文章目录
目录
- 单链表经典算法OJ题目
- 基于单链表再实现通讯录项目
1. 单链表经典算法OJ题目
1.1 移除链表元素
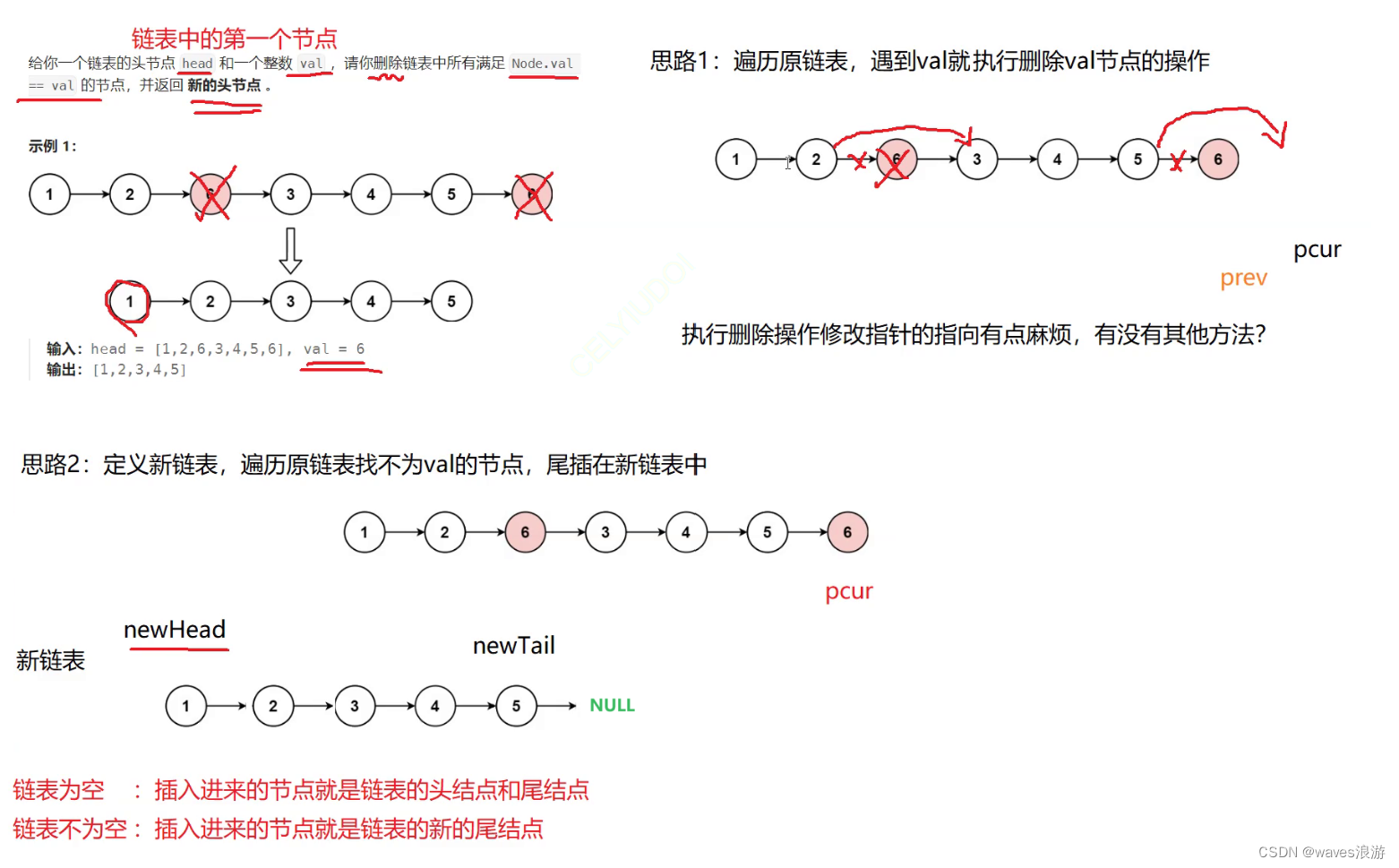
#include<stdio.h>typedefstructListNode{int val;structListNode* next;}ListNode;structListNode*removeElements(structListNode* head,int val){//定义新链表的头尾指针
ListNode* newHead,* newTail;
newHead = newTail =NULL;
ListNode* pcur = head;while(pcur){//不是val,尾插到新链表if(pcur->val != val){if(NULL== newHead){//链表为空
newHead = newTail = pcur;}else{//链表不为空
newTail->next = pcur;
newTail = newTail->next;}
pcur = pcur->next;}else{
ListNode* del = pcur;
pcur = pcur->next;free(del);
del =NULL;}}if(newTail)//为了防止传过来的是空链表,newTail为空;或者链表中都是同一个值,而正好删除的是这个值,删完之后新链表中newTail依然是空{
newTail->next =NULL;}return newHead;}
1.2 链表的中间节点
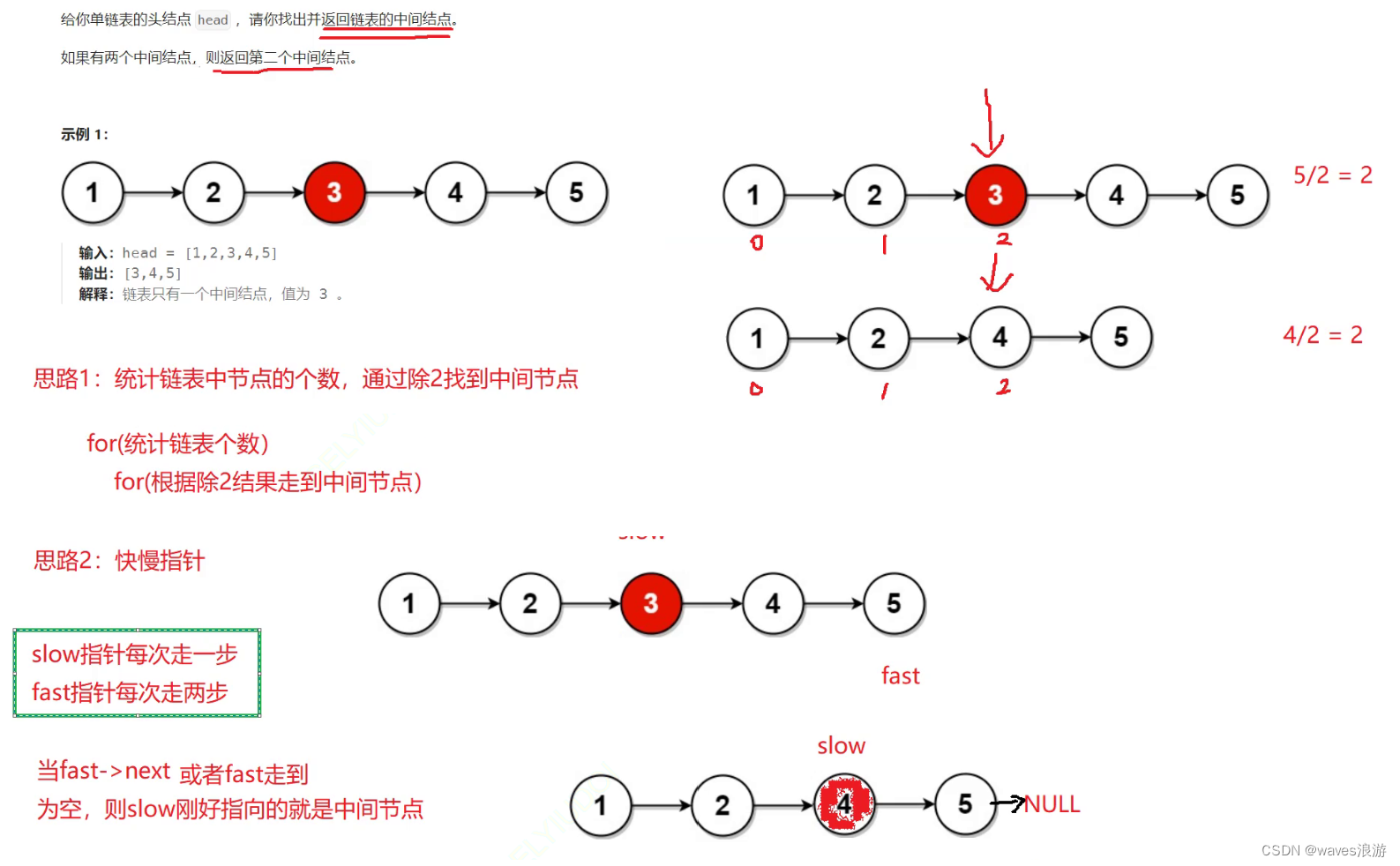
typedefstructListNode{int val;structListNode* next;}ListNode;structListNode*middleNode(structListNode* head){
ListNode* slow,* fast;
slow = fast = head;//满足任意一个条件就跳出循环while(fast && fast->next)//有一个为假都不应该进入循环{//慢指针每次走一步,快指针每次走两步
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;}return slow;}
1.3 反转链表
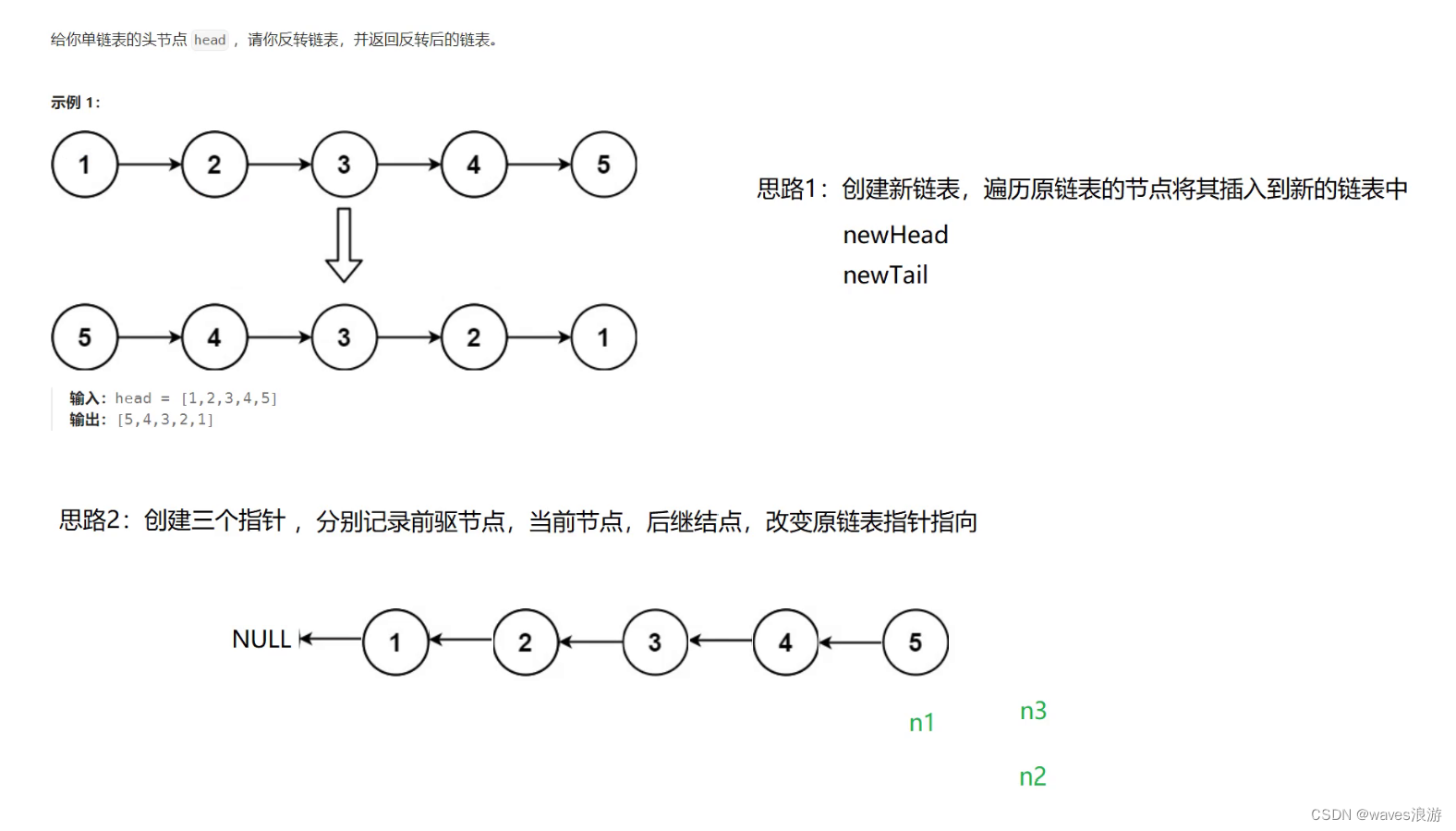
#include<stdio.h>typedefstructListNode{int val;structListNode* next;}ListNode;structListNode*reverseList(structListNode* head){//处理空链表if(NULL== head){return head;}//先创建三个指针
ListNode* n1,* n2,* n3;
n1 =NULL, n2 = head, n3 = head->next;//遍历原链表,修改节点指针的指向while(n2){//修改n2的指向
n2->next = n1;//修改三个指针的位置
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;if(n3){
n3 = n3->next;}}return n1;}
1.4 合并两个有序链表
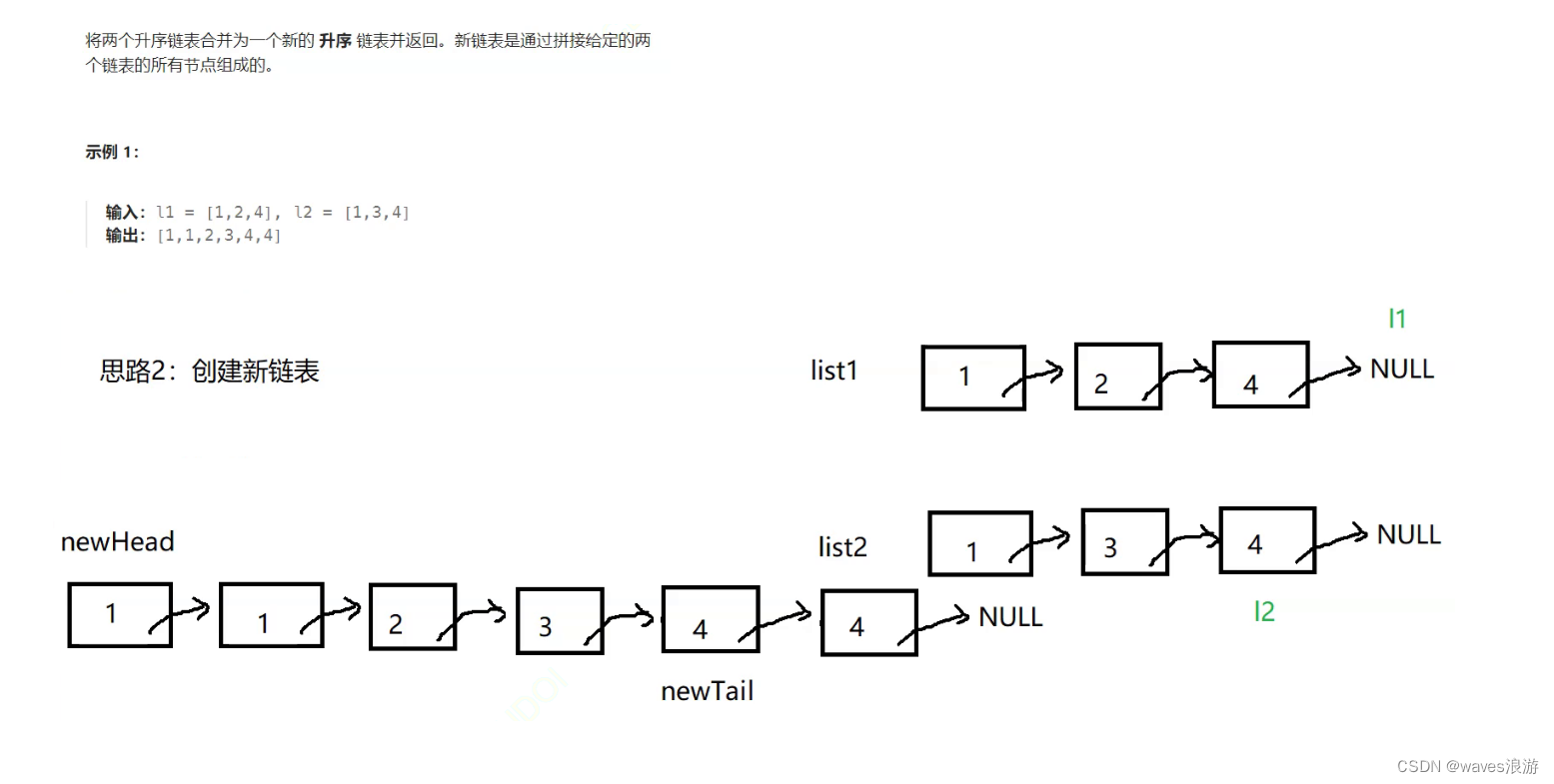
#include<stdio.h>typedefstructListNode{int val;structListNode* next;}ListNode;structListNode*mergeTwoLists(structListNode* list1,structListNode* list2){if(NULL== list1){return list2;}if(NULL== list2){return list1;}
ListNode* l1,* l2;
l1 = list1, l2 = list2;
ListNode* newHead,* newTail;
newHead = newTail =NULL;while(l1 && l2){if(l1->val < l2->val){//l1小,插入到新链表中if(NULL== newHead){//链表为空,头尾指针都指向该节点
newHead = newTail = l1;}else{//链表不为空
newTail->next = l1;
newTail = newTail->next;}
l1 = l1->next;}else{//l2小,插入到新链表中if(NULL== newHead){//链表为空
newHead = newTail = l2;}else{//链表不为空
newTail->next = l2;
newTail = newTail->next;}
l2 = l2->next;}}//跳出循环存在两种情况:要么l1走到空了l2不为空,要么l2走到空了l1不为空//不可能存在都为空的情况if(l1){
newTail->next = l1;}if(l2){
newTail->next = l2;}return newHead;}
但是我们会发现以上代码在l1小或l2小时把数据插入到新链表中都要判断链表是否为空,出现了代码的重复,我们应该如何优化呢?
代码重复的根源在于链表可能会出现为空的情况,那么我们就创建一个头节点(这里的头就是带头链表中的头,是哨兵位,不存储有效的数值),让链表不可能存在为空的情况,就可以避免代码重复。
#include<stdio.h>#include<stdlib.h>typedefstructListNode{int val;structListNode* next;}ListNode;structListNode*mergeTwoLists(structListNode* list1,structListNode* list2){if(NULL== list1){return list2;}if(NULL== list2){return list1;}
ListNode* l1,* l2;
l1 = list1, l2 = list2;
ListNode* newHead,* newTail;
newHead = newTail =(ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));while(l1 && l2){if(l1->val < l2->val){//l1小,插入到新链表中
newTail->next = l1;
newTail = newTail->next;
l1 = l1->next;}else{//l2小,插入到新链表中
newTail->next = l2;
newTail = newTail->next;
l2 = l2->next;}}//跳出循环存在两种情况:要么l1走到空了l2不为空,要么l2走到空了l1不为空//不可能存在都为空的情况if(l1){
newTail->next = l1;}if(l2){
newTail->next = l2;}//malloc了空间,但是这块空间实际用不了,应该将其释放掉
ListNode* ret = newHead->next;free(newHead);
newHead = newTail =NULL;return ret;}
1.5 分割链表

#include<stdio.h>#include<stdlib.h>typedefstructListNode{int val;structListNode* next;}ListNode;structListNode*partition(structListNode* head,int x){if(NULL== head){return head;}//创建带头的大小链表
ListNode* lessHead,* lessTail;
ListNode* greaterHead,* greaterTail;
lessHead = lessTail =(ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
greaterHead = greaterTail =(ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));//遍历原链表,将节点放到对应的新链表中
ListNode* pcur = head;while(pcur){if(pcur->val < x){//放到小链表中
lessTail->next = pcur;
lessTail = lessTail->next;}else{//放到大链表中
greaterTail->next = pcur;
greaterTail = greaterTail->next;}
pcur = pcur->next;}
greaterTail->next =NULL;//大小链表进行首尾相连
lessTail->next = greaterHead->next;
ListNode* ret = lessHead->next;free(greaterHead);
greaterHead = greaterTail =NULL;free(lessHead);
lessHead = lessTail =NULL;return ret;}
1.6 环形链表的约瑟夫问题
著名的Josephus问题:
据说著名犹太历史学家Josephus有过以下的故事:在罗马人占领乔塔帕特后,39个犹太人与Josephus及他的朋友躲到⼀个洞中,39个犹太人决定宁愿死也不要被人抓到,于是决定了一个自杀方式,41个人排成⼀个圆圈,由第1个人开始报数,每报数到第3人该人就必须自杀,然后再由下⼀个重新报数,直到所有人都自杀身亡为止。然而Josephus和他的朋友并不想遵从,Josephus要他的朋友先假装遵从,他将朋友与自己安排在第16个与第31个位置,于是逃过了这场死亡游戏。
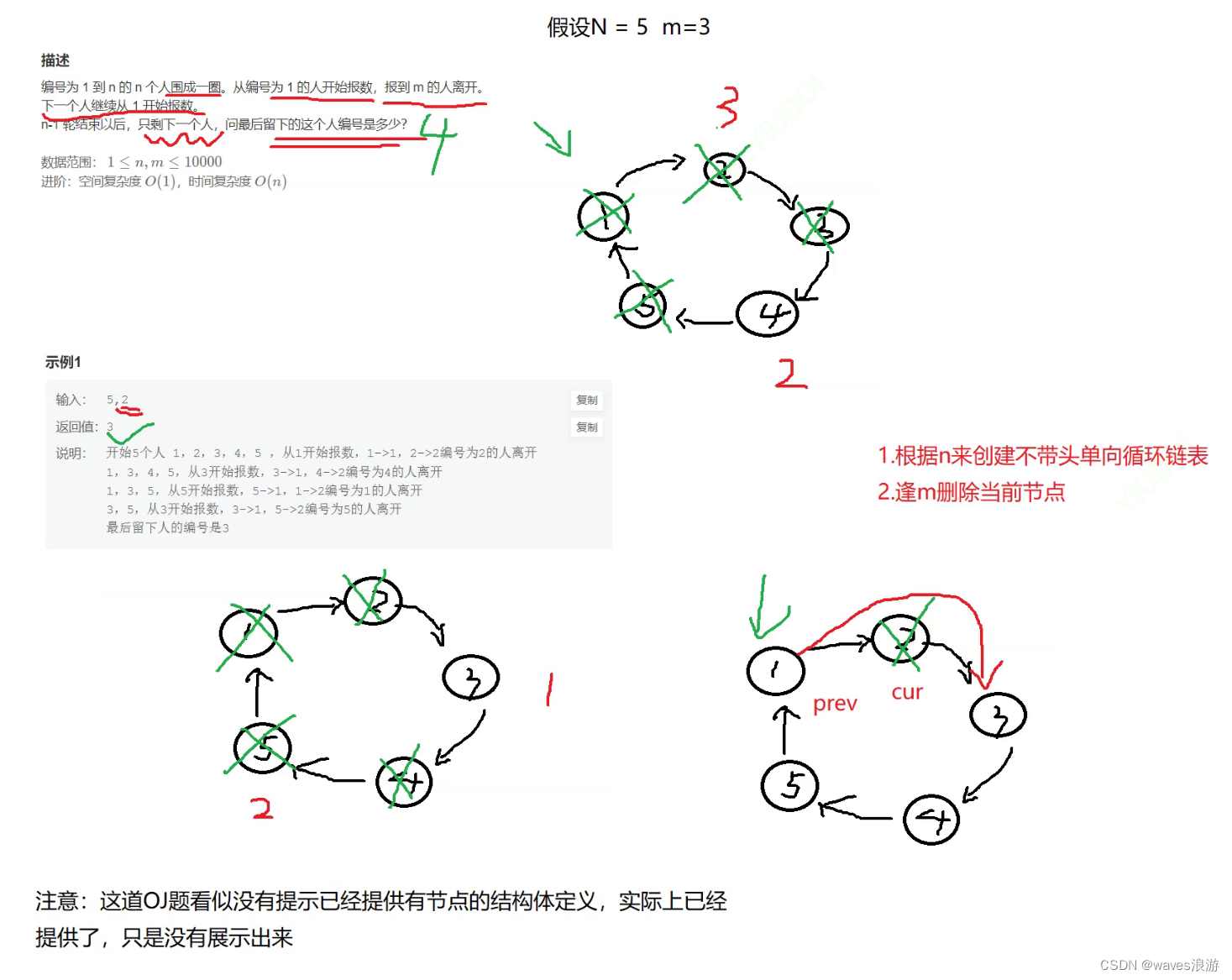
#include<stdio.h>#include<stdlib.h>typedefstructListNode{int val;structListNode* next;}ListNode;
ListNode*BuyNode(int x){
ListNode* newNode =(ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));if(NULL== newNode){perror("BuyNode");exit(1);}
newNode->val = x;
newNode->next =NULL;return newNode;}
ListNode*createList(int n){
ListNode* phead =BuyNode(1);
ListNode* ptail = phead;for(int i =2; i <= n; i++){
ptail->next =BuyNode(i);
ptail = ptail->next;}//链表要首尾相连使其循环起来
ptail->next = phead;return ptail;//返回ptail的目的是避免prev为空,解决m = 1时出现的问题;这样写既能知道第一个节点的前驱节点,也能够通过尾节点找到第一个节点}intysf(int n,int m){//创建不带头单向循环链表
ListNode* prev =createList(n);//定义prev来接收尾节点指针//逢m删除节点
ListNode* pcur = prev->next;int count =1;while(pcur->next != pcur){if(m == count){//删除当前节点pcur
prev->next = pcur->next;free(pcur);//删除pcur节点之后,要让pcur走到新的位置,count置为初始值
pcur = prev->next;
count =1;}else{//pcur往后走
prev = pcur;
pcur = pcur->next;
count++;}}//此时pcur节点就是幸存下来的唯一的一个节点return pcur->val;}
2. 基于单链表再实现通讯录项目
这里基于单链表实现通讯录项目和之前基于顺序表实现通讯录项目的步骤大致相同,思路是相通的,因此可以参考之前顺序表的应用这篇文章。
版权归原作者 waves浪游 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。