关系映射
1. 关联映射概述
在关系型数据库中,多表之间存在着三种关联关系,分别为一对一,一对多和多对多,如图
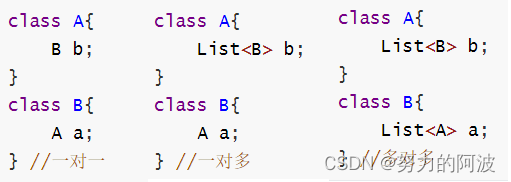
- 一对一的关系:就是在本类中定义对方类型的对象,如A类中定义B类类型的属性b,B类中定义A类类型的属性a。
- 一对多的关系:就是一个A类类型对应多个B类类型的情况,需要在A类中以集合的方式引入B类类型的对象,在B类中定义A类类型的属性a。
- 多对多的关系:在A类中定义B类类型的集合,在B类中定义A类类型的集合。
2. 环境搭建
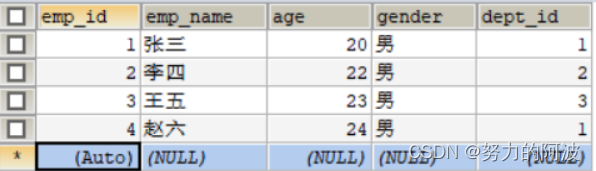
创建t_emp表
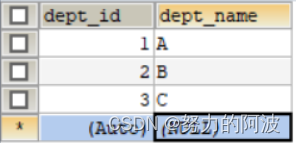
t_dept表
实体类Dept
packagecom.atguigu.mybatis.pojo;importjava.util.List;publicclassDept{privateInteger deptId;privateString deptName;privateList<Emp> emps;publicDept(){}publicDept(Integer deptId,String deptName){this.deptId = deptId;this.deptName = deptName;}publicIntegergetDeptId(){return deptId;}publicvoidsetDeptId(Integer deptId){this.deptId = deptId;}publicStringgetDeptName(){return deptName;}publicvoidsetDeptName(String deptName){this.deptName = deptName;}publicList<Emp>getEmps(){return emps;}publicvoidsetEmps(List<Emp> emps){this.emps = emps;}@OverridepublicStringtoString(){return"Dept{"+"deptId="+ deptId +", deptName='"+ deptName +'\''+", emps="+ emps +'}';}}
实体类Emp
packagecom.atguigu.mybatis.pojo;publicclassEmp{privateInteger empId;privateString empName;privateInteger age;privateString gender;privateDept dept;publicEmp(){}publicEmp(Integer empId,String empName,Integer age,String gender){this.empId = empId;this.empName = empName;this.age = age;this.gender = gender;}publicIntegergetEmpId(){return empId;}publicvoidsetEmpId(Integer empId){this.empId = empId;}publicStringgetEmpName(){return empName;}publicvoidsetEmpName(String empName){this.empName = empName;}publicIntegergetAge(){return age;}publicvoidsetAge(Integer age){this.age = age;}publicStringgetGender(){return gender;}publicvoidsetGender(String gender){this.gender = gender;}@OverridepublicStringtoString(){return"Emp{"+"empId="+ empId +", empName='"+ empName +'\''+", age="+ age +", gender='"+ gender +'\''+", dept="+ dept +'}';}publicDeptgetDept(){return dept;}publicvoidsetDept(Dept dept){this.dept = dept;}}
3.处理字段名和属性名不一致的情况
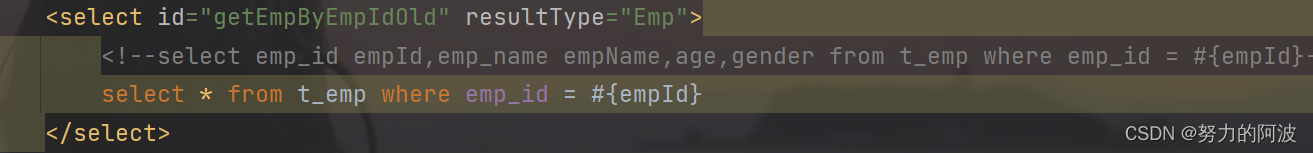
SQL语句
接口:
publicinterfaceEmpMapper{EmpgetEmpById(@Param("empId")Integer empId);}
测试方法:
publicvoidtest(){SqlSessionUtils sqlSessionUtils =newSqlSessionUtils();SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionUtils.getSqlSession();EmpMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapper.class);Emp empById = mapper.getEmpById(1);System.out.println(empById.toString());}
执行测试方法后会得到如下结果:
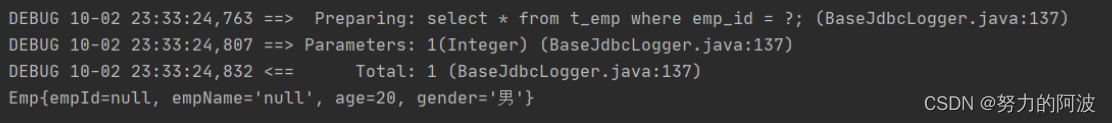
可以看到,我们的SQl语句并没有问题,但为什么查询出的结果会有NUll出现呢,这就是因为我们的**数据库中的字段名于
Emp
实体类的属性名不一致**,因此出现了无法对应的情况。
解决办法:
1.可以通过为字段起别名的方式,保证和实体类中的属性名保持一致
select emp_id empId,emp_name empName,age,gender from t_emp where emp_id =#{empId};
再次执行尝试:
2.可以在MyBatis的核心配置文件中设置一个全局配置信息mapUnderscoreToCamelCase,
此属性可以在查询表中数据时,自动将_类型的字段名,即下划线转换为驼峰
举个栗子:
例如:字段名
user_id
,设置了
mapUnderscoreToCamelCase
,此时字段名就会转换为
userId
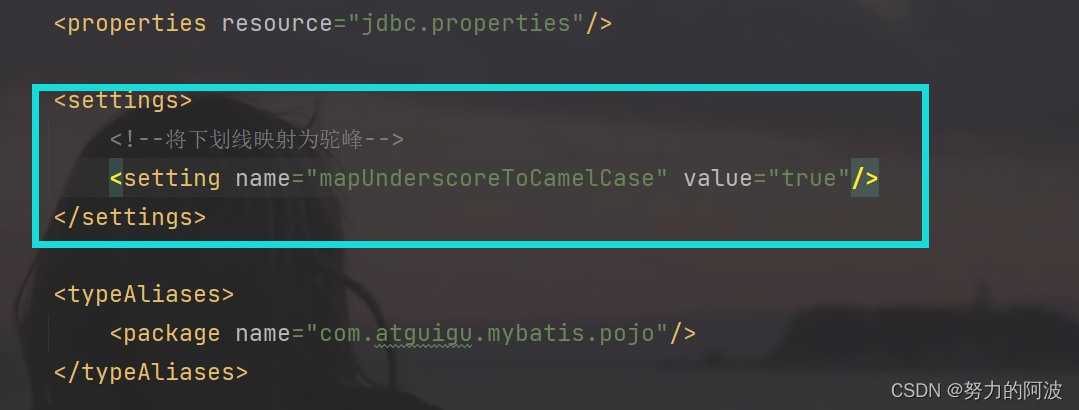
<settings><settingname="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase"value="true"/></settings>
4. 处理一对一映射
调节数据库字段与实体类的属性对应需要标签
resultMap
,如上文那个简单的查询例子就可以这样写:
<resultMapid="empResultMap"type="Emp"><idproperty="empId"column="emp_id"></id><resultproperty="empName"column="emp_name"></result><resultproperty="age"column="age"></result><resultproperty="gender"column="gender"></result></resultMap><selectid="getEmpById"resultMap="empResultMap">
select * from t_emp where emp_id = #{empId};
</select>
属性:
- id:表示自定义映射的唯一标识
- type:查询的数据要映射的实体类的类型
子标签:
- id:设置主键的映射关系
- result:设置普通字段的映射关系
- association :设置多对一的映射关系
- collection:设置一对多的映射关系
- 属性:- property:设置映射关系中实体类中的属性名- column:设置映射关系中表中的字段名
5. 处理多对一映射
5.1 级联方式处理
<resultMapid="empAndDeptResultMap"type="Emp"><idcolumn="emp_id"property="empId"></id><resultcolumn="emp_name"property="empName"></result><resultcolumn="age"property="age"></result><resultcolumn="gender"property="gender"></result><!--部门中的字段dept_id与Emp实体类中的属性dept中的deptId相对应 --><!--部门中的字段dept_name与Emp实体类中的属性dept中的deptName相对应 --><resultcolumn="dept_id"property="dept.deptId"></result><resultcolumn="dept_name"property="dept.deptName"></result></resultMap><selectid="getEmpAndDeptById"resultMap="empAndDeptResultMap">
SELECT t_emp.*,t_dept.* FROM t_emp
LEFT JOIN t_dept
ON t_emp.dept_id=t_dept.dept_id
where t_emp.emp_id=#{empId}
</select>
接口:
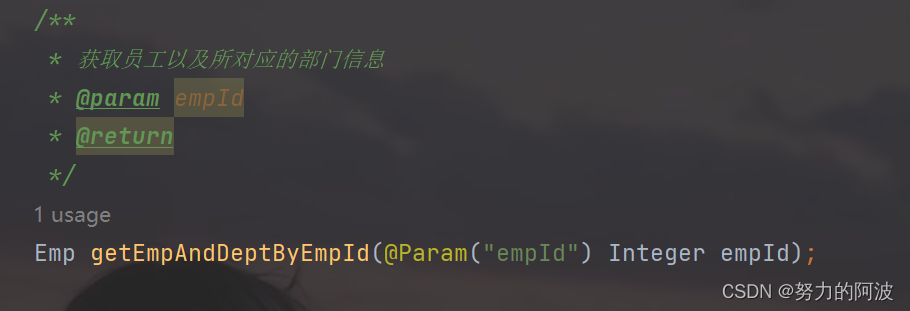
测试方法:
publicvoidtest(){SqlSessionUtils sqlSessionUtils =newSqlSessionUtils();SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionUtils.getSqlSession();EmpMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapper.class);Emp empAndDeptById = mapper.getEmpAndDeptById(1);System.out.println(empAndDeptById);}
查询结果:

5.2 使用association处理映射关系
<resultMapid="empAndDeptResultMap"type="Emp"><idcolumn="emp_id"property="empId"></id><resultcolumn="emp_name"property="empName"></result><resultcolumn="age"property="age"></result><resultcolumn="gender"property="gender"></result><associationproperty="dept"javaType="Dept"><idcolumn="dept_id"property="deptId"></id><resultcolumn="dept_name"property="deptName"></result></association></resultMap>
5.3 分步查询
第一步:查询员工信息

<resultMapid="empAndDeptByStepResultMap"type="Emp"><idcolumn="emp_id"property="empId"></id><resultcolumn="emp_name"property="empName"></result><resultcolumn="age"property="age"></result><resultcolumn="gender"property="gender"></result><associationproperty="dept"select="com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper.DeptMapper.getDeptByStep"column="dept_id"></association></resultMap><selectid="getEmpAndDeptByStep"resultMap="empAndDeptByStepResultMap">
select * from t_emp where emp_id=#{empId};
</select>
注意:
select:设置分步查询,查询某个属性的值的sql的标识(namespace.sqlid)
column:将sql以及查询结果中的某个字段设置为分步查询的条件
第二步:根据员工所对应的部门 id 查询部门信息
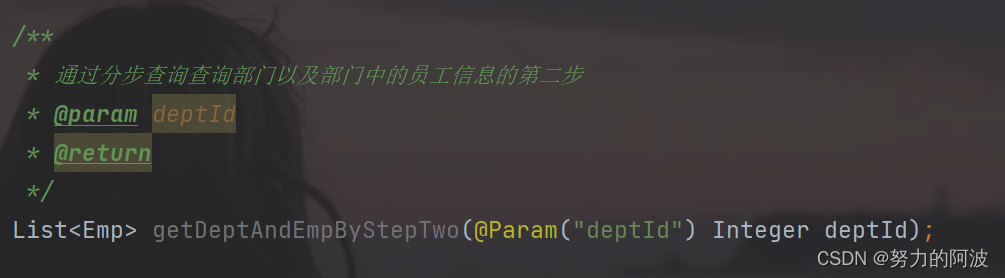
<selectid="getDeptByStep"resultType="com.atguigu.mybatis.pojo.Dept">
select * from t_dept where dept_id=#{deptId};
</select>
测试方法:
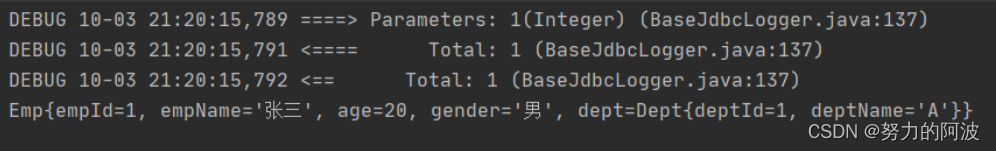
publicvoidtest(){SqlSessionUtils sqlSessionUtils =newSqlSessionUtils();SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionUtils.getSqlSession();EmpMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapper.class);Emp empAndDeptByStep = mapper.getEmpAndDeptByStep(1);System.out.println(empAndDeptByStep);}
执行结果:
分步查询的优点:
可以实现延迟加载
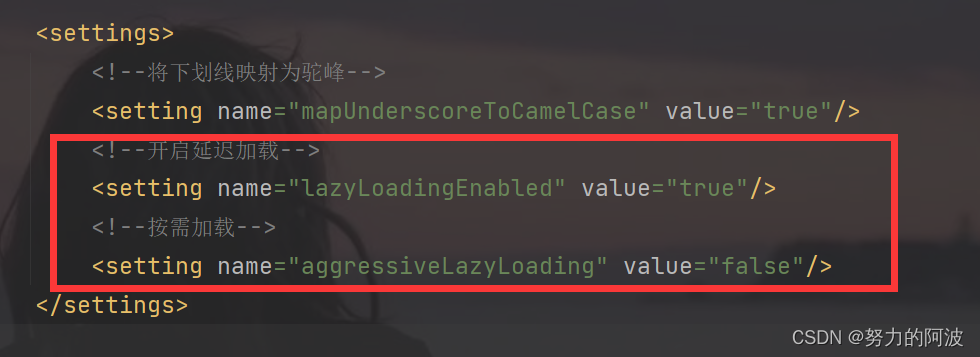
但是必须在核心配置文件中设置全局配置信息:
lazyLoadingEnabled:延迟加载的全局开关。当开启时,所有关联对象都会延迟加载aggressiveLazyLoading:当开启时,任何方法的调用都会加载该对象的所有属性。否则,每个属性会按需加载 此时就可以实现按需加载,获取的数据是什么,就只会执行相应的 sql 。- 此时可通 association和 collection 中的
fetchType属性设置当前的分步查询是否使用延迟加载, fetchType=“lazy(延迟加载) | eager(立即加载)”
6. 处理一对多查询
接口: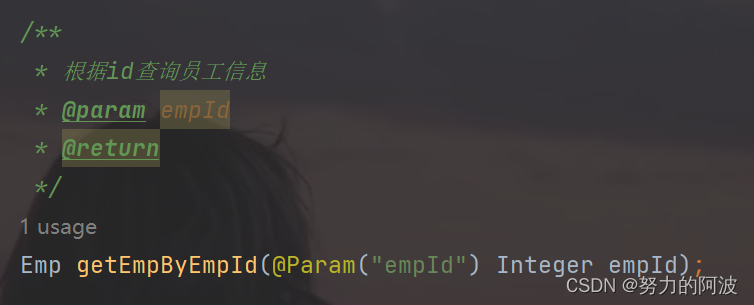
使用
collection
处理
- collection :设置一对多的映射关系
- ofType :设置 collection 标签所处理的集合属性中存储数据的类型
<resultMapid="DeptAndEmpByDeptIdResultMap"type="Dept"><idcolumn="dept_id"property="deptId"></id><resultcolumn="dept_name"property="deptName"></result><collectionproperty="emps"ofType="Emp"><idcolumn="emp_id"property="empId"></id><resultcolumn="emp_name"property="empName"></result><resultcolumn="age"property="age"></result><resultcolumn="gender"property="gender"></result></collection></resultMap><selectid="getDeptAndEmpByDeptId"resultMap="DeptAndEmpByDeptIdResultMap">
SELECT t_emp.*,t_dept.* FROM t_dept
LEFT JOIN t_emp
ON t_emp.dept_id=t_dept.dept_id
WHERE t_dept.dept_id=#{deptId}
</select>
测试:
publicvoidtest4(){SqlSessionUtils sqlSessionUtils =newSqlSessionUtils();SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionUtils.getSqlSession();DeptMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(DeptMapper.class);Dept deptAndEmpByDeptId = mapper.getDeptAndEmpByDeptId(1);System.out.println(deptAndEmpByDeptId);}
执行结果:

7. 小结
关系映射主要处理复杂的SQl查询,如子查询,多表联查等复杂查询,应用此种需求时可以考虑使用。
版权归原作者 努力的阿波 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。