1、什么是动态路由?
2、动态路由的好处
3、动态路由如何实现
1、什么是动态路由?
动态路由,动态即不是写死的,是可变的。我们可以根据自己不同的需求加载不同的路由,做到不同的实现及页面的渲染。动态的路由存储可分为两种,一种是将路由存储到前端。另一种则是将路由存储到数据库。动态路由的使用一般结合角色权限控制一起使用。
总结:
1:路由可变,不是写死的,动态加载;
2:存储分两种:存储前端、存储数据库
2、动态路由的好处
使用动态路由可以跟灵活,无需手工维护,我们可以使用一个页面对路由进行维护。如果将路由存储到数据库,还可以增加安全性。
总结:
1:灵活,无需手工维护;
2:增加安全性
3、动态路由如何实现
在此以路由存储在数据库为例
流程:一般我们在登录的时候,根据登录用户的角色返回此角色可以访问的页面的路由,前端将路由存储到vuex(vuex存储的数据必须可持久的,不要一刷新页面就不见),我们在路由前置守卫处动态添加拿到的路由,对页面进行渲染。
1)此为我的router目录,index.js对路由添加,守卫拦截等处理。static-route.js为前端定义的静态路由,不需要动态加载的,如登陆页面,忘记密码页面,404页面等。
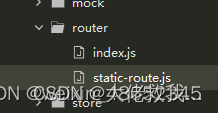
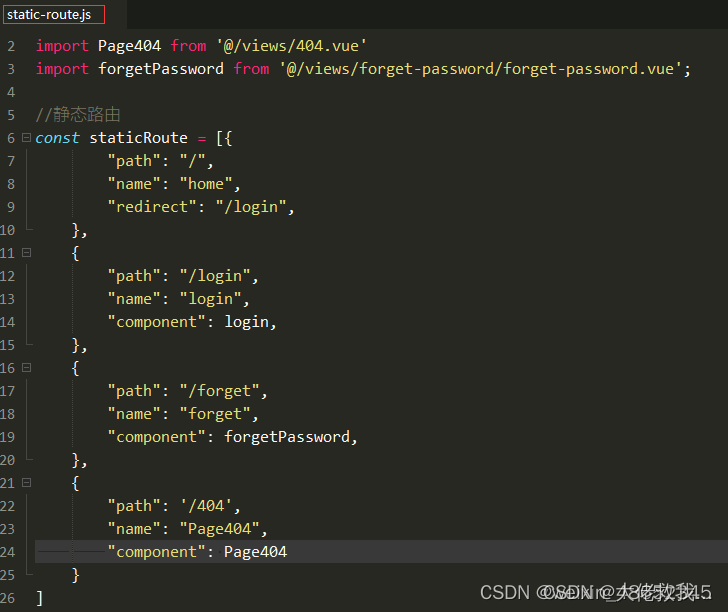
index.js文件
import Vue from 'vue'
import $cookies from 'vue-cookies'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import store from '../store'
import staticRoute from './static-route.js'
Vue.use(VueRouter)
const router = new VueRouter({
mode: 'history',
base: process.env.BASE_URL,
routes: staticRoute //staticRoute为静态路由,不需动态添加
})
let isToken = true
router.beforeEach(async (to, from, next) => {
//定义isToken为true和vuex不为空时添加路由
if (isToken && store.state.routers.routers.length != 0) {
//从vuex中获取动态路由
const accessRouteses = await store.state.routers.routers;
//动态路由循环解析和添加
accessRouteses.forEach(v => {
v.children = routerChildren(v.children);
v.component = routerCom(v.component);
router.addRoute(v); //添加
})
isToken = false //将isToken赋为 false ,否则会一直循环,崩溃
next({
...to, // next({ ...to })的目的,是保证路由添加完了再进入页面 (可以理解为重进一次)
replace: true, // 重进一次, 不保留重复历史
})
} else {
if (to.name == null) {
next("/404")
} else {
if (to.meta.title) { //判断是否有标题
document.title = to.meta.title //给相应页面添加标题
}
next()
}
}
})
function routerCom(path) { //对路由的component解析
return (resolve) => require([`@/views/${path}`], resolve);
}
function routerChildren(children) { //对子路由的component解析
children.forEach(v => {
v.component = routerCom(v.component);
if (v.children != undefined) {
v.children = routerChildren(v.children)
}
})
return children
}
export default router
2)登陆成功后将获取到的动态路由存储到vuex
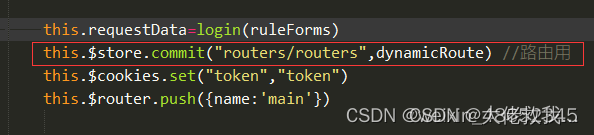
vuex—>index.js文件
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
//数据持久化
import createPersistedState from "vuex-persistedstate";
Vue.use(Vuex)
const routers = {
namespaced: true,
state: () => ({
routers:"",
}),
mutations: {
routers(state, newsdata) {
state.routers = newsdata
},
},
actions: {
routers(context) {
context.commit('routers')
},
},
getters: {
routers(state) {
console.log("getters", state)
return state.routers
},
}
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
routers: routers,
},
// 数据持久化
plugins: [createPersistedState({
//key是存储数据的键名
key: 'routersData',
//paths是存储state中的那些数据,如果是模块下具体的数据需要加上模块名称,如user.token
paths: ["routers.routers"]
})]
})
export default store
我的动态路由模板
//动态路由
const dynamicRoute = [{
"path": "/main",
"name": "main",
"redirect": "/main/index",
"component": "main/main.vue",
"children": [{
"path": "index",
"name": "index",
"component": "index/index.vue",
"meta": {
"name": "index",
"title": "首页",
"icon": "el-icon-location",
"menu":true //true为菜单栏
}
},
{
"path": "Configuration",
"name": "Configuration",
"redirect": "Configuration/route",
"component": "Configuration/index.vue",
"roles": ['developer', "admin"], // developer、admin角色的用户才能访问该页面
"meta": {
"title": "配置",
"icon": "el-icon-location",
"menu":true
},
"children": [{
"path": "route",
"name": "route",
"component": "Configuration/route/index.vue",
"meta": {
"title": "菜单",
"icon": "",
"menu":true
},
}, {
"path": "user",
"name": "user",
"component": "Configuration/user/index.vue",
"meta": {
"title": "用户管理",
"icon": "el-icon-location",
"menu":true
},
},
{
"path": "admin",
"name": "admin",
"component": "Configuration/admin/index.vue",
"meta": {
"title": "管理员管理",
"icon": "",
"menu":true
},
},
{
"path": "userEdit",
"name": "userEdit",
"component": "Configuration/user/user-Edit.vue",
"meta": {
"title": "编辑用户",
"icon": "",
"menu":false
},
},
]
},
{
"path": "check",
"name": "check",
"redirect": "check/user",
"component": "check/index.vue",
"roles": ['developer', "admin", "check"], // developer、admin角色的用户才能访问该页面
"meta": {
"title": "审核",
"icon": "el-icon-location",
"menu":true
},
"children": [{
"path": "user",
"name": "checkUser",
"component": "check/check-user/index.vue",
"meta": {
"title": "用户实名审核",
"icon": "el-icon-location",
"menu":true
}
},
{
"path": "enterprise",
"name": "checkEnterprise",
"component": "check/check-enterprise/index.vue",
"meta": {
"title": "企业认证审核",
"icon": "el-icon-location",
"menu":true
},
},
{
"path": "checkNormImage",
"name": "checkNormImage",
"component": "check/check-norm-image/index.vue",
"meta": {
"title": "标准照认证审核",
"icon": "el-icon-location",
"menu":true
},
},
{
"path": "checkHiringJobs",
"name": "checkHiringJobs",
"component": "check/check-hiring-Jobs/index.vue",
"meta": {
"title": "求职、招聘认证审核",
"icon": "el-icon-location",
"menu":true
},
}
]
}
]
}, ]
export default dynamicRoute
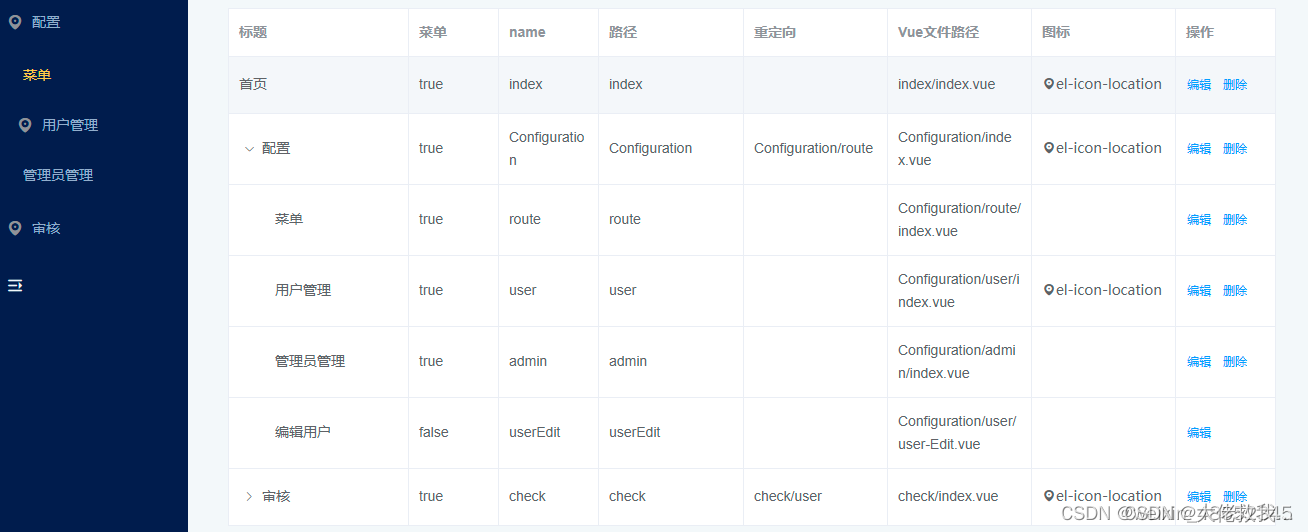
路由界面
讲一讲遇到的坑及注意点
- “component”: “check/check-norm-image/index.vue”, 用字符串再在解析,不要像静态路由一样。否则第一次进去可以,刷新就变空白
- 此处为重要的一点,直接用next()不行
next({ ...to, // next({ ...to })的目的,是保证路由添加完了再进入页面 (可以理解为重进一次) replace: true, // 重进一次, 不保留重复历史 })3)由于添加完路由还会重复执行一遍路由守卫,所有必须确保不要一直死循环添加路由。否则直接崩溃。这里我用的是isToken变量确保不循环。
版权归原作者 【南汐】前端 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。