Vuex是做什么的?
Vue官方:状态管理工具
状态管理是什么?
需要在多个组件中共享的状态、且是响应式的、一个变,全都改变。
例如一些全局要用的的状态信息:用户登录状态、用户名称、地理位置信息、购物车中商品、等等
这时候我们就需要这么一个工具来进行全局的状态管理,Vuex就是这样的一个工具。
单页面的状态管理
View–>Actions—>State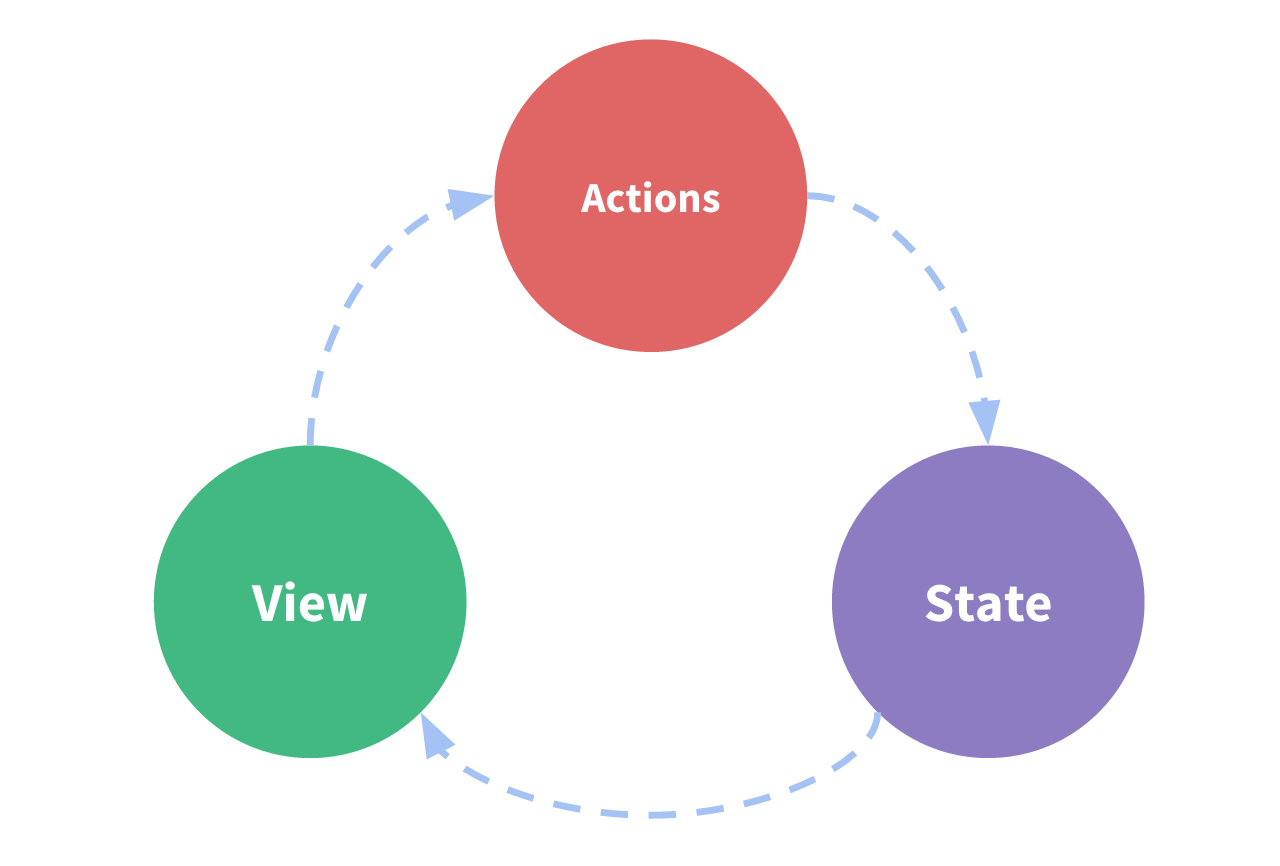
视图层(view)触发操作(action)更改状态(state)响应回视图层(view)
vuex(Vue3.2版本)
store/index.js 创建store对象并导出store
import{ createStore }from'vuex'exportdefaultcreateStore({
state:{},
mutations:{},
actions:{},
modules:{}})
main.js 引入并使用
...import store from'./store'...
app.use(store)
多页状态管理
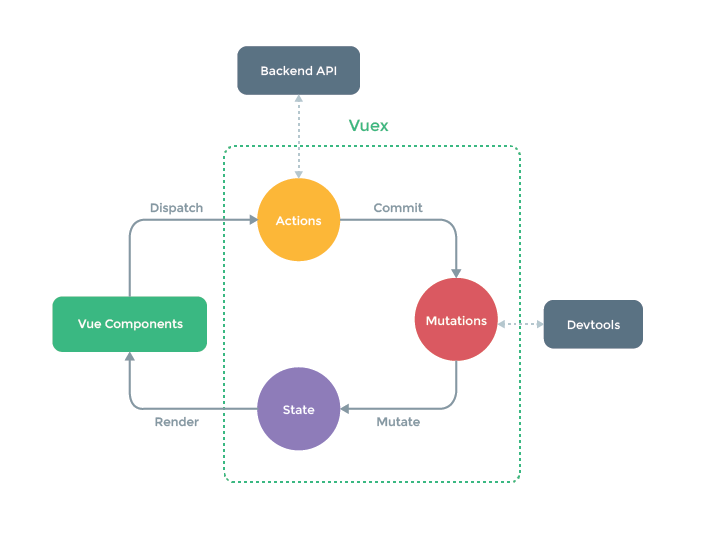
vuex store对象属性介绍
Vue3中获取 store 实例对象的方法
vue2 中可以通过
this.$store.xxx
的方式拿到 store 的实例对象。
vue3 中的 setup 在 beforecreate 和 created 前执行,此时 vue对象还未被创建,没有了之前的this,所以此处我们需要用到另一种方法来获取到 store 对象。
import{ useStore }from'vuex'// 引入useStore 方法const store =useStore()// 该方法用于返回store 实例
console.log(store)// store 实例对象
1.
state
存放数据的地方
state:{
count:100,
num:10},
使用:使用方法大致与vue2.x中的版本相同,通过
$store.state.属性名
来获取state中的属性。
//template中<span>{{$store.state.count}}</span><span>{{$store.state.num}}</span>
可以在
state中直接进行数据变化的操作,但Vue不建议这么做。因为对于vue开发工具 devtools 来说,直接在state中进行数据改变,devtools是跟踪不到的。vuex中希望**通过
action(进行异步操作**)或是
mutations(同步操作)来进行数据改变的操作,这样在 devtools 中才能直接观察出数据的变化以及记录,方便开发者调试。
**另外,在vue3 中对state 中对象新增属性或删除时,不再需要通过
vue.set()
, 或是
vue.delete()
来进行对象的响应式处理了,直接新增的对象属性已经具有响应式。**
2.
mutations
vuex的store状态更新的唯一方式:提交 mutation
同步操作可以直接在mutatuions中直接进行
mutions 主要包含2部分:
- 字符串的事件类型 (type)
- 一个回调函数(handler)该回调函数的第一个参数是 state
mutations:{// 传入 stateincrement(state){
state.count++}}
template 中通过
$store.commit('方法名')
触发
在 vue3.x 中需要拿到** store 实例的话,需要调用
useStore
**这样一个函数,在 vuex 中导入
// 导入 useStore 函数import{ useStore }from'vuex'const store =useStore()
store.commit('increment')
mution 的参数与传参方法
mution 接收参数直接写在定义的方法里边即可接受传递的参数
// ...state定义count
mutations:{sum(state, num){
state.count += num
}}
通过 commit 的payload 进行参数传递
使用
store.commit('mution中函数名', '需要传递的参数' )
在commit里添加参数的方式进行传递
<h2>{{this.$store.state.count}}</h2><button@click="add(10)">++</button>
...
<scriptsetup>// 获取store实例,获取方式看上边获取store实例方法constadd=(num)=>{
store.commit('sum', num)}</script>
mution 的提交风格
前面提到了 mution 主要包含 type 和 回调函数 两部分, 和通过commit payload的方式进行参数传递(提交),下面我们可以
用这种方式进行 mution 的提交
constadd=(num)=>{
store.commit({
type:'sum',// 类型就是mution中定义的方法名称
num
})}...
mutations:{sum(state, payload){
state.count += payload.num
}}
3.
actions
异步操作在action中进行,再传递到mutation
action基本使用如下:
action 中定义的方法默认参数为**
context
上下文**, 可以理解为 store 对象
**通过 context 上下文对象,拿到store,通过
commit
触发 mution 中的方法**,以此来完成异步操作
...
mutations:{sum(state, num){
state.count += num
}},
actions:{// context 上下文对象,可以理解为storesum_actions(context, num){setTimeout(()=>{
context.commit('sum', num)// 通过context去触发mutions中的sum},1000)}},
**在template 中通过
dispatch
调用action 中定义的sum_action 方法**
// ...template
store.dispatch('sum_actions', num)
通过 promise 实现异步操作完成,通知组件异步执行成功或是失败。
// ...constaddAction=(num)=>{
store.dispatch('sum_actions',{
num
}).then((res)=>{
console.log(res)}).catch((err)=>{
console.log(err)})}
sun_action方法返回一个promise,当累加的值大于30时不再累加,抛出错误。
actions:{sum_actions(context, payload){returnnewPromise((resolve, reject)=>{setTimeout(()=>{// 通过 context 上下文对象拿到 countif(context.state.count <30){
context.commit('sum', payload.num)resolve('异步操作执行成功')}else{reject(newError('异步操作执行错误'))}},1000)})}},
4.
getters
类似于组件的计算属性
import{ createStore }from'vuex'exportdefaultcreateStore({
state:{
students:[{ name:'mjy', age:'18'},{ name:'cjy', age:'22'},{ name:'ajy', age:'21'}]},
getters:{more20stu(state){return state.students.filter(item => item.age >=20)}}})
使用 通过
$store.getters.方法名
进行调用
//...template
<h2>{{$store.getters.more20stu}}</h2> // 展示出小于20岁的学生
getters 的入参, getters 可以接收两个参数,一个是
state
, 一个是自身的
getters
,并对自身存在的方法进行调用。
getters:{more20stu(state, getters){return getters.more20stu.length}}
getters 的参数与传参方法
上面是getters固定的两个参数,如果你想给getters传递参数,让其筛选大于 age 的人,可以这么做
返回一个 function 该 function 接受 Age,并处理
getters:{more20stu(state, getters){return getters.more20stu.length},moreAgestu(state){returnfunction(Age){return state.students.filter(item =>
item.age >= Age
)}}// 该写法与上边写法相同但更简洁,用到了ES6中的箭头函数,如想了解es6箭头函数的写法// 可以看这篇文章 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45934504/article/details/123405813?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
moreAgestu_Es6: state =>{return Age =>{return state.students.filter(item => item.age >= Age)}}}
使用
//...template
<h2>{{$store.getters.more20stu}}</h2> // 展示出小于20岁的学生
<h2>{{$store.getters.moreAgestu(18)}}</h2> // 通过参数传递, 展示出年龄小于18的学生
5.
modules
当应用变得复杂时,state中管理的变量变多,store对象就有可能变得相当臃肿。
为了解决这个问题,vuex允许我们将store分割成模块化(modules),而每个模块拥有着自己的state、mutation、action、getters等
在store文件中新建modules文件夹
在modules中可以创建单一的模块,一个模块处理一个模块的功能
store/modules/user.js
处理用户相关功能
store/modules/pay.js
处理支付相关功能
store/modules/cat.js
处理购物车相关功能
// user.js模块
// 导出
export default {
namespaced: true, // 为每个模块添加一个前缀名,保证模块命明不冲突
state: () => {},
mutations: {},
actions: {}
}
最终通过
store/index.js
中进行引入
// store/index.jsimport{ createStore }from'vuex'import user from'./modules/user.js'import user from'./modules/pay.js'import user from'./modules/cat.js'exportdefaultcreateStore({
modules:{
user,
pay,
cat
}})
在template中模块中的写法和无模块的写法大同小异,带上模块的名称即可
<h2>{{$store.state.user.count}}</h2>
store.commit('user/sum', num)// 参数带上模块名称
store.dispatch('user/sum_actions', sum)
版权归原作者 淹死的鱼u 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。