文章目录
mysql的基本查询
数据库的基本操作有四种,增删查改,增加数据,删除数据,查找数据,修改数据
insert插入语句
Create
创建表
createtable t20(
id intunsignedprimarykeyauto_incrementcomment'主键',
sn intunsignednotnull unqiue comment'学号',
name varchar(20)notnull,
qq varchar(12))engine=InnoDBdefault chsrset=utf8;
插入语句
单行插入
insert t20(sn,name,qq)values(123,'猪八戒','1234567');
多行行插入
insert t20(sn,name,qq)values(123,'猪八戒','1234567'),(125,'hello','456789');
insertinto t20(id,name,qq)values(5,'hsjl','585785');
当出现主键和唯一键冲突
insertinto t10 values(1,123,'猪悟能','55555')onduplicatekey name='猪悟能',qq='555555';//该语句可以在出现主键或者唯一键冲突时进行更新
替换replace
主键或者唯一教案没有冲突,则直接插入
主键或者唯一键由冲突,则删除后再插入
replaceinto t20 values(3.125,'李四','55618415');

select查询语句
查询语句
6.2.1select 查询
如下所示,我们建立一张学生成绩表,然后后面的例子以下面这张表为例子进行说明
-- 创建数据库dropdatabaseifexists student;createdatabaseifnotexists student defaultcharacterset utf8 collate utf8_general_ci;-- 使用数据库use student;-- 创建数据库表droptableifexists exam_result;createtable exam_result (
id intnotnullprimarykeyauto_incrementcomment'编号',
name varchar(20)notnulldefault''comment'姓名',
chinese float(3,1)notnulldefault0.0comment'语文成绩',
english float(3,1)notnulldefault0.0comment'英语成绩',
math float(3,1)notnulldefault0.0comment'数学成绩');-- 插入数据insertinto exam_result (name, chinese, english, math)values('李涛',89,78,90);insertinto exam_result (name, chinese, english, math)values('唐僧',67,98,56);insertinto exam_result (name, chinese, english, math)values('孙悟空',87,78,77);insertinto exam_result (name, chinese, english, math)values('老妖婆',88,98,90);insertinto exam_result (name, chinese, english, math)values('红孩儿',82,84,67);insertinto exam_result (name, chinese, english, math)values('如来佛祖',55,85,45);insertinto exam_result (name, chinese, english, math)values('菩萨',75,65,30);-- 查询全部数据select id ,name , chinese, english, math from exam_result;
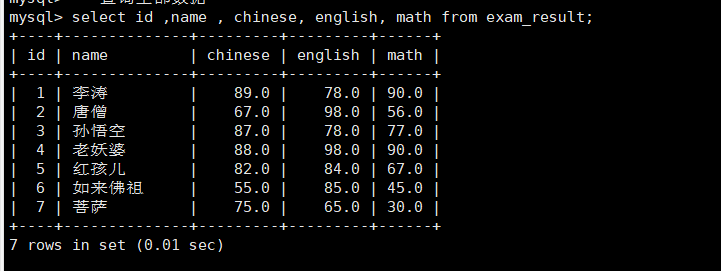
全列查询
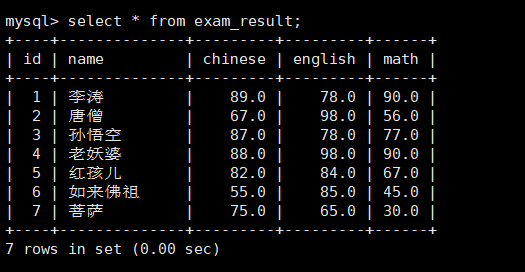
//通常情况下不建议使用*进行全列查询select*from exam_result;
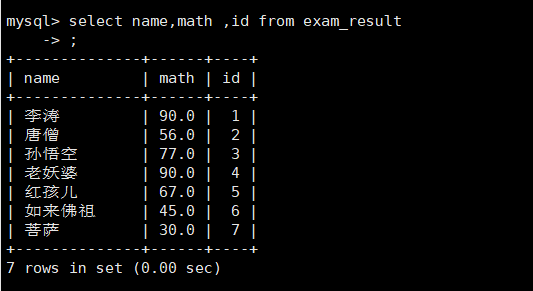
查询指定列
select name,math ,id from exam_result
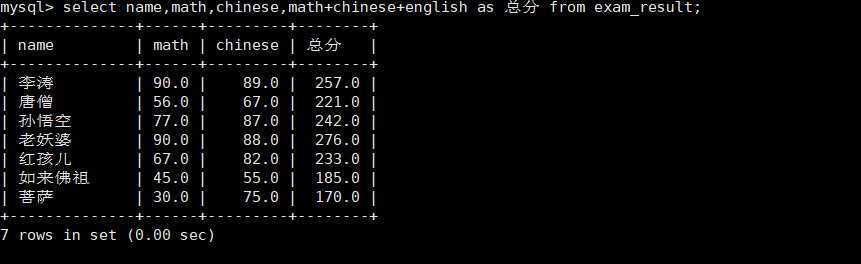
查询字段包含表达式
mysql会自动计算表达式的值
select name,math,chinese,math+chinese+english as 总分 from exam_result;
为查询结果指定别名
select name as'姓名',age as'年龄'from student
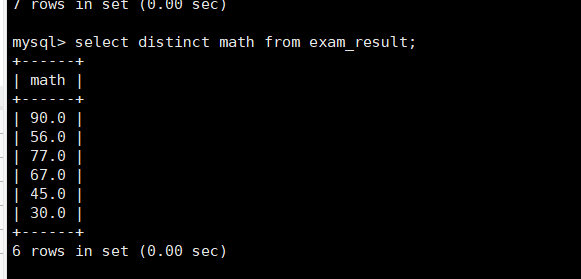
去重distinct
重复的数据去除
selectdistinct math from exam_result;
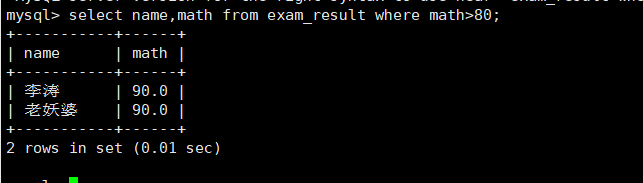
条件筛选
select name,math from exam_result where math>80;
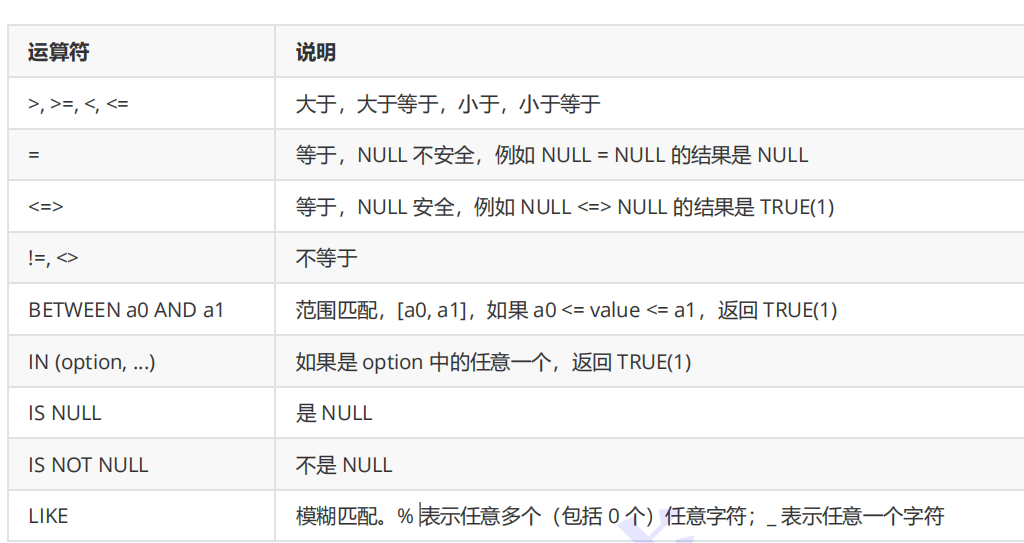
where条件
比较运算符
逻辑运算符
运算符说明AND多个条件必须都为TRUE,结果才为TRUEOR任意一个条件为 true 结果为trueNOT条件为true,结果为false
数学成绩是58,59或者98 ,99的同学
select name,math from exam_result where math in(58,59,98,99);

模糊匹配
关键字:like,% _
利用该关键字可以进行字符串的匹配
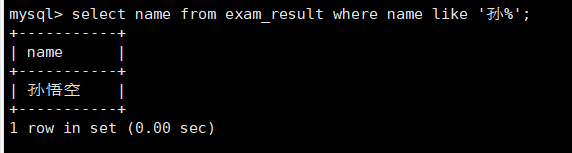
如下面的例子,找出姓孙的同学
’孙%‘:代表第一个字符为’孙‘后面可以有无限多个字符,只要第一个字符匹配就行
select name from exam_result where name like'孙%';
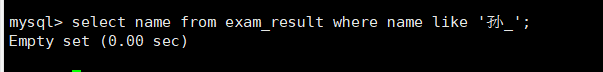
找到’孙某‘同学
注意这里孙某意味着只有两个字符,第一个字符为孙,后面只能有一个字符,_代表一个字符,‘孙 _’就代表只有两个字符并且姓孙的同学
select name from exam_result where name like'孙_';
as关键字
利用as关键字可以对列名进行重命名,例如下面我们将 chinese+englist+math重命名为‘总分’,就是在中间加入as关键字
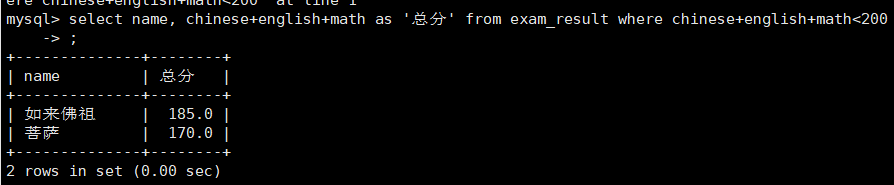
挑选总分在200以下的同学
select name ,chinese+english+math as'总分'from exam_result where chinese+english+math<200
where后续的子句本身就是在我们select期间要进行作为条件筛选的
语文成绩>80并且不姓孙
select name ,chinese from exam_result where chinese>80and name notlike'孙%';
![mg-p2lkpUnG-1650876195319]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/5f03f91688a741319803791cb2da0f02.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBA44CA6JC956aF,size_20,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
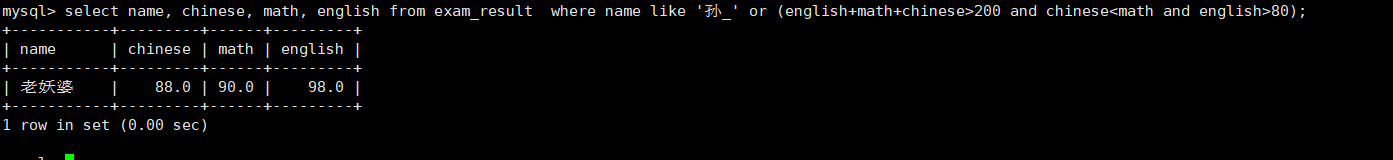
孙某同学,否则要求总成绩>200并且语文成绩<数学成绩并且英文成绩>80
select name chinese math english from exam_result wherelike'孙_'or(english+math+chinese>200and chinese<math and english>80);
结果排序
关键字:orderbyasc 升序,在不指定的情况下默认为升序
desc 降序
注意:orderby没有子句的查询,返回的顺序是未定义的,永远不要依赖这个顺序
select name,math from exam_result orderby math;//默认是升序排列select name,math from exam_result orderby math desc;
挑选同学及qq号,按照qq号码进行排序
select name,qq from t20 where sn isnotnullorderby qq ;
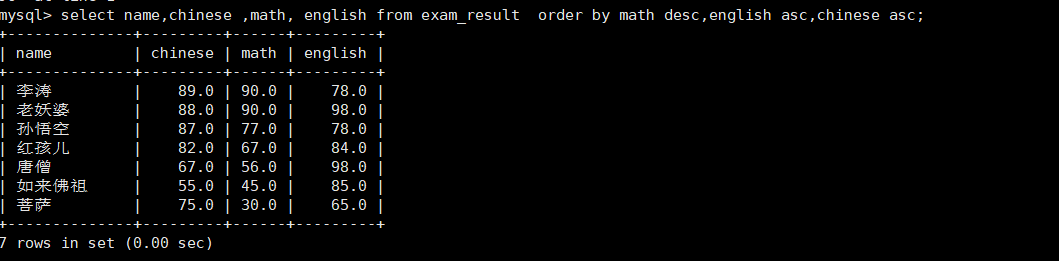
查询各科成绩,一次按照数学降序,英语升序,语文升序的方式显示
select name,chinese ,math, english from exam_result orderby math desc,english asc,chinese asc;
select name,chinses+math+englist as total from exam_result whereorderby total;
筛选分页结果
limit
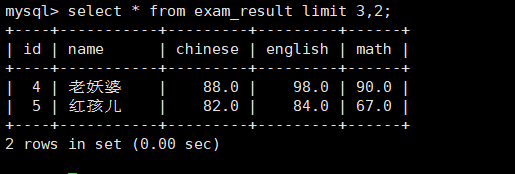
select*fromlimit3;//显示前3行select*fromlimit3,2;//从3号下标开始显示2个select*from exam_result limit2offset3;//和上面那个其实是一样的作用
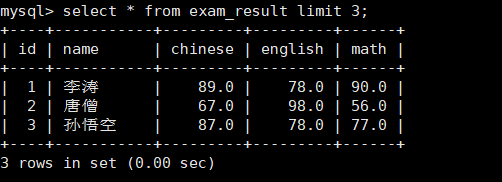
select*from exam_result limit3;
select*from exam_result limit3,2;
Update更新数据
语法
update table_name setcolumn=expr [,column=expr][where...][orderby][limit...]
更新数据
修改数据之前必须先找到数据然后才能进行修改
将孙权同学的数学成绩变为89分
update exam_result set math=80where name='孙权';
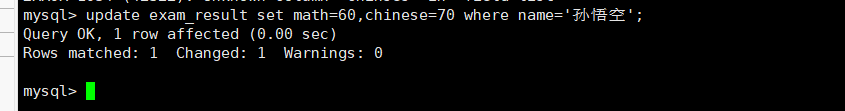
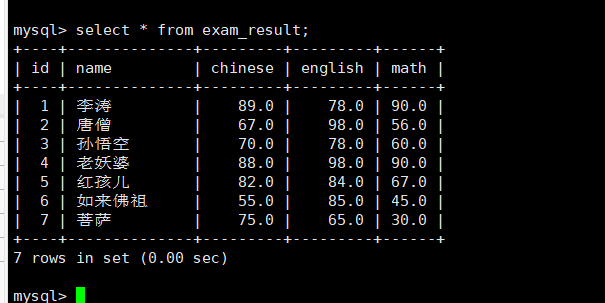
将孙悟空的math改为60分,Chinese改为70分
update exam_result set math=60,chinses=70where name='孙悟空';
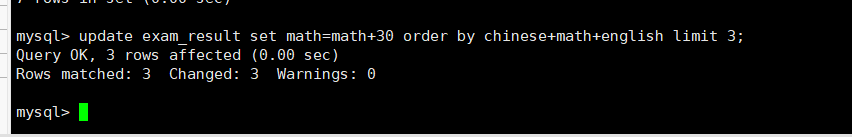
总成绩倒数前三的三名同学数学成绩+30分
update exam_result set math=math+30orderby chinese+math+english limit3;
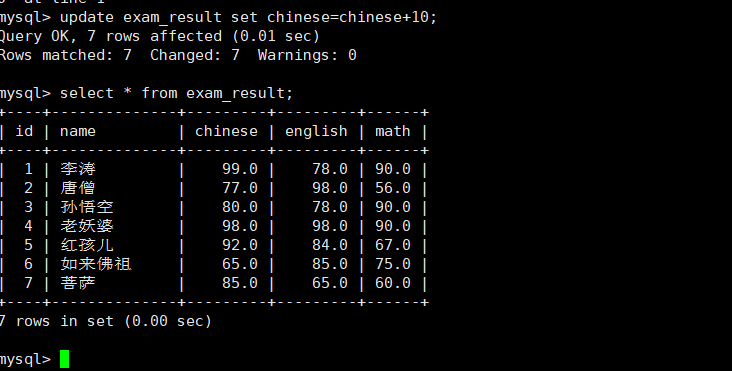
将所有人的语文成绩+10分
update exam_result set chinese=chinses+10;
delete删除数据
deletefrom table_name [where...][orderby...][limit...]
删除
删除之前要找到数据
deletefrom exam_result where name='孙悟空';
删除总分是倒数三名的学生
deletefrom exam_result where name in(select name orderby english+math+chinses desclimit3);
清空表数据
deletefrom exam_result ;
截断表
truncate[table] table_name;
注意:这个操作慎用
1.只能对整表操作,不能像delete一样对部分数据操作
2.实际上MySQL不会对数据操作,所以比delete更快,但是truncate在删除数据的时候,并不经过真正的事务,所以无法回滚
3.此操作会重置AUTO_INCREMENT项
插入查询结果
createtableifnotexists dup_table(
id int,
name varchar(20));
insertinto dup_table values(100,'aaa'),(200,'bbb'),(300,'ccc'),(100,'aaa');
表格去重
createtableifnotexists no_dup_table like dup_table;
insertinto no_dup_table selectdistinct*from dup_table;
renametable dup_taable to dup_table_back,no_dup_table to dup_table;
聚合函数
count():统计次数
sum():求总和
avg():平均值
max():最大值
min():最小值
聚合函数一般与下面的group by子句一起使用
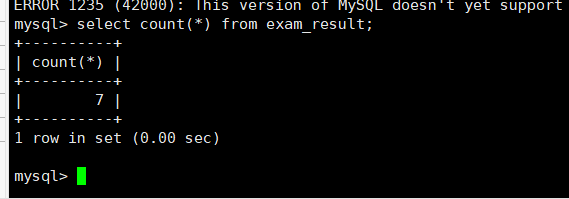
select*count(*)from exam_result;
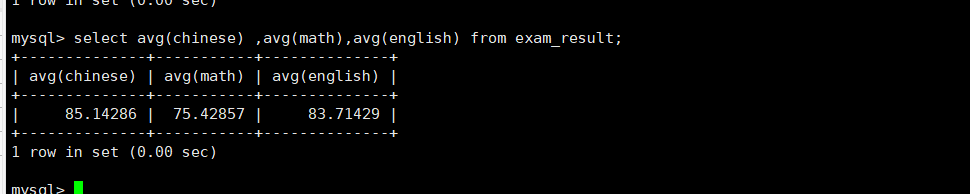
计算每个课程的平均分
selectavg(chinese),avg(math),avg(english)from exam_result;
group by子句的使用
groupby可以进行分组查询
凡是在select后面的列名称,如果后续我们要进行group by分组,那么凡是在select中出现的原表中的列名称也必须在group by中出现
group by 是一个分组函数,要筛查的数据列,都应该要考虑,分组的时候,如果当前的分组条件相同,接下来的分组依据是什么?
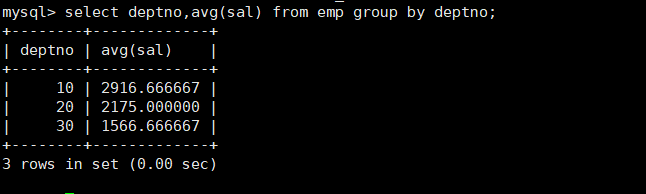
例如有一张员工表,里面有不同的部门,我们按照部分进行分组,查看每个部门的平均工资
select deptno,avg(sal)from emp groupby deptno;
having
having 和groupby搭配使用,对分组进行筛选,作用有点像where
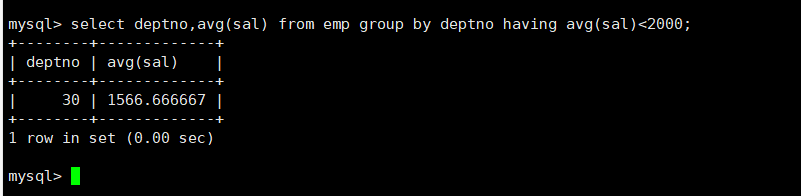
例如:选择平均工资低于2000的部门
select deptno,avg(sal)from emp groupby deptno havingavg(sal)<2000;
by中出现
group by 是一个分组函数,要筛查的数据列,都应该要考虑,分组的时候,如果当前的分组条件相同,接下来的分组依据是什么?
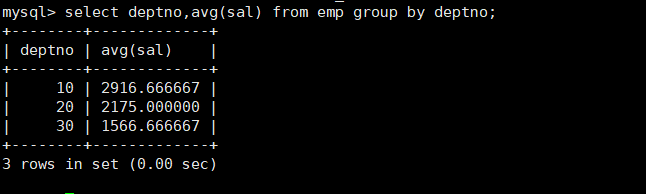
例如有一张员工表,里面有不同的部门,我们按照部分进行分组,查看每个部门的平均工资
select deptno,avg(sal)from emp groupby deptno;
having
having 和groupby搭配使用,对分组进行筛选,作用有点像where
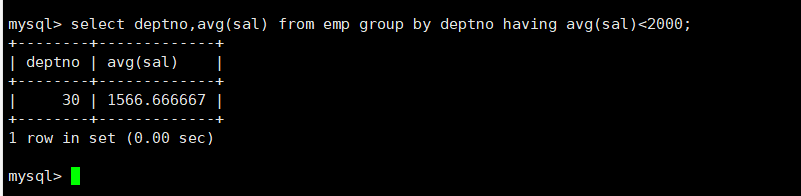
例如:选择平均工资低于2000的部门
select deptno,avg(sal)from emp groupby deptno havingavg(sal)<2000;
版权归原作者 落禅 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。