文章目录
1. 背景
在现代软件开发中,面向切面编程(
AOP
)是一种强大的编程范式,允许开发者跨越应用程序的多个部分定义横切关注点(如日志记录、事务管理等)。本文将介绍如何在
Spring
框架中通过
AspectJ
注解以及对应的
XML
配置来实现
AOP
,在不改变主业务逻辑的情况下增强应用程序的功能。
2. 基于AspectJ注解来实现AOP
对于一个使用
Maven
的
Spring
项目,需要在
pom.xml
中添加以下依赖:
<dependencies><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-context</artifactId><version>5.3.10</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.aspectj</groupId><artifactId>aspectjrt</artifactId><version>1.9.6</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.aspectj</groupId><artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId><version>1.9.6</version></dependency></dependencies>
确保版本号与使用的
Spring
版本相匹配,可以自行调整。
- 创建业务逻辑接口MyService:
packagecom.example.demo.aop;publicinterfaceMyService{voidperformAction();}
- 创建业务逻辑类MyServiceImpl.java:
packagecom.example.demo.aop;importorg.springframework.stereotype.Service;@ServicepublicclassMyServiceImplimplementsMyService{@OverridepublicvoidperformAction(){System.out.println("Performing an action in MyService");}}
- 定义切面
创建切面类
MyAspect.java
,并使用注解定义切面和通知:
packagecom.example.demo.aop;importorg.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;importorg.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;importorg.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Aspect@ComponentpublicclassMyAspect{@Before("execution(* com.example.demo.aop.MyServiceImpl.performAction(..))")publicvoidlogBeforeAction(){System.out.println("Before performing action");}}
@Aspect
注解是用来标识一个类作为
AspectJ
切面的一种方式,这在基于注解的
AOP
配置中是必需的。它相当于
XML
配置中定义切面的方式,但使用注解可以更加直观和便捷地在类级别上声明切面,而无需繁琐的
XML
配置。
- 配置Spring以启用注解和AOP
创建一个
Java
配置类来代替
XML
配置,使用
@Configuration
注解标记为配置类,并通过
@ComponentScan
注解来启用组件扫描,通过
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
启用
AspectJ
自动代理:
packagecom.example.demo.config;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;@Configuration@ComponentScan("com.example")@EnableAspectJAutoProxypublicclassAppConfig{}
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
注解在
Spring
中用于启用对
AspectJ
风格的切面的支持。它告诉
Spring
框架去寻找带有
@Aspect
注解的类,并将它们注册为
Spring
应用上下文中的切面,以便在运行时通过代理方式应用这些切面定义的通知(
Advice
)和切点(
Pointcuts
)。
如果不写
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
,
Spring
将不会自动处理
@Aspect
注解定义的切面,则定义的那些前置通知(
@Before
)、后置通知(
@After
、
@AfterReturning
、
@AfterThrowing
)和环绕通知(
@Around
)将不会被自动应用到目标方法上。这意味着定义的
AOP
逻辑不会被执行,失去了
AOP
带来的功能增强。
@Before
注解定义了一个前置通知(
Advice
),它会在指定方法执行之前运行。切点表达式
execution(* com.example.demo.aop.MyServiceImpl.performAction(..))
精确地定义了这些连接点的位置。在这个例子中,切点表达式指定了
MyServiceImpl
类中的
performAction
方法作为连接点,而
@Before
注解标识的方法(
logBeforeAction
)将在这个连接点之前执行,即
logBeforeAction
方法(前置通知)会在
performAction
执行之前被执行。
- 创建主类和测试AOP功能
主程序如下:
packagecom.example.demo;importcom.example.demo.aop.MyService;importcom.example.demo.config.AppConfig;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;publicclassDemoApplication{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context =newAnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);MyService service = context.getBean(MyService.class);
service.performAction();}}
运行结果如下:
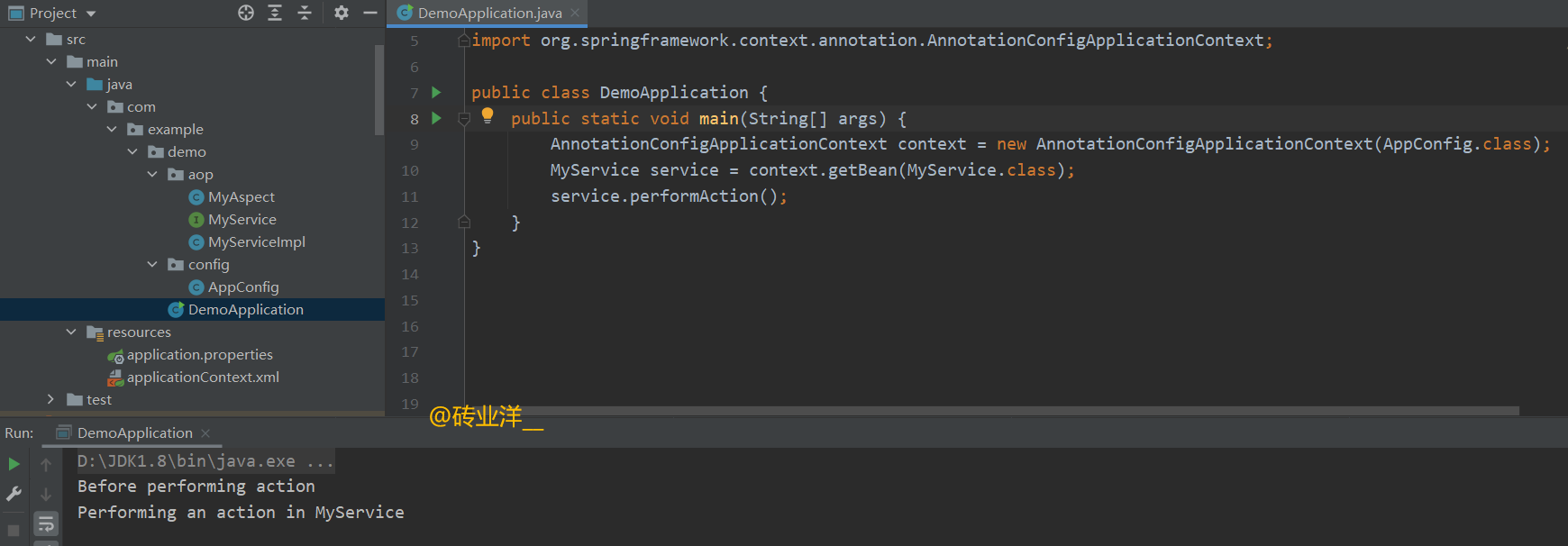
3. XML实现和注解实现AOP的代码对比
对于上面的代码,我们将原有基于注解的
AOP
配置改写为完全基于
XML
的形式,方便大家对比。首先需要移除切面类和业务逻辑类上的所有
Spring
相关注解,然后在
XML
文件中配置相应的
bean
和
AOP
逻辑。
移除注解
首先,我们移除业务逻辑类和切面类上的所有注解。
MyService.java (无变化,接口保持原样):
packagecom.example.demo.aop;publicinterfaceMyService{voidperformAction();}
MyServiceImpl.java (移除@Service注解):
packagecom.example.demo.aop;publicclassMyServiceImplimplementsMyService{@OverridepublicvoidperformAction(){System.out.println("Performing an action in MyService");}}
MyAspect.java (移除@Aspect和@Component注解,同时去掉方法上的@Before注解):
packagecom.example.demo.aop;publicclassMyAspect{publicvoidlogBeforeAction(){System.out.println("Before performing action");}}
XML配置
接下来,**删除
AppConfig
配置类**,在
Spring
的
XML
配置文件中定义
beans
和
AOP
配置。
applicationContext.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beansxmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"><!-- 定义业务逻辑bean --><beanid="myService"class="com.example.demo.aop.MyServiceImpl"/><!-- 定义切面 --><beanid="myAspect"class="com.example.demo.aop.MyAspect"/><!-- AOP配置 --><aop:config><aop:aspectid="aspect"ref="myAspect"><aop:pointcutid="serviceOperation"expression="execution(* com.example.demo.aop.MyService.performAction(..))"/><aop:beforepointcut-ref="serviceOperation"method="logBeforeAction"/></aop:aspect></aop:config></beans>
在这个
XML
配置中,我们手动注册了
MyServiceImpl
和
MyAspect
作为
beans
,并通过
<aop:config>
元素定义了
AOP
逻辑。我们创建了一个切点
serviceOperation
,用于匹配
MyService.performAction(..)
方法的执行,并定义了一个前置通知,当匹配的方法被调用时,
MyAspect
的
logBeforeAction
方法将被执行。
主类和测试AOP功能
主类
DemoApplication
的代码不需要改变,只是在创建
ApplicationContext
时使用
XML
配置文件而不是
Java
配置类:
packagecom.example.demo;importcom.example.demo.aop.MyService;importorg.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;publicclassDemoApplication{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context =newClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");MyService service = context.getBean(MyService.class);
service.performAction();}}
运行结果是一样的
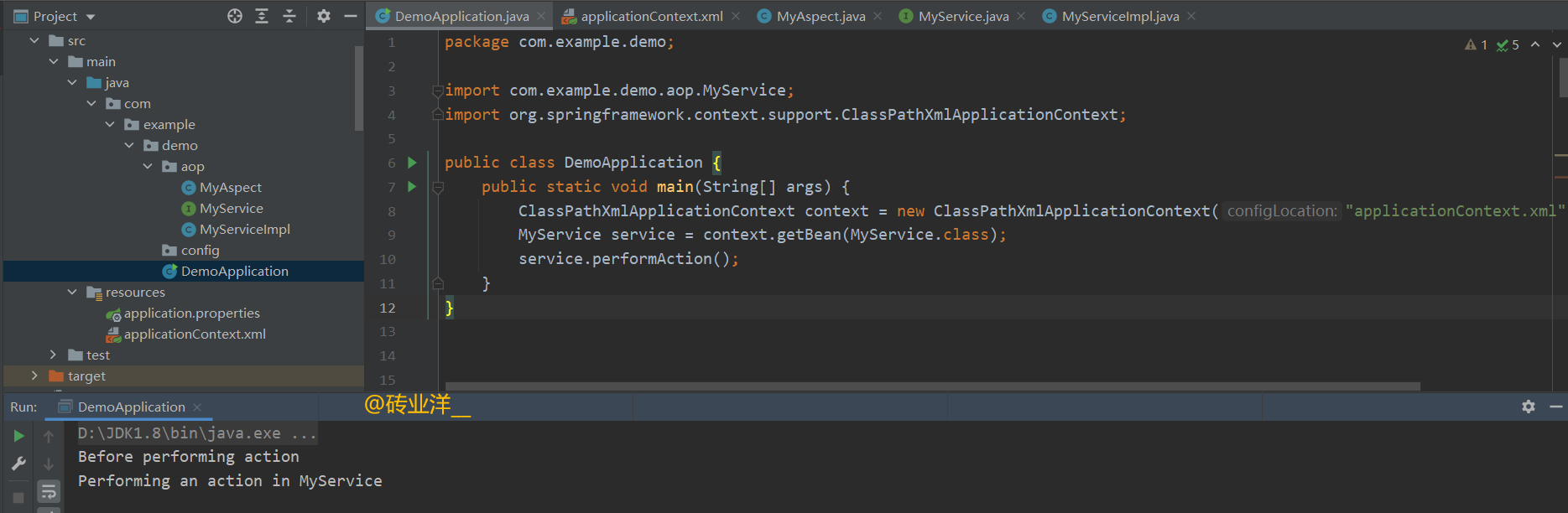
4. AOP通知讲解
在
Spring AOP
中,通知(
Advice
)定义了切面(
Aspect
)在目标方法调用过程中的具体行为。
Spring AOP
支持五种类型的通知,它们分别是:前置通知(
Before
)、后置通知(
After
)、返回通知(
After Returning
)、异常通知(
After Throwing
)和环绕通知(
Around
)。通过使用这些通知,开发者可以在目标方法的不同执行点插入自定义的逻辑。
- @Before(前置通知)
前置通知是在目标方法执行之前执行的通知,通常用于执行一些预处理任务,如日志记录、安全检查等。
@Before("execution(* com.example.demo.aop.MyServiceImpl.performAction(..))")publicvoidlogBeforeAction(){System.out.println("Before performing action");}
- @AfterReturning(返回通知)
返回通知在目标方法成功执行之后执行,可以访问方法的返回值。
@AfterReturning(pointcut ="execution(* com.example.demo.aop.MyServiceImpl.performAction(..))", returning ="result")publicvoidlogAfterReturning(Object result){System.out.println("Method returned value is : "+ result);}
这里在
@AfterReturning
注解中指定
returning = "result"
时,
Spring AOP
框架将目标方法的返回值传递给切面方法的名为
result
的参数,因此,切面方法需要有一个与之匹配的参数,类型兼容目标方法的返回类型。如果两者不匹配,
Spring
在启动时会抛出异常,因为它无法将返回值绑定到切面方法的参数。
- @AfterThrowing(异常通知)
异常通知在目标方法抛出异常时执行,允许访问抛出的异常。
@AfterThrowing(pointcut ="execution(* com.example.demo.aop.MyServiceImpl.performAction(..))", throwing ="ex")publicvoidlogAfterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint,Throwable ex){String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();System.out.println("@AfterThrowing: Exception in method: "+ methodName +"; Exception: "+ ex.toString());}
在
@AfterThrowing
注解的方法中包含
JoinPoint
参数是可选的,当想知道哪个连接点(即方法)引发了异常的详细信息时非常有用,假设有多个方法可能抛出相同类型的异常,而我们想在日志中明确指出是哪个方法引发了异常。通过访问
JoinPoint
提供的信息,可以记录下引发异常的方法名称和其他上下文信息,从而使得日志更加清晰和有用。
- @After(后置通知)
后置通知在目标方法执行之后执行,无论方法执行是否成功,即便发生异常,仍然会执行。它类似于
finally
块。
@After("execution(* com.example.demo.aop.MyServiceImpl.performAction(..))")publicvoidlogAfter(){System.out.println("After performing action");}
- @Around(环绕通知)
环绕通知围绕目标方法执行,可以在方法调用前后执行自定义逻辑,同时决定是否继续执行目标方法。环绕通知提供了最大的灵活性和控制力。
@Around("execution(* com.example.demo.aop.MyServiceImpl.performAction(..))")publicObjectlogAround(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint)throwsThrowable{System.out.println("Before method execution");Object result = joinPoint.proceed();// 继续执行目标方法System.out.println("After method execution");return result;}
接下来,我们来演示一下,全部代码如下:
服务接口(MyService.java):
packagecom.example.demo.aop;publicinterfaceMyService{StringperformAction(String input);}
服务实现(MyServiceImpl.java):
修改
performAction
方法,使其在接收到特定输入时抛出异常
packagecom.example.demo.aop;importorg.springframework.stereotype.Service;@ServicepublicclassMyServiceImplimplementsMyService{@OverridepublicStringperformAction(String input){System.out.println("Performing action with: "+ input);if("error".equals(input)){thrownewRuntimeException("Simulated error");}return"Processed "+ input;}}
完整的切面类(包含所有通知类型)
切面类(
MyAspect.java
) - 保持不变,确保包含所有类型的通知:
packagecom.example.demo.aop;importorg.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;importorg.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;importorg.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;importorg.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Aspect@ComponentpublicclassMyAspect{@Before("execution(* com.example.demo.aop.MyService.performAction(..))")publicvoidbeforeAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint){System.out.println("@Before: Before calling performAction");}@After("execution(* com.example.demo.aop.MyService.performAction(..))")publicvoidafterAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint){System.out.println("@After: After calling performAction");}@AfterReturning(pointcut ="execution(* com.example.demo.aop.MyService.performAction(..))", returning ="result")publicvoidafterReturningAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object result){System.out.println("@AfterReturning: Method returned value is : "+ result);}@AfterThrowing(pointcut ="execution(* com.example.demo.aop.MyService.performAction(..))", throwing ="ex")publicvoidafterThrowingAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint,Throwable ex){String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();System.out.println("@AfterThrowing: Exception in method: "+ methodName +"; Exception: "+ ex.toString());}@Around("execution(* com.example.demo.aop.MyService.performAction(..))")publicObjectaroundAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint)throwsThrowable{System.out.println("@Around: Before method execution");Object result =null;try{
result = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();}catch(Throwable throwable){// 如果执行方法出现异常,打印这里System.out.println("@Around: Exception in method execution");throw throwable;}// 如果执行方法正常,打印这里System.out.println("@Around: After method execution");return result;}}
这里要强调几点:
@Around环绕通知常见用例是异常捕获和重新抛出。在这个例子中,我们通过ProceedingJoinPoint的proceed()方法调用目标方法。如果目标方法执行成功,记录执行后的消息并返回结果。如果在执行过程中发生异常,在控制台上打印出异常信息,然后重新抛出这个异常。这样做可以确保异常不会被吞没,而是可以被上层调用者捕获或由其他异常通知处理。@AfterThrowing注解标明这个通知只有在目标方法因为异常而终止时才会执行。throwing属性指定了绑定到通知方法参数上的异常对象的名称。这样当异常发生时,异常对象会被传递到afterThrowingAdvice方法中,方法中可以对异常进行记录或处理。@AfterThrowing和@AfterReturning通知不会在同一个方法调用中同时执行。这两个通知的触发条件是互斥的。@AfterReturning通知只有在目标方法成功执行并正常返回后才会被触发,这个通知可以访问方法的返回值。@AfterThrowing通知只有在目标方法抛出异常时才会被触发,这个通知可以访问抛出的异常对象。- 假设想要某个逻辑总是在方法返回时执行,不管是抛出异常还是正常返回,则考虑放在
@After或者@Around通知里执行。
配置类
packagecom.example.demo.config;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;@Configuration@ComponentScan("com.example")@EnableAspectJAutoProxypublicclassAppConfig{}
测试不同情况
为了测试所有通知类型的触发,在主类中执行
performAction
方法两次:一次传入正常参数,一次传入会导致异常的参数。
主程序如下:
packagecom.example.demo;importcom.example.demo.aop.MyService;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;publicclassDemoApplication{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context =newAnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);MyService service = context.getBean(MyService.class);try{// 正常情况System.out.println("Calling performAction with 'test'");
service.performAction("test");// 异常情况System.out.println("\nCalling performAction with 'error'");
service.performAction("error");}catch(Exception e){System.out.println("Exception caught in DemoApplication: "+ e.getMessage());}}}
在这个例子中,当
performAction
方法被第二次调用并传入
"error"
作为参数时,将会抛出异常,从而触发
@AfterThrowing
通知。
运行结果如下:
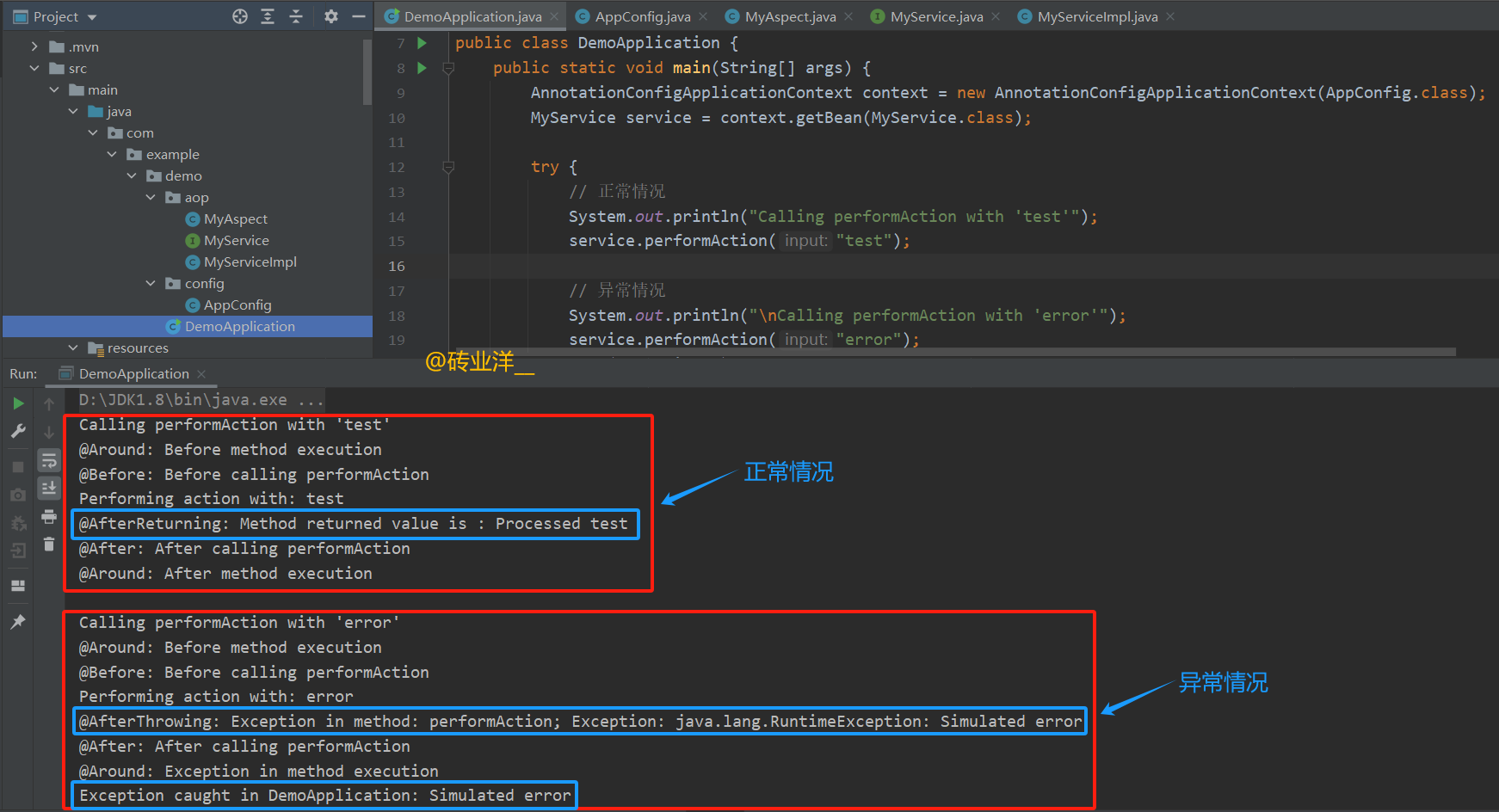
5. AOP时序图
这里展示在
Spring AOP
框架中一个方法调用的典型处理流程,包括不同类型的通知(
Advice
)的执行时机。
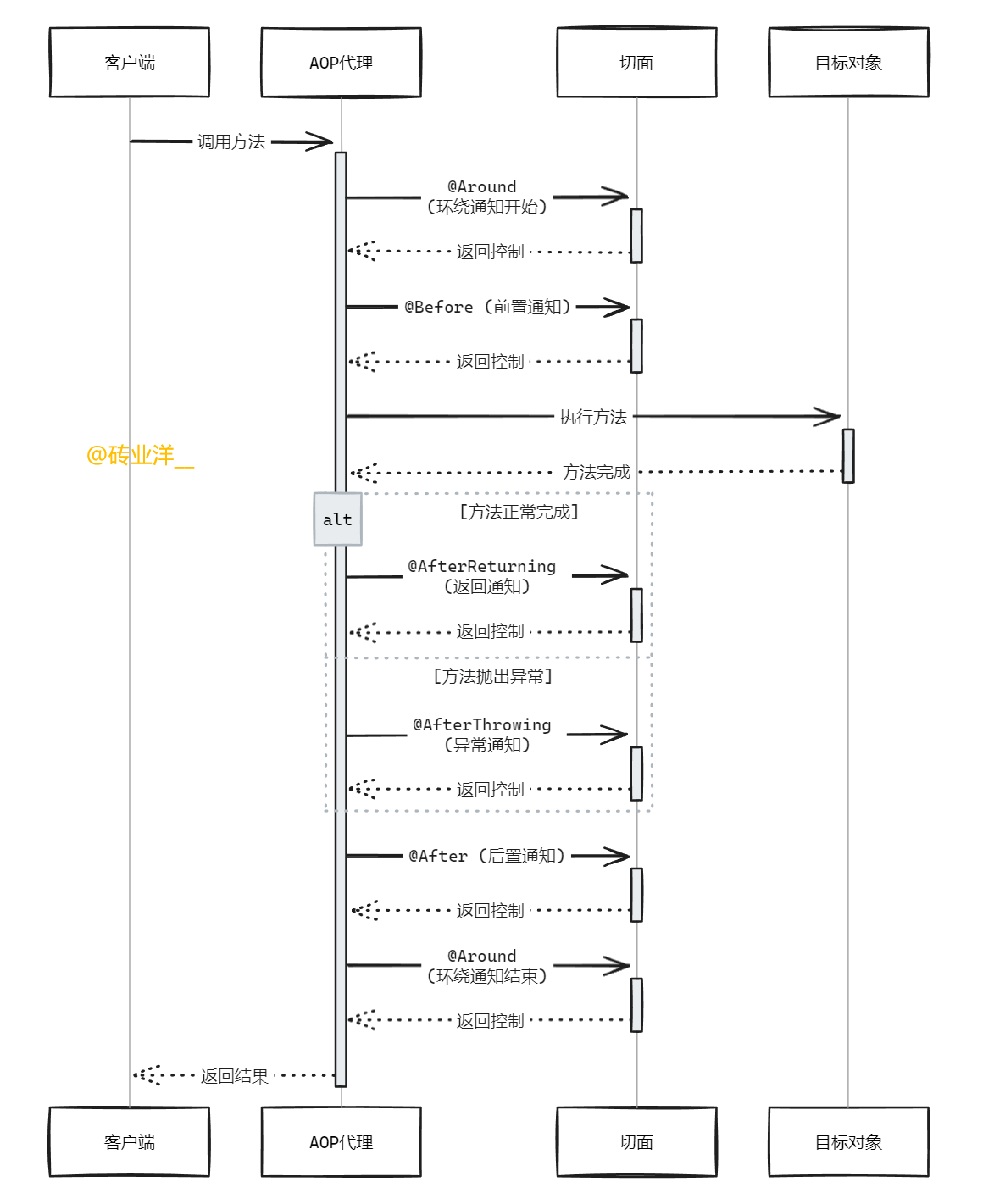
- 客户端调用方法:
- 客户端(
Client)发起对某个方法的调用。这个调用首先被AOP代理(AOP Proxy)接收,这是因为在Spring AOP中,代理负责在真实对象(Target)和外界之间进行中介。
- 环绕通知开始 (
@Around):
AOP代理首先调用切面(Aspect)中定义的环绕通知的开始部分。环绕通知可以在方法执行前后执行代码,并且能决定是否继续执行方法或直接返回自定义结果。这里的“开始部分”通常包括方法执行前的逻辑。
- 前置通知 (
@Before):
- 在目标方法执行之前,执行前置通知。这用于在方法执行前执行如日志记录、安全检查等操作。
- 执行目标方法:
- 如果环绕通知和前置通知没有中断执行流程,代理会调用目标对象(
Target)的实际方法。
- 方法完成:
- 方法执行完成后,控制权返回到
AOP代理。这里的“完成”可以是成功结束,也可以是抛出异常。
- 返回通知或异常通知:
- 返回通知 (
@AfterReturning):如果方法成功完成,即没有抛出异常,执行返回通知。这可以用来处理方法的返回值或进行某些后续操作。 - 异常通知 (
@AfterThrowing):如果方法执行过程中抛出异常,执行异常通知。这通常用于异常记录或进行异常处理。
- 后置通知 (
@After):
- 独立于方法执行结果,后置通知总是会执行。这类似于在编程中的
finally块,常用于资源清理。
- 环绕通知结束 (
@Around):
- 在所有其他通知执行完毕后,环绕通知的结束部分被执行。这可以用于执行清理工作,或者在方法执行后修改返回值。
- 返回结果:
- 最终,
AOP代理将处理的结果返回给客户端。这个结果可能是方法的返回值,或者通过环绕通知修改后的值,或者是异常通知中处理的结果。
欢迎一键三连~
有问题请留言,大家一起探讨学习
----------------------Talk is cheap, show me the code-----------------------
版权归原作者 砖业洋__ 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。