一、Pinia介绍
pinia是什么?
- pinia是一个用于vue的状态管理库,类似于vuex,是vue的另一种状态管理工具
与vuex相比
与 Vuex 相比,Pinia 提供了一个更简单的 API,具有更少的规范,提供了 Composition-API 风格的 API,最重要的是,在与 TypeScript 一起使用时具有可靠的类型推断支持。
- 可以对Vue2和Vue3做到很好的支持,也就是老项目也可以使用Pinia。
- 抛弃了Mutations的操作,只有state、getters和actions.极大的简化了状态管理库的使用,让代码编写更加容易直观。
- 不需要modules嵌套模块,符合Vue3的Composition api ,让代码更加扁平化。
- 完整的TypeScript支持。Vue3版本的一大优势就是对TypeScript的支持,所以Pinia也做到了完整的支持。Vuex对TS的语法支持不是完整的。
- 代码更加简洁,可以实现很好的代码自动分割。Vue2的时代,写代码需要来回翻滚屏幕屏幕找变量,非常的麻烦,Vue3的Composition api完美了解决这个问题。 可以实现代码自动分割,pinia也同样继承了这个优点。
为什么要使用 Pinia:
Pinia 是 Vue 的存储库,它允许跨组件/页面共享状态。
如果您熟悉 Composition API,您可能会认为您已经可以通过一个简单的
export const state = reactive({})
. 这对于单页应用程序来说是正确的,但如果它是服务器端呈现的,会使您的应用程序暴露于安全漏洞。 但即使在小型单页应用程序中,您也可以从使用 Pinia 中获得很多好处:
- dev-tools 支持 - 跟踪动作、突变的时间线- Store 出现在使用它们的组件中- time travel 和 更容易的调试
- 热模块更换 - 在不重新加载页面的情况下修改您的 Store- 在开发时保持任何现有状态
- 插件:使用插件扩展 Pinia 功能
- 为 JS 用户提供适当的 TypeScript 支持或 autocompletion
- 服务器端渲染支持
二、使用Pinia
引入pinia
在main.js中:
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import router from "./router/index.js"
import { createPinia } from 'pinia'
let app=createApp(App)
app.use(createPinia())
app.use(router)
app.mount('#app')
示例:
在src目录下新建store文件夹
新建仓库hive.js文件
定义store(仓库)
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
//传入两个参数 第一个参数是id 可以在devtool中通过id来查看
//第二个是配置项 state 为数据 getter类似计算属性 action 修改数据的方法 支持同步异步
export const useHive = defineStore('hive', {
state: () =>{
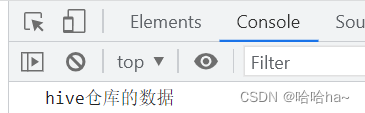
return {msg:"hive仓库的数据"}
}
//类似于computed 可以帮我们去修饰我们的值
getters:{
},
//可以操作异步 和 同步提交state
actions:{
}
})
//按需导出useHive 引入时与此同名且写在{}里面
组件中使用:
<script setup>
import { useHive } from "../store/hive.js";
let store = useHive();
console.log(store.msg);
</script>
结果显示:
三、修改状态
(一) 单独修改
1)直接修改:
示例:
Box1组件中修改:
<template>
<div>
<h2>box组件</h2>
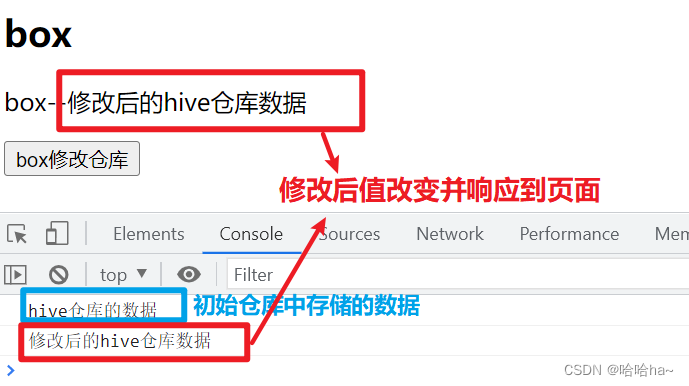
<p>box--{{store.msg}}</p>
<button @click="change">box修改仓库数据</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { useHive } from "../store/hive.js";
let store = useHive();
let change = () => {
store.msg = "修改后的hive仓库数据";
console.log(store.msg);
};
</script>
结果显示:
store是一个响应性对象 因此可以修改并刷新页面
2)解构修改
只是简单的解构之后修改是不行的,因为解构后得msg为非响应式变量 同toRefs知识点
因此需要利用toRefs把响应式对象的属性解构为响应性的变量,修改时一定不要忘记加.value
示例:
<template>
<div>
<h1>page2</h1>
<p>{{msg}}</p>
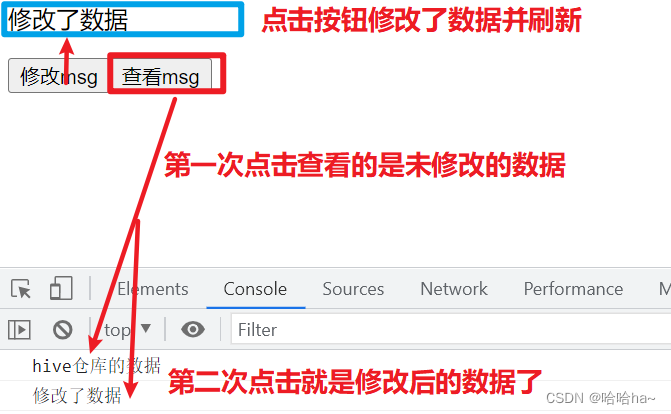
<button @click="change">修改msg</button>
<button @click="look">查看msg</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import {useHive} from "../router/hive.js"
import {toRefs} from "vue"
let data=useHive()
let {msg}=toRefs(data) //msg是响应性的 并且关联了data
let change=()=>{
msg.value="修改了数据"
}
let look=()=>{
console.log(msg.value)
}
</script>
显示结果:
3)将状态重置到其初始值
示例:
<template>
<div>
<h1>page2</h1>
<p>{{msg}}</p>
<button @click="change">修改msg</button>
<button @click="look">查看msg</button>
<button @click="reset1">重置仓库</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { useHive } from "../store/hive.js";
import {toRefs} from "vue"
let data=useHive()
let {msg}=toRefs(data) //msg是响应性的 并且关联了data
let change=()=>{
msg.value="修改了数据"
}
let look=()=>{
console.log(msg.value)
}
// 将状态 重置 到其初始值
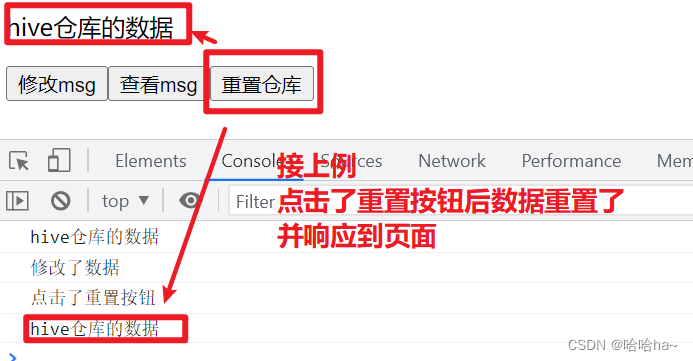
let reset1=()=>{
console.log("点击了重置按钮")
data.$reset()
}
</script>
结果显示:
(二) 批量修改
新建仓库user.js文件:
import {defineStore} from "pinia"
let a=defineStore("user",{
state() {
return{
count:20,
price:15
}
}
})
export default a;
//默认导出 变量名随便写 引入时不需要写{}
** (1) 示例**
<template>
<div>
<p>{{store.count}}--{{store.price}}</p>
<button @click="change1">批量修改1</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import MyStore from "../store/user.js"
let store=MyStore()
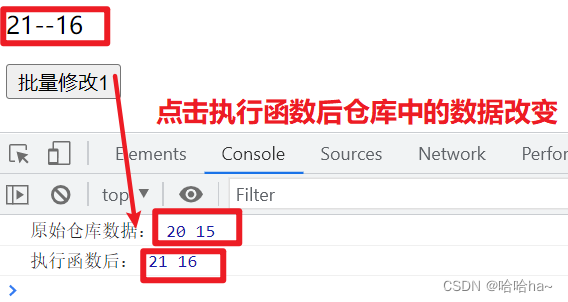
console.log(store.count,store.price)
function change1(){
store.count++
store.price++
console.log("执行函数后:",store.count,store.price)
}
</script>
结果显示:
** (2) 示例**
<template>
<div>
<p>{{store.count}}--{{store.price}}</p>
<button @click="change2">批量修改2</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import MyStore from "../store/user.js"
let store=MyStore()
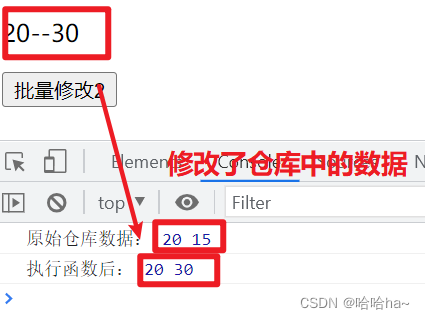
console.log("原始仓库数据:",store.count,store.price)
function change2(){
//对比,仓库中有重复的数据就覆盖
store.$patch({
count:20,
price:30,
})
console.log("执行函数后:",store.count,store.price)
}
</script>
结果显示:
** (3) 示例**
<template>
<div>
<p>{{store.count}}--{{store.price}}</p>
<button @click="change3">批量修改3</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import MyStore from "../store/user.js"
let store=MyStore()
console.log("原始仓库数据:",store.count,store.price)
function change3(){
//批量修改3
store.$patch(()=>{
store.count++
store.price++
})
console.log("执行函数后:",store.count,store.price)
}
</script>
结果显示:

(三)订阅修改
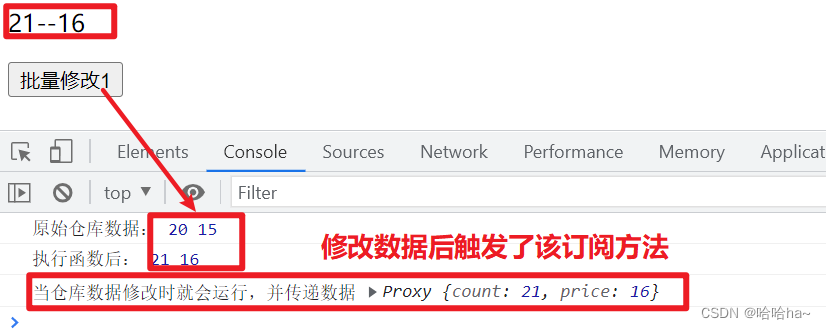
通过 store 的 $subscribe() 方法查看状态及其变化,状态修改时就会触发一次
示例:
<template>
<div>
<p>{{store.count}}--{{store.price}}</p>
<button @click="change1">批量修改1</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import MyStore from "../store/user.js"
let store=MyStore()
console.log(store.count,store.price)
function change1(){
store.count++
store.price++
console.log("执行函数后:",store.count,store.price)
}
store.$subscribe((n1,state)=>{
//相当于是个监听器
console.log("当仓库数据修改时就会运行,并传递数据",state)
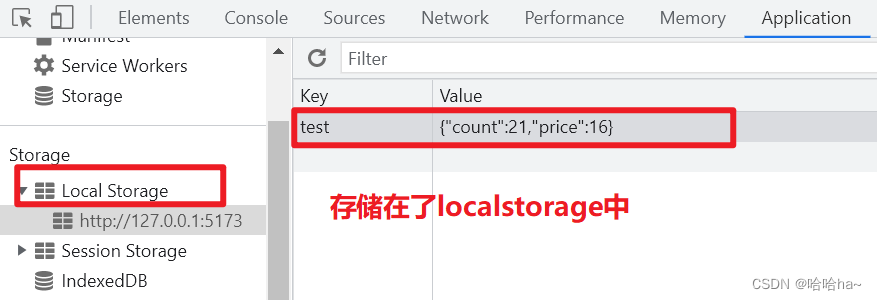
//将变化的结果存到本地持久化存储中
localStorage.setItem('test', JSON.stringify(state))
})
</script>
结果显示:
四、getter
getter 完全等同于 Store 状态的计算值。
它们可以用
defineStore()中的getters属性定义。他们接收“状态”作为第一个参数以鼓励箭头函数的使用,普通函数内部可以用this代表state
当计算属性用 仅当依赖数据发生改变时才会触发执行 在组件中直接使用
新建仓库getage.js文件:
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
export const useGetage=defineStore("getage",{
state: () =>{
return {msg:"getage仓库的数据",birth:"2001-04-16"}
},
getters:{
age(state){
console.log("运行了一次")
return new Date().getFullYear()- new Date(state.birth).getFullYear()
}
},
//state形参是给箭头函数用的 相当于普通函数的this
})
示例:
<template>
<div>
<p>{{store.birth}}--{{store.msg}}--{{store.age}}</p>
<button @click="changemsg">getter-changemsg</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import {useGetage} from "../store/getage.js"
let store=useGetage()
console.log(store.age)
function changemsg(){
store.msg="msg信息"
store.birth="2001-05-08"
}
</script>
结果显示: 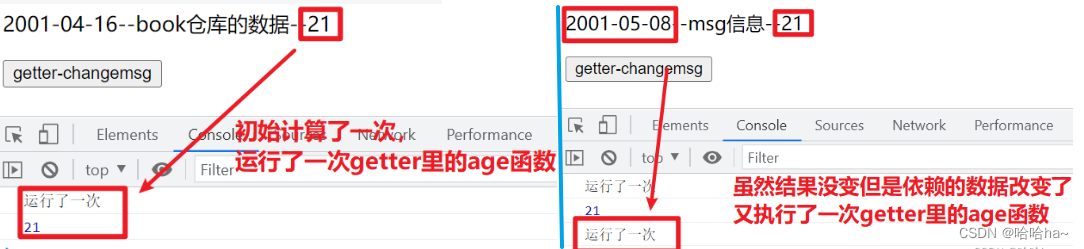
五、actions
在pinia中没有提供mutaion 因为Actions就够了(它可以异步同步的统一修改状态)
提供这个功能 就是为了项目中的公共修改状态的业务统一
新建仓库main.js文件:
export const useStore = defineStore('main', {
state: () => ({
counter: 0,
}),
actions: {
increment() {
this.counter++ //1.有this
},
randomizeCounter(state) {//2.有参数 state
state.counter = Math.round(100 * Math.random())
},
randomizeCounter(state) {
//异步函数 可以在异步函数的回调中修改仓库
axios("/test").then(res=>{
state.counter = res.data.length
})
}
},
})
组件中的使用:
setup() {
const store = useStore()
store.increment()
store.randomizeCounter()
}
六、模块化
一个文件一个小仓库,仓库之间可以相互访问数据,相互引用和修改
不同组件也可以访问任意小仓库数据
store/a.js文件
export const a = defineStore('a', { state: () => ({ counter: 0, }) })store/b.js文件
export const b = defineStore('b', { state: () => ({ counter: 0, }), actions: { fn(state){state.counter=100} } })Box组件同时使用a,b两个仓库的数据
import {a} from "@/store/a.js" import {b} from "@/store/b.js" let store1=a() store1.counter let store2=b() store2.countera仓库使用b仓库的数据:
跟组件一样的使用方式import {b} from "@/store/b.js" let storeb=b() storeb.counter storeb.fn()
版权归原作者 哈哈ha~ 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。