简介:
1、前言:
- 位图:放大会失真图像边缘有锯齿;是由像素点组成;前端的 Canvas 就是位图效果。
- 矢量图:放大不会失真;使用 XML 描述图形。
- 对于初学 SVG 的前端来说,可以简单的理解为 “SVG 是一套新标签”。所以可以使用 CSS 来设置样式,也可以使用 JS 对 SVG 进行操作。
- 在不设置宽高的情况下,默认为300 * 150,当内部元素大于300 * 150时,大于部分会被隐藏
2、viewBox 属性定义了SVG中可以显示的区域。
语法:viewBox=“x y w h” x、y为起始点,w、h为显示区域的宽高。
示例:
<svgwidth="300"height="300"viewBox="0 0 100 100"><circlecx="100"cy="100"r="100"/></svg>

为什么不是一个100大小的圆显示在画布上呢?
viewBox定义了一个:从(0, 0)点开始,宽高为100 * 100的显示区域。而这个100 * 100的显示区域会放到300 * 300(svg宽高)的SVG中去显示,整体就放大了3倍
3、version
version属性用于指明SVG的版本,也就是指明SVG文档应该遵循的规范。version属性纯粹就是一个说明,对渲染或处理没有任何影响。且目前只有1.0 和 1.1这两个版本。
<svgversion="1.1">
// ...
</svg>
4、xmlns和xmlns:xlink
5、用
创建组合对象
两种方法可以使我们的图标随时可用:将它们转换为组合,或转换为模板。我们将把前面的一半图标转换成组合,然后把剩下的一半变成模板,这样我们就可以说明他们之间的区别
要把我们的一个图标转换成一个组合,我们要做的就是用标签
来包裹它。为了使这个组合可用,我们还需要给它一个唯一的ID。
<gid="leftalign"><!-- 左对齐图标 --><linex1="3"y1="3"x2="48"y2="3"></line><linex1="3"y1="19"x2="65"y2="19"></line><linex1="3"y1="35"x2="48"y2="35"></line><linex1="3"y1="51"x2="65"y2="51"></line></g>
6、使用
来放置组合
在
元素内部我们现在有1个图标被定义成组合,我们准备在 SVG 中使用它们。为了使用它们,我们需要做的就是添加一个
元素(确保在
元素以外且之后的地方添加它),并设置一个 href 属性指向想要的那个图标的 ID。
<usehref="#leftalign"x="100"y="100"></use>
7、使用 symbols 创建模板对象
除了组合之外,你也可以使用模板来定义你的图标
模板几乎和组合一样,但是你可以获得额外的设置来控制视口(viewbox)和长宽比。
viewBox的属性 让我们可以定义每个模板的可见部分应该是什么。属性4个值。前两个定义图标的左上角,第三和第四分别定义它的宽度和高度
<symbolid="alert"viewBox="0 0 86 86"><!-- 警示图标 --><ellipsecx="43"cy="43"rx="40"ry="40"></ellipse><ellipsestyle="fill:black;"cx="43"cy="65"rx="5"ry="5"></ellipse><linestyle="stroke-width: 8;"x1="43"y1="19"x2="43"y2="48"></line></symbol>
8、使用
来放置模板
我们可以像使用我们的组合一样使用我们的模板图标。不过我们也会提供已经设好了宽高属性为 100px 的图标。
试着给使用基于组合图标的
元素上添加宽高的属性。发现没什么变化。这是因为浏览器依靠的是 viewBox 的值(组合没有这个值)来确定如何缩放图标。
一、图形标签
1、矩形
矩形使用
标签,默认填充色是黑色,当只设置宽高时,渲染出来的矩形就是黑色的矩形。
矩形基础属性
- x: 左上角x轴坐标 偏移距离
- y: 左上角y轴坐标
- width: 宽度
- height: 高度
- rx: 圆角,x轴的半径
- ry: 圆角,y轴的半径
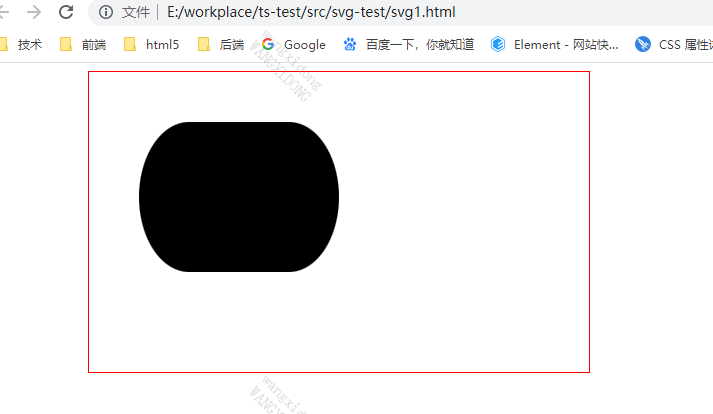
<!DOCTYPEhtml><svgwidth="500"height="300"style="border: 1px solid red;margin-left: 100px;"><rectx="50"y="50"width="200"height="150"rx="50"ry="50"></rect></svg>
rx\ry 理解,画一个椭圆来切调不相交的部分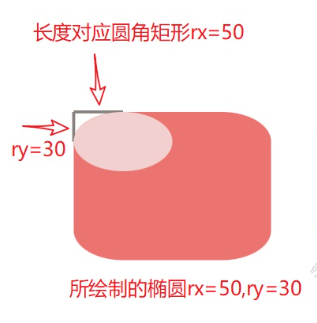
2、圆形
圆形使用
标签,基础属性有:
- cx: 圆心在x轴的坐标
- cy: 圆心在y轴的坐标
- r: 半径
<!DOCTYPEhtml><svgwidth="500"height="300"style="border: 1px solid red;margin-left: 100px;"><circlecx="350"cy="150"r="20"></circle></svg>

3、椭圆 ellipse
椭圆使用
标签,基础属性有:
- cx: 圆心在x轴的坐标
- cy: 圆心在y轴的坐标
- rx: x轴的半径
- ry: y轴的半径
<!DOCTYPEhtml><svgwidth="500"height="300"style="border: 1px solid red;margin-left: 100px;"><ellipsecx="450"cy="150"rx="40"ry="30"></ellipse></svg>
4、直线 line
直线使用
标签,基础属性有:
- x1: 起始点x坐标
- y1: 起始点y坐标
- x2: 结束点x坐标
- y2: 结束点y坐标
- stroke: 描边颜色
<svgwidth="400"height="300"style="border: 1px solid red;margin: 10px"><linex1="10"y1="10"x2="10"y2="50"stroke="#000"></line></svg>
5、折线polyline
使用
可以绘制折线,基础属性有:
- points: 点集
- stroke: 描边颜色
- fill: 填充颜色
<svgwidth="400"height="300"style="border: 1px solid red;margin: 10px"><polylinepoints="20 10, 100 10, 100 40"stroke="red"fill="none"></polyline><polylinepoints="20 10, 100 10, 100 40"stroke="red"fill="red"></polyline></svg>

6、多边形 polygon
多边形使用
标签,基础属性和
差不多:
points: 点集
stroke: 描边颜色
fill: 填充颜色
会自动闭合(自动将起始点和结束点链接起来)。
<svgwidth="400"height="300"style="border: 1px solid red;margin: 10px"><polygonpoints="10 200, 200 80, 230 230"></polygon></svg>
二、路径path
在 SVG 里,所有基本图形都是
的简写。所有描述轮廓的数据都放在 d 属性里,d 是 data 的简写。
d 属性又包括以下主要的关键字(注意大小写!):
- M: 起始点坐标,moveto 的意思。每个路径都必须以 M 开始。M 传入 x 和 y 坐标,用逗号或者空格隔开。
- L: 轮廓坐标,lineto 的意思。L 是跟在 M 后面的。它也是可以传入一个或多个坐标。大写的 L 是一个绝对位置。
- l: 这是小写 L,和 L 的作用差不多,但 l 是一个相对位置。
- H: 和上一个点的Y坐标相等,是 horizontal lineto 的意思。它是一个绝对位置。
- h: 和 H 差不多,但 h 使用的是相对定位。
- V: 和上一个点的X坐标相等,是vertical lineto 的意思。它是一个绝对位置。
- v: 这是一个小写的 v ,和大写 V 的差不多,但小写 v 是一个相对定位。
- Z: 关闭当前路径,closepath 的意思。它会绘制一条直线回到当前子路径的起点。
- Q 二次贝塞尔曲线
- T 延长二次贝塞尔曲线的简化命令
- C 用来绘制一条三次贝塞尔曲线,相对于二次贝塞尔曲线多了一个控制点
- S 三次贝塞尔曲线的S命令和二次贝塞尔曲线的T命令比较相似。S命令也可以用来创建与前面一样的贝塞尔曲线,但如果S命令跟在一个C命令或者另一个S命令的后面,那么它的第一个控制点,就会被假设成前一个控制点的对称点。
- A 用于画弧形,它可以截取圆或椭圆的弧形成的曲线
画直线demo
<svgwidth="400"height="300"style="border: 1px solid red;margin: 10px"><pathd="M 300 100 L 300 130 L 350 160"stroke="blue"fill="none"></path><pathd="M 300 200 L 300 230 L 350 260 Z"stroke="green"fill="none"></path><!-- 同上,用 V 省略了 水平坐标 --><pathd="M 300 200 V 230 L 350 260 Z"stroke="green"fill="none"></path><!-- 同上 全L 可直接省略 --><pathd="M 300 200 300 230 350 260 Z"stroke="green"fill="none"></path></svg>
画圆弧demo
A(rx, ry, xr, laf, sf, x, y)
在 SVG 中可以使用 path 配合 A属性 绘制椭圆弧。
- rx: 椭圆X轴半径
- ry: 椭圆Y轴半径
- xr: 椭圆旋转角度
- laf: 是否选择弧长较长的那一段。0: 短边(小于180度); 1: 长边(大于等于180度)
- sf: 是否顺时针绘制。0: 逆时针; 1: 顺时针
- x: 终点X轴坐标
- y: 终点Y轴坐标
上面的公式中并没有开始点,开始点是由 M 决定的。
<pathd="M 300 200 A 50 50 0 0 1 400 200 Z"stroke="green"fill="none"></path>
三、设置样式的方式和css一样
fill + style + class + 外部引入, 注意这个样式只能是svg自己的样式才生效
比如我设置一个style=“background-color: red” 不管用,得设置成 style=“fill: red”
四、常用样式设置
1、fill 填充
填充图案颜色,可以设置 fill 属性。这个属性在前面的例子也使用过多次。
可以使用 none 或者 transparent 将填充色设置成透明
2、填充色的不透明度 fill-opacity
可以设置 fill-opacity 属性,也可以在 fill 属性中使用 RGBA 或者 HSLA。
本例使用 fill-opacity 设置,它的取值是 0 - 1,0 代表完全透明,1 代表完全不透明。小于 0 的值会被改为 0,大于 1 的值会被改为 1 。
<svgwidth="400"height="400"style="border: 1px solid red;"><rectx="100"y="100"width="200"height="100"fill="red"fill-opacity="0.2"/></svg>

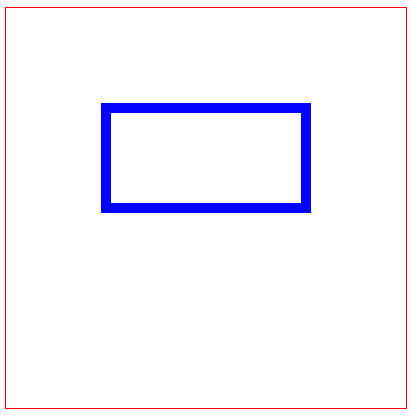
3、描边stroke
(1)描边宽度 stroke-width
<svgwidth="400"height="400"style="border: 1px solid red;"><rectx="100"y="100"width="200"height="100"fill="none"stroke="blue"stroke-width="10"/></svg>
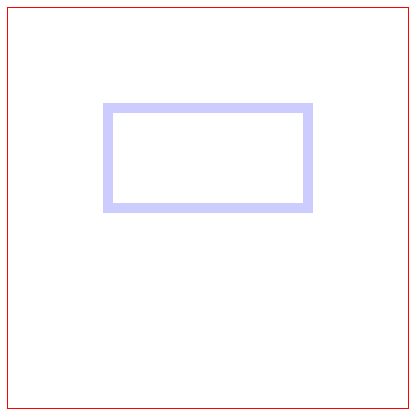
(2)描边的透明度stroke-opacity
<svgwidth="400"height="400"style="border: 1px solid red;"><rectx="100"y="100"width="200"height="100"fill="none"stroke="blue"stroke-opacity="0.3"/></svg>
(3)描边虚线 stroke-dasharray
stroke-dasharray 接收一串数字,这串数字可以用来代表 线的长度和空隙的长度,数字之间用逗号或者空格分隔。
建议传入偶数个数字。但如果你传入了奇数个数字,SVG 会将这串数字重复一遍,使它的数量变成 偶数个 。
<svg><linex1="30"y1="70"x2="300"y2="70"stroke="blue"stroke-width="5"stroke-dasharray="20 10"/></svg>

(4)虚线偏移量 stroke-dashoffset
接收一个数值类型的值
<svg><linex1="0"y1="30"x2="300"y2="30"stroke="blue"stroke-width="5"stroke-dasharray="20 10"/><linex1="0"y1="70"x2="300"y2="70"stroke="blue"stroke-width="5"stroke-dasharray="20 10"stroke-dashoffset="20"/></svg>

(5)线帽 stroke-linecap
线的起始点和结束点的样式,用 stroke-linecap 属性可以设置线帽样式。
线帽有3个值:
- butt: 平头(默认值)
- round: 圆头
- square: 方头
默认的linecap是占用线条的长度的,所以在一个svg画布上需要预留线帽的空间。
<svgwidth="300"height="300"><!-- 默认 平头 --><linex1="5"y1="5"x2="200"y2="5"stroke="red"stroke-width="10"style="stroke-linecap: butt;"/><!-- 圆头 --><pathstroke-linecap="round"stroke="orange"stroke-width="10"d="M5 20 L200 20"/><linex1="5"y1="40"x2="200"y2="40"stroke="blue"stroke-width="10"stroke-linecap="round"/><!-- 方头 --><linex1="5"y1="60"x2="200"y2="60"stroke="green"stroke-width="10"stroke-linecap="square"/></svg>

(6)拐角 stroke-linejoin
拐角就是折线的交接点,可以使用 stroke-linejoin 设置,它接收以下属性:
- miter: 尖角(默认)
- round: 圆角
- bevel: 平角
<svgwidth="260"height="260"><!-- 尖角 默认 --><pathd="M10 10 200 10 200 200"stroke-width="10"stroke="red"stroke-linejoin="miter"fill="none"></path><!-- 圆角 --><pathd="M10 30 180 30 180 200"stroke-width="10"stroke="orange"stroke-linejoin="round"fill="none"></path><!-- 平角 --><pathd="M10 50 160 50 160 200"stroke-width="10"stroke="blue"stroke-linejoin="bevel"fill="none"></path></svg>
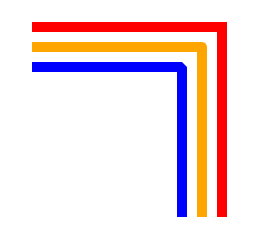
(7)消除锯齿 shape-rendering
如果你觉得 SVG 在浏览器显示出来的图像有点模糊,那可能是开启了 反锯齿 功能,可以通过 CSS 属性关闭该功能。
shape-rendering: crispEdges;
将该属性设置到对应的 svg 元素上,就会关闭反锯齿功能,突显看起来就会清晰很对,但在某些情况关闭了该功能会让图像看起来有点毛躁的感觉。
如果想开启反锯齿功能,可以这样设置:shape-rendering: geometricPrecision;
- 示例 ( 没有看出来效果 )
<svg><rectx="10"y="10"width="100"height="100"fill="orange"style="shape-rendering: crispEdges"></rect></svg>

五、文本元素 text
使用
标签渲染文本。文本是有 “基线”。和 Canvas 一样,SVG 的文本对齐方式是以第一个字基线的左下角为基准
<svgwidth="400"height="400"style="border: 1px solid red;"><text>呀呼嘿</text></svg>
如图所示文字并没有显示出来,因为对齐方式是以第一个字的基线的左下角为参考,默认的位置坐标是 (0, 0)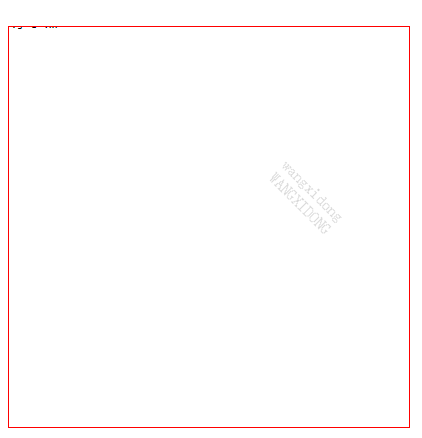
如果想显示出来必须向下移动字体的px,默认为html高度 16px, 此处移动16px
1、设置字号 font-size
2、设置字体粗细 font-weight
使用 font-weight 可以将文本设置成粗体。
- normal: 默认(非粗体)
- bold: 粗体
这和 CSS 是一样的
3、装饰线 text-decoration
和 CSS 一样,可以使用 text-decoration 设置装饰线
- none:默认
- underline: 下划线
- overline: 上划线
- line-through: 删除线
<svgwidth="400"height="400"style="border: 1px solid red;"><!-- 默认 --><texty="30"font-size="30"text-decoration="none">
呀呼嘿
</text><!-- 上划线 --><texty="100"font-size="30"text-decoration="overline">
呀呼嘿
</text><!-- 删除线 --><texty="170"font-size="30"text-decoration="line-through">
呀呼嘿
</text><!-- 下划线 --><texty="240"font-size="30"text-decoration="underline">
呀呼嘿
</text></svg>

4、文本对齐
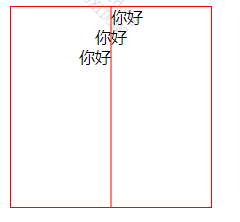
(1)水平对齐方式 text-anchor
可以通过 text-anchor 属性设置文本水平对齐方式。
如果本子是从左向右书写,那这几个参数的意思就是:
- start: 左对齐
- middle: 居中对齐
- end: 右对齐
<svgwidth="200"height="200"style="border: 1px solid red;"><!-- 参考线 --><pathd="M 100 0 100 200"stroke="red"></path><textx="100"y="16"text-anchor="start">你好</text><textx="100"y="36"text-anchor="middle">你好</text><textx="100"y="56"text-anchor="end">你好</text></svg>
(2)多行文可以使用本
标签辅助实现
<svgwidth="400"height="400"style="border: 1px solid red;"><textfill="blue"><tspanx="10"y="30"fill="red">雷猴</tspan><tspanx="10"y="60">鲨鱼辣椒</tspan><tspanx="10"y="90">蟑螂恶霸</tspan><tspanx="10"y="120">蝎子莱莱</tspan></text></svg>

要放在
里,而且会继承
设置的样式。
如果在
里设置的样式和
的样式有冲突,最后会使用
的样式。
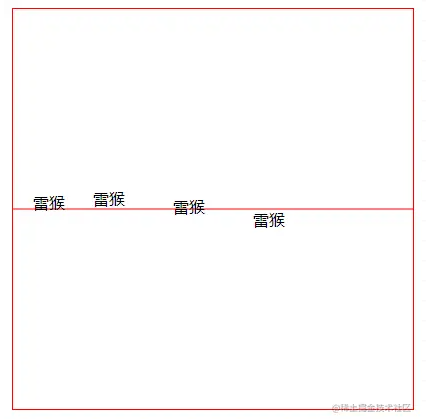
(3)垂直对齐方式 dominant-baseline
可以通过 dominant-baseline 属性设置文本垂直对齐方式
- auto: 默认的对齐方式,保持与父元素相同的配置。
- text-after-edge: 在基线上方
- middle: 居中基线
- text-before-edge: 在基线下方
<svgwidth="400"height="400"style="border: 1px solid red;"><!-- 参考线 --><pathd="M 0 200 400 200"stroke="red"></path><!-- 默认 --><textx="20"y="200"dominant-baseline="auto">
雷猴
</text><!-- 在基线上方 --><textx="80"y="200"dominant-baseline="text-after-edge">
雷猴
</text><!-- 居中基线 --><textx="160"y="200"dominant-baseline="middle">
雷猴
</text><!-- 在基线下方 --><textx="240"y="200"dominant-baseline="text-before-edge">
雷猴
</text></svg>
(4)纵向文字 writing-mode
将 writing-mode 设置成 tb 就可以让文字纵向排列。
需要注意英文和中文的文字角度!
<svgwidth="400"height="400"style="border: 1px solid red;"><textx="20"y="20"writing-mode="tb">Hello World!</text><textx="100"y="20"writing-mode="tb">鲨鱼辣椒</text></svg>
5、属性
(1) x和y属性决定了文字的绘制起点。
x和y的值可以是一个数列。如果设置为了一个数列则会应用到每一个字符上
<svgwidth="300"height="300"><textx="30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270"y="60 90 120 150 180 150 120 90 60"fill="#f00"stroke="#0f0"font-size="50"font-weight="bold">
Hello Svg !
</text></svg>

(2) dx和dy
dx和dy属性与x和y属性不同的是,x和y属性是绝对的坐标,而dx和dy属性是相对于当前位置的偏移量。
参数也可以是一个数列。如果设置为了一个数列则会应用到每一个字符上
<svgwidth="500"height="500"><textdx="50 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10"dy="50 20 -20 20 -20 20 -20 20 -20"fill="#f00"stroke="#0f0"font-size="50"font-weight="bold">
Hello Svg !
</text></svg>

(3) rotate属性
rotate属性可以把文字旋转一个角度。也可以是数列同上
<svgwidth="500"height="500"><textx="50"y="50"rotate="10"fill="#f00"stroke="#0f0"font-size="50"font-weight="bold">
Hello Svg !
</text></svg>

(4) textLength
textLength属性给定了一个字符串的计算长度。在文字的长度和textLength属性给定的长度不一致的情况下渲染引擎会精细调整字型的位置。
<svgwidth="550"height="500"><textx="50"y="50"textLength="150"fill="#f00"stroke="#0f0"font-size="50"font-weight="bold">
Hello Svg !
</text><textx="50"y="100"textLength="500"fill="#f00"stroke="#0f0"font-size="50"font-weight="bold">
Hello Svg !
</text></svg>

(5) lengthAdjust
lengthadjust属性可以控制文本以什么方式伸展到由_textLength_属性定义的长度。
- spacing:只拉伸或压缩间距(文字不变形)
- spacingAndGlyphs:同时拉伸或压缩间距和文字本身(文字变形)
<svgwidth="500"height="500"><textx="50"y="50"textLength="200"lengthadjust="spacing"fill="#f00"stroke="#0f0"font-size="50"font-weight="bold">
Welcome to the world of svg !
</text><textx="50"y="100"textLength="200"lengthadjust="spacingAndGlyphs"fill="#f00"stroke="#0f0"font-size="50"font-weight="bold">
Welcome to the world of svg !
</text><textx="50"y="150"textLength="400"lengthadjust="spacing"fill="#f00"stroke="#0f0"font-size="50"font-weight="bold">
Hi svg !
</text><textx="50"y="200"textLength="400"lengthadjust="spacingAndGlyphs"fill="#f00"stroke="#0f0"font-size="50"font-weight="bold">
Hi svg !
</text></svg>

(6) fill和stroke
填充和轮廓也都可以应用于文字
<svgwidth="300"height="300"><textx="50"y="50"fill="#f00"stroke="#0f0"font-weight="bold">Hello Svg !</text></svg>

重要 (7) textPath 非常牛
textPath标签可以利用它的xlink:href属性取得一个任意路径,并且可以让字符顺着路径渲染。
<svgwidth="600"height="500"><pathid="pathM"d="M 50 50 100 100 200 50 300 100"fill="none"/><pathid="pathQ"d="M50 100 Q 175 200 300 100 T 600 100"fill="none"/><text><textPathxlink:href="#pathM"> Welcome to the world of SVG ! </textPath></text><text><textPathxlink:href="#pathQ"> Welcome to the world of SVG ! Welcome to the world of SVG ! </textPath></text></svg>

六、超链接
和 HTML 一样,超链接可以使用 标签实现。
在 SVG 里,链接要放在 xlink:href 属性里。
如果希望鼠标放到链接上出现提示信息,可以在 xlink:title 属性里编写提示信息。
- 如需在新窗口打开链接,可以设置 target=“_blank” 。不设置的话就在当前窗口打开
<svgwidth="400"height="400"style="border: 1px solid red;"><axlink:href="../imgs/1.jpg"xlink:title="想到高兴的事"><textx="20"y="20">快乐</text></a></svg>

七、图片
在 SVG 中可以使用 标签加载图片,包括位图。
是使用 xlink:href 属性获取图片的
<svgwidth="400"height="400"style="border: 1px solid red;"><imagexlink:href="./img.jpg"></image></svg>
有问题:会在地址前自动加上 file:///,在我电脑上正常,公司电脑不行,这是为什么呢
八、渐变
渐变都分为两种渐变:线性渐变和径向渐变
但需要注意的是这里我们需要接触两个新的标签:
- defs标签用来定义渐变
- stop标签用来定义渐变的颜色坡度,具有三个属性:offset定义渐变开始和结束的位置、stop-color(定义颜色)和stop-opacity(定义透明度)
参数:x1、y1定义线性渐变的起点, x2、y2定义渐变的终点。仅仅是控制渐变的方向
1、线性渐变
<svgwidth="300"height="300"><defs><linearGradientid="linearGradient"x1="0"y1="0"x2="100%"y2="0"><stopoffset="0%"stop-color="#189faa"></stop><stopoffset="100%"stop-color="#fff382"></stop></linearGradient><linearGradientid="linearGradient1"x1="0"y1="0"x2="0%"y2="100%"><stopoffset="0%"stop-color="#189faa"></stop><stopoffset="100%"stop-color="#fff382"></stop></linearGradient></defs><ellipsecx="150"cy="100"rx="100"ry="50"fill="url(#linearGradient)"></ellipse><ellipsecx="150"cy="220"rx="100"ry="50"fill="url(#linearGradient1)"></ellipse></svg>

2、径向渐变
径向渐变(radialGradient)其实就是以一个点做放射性的渐变。
参数: cx、cy、r分别为圆的坐标和半径,也就是渐变的范围,fx、fy定义渐变的中心点,也叫渐变的焦点。
<svgwidth="500"height="400"><defs><radialGradientid="radialGradient"cx="50%"cy="50%"r="50%"fx="50%"fy="50%"><stopoffset="0%"stop-color="rgb(255, 255, 0)"/><stopoffset="100%"stop-color="rgb(255, 0, 0)"/></radialGradient><radialGradientid="radialGradient1"cx="50%"cy="50%"r="50%"fx="50%"fy="0%"><stopoffset="0%"stop-color="rgb(255, 255, 0)"/><stopoffset="100%"stop-color="rgb(255, 0, 0)"/></radialGradient><radialGradientid="radialGradient2"cx="50%"cy="50%"r="50%"fx="0%"fy="50%"><stopoffset="0%"stop-color="rgb(255, 255, 0)"/><stopoffset="100%"stop-color="rgb(255, 0, 0)"/></radialGradient></defs><ellipsecx="100"cy="100"rx="100"ry="50"fill="url(#radialGradient)"/><ellipsecx="100"cy="210"rx="100"ry="50"fill="url(#radialGradient1)"/><ellipsecx="100"cy="320"rx="100"ry="50"fill="url(#radialGradient2)"/></svg>
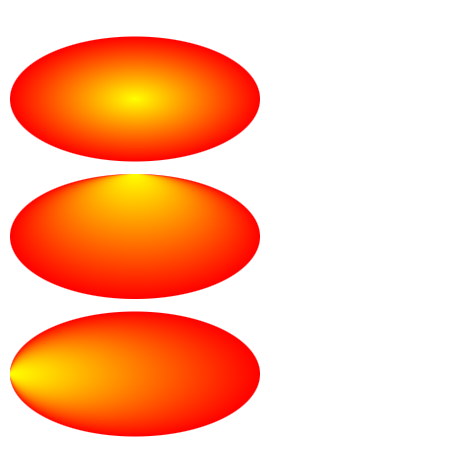
不管是线性渐变还是径向渐变,他们不仅可以用于图形还是用于文字
<svgwidth="500"height="400"><defs><linearGradientid="linearGradient"x1="0"y1="0"x2="100%"y2="0"><stopoffset="0%"stop-color="rgb(255,255,0)"/><stopoffset="100%"stop-color="rgb(255,0,0)"/></linearGradient><radialGradientid="radialGradient"cx="50%"cy="50%"r="50%"fx="50%"fy="100%"><stopoffset="0%"stop-color="rgb(255, 255, 0)"/><stopoffset="100%"stop-color="rgb(255, 0, 0)"/></radialGradient></defs><textfill="url(#linearGradient)"font-size="30"font-family="Verdana"x="50"y="100">我是一个小苹果</text><textfill="url(#radialGradient)"font-size="30"font-family="Verdana"x="50"y="200">我是一个小苹果</text></svg>

九、裁剪和蒙版
1、裁剪
裁剪的功能主要是使用clipPath标签定义一条裁剪路径,然后用来裁剪掉元素的部分内容。且任何透明度的效果都是无效的,它只能要么裁剪掉要么不裁剪。
<svgwidth="300"height="300"><defs><clipPathid="clipPath"><pathd="M10 50 A50 50 0 0 1 100 50 A50 50 0 0 1 190 50 Q210 100 100 200 Q-5 100 10 50 Z"/></clipPath></defs><rectx="0"y="0"width="200"height="200"fill="#f00"clip-path="url(#clipPath)"/></svg>

2、蒙版
蒙层的功能主要实现标签就是mask标签,他的功能和名字正好相反,他不是用来遮住元素的部分内容,而是用来显示元素中mask标签遮住的内容。 他和clipPath标签不同的是他允许使用透明度(透明度为0则无蒙层效果)和灰度值遮罩计算得的软边缘
<svgwidth="300"height="300"><defs><maskid="Mask"><pathd="M10 50 A50 50 0 0 1 100 50 A50 50 0 0 1 190 50 Q210 100 100 200 Q-5 100 10 50 Z"fill="#fff"fill-opacity="0.5"/></mask></defs><rectx="0"y="0"width="200"height="200"fill="#f00"mask="url(#Mask)"/></svg>

十、动画 (核心)
1、基础动画
1)translate(平移)
语法:transform=“translate(x, y)”
参数:x为X轴上的平移距离,y为Y轴上的平移距离
<svgwidth="300"height="300"><rectx="10"y="10"width="50"height="50"fill="#189faa"></rect><rectx="10"y="10"width="50"height="50"fill="#189faa"transform="translate(50, 50)"></rect><rectx="10"y="10"width="50"height="50"fill="#189faa"transform="translate(100, 100)"></rect></svg>

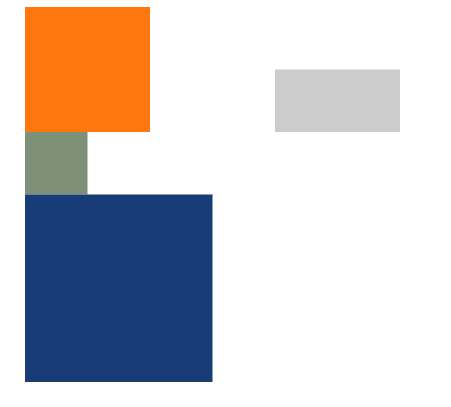
2)scale(缩放)
语法:transform=“scale(x, y)”
参数:x为X轴上的缩放大小,y为Y轴上的缩放大小,当两个值一样时,写一个值就可以。
<svgwidth="500"height="500"><rectx="0"y="0"width="100"height="100"fill="#ff770f"/><rectx="0"y="200"width="100"height="100"fill="#7e9178"transform="scale(0.5)"/><rectx="0"y="100"width="100"height="100"fill="#183c78"transform="scale(1.5)"/><rectx="200"y="100"width="100"height="100"fill="#cccccc"transform="scale(1, 0.5)"/></svg>

3) rotate(旋转)
语法:transform=“rotate(deg)”
参数:deg为旋转的角度,45度就写45度。
<svgwidth="500"height="500"><rectx="200"y="0"width="100"height="100"fill="#ff770f"/><rectx="200"y="0"width="100"height="100"fill="#cccccc"transform="rotate(20)"/><rectx="200"y="0"width="100"height="100"fill="#7e9178"transform="rotate(40)"/><rectx="200"y="0"width="100"height="100"fill="#183c78"transform="rotate(60)"/></svg>
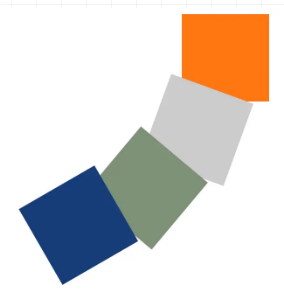
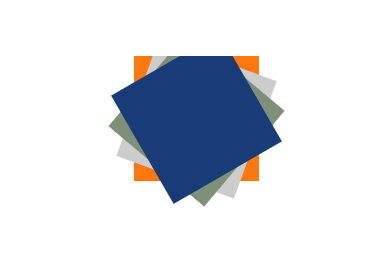
是不是觉得效果和我们想想中的不一样?我就只想旋转,为什么感觉还发生了位移呢?
其实这是因为元素的旋转中心点是(0, 0)。如果我们想要只是选中而不位移,那么就需要把旋转的中心点设置在元素的中心点。
上面橙色方块的中心点经过计算可知 (250, 50)
通过 transform-origin 设置中心点
<svgwidth="500"height="500"><rectx="200"y="0"width="100"height="100"fill="#ff770f"/><rectx="200"y="0"width="100"height="100"fill="#cccccc"transform-origin="250 50"transform="rotate(20)"/><rectx="200"y="0"width="100"height="100"fill="#7e9178"transform-origin="250 50"transform="rotate(40)"/><rectx="200"y="0"width="100"height="100"fill="#183c78"transform-origin="250 50"transform="rotate(60)"/></svg>
4) skew(倾斜)
语法:transform=“skewX(x) skewY(y)”
参数:x为X轴上的倾斜度,y为Y轴上的倾斜度。
在SVG中skew属性需要分开设置,x轴设置为skewX,y轴设置为skewY,不能合并起来用,写成 skew(x, y) 是不生效的。
<svgwidth="500"height="500"><rectx="0"y="0"width="100"height="100"fill="#ff770f"/><rectx="50"y="100"width="100"height="100"fill="#cccccc"transform="skewX(10)"/><rectx="50"y="200"width="100"height="100"fill="#7e9178"transform="skewY(20)"/><rectx="100"y="300"width="100"height="100"fill="#183c78"transform="skewX(10) skewY(20)"/></svg>
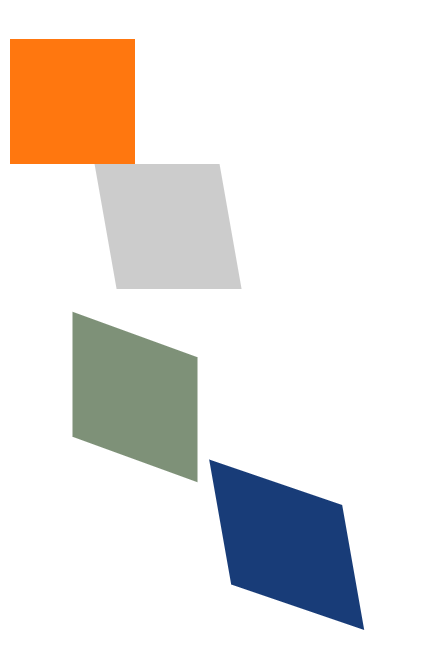
2、js动画
SVG不能动态的修改动画内容
所以考虑用js实现
<svgwidth="300"height="300"><rectid="rect"x="0"y="0"width="50"height="50"fill="#189faa"></rect></svg><script>let dom = document.getElementById('rect')let x =0let y =1let temp =setInterval(()=>{if(x <300&& y <300){
x++
y++
dom.setAttribute('transform',`translate(${x}, ${y})`)}else{
dom.setAttribute('transform',`translate(0, 0)`)
x =0
y =0}},10)</script>

3、css动画
结合CSS来尝试做一下svg的线条动画。这里我们需要用上三个属性:分别是 stroke、stroke-dasharray、stroke-dashoffset。
<head><metaname="viewport"content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><metahttp-equiv="Content-Type"content="text/html;charset=UTF-8"><style>svg{display: block;margin: 50px auto;}#line{stroke-dasharray: 500;stroke-dashoffset: 500;animation: move 2s linear infinite;}@keyframes move{to{stroke-dashoffset: 0;}}</style></head><body><svgwidth="500"height="500"xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"version="1.1"><lineid="line"x1="0"x2="500"y1="0"y2="0"stroke="orange"stroke-width="10"/></svg></body>
4、GreenSock 动画平台
版权归原作者 用户小王 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。