当前线程名: "+Thread.currentThread().getName()+", 任务 "+ name +" is running!");Thread.sleep(200);}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();}}publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){//线程池ExecutorService pools =newThreadPoolExecutor(1,1,1,TimeUnit.SECONDS,newArrayBlockingQueue<>(1),Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),newThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy());ThreadPoolExecutorTest run =null;// 循环创建线程for(int i =0; i <5; i++){
run =newThreadPoolExecutorTest(""+ i);// 将任务添加到线程池中
pools.execute(run);}//关闭线程池
pools.shutdown();}}
3)DiscardOldestPolicy实战
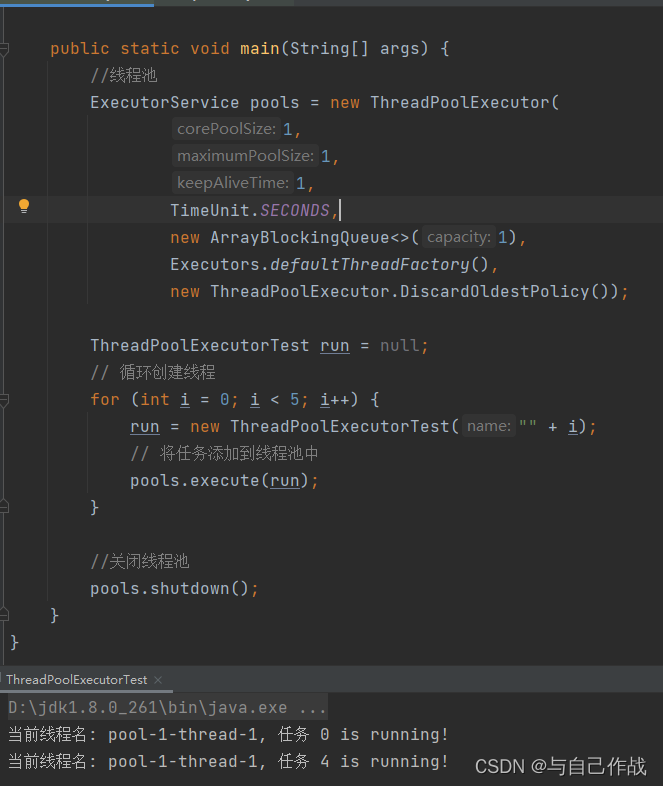
importjava.util.concurrent.*;publicclassThreadPoolExecutorTestimplementsRunnable{privateString name;publicThreadPoolExecutorTest(String name){this.name = name;}@Overridepublicvoidrun(){try{System.out.println("当前线程名: "+Thread.currentThread().getName()+", 任务 "+ name +" is running!");Thread.sleep(200);}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();}}publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){//线程池ExecutorService pools =newThreadPoolExecutor(1,1,1,TimeUnit.SECONDS,newArrayBlockingQueue<>(1),Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),newThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy());ThreadPoolExecutorTest run =null;// 循环创建线程for(int i =0; i <5; i++){
run =newThreadPoolExecutorTest(""+ i);// 将任务添加到线程池中
pools.execute(run);}//关闭线程池
pools.shutdown();}}
4)CallerRunsPolicy实战
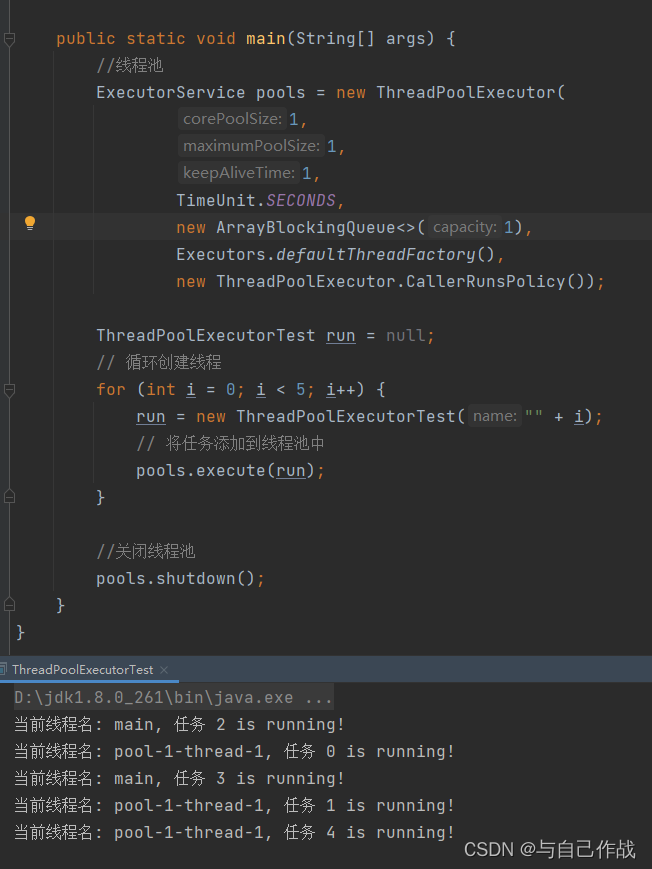
importjava.util.concurrent.*;publicclassThreadPoolExecutorTestimplementsRunnable{privateString name;publicThreadPoolExecutorTest(String name){this.name = name;}@Overridepublicvoidrun(){try{System.out.println("当前线程名: "+Thread.currentThread().getName()+", 任务 "+ name +" is running!");Thread.sleep(200);}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();}}publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){//线程池ExecutorService pools =newThreadPoolExecutor(1,1,1,TimeUnit.SECONDS,newArrayBlockingQueue<>(1),Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),newThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());ThreadPoolExecutorTest run =null;// 循环创建线程for(int i =0; i <5; i++){
run =newThreadPoolExecutorTest(""+ i);// 将任务添加到线程池中
pools.execute(run);}//关闭线程池
pools.shutdown();}}
3、线程池处理Callable
ExecutorService方法解释
void execute(Runnable command)
执行任务/命令,没有返回值,一般用来执行 Runnable 任务
Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task)
执行任务,返回未来任务对象获取线程结果,一般拿来执行 Callable 任务
void shutdown()
等任务执行完毕后关闭线程池
List<Runnable> shutdownNow()
立刻关闭,停止正在执行的任务,并返回队列中未执行的任务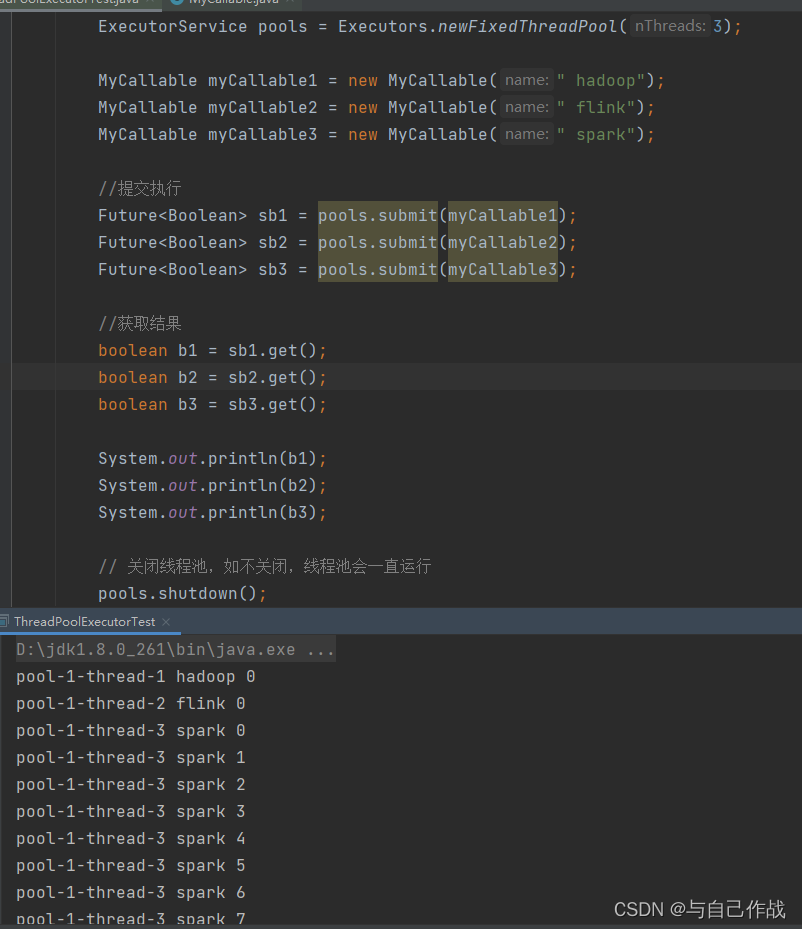
importjava.util.concurrent.Callable;publicclassMyCallableimplementsCallable{privateString name;publicMyCallable(String name){this.name = name;}@OverridepublicObjectcall()throwsException{for(int i =0; i <10; i++){System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ name +" "+ i);}returntrue;}}
importjava.util.concurrent.*;publicclassThreadPoolExecutorTest{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args)throwsExecutionException,InterruptedException{//创建线程池ExecutorService pools =Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);MyCallable myCallable1 =newMyCallable(" hadoop");MyCallable myCallable2 =newMyCallable(" flink");MyCallable myCallable3 =newMyCallable(" spark");//提交执行Future<Boolean> sb1 = pools.submit(myCallable1);Future<Boolean> sb2 = pools.submit(myCallable2);Future<Boolean> sb3 = pools.submit(myCallable3);//获取结果boolean b1 = sb1.get();boolean b2 = sb2.get();boolean b3 = sb3.get();System.out.println(b1);System.out.println(b2);System.out.println(b3);// 关闭线程池,如不关闭,线程池会一直运行
pools.shutdown();}}
4、Callable和Runnable接口的区别
Callable接口中的Call方法有返回值,Runnable接口中的Run方法没有返回值
Callable接口中的Call方法有声明异常,Runnable接口中的Run方法没有异常
版权归原作者 与自己作战 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。