文章目录
WebService
Web服务(Web Services)是一种基于网络的标准化的软件系统,允许不同的应用程序通过网络相互通信和交互。它们使用标准化的网络协议和数据格式,使得不同平台、不同语言编写的应用程序能够互相通信和交换数据。
在现代软件开发中,构建可靠的Web服务是至关重要的。Apache CXF是一个功能强大的Java框架,用于构建Web服务和Web应用程序。结合Spring Boot,我们可以快速搭建一个简单的WebService。本文将介绍如何使用Apache CXF和Spring Boot创建一个简单的WebService,并进行基本的测试。
1.简单介绍WebService
1.1. 类型
Web服务通常分为两种主要类型:
- SOAP Web服务:基于SOAP(Simple Object Access Protocol)协议的Web服务。SOAP是一种用于交换结构化信息的协议,它使用XML作为消息格式,并通常通过HTTP协议进行传输。
- RESTful Web服务:基于REST(Representational State Transfer)原则的Web服务。RESTful服务使用标准的HTTP方法(如GET、POST、PUT、DELETE)来执行操作,并通常返回JSON或XML格式的数据。
1.2. 架构
Web服务的架构通常包括以下关键组件:
- 服务提供者(Service Provider):提供Web服务的实体。它们发布服务并处理来自客户端的请求。
- 服务请求者(Service Requestor):使用Web服务的客户端应用程序。它们向服务提供者发送请求并处理响应。
- 服务描述(Service Description):Web服务的描述文件,通常使用WSDL(Web Services Description Language)或OpenAPI等格式来描述服务的接口和操作。
- 消息格式(Message Format):Web服务使用的数据交换格式,通常是XML或JSON。
- 通信协议(Communication Protocol):Web服务之间通信的协议,常见的包括HTTP、HTTPS、SMTP等。
1.3. 主要特点
Web服务具有以下主要特点:
- 跨平台性(Platform Independence):由于Web服务使用标准化的协议和数据格式,因此它们可以在不同的平台和操作系统上运行。
- 松耦合(Loose Coupling):Web服务通过标准化接口进行通信,服务提供者和请求者之间的耦合度较低,可以独立开发和部署。
- 可组合性(Composability):可以通过组合多个Web服务来创建复杂的应用程序。
- 可重用性(Reusability):Web服务可以被多个应用程序重复使用,从而提高了软件开发效率。
- 易于维护(Maintainability):由于Web服务使用标准化的接口和协议,因此易于维护和更新。
1.4. 使用场景
Web服务在许多场景下都得到了广泛应用,包括但不限于:
- 企业应用集成(Enterprise Application Integration,EAI):将不同的企业应用程序和系统集成在一起,实现数据和业务流程的无缝交互。
- 分布式系统:构建分布式系统和服务导向架构(Service-Oriented Architecture,SOA),提供跨网络的服务和资源共享。
- 移动应用程序开发:通过Web服务为移动应用程序提供数据和功能支持,与后端服务器进行通信和交互。
- 云计算:在云平台上部署和管理Web服务,提供云端服务和资源。
1.5. Web服务标准和技术
一些常见的Web服务标准和技术包括:
- SOAP(Simple Object Access Protocol):用于构建基于XML的Web服务的协议。
- WSDL(Web Services Description Language):用于描述Web服务的接口和操作的XML格式的语言。
- UDDI(Universal Description, Discovery, and Integration):用于注册和发现Web服务的协议和规范。
- REST(Representational State Transfer):一种基于HTTP协议的软件架构风格,用于构建RESTful Web服务。
- JSON(JavaScript Object Notation):一种轻量级的数据交换格式,通常用于RESTful Web服务的数据格式。
2.案例-WebServiceDemo
2.1.引入配置文件
首先,我们需要在项目中添加必要的依赖项。这些依赖项将帮助我们集成Apache CXF到Spring Boot应用程序中。我的使用的是gradle构建的项目
// 引入WebService
implementation 'org.apache.cxf:cxf-rt-frontend-jaxws:3.2.0'
implementation 'org.apache.cxf:cxf-rt-transports-http:3.2.0'
<dependency><groupId>org.apache.cxf</groupId><artifactId>cxf-rt-frontend-jaxws</artifactId><version>3.2.0</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.apache.cxf</groupId><artifactId>cxf-rt-transports-http</artifactId><version>3.2.0</version></dependency>
2.2.创建接口
importcom.fhr.student.entity.Student;importjavax.jws.WebParam;importjavax.jws.WebService;@WebServicepublicinterfaceStudentService{/**
* 根据姓名获取学生信息
* @param userName 学生姓名
* @return 学生信息
*/StudentgetStudentInfoByName(@WebParam(name ="userName")String userName);}
2.3.创建接口实现类
importcom.fhr.service.StudentService;importcom.fhr.student.entity.Student;importorg.springframework.stereotype.Component;importjavax.jws.WebService;/**
* targetNamespace:目标命名控件,一般由接口所在包路径命名,不过是由里往外写:比如:我接口所在路径为:com.fhr.service 写为:http://service.fhr.com/
*/@Component@WebService(targetNamespace ="http://service.fhr.com/",endpointInterface ="com.fhr.service.StudentService")publicclassStudentImplimplementsStudentService{/**
* 根据学生姓名获取学生信息
* @param userName 学生姓名
* @return 学生信息
*/@OverridepublicStudentgetStudentInfoByName(String userName){// TODO这里应该查询数据库System.out.println("传入的参数为:"+userName);Student student =newStudent();
student.setUserName(userName);
student.setClassName("高三一班");
student.setAge(14);return student;}}
2.4.创建WebService配置类
我们需要配置CXF和发布WebService的端点。我们使用Spring Boot的配置类来完成这个任务。
importcom.fhr.service.StudentService;importorg.apache.cxf.Bus;importorg.apache.cxf.bus.spring.SpringBus;importorg.apache.cxf.jaxws.EndpointImpl;importorg.apache.cxf.transport.servlet.CXFServlet;importorg.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletRegistrationBean;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;importjavax.xml.ws.Endpoint;@ConfigurationpublicclassWebServiceConfig{// 创建一个SpringBus Bean,作为Apache CXF的默认总线@Bean(name =Bus.DEFAULT_BUS_ID)publicSpringBusspringBus(){returnnewSpringBus();}// 注册CXF Servlet,用于处理WebService请求@Bean(name ="wbsBean")publicServletRegistrationBeandispatcherServlet(){// 创建一个ServletRegistrationBean,将CXFServlet映射到指定路径ServletRegistrationBean wbsServlet =newServletRegistrationBean(newCXFServlet(),"/wbs/*");return wbsServlet;}// 定义WebService端点@BeanpublicEndpointendpointPurchase(SpringBus springBus,StudentService studentService){// 创建EndpointImpl对象,并将SpringBus和WebService实现类传入EndpointImpl endpoint =newEndpointImpl(springBus, studentService);// 将端点发布到指定路径
endpoint.publish("/user-server");// 打印发布成功消息,显示服务的访问地址System.out.println("服务发布成功!地址为:http://localhost:8081/wbs/user-server");// 返回端点对象return endpoint;}}
2.5.测试
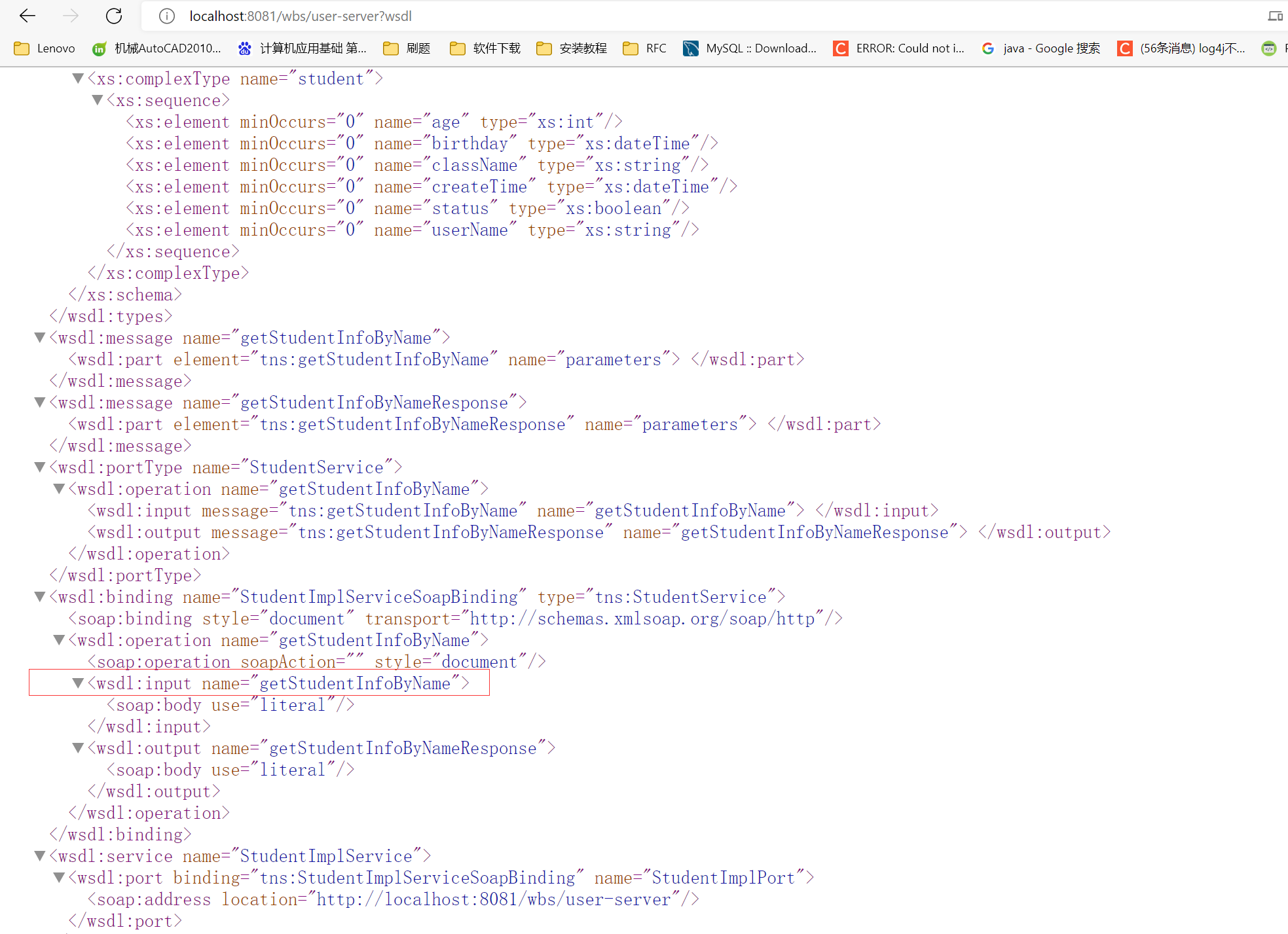
启动项目后,您可以在浏览器中输入
http://localhost:8081/wbs/user-server?wsdl来查看WebService的WSDL文档。
# 启动项目
在浏览器的地址中输入 http://localhost:8081/wbs/user-server?wsdl
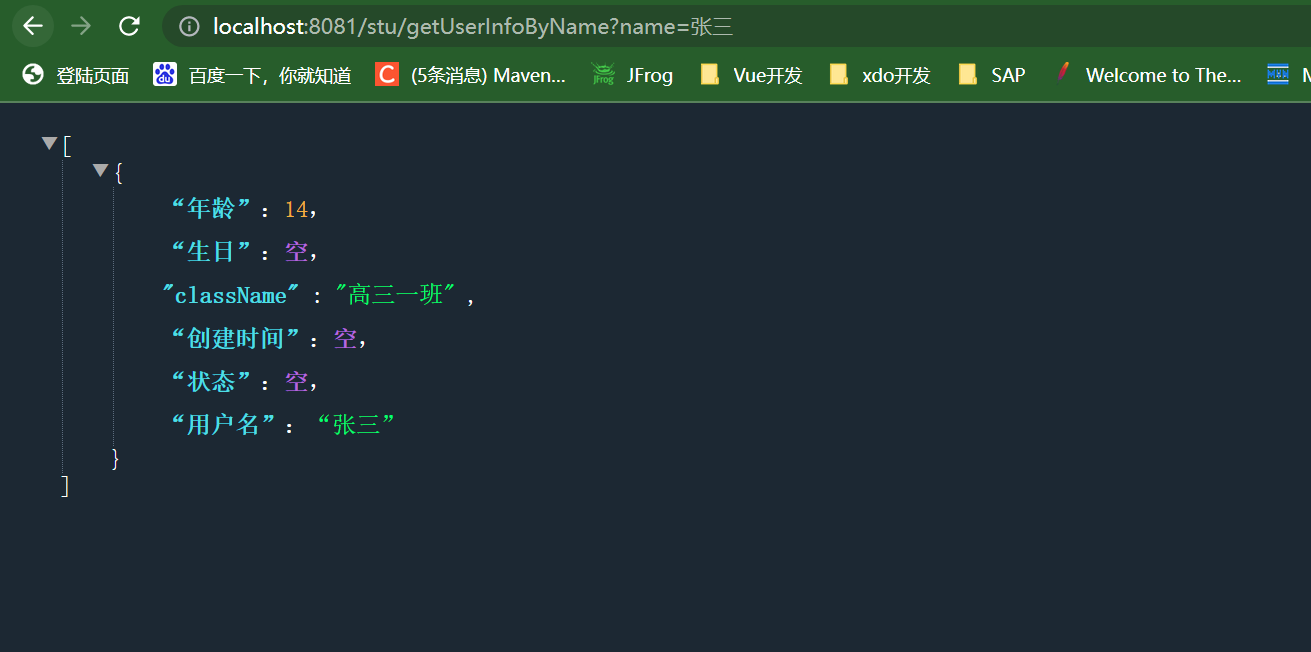
# 测试客户端
为了方便直接在本地项目测试
在浏览器中输入 测试
importorg.apache.cxf.endpoint.Client;importorg.apache.cxf.jaxws.endpoint.dynamic.JaxWsDynamicClientFactory;importorg.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;importorg.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;importorg.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;importorg.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;@RestController@RequestMapping("/stu")publicclassStudentController{// 定义了一个映射到路径"/stu/getUserInfoByName"的GET请求处理方法@GetMapping("/getUserInfoByName")publicObject[]getUserInfoByName(@RequestParam("name")String name){// 创建JaxWsDynamicClientFactory实例,用于动态创建客户端JaxWsDynamicClientFactory proxyFactoryBean =JaxWsDynamicClientFactory.newInstance();// 使用动态客户端工厂创建客户端对象,并指定WebService的WSDL地址Client client = proxyFactoryBean.createClient("http://localhost:8081/wbs/user-server?wsdl");// 定义一个Object数组用于存储调用WebService方法后的返回结果Object[] objects =newObject[0];// 调用远程WebService方法try{// 调用客户端的invoke方法,传入方法名和参数,获取WebService方法的返回结果
objects = client.invoke("getStudentInfoByName", name);}catch(Exception e){// 捕获异常,打印异常信息
e.printStackTrace();}// 返回WebService方法的返回结果return objects;}}
版权归原作者 小饭团~ 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。