

🌈个人主页: 鑫宝Code
🔥热门专栏: 闲话杂谈| 炫酷HTML | JavaScript基础 **
💫个人格言: "如无必要,勿增实体" **

文章目录
状态管理之Redux

引言
Redux 作为一个优秀的状态管理工具,在 React 生态系统中占据着重要地位。本文将深入探讨 Redux 的核心工作原理,帮助开发者更好地理解和使用这个工具。
1. Redux 的核心概念
1.1 单一数据源(Single Source of Truth)
Redux 使用单一的 store 来存储应用的所有状态。这意味着:
- 整个应用的状态被存储在一个对象树中
- 这个对象树只存在于唯一的 store 中
- 状态是只读的,唯一改变状态的方式是触发 action
const store ={
todos:[],
visibilityFilter:'SHOW_ALL',
user:{
id:null,
name:null}}
1.2 State 是只读的
在 Redux 中,改变状态的唯一方式是触发(dispatch)一个 action。这确保了:
- 视图和网络请求都不能直接修改状态
- 所有的修改都被集中化处理
- 修改都是按顺序一个接一个地执行
// Action 的结构const action ={
type:'ADD_TODO',
payload:{
text:'学习 Redux',
completed:false}}
1.3 使用纯函数执行修改
Reducer 是一个纯函数,它接收先前的状态和一个 action,返回新的状态:
consttodoReducer=(state =[], action)=>{switch(action.type){case'ADD_TODO':return[...state, action.payload]case'TOGGLE_TODO':return state.map(todo=>
todo.id === action.payload.id
?{...todo, completed:!todo.completed }: todo
)default:return state
}}
2. Redux 工作流程
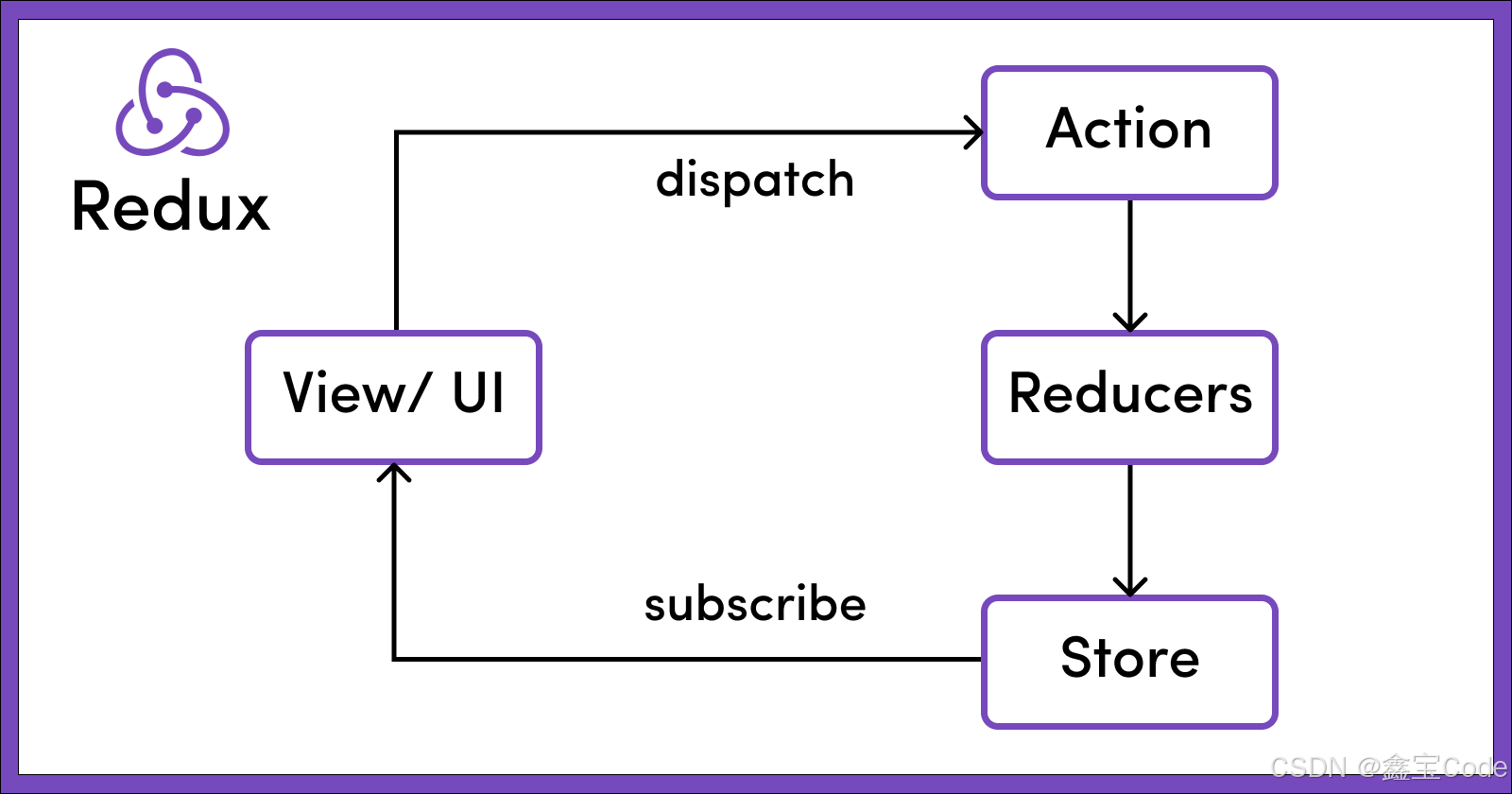
2.1 数据流向
Redux 采用严格的单向数据流,主要包含以下步骤:
- 用户在界面触发事件
- 调用 dispatch(action)
- Redux store 调用 reducer 函数
- Root reducer 把多个子 reducer 输出合并成一个单一的状态树
- Redux store 保存了 reducer 返回的完整状态树
2.2 中间件机制
中间件提供了一个分类处理 action 的机制:
// 中间件示例constlogger=store=>next=>action=>{
console.log('dispatching', action)let result =next(action)
console.log('next state', store.getState())return result
}
3. Redux 内部实现原理
3.1 createStore 的实现
createStore 是 Redux 最核心的 API:
functioncreateStore(reducer, preloadedState, enhancer){let currentReducer = reducer
let currentState = preloadedState
let currentListeners =[]functiongetState(){return currentState
}functionsubscribe(listener){
currentListeners.push(listener)returnfunctionunsubscribe(){const index = currentListeners.indexOf(listener)
currentListeners.splice(index,1)}}functiondispatch(action){
currentState =currentReducer(currentState, action)
currentListeners.forEach(listener=>listener())return action
}return{
getState,
subscribe,
dispatch
}}
3.2 combineReducers 的实现
combineReducers 用于合并多个 reducer:
functioncombineReducers(reducers){returnfunctioncombination(state ={}, action){const nextState ={}let hasChanged =falsefor(let key in reducers){const reducer = reducers[key]const previousStateForKey = state[key]const nextStateForKey =reducer(previousStateForKey, action)
nextState[key]= nextStateForKey
hasChanged = hasChanged || nextStateForKey !== previousStateForKey
}return hasChanged ? nextState : state
}}
4. Redux 性能优化

4.1 reselect 的使用
使用 reselect 可以避免不必要的重复计算:
import{ createSelector }from'reselect'constgetTodos=state=> state.todos
constgetVisibilityFilter=state=> state.visibilityFilter
const getVisibleTodos =createSelector([getTodos, getVisibilityFilter],(todos, filter)=>{switch(filter){case'SHOW_ALL':return todos
case'SHOW_COMPLETED':return todos.filter(t=> t.completed)case'SHOW_ACTIVE':return todos.filter(t=>!t.completed)}})
4.2 不可变性的保持
确保状态更新的不可变性是 Redux 性能优化的关键:
// 不推荐
state.todos[0].completed =true// 推荐return{...state,
todos: state.todos.map((todo, index)=>
index ===0?{...todo, completed:true}: todo
)}
5. 实际应用中的最佳实践
5.1 Action 创建函数
使用 action 创建函数来生成 action:
constaddTodo=text=>({
type:'ADD_TODO',
payload:{
id: nextTodoId++,
text,
completed:false}})
5.2 异步 Action 处理
使用 redux-thunk 处理异步操作:
constfetchTodos=()=>{returnasyncdispatch=>{dispatch({ type:'FETCH_TODOS_REQUEST'})try{const response =await api.fetchTodos()dispatch({
type:'FETCH_TODOS_SUCCESS',
payload: response.data
})}catch(error){dispatch({
type:'FETCH_TODOS_FAILURE',
error: error.message
})}}}
总结
Redux 通过其简单而强大的设计原则,为 React 应用提供了可预测的状态管理能力。理解其工作原理对于构建大型应用至关重要。核心要点包括:
- 单一数据源
- 状态只读
- 使用纯函数进行修改
- 单向数据流
- 中间件机制
通过合理运用这些原则,我们可以构建出更加可维护和可扩展的应用。同时,通过使用 reselect、保持不可变性等优化手段,还能确保应用具有良好的性能表现。

版权归原作者 鑫宝Code 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。