文章目录
使用Python语言开发Spark程序代码
- Spark Standalone的PySpark的搭建----bin/pyspark --master spark://node1:7077
- Spark StandaloneHA的搭建—Master的单点故障(node1,node2),zk的leader选举机制,1-2min还原
- 【scala版本的交互式界面】bin/spark-shell --master xxx
- 【python版本交互式界面】bin/pyspark --master xxx
- 【提交任务】bin/spark-submit --master xxxx
【学会配置】Windows的PySpark环境配置
- 1-安装Andaconda
- 2-在Anaconda Prompt中安装PySpark
- 3-执行安装
- 4-使用Pycharm构建Project(准备工作)
- 需要配置anaconda的环境变量–参考课件
- 需要配置hadoop3.3.0的安装包,里面有winutils,防止pycharm写代码的过程中报错
补充: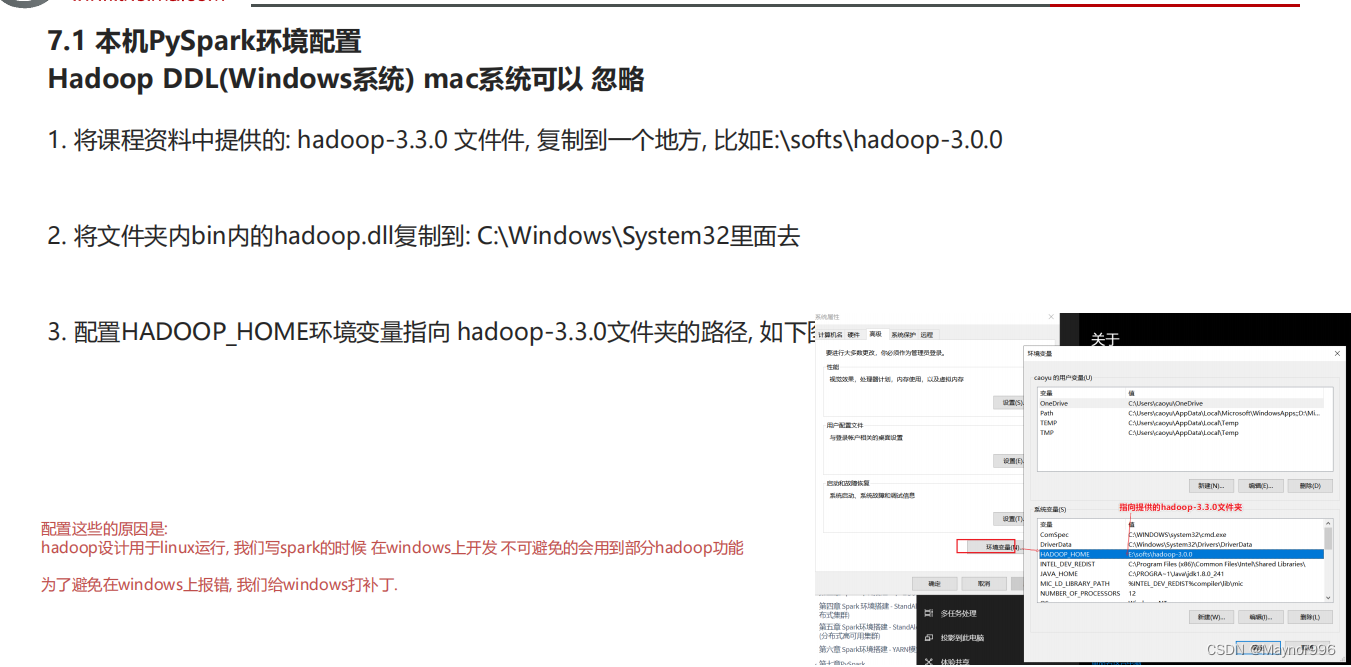

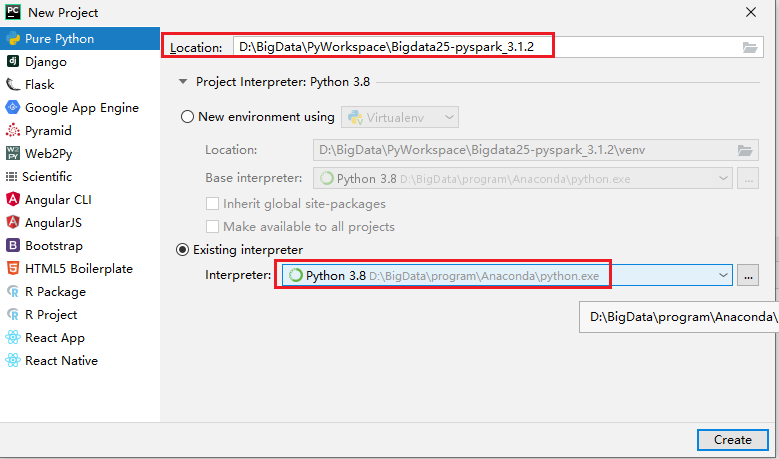
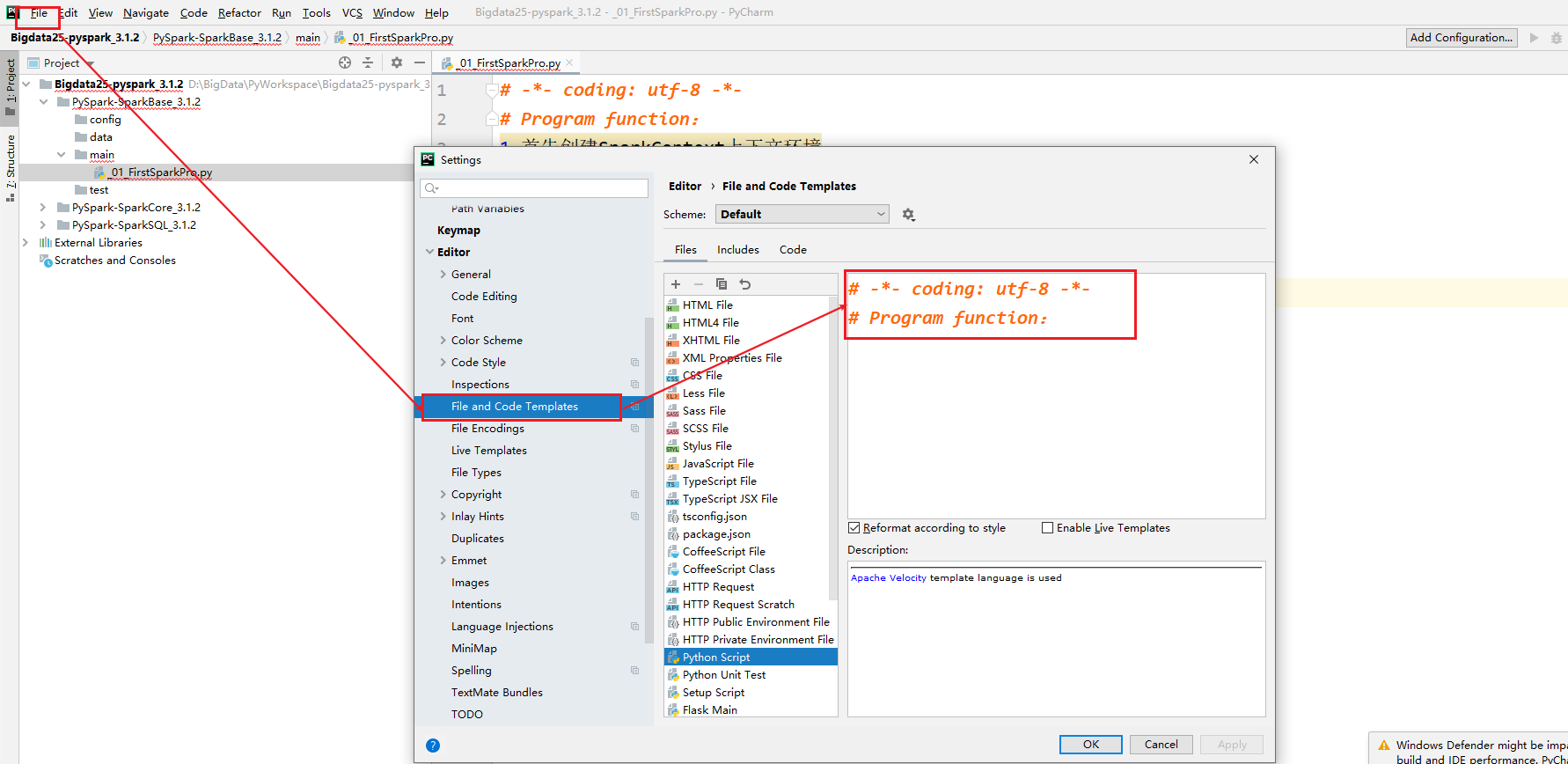
PyCharm构建Python project
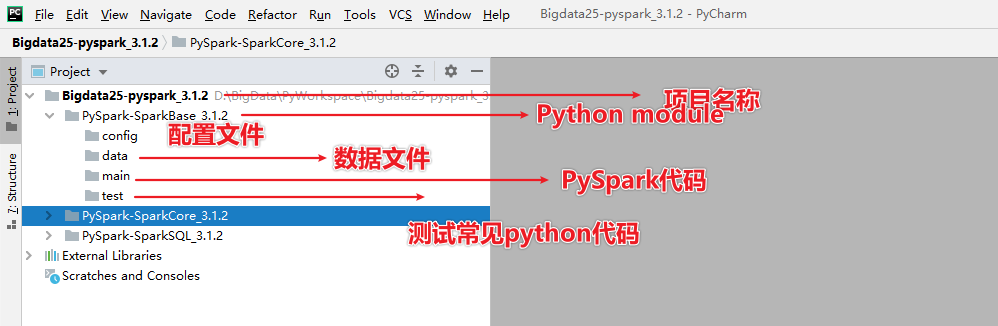
- 项目规划
- 项目名称:Bigdata25-pyspark_3.1.2
- 模块名称:PySpark-SparkBase_3.1.2,PySpark-SparkCore_3.1.2,PySpark-SparkSQL_3.1.2
- 文件夹:
- main pyspark的代码
- data 数据文件
- config 配置文件
- test 常见python测试代码放在test中
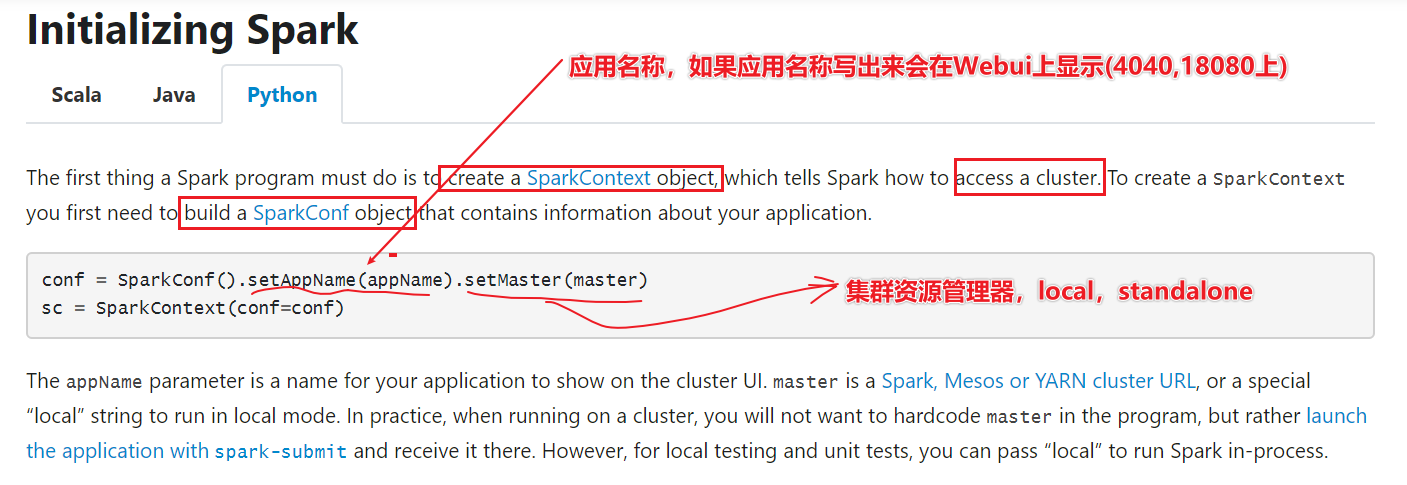
应用入口:SparkContext
WordCount代码实战
- 需求:给你一个文本文件,统计出单词的数量
- 算子:rdd的api的操作,就是算子,flatMap扁平化算子,map转换算子
- Transformation算子
- Action算子
- 步骤:
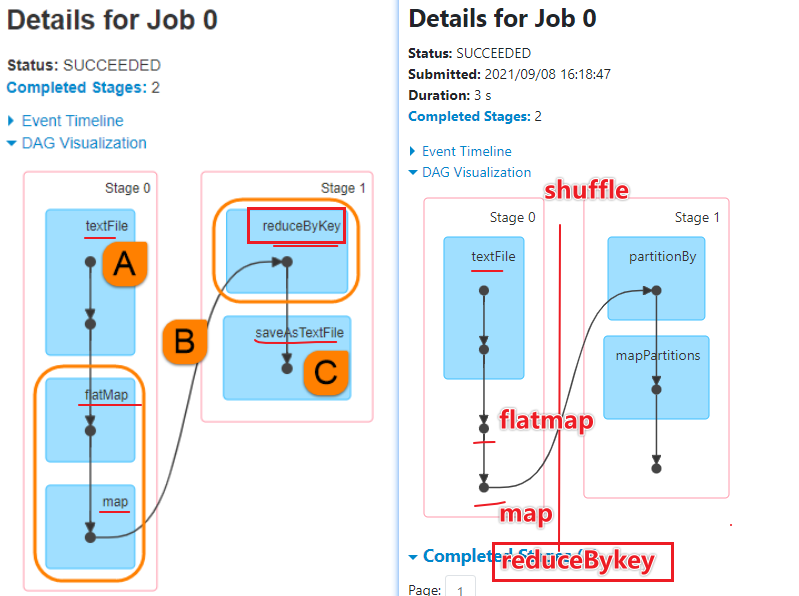
- 1-首先创建SparkContext上下文环境 2-从外部文件数据源读取数据 3-执行flatmap执行扁平化操作 4-执行map转化操作,得到(word,1) 5-reduceByKey将相同Key的Value数据累加操作 6-将结果输出到文件系统或打印
- 代码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Program function: Spark的第一个程序 # 1-思考:sparkconf和sparkcontext从哪里导保 # 2-如何理解算子?Spark中算子有2种, # 一种称之为Transformation算子(flatMapRDD-mapRDD-reduceBykeyRDD), # 一种称之为Action算子(输出到控制台,或文件系统或hdfs),比如collect或saveAsTextFile都是Action算子 from pyspark import SparkConf,SparkContext if __name__ == '__main__': # 1 - 首先创建SparkContext上下文环境 conf = SparkConf().setAppName("FirstSpark").setMaster("local[*]") sc = SparkContext(conf=conf) sc.setLogLevel("WARN")#日志输出级别 # 2 - 从外部文件数据源读取数据 fileRDD = sc.textFile("D:\BigData\PyWorkspace\Bigdata25-pyspark_3.1.2\PySpark-SparkBase_3.1.2\data\words.txt") # print(type(fileRDD))#<class 'pyspark.rdd.RDD'> # all the data is loaded into the driver's memory. # print(fileRDD.collect()) # ['hello you Spark Flink', 'hello me hello she Spark'] # 3 - 执行flatmap执行扁平化操作 flat_mapRDD = fileRDD.flatMap(lambda words: words.split(" ")) # print(type(flat_mapRDD)) # print(flat_mapRDD.collect()) #['hello', 'you', 'Spark', 'Flink', 'hello', 'me', 'hello', 'she', 'Spark'] # # 4 - 执行map转化操作,得到(word, 1) rdd_mapRDD = flat_mapRDD.map(lambda word: (word, 1)) # print(type(rdd_mapRDD))#<class 'pyspark.rdd.PipelinedRDD'> # print(rdd_mapRDD.collect()) # [('hello', 1), ('you', 1), ('Spark', 1), ('Flink', 1), ('hello', 1), ('me', 1), ('hello', 1), ('she', 1), ('Spark', 1)] # 5 - reduceByKey将相同Key的Value数据累加操作 resultRDD = rdd_mapRDD.reduceByKey(lambda x, y: x + y) # print(type(resultRDD)) # print(resultRDD.collect()) # [('Spark', 2), ('Flink', 1), ('hello', 3), ('you', 1), ('me', 1), ('she', 1)] # 6 - 将结果输出到文件系统或打印 resultRDD.saveAsTextFile("D:\BigData\PyWorkspace\Bigdata25-pyspark_3.1.2\PySpark-SparkBase_3.1.2\data\output\wordsAdd") # 7-停止SparkContext sc.stop()#Shut down the SparkContext.
- 总结:
TopK需求
需求:[(‘Spark’, 2), (‘Flink’, 1), (‘hello’, 3), (‘you’, 1), (‘me’, 1), (‘she’, 1)]
排序:[ (‘hello’, 3),(‘Spark’, 2),]
共识:Spark核心或灵魂是rdd,spark的所有操作都是基于rdd的操作
代码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# Program function: 针对于value单词统计计数的排序# 1-思考:sparkconf和sparkcontext从哪里导保# 2-如何理解算子?Spark中算子有2种,# 一种称之为Transformation算子(flatMapRDD-mapRDD-reduceBykeyRDD),# 一种称之为Action算子(输出到控制台,或文件系统或hdfs),比如collect或saveAsTextFile都是Action算子from pyspark import SparkConf, SparkContext if __name__ =='__main__':# 1 - 首先创建SparkContext上下文环境 conf = SparkConf().setAppName("FirstSpark").setMaster("local[*]") sc = SparkContext(conf=conf) sc.setLogLevel("WARN")# 日志输出级别# 2 - 从外部文件数据源读取数据 fileRDD = sc.textFile("D:\BigData\PyWorkspace\Bigdata25-pyspark_3.1.2\PySpark-SparkBase_3.1.2\data\words.txt")# print(type(fileRDD))#<class 'pyspark.rdd.RDD'># all the data is loaded into the driver's memory.# print(fileRDD.collect())# ['hello you Spark Flink', 'hello me hello she Spark']# 3 - 执行flatmap执行扁平化操作 flat_mapRDD = fileRDD.flatMap(lambda words: words.split(" "))# print(type(flat_mapRDD))# print(flat_mapRDD.collect())# ['hello', 'you', 'Spark', 'Flink', 'hello', 'me', 'hello', 'she', 'Spark']# # 4 - 执行map转化操作,得到(word, 1) rdd_mapRDD = flat_mapRDD.map(lambda word:(word,1))# print(type(rdd_mapRDD))#<class 'pyspark.rdd.PipelinedRDD'># print(rdd_mapRDD.collect())# [('hello', 1), ('you', 1), ('Spark', 1), ('Flink', 1), ('hello', 1), ('me', 1), ('hello', 1), ('she', 1), ('Spark', 1)]# 5 - reduceByKey将相同Key的Value数据累加操作 resultRDD = rdd_mapRDD.reduceByKey(lambda x, y: x + y)# print(type(resultRDD))print(resultRDD.collect())# [('Spark', 2), ('Flink', 1), ('hello', 3), ('you', 1), ('me', 1), ('she', 1)]# 6 针对于value单词统计计数的排序print("==============================sortBY=============================")print(resultRDD.sortBy(lambda x: x[1], ascending=False).take(3))# [('hello', 3), ('Spark', 2), ('Flink', 1)]print(resultRDD.sortBy(lambda x: x[1], ascending=False).top(3,lambda x: x[1]))print("==============================sortBykey=============================")print(resultRDD.map(lambda x:(x[1], x[0])).collect())# [(2, 'Spark'), (1, 'Flink'), (3, 'hello'), (1, 'you'), (1, 'me'), (1, 'she')]print(resultRDD.map(lambda x:(x[1], x[0])).sortByKey(False).take(3))#[(3, 'hello'), (2, 'Spark'), (1, 'Flink')]# 7-停止SparkContext sc.stop()# Shut down the SparkContext.
- sortBy
- sortByKey操作
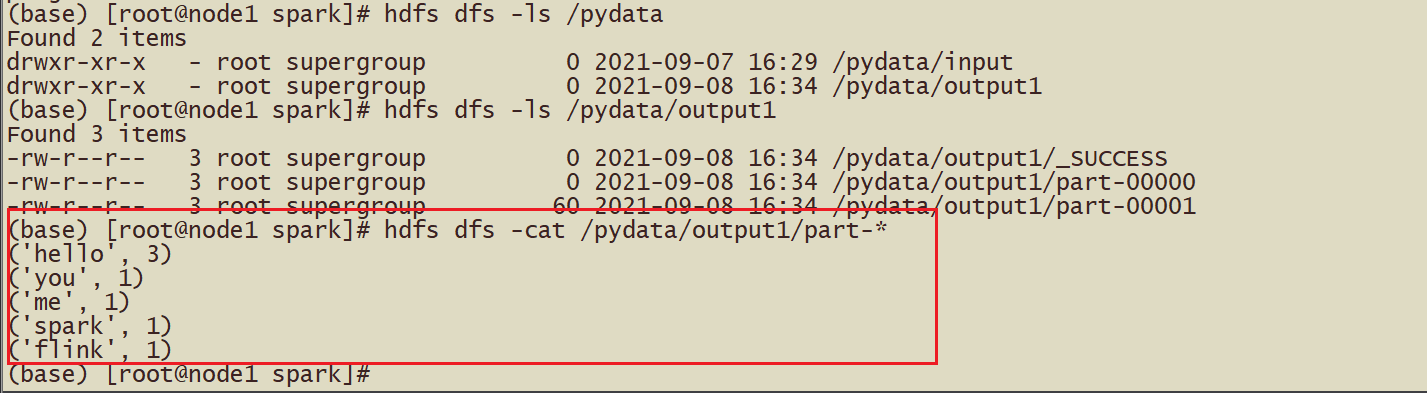
从HDFS读取数据
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# Program function: 从HDFS读取文件from pyspark import SparkConf, SparkContext import time if __name__ =='__main__':# 1 - 首先创建SparkContext上下文环境 conf = SparkConf().setAppName("FromHDFS").setMaster("local[*]") sc = SparkContext(conf=conf) sc.setLogLevel("WARN")# 日志输出级别# 2 - 从外部文件数据源读取数据 fileRDD = sc.textFile("hdfs://node1:9820/pydata/input/hello.txt")# ['hello you Spark Flink', 'hello me hello she Spark']# 3 - 执行flatmap执行扁平化操作 flat_mapRDD = fileRDD.flatMap(lambda words: words.split(" "))# ['hello', 'you', 'Spark', 'Flink', 'hello', 'me', 'hello', 'she', 'Spark']# # 4 - 执行map转化操作,得到(word, 1) rdd_mapRDD = flat_mapRDD.map(lambda word:(word,1))# [('hello', 1), ('you', 1), ('Spark', 1), ('Flink', 1), ('hello', 1), ('me', 1), ('hello', 1), ('she', 1), ('Spark', 1)]# 5 - reduceByKey将相同Key的Value数据累加操作 resultRDD = rdd_mapRDD.reduceByKey(lambda x, y: x + y)# print(type(resultRDD))print(resultRDD.collect())# 休息几分钟 time.sleep(600)# 7-停止SparkContext sc.stop()# Shut down the SparkContext.
提交代码到集群执行
- 关键:sys.argv[1],
- 代码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Program function: 提交任务执行 import sys from pyspark import SparkConf, SparkContext if __name__ == '__main__': # 1 - 首先创建SparkContext上下文环境 conf = SparkConf().setAppName("FromHDFS").setMaster("local[*]") sc = SparkContext(conf=conf) sc.setLogLevel("WARN") # 日志输出级别 # 2 - 从外部文件数据源读取数据 # hdfs://node1:9820/pydata/input/hello.txt fileRDD = sc.textFile(sys.argv[1]) # ['hello you Spark Flink', 'hello me hello she Spark'] # 3 - 执行flatmap执行扁平化操作 flat_mapRDD = fileRDD.flatMap(lambda words: words.split(" ")) # ['hello', 'you', 'Spark', 'Flink', 'hello', 'me', 'hello', 'she', 'Spark'] # # 4 - 执行map转化操作,得到(word, 1) rdd_mapRDD = flat_mapRDD.map(lambda word: (word, 1)) # [('hello', 1), ('you', 1), ('Spark', 1), ('Flink', 1), ('hello', 1), ('me', 1), ('hello', 1), ('she', 1), ('Spark', 1)] # 5 - reduceByKey将相同Key的Value数据累加操作 resultRDD = rdd_mapRDD.reduceByKey(lambda x, y: x + y) # print(type(resultRDD)) resultRDD.saveAsTextFile(sys.argv[2]) # 7-停止SparkContext sc.stop() # Shut down the SparkContext.
- 结果:
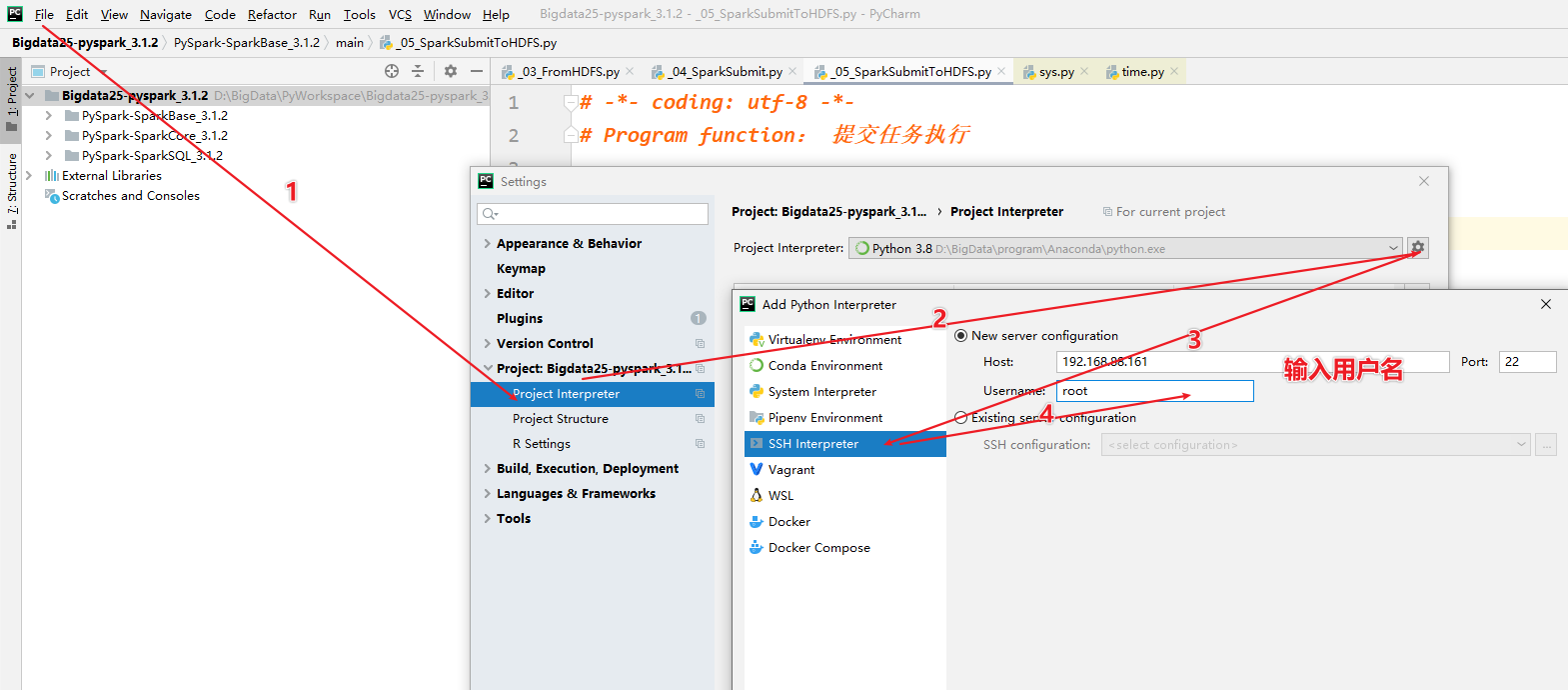
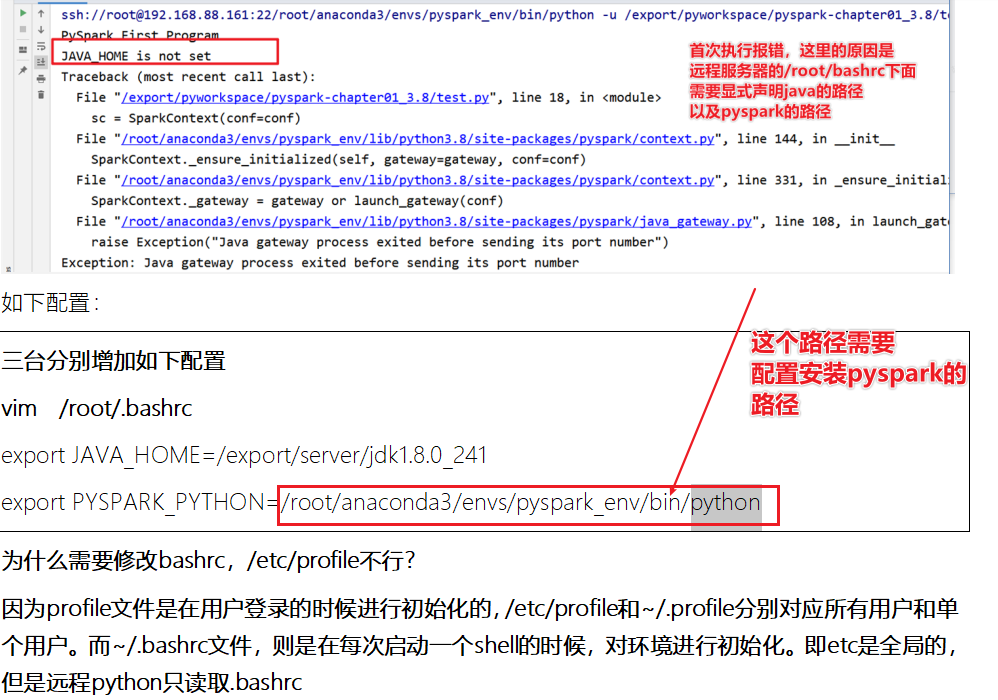
[掌握-扩展阅读]远程PySpark环境配置
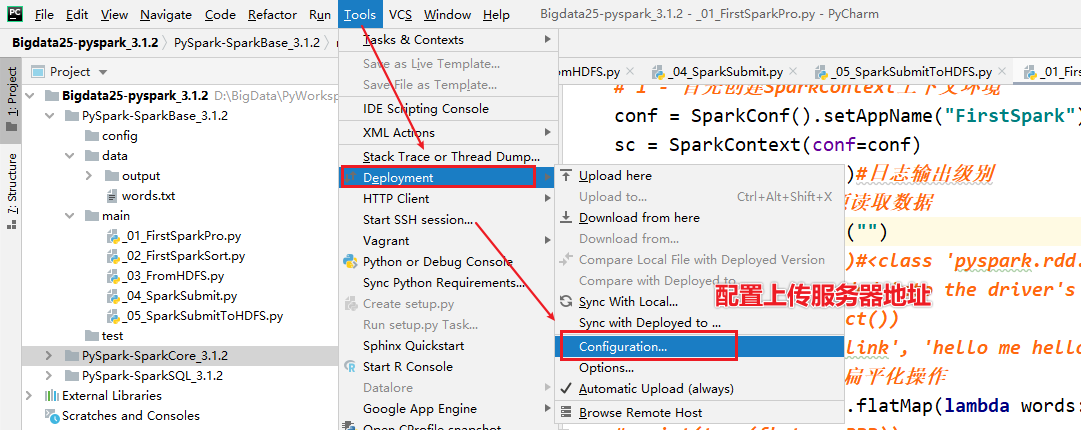
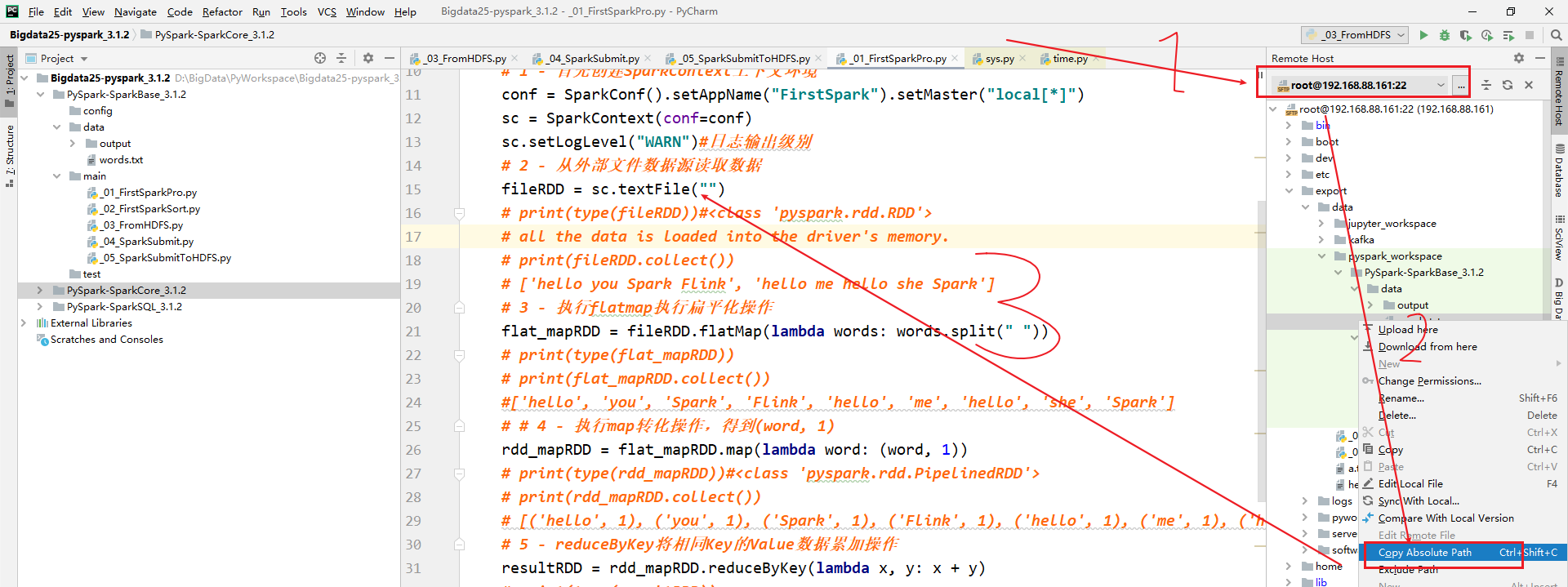
- 需求:需要将PyCharm连接服务器,同步本地写的代码到服务器上,使用服务器上的Python解析器执行
- 步骤:
- 1-准备PyCharm的连接
- 2-需要了解服务器的地址,端口号,用户名,密码
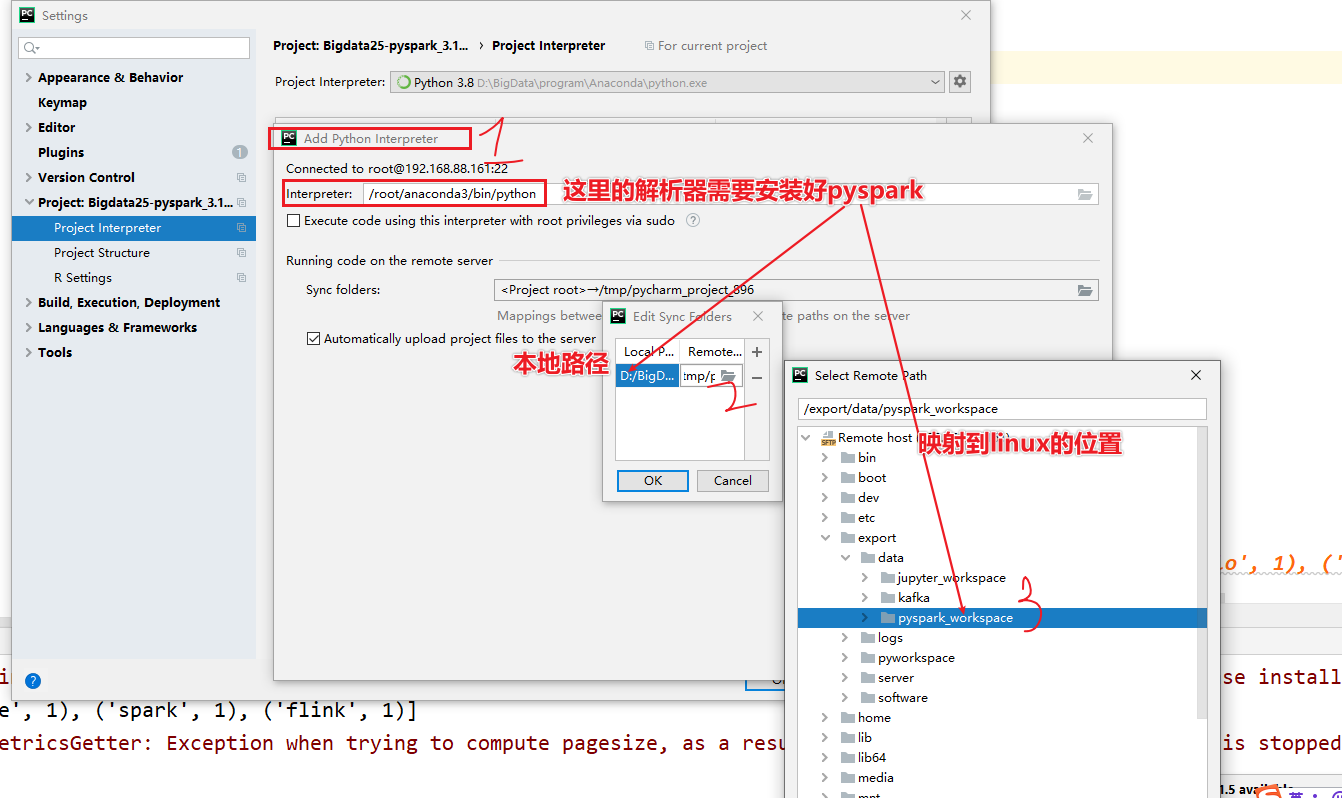
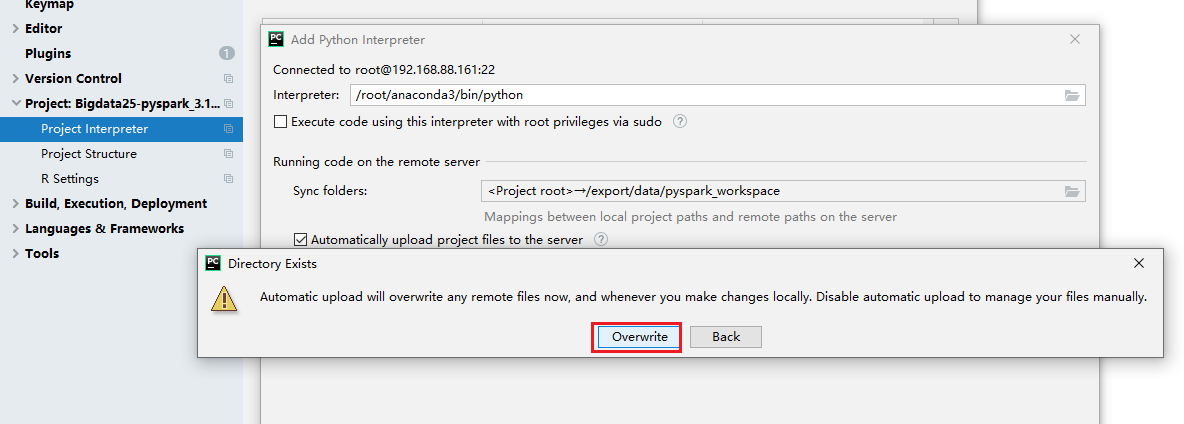
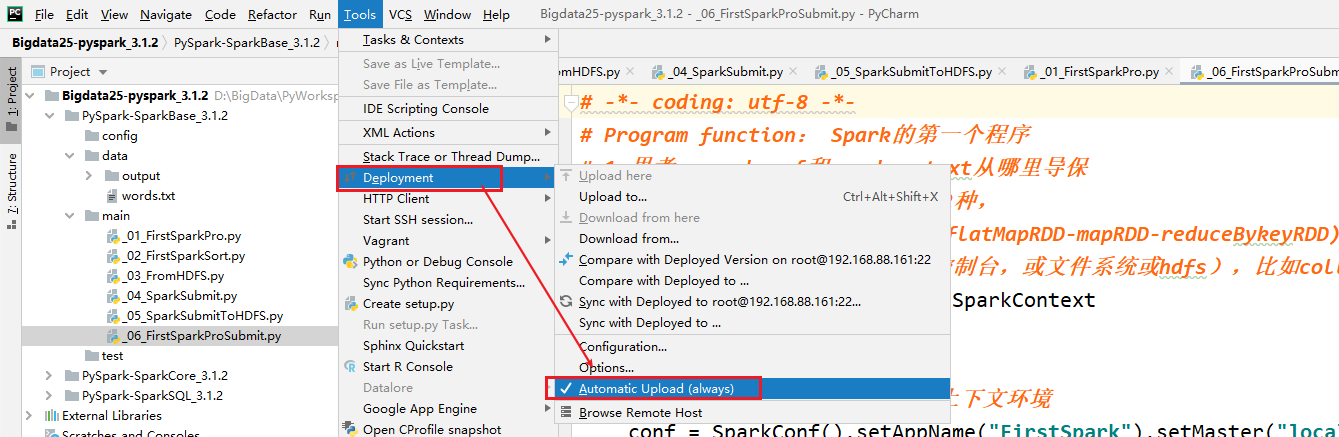
- 设置自动的上传,如果不太好使,重启pycharm
- 3-pycharm读取的文件都需要上传到linux中,复制相对路径
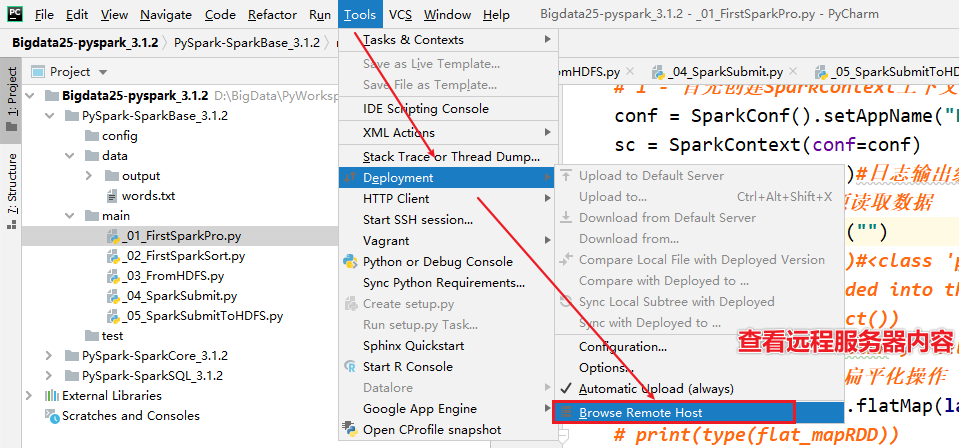
- 4-执行代码在远程服务器上
- 5-执行代码
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Program function: Spark的第一个程序 # 1-思考:sparkconf和sparkcontext从哪里导保 # 2-如何理解算子?Spark中算子有2种, # 一种称之为Transformation算子(flatMapRDD-mapRDD-reduceBykeyRDD), # 一种称之为Action算子(输出到控制台,或文件系统或hdfs),比如collect或saveAsTextFile都是Action算子 from pyspark import SparkConf, SparkContext if __name__ == '__main__': # 1 - 首先创建SparkContext上下文环境 conf = SparkConf().setAppName("FirstSpark").setMaster("local[*]") sc = SparkContext(conf=conf) sc.setLogLevel("WARN") # 日志输出级别 # 2 - 从外部文件数据源读取数据 fileRDD = sc.textFile("/export/data/pyspark_workspace/PySpark-SparkBase_3.1.2/data/words.txt") # fileRDD = sc.parallelize(["hello you", "hello me", "hello spark"]) # 3 - 执行flatmap执行扁平化操作 flat_mapRDD = fileRDD.flatMap(lambda words: words.split(" ")) # print(type(flat_mapRDD)) # print(flat_mapRDD.collect()) # ['hello', 'you', 'Spark', 'Flink', 'hello', 'me', 'hello', 'she', 'Spark'] # # 4 - 执行map转化操作,得到(word, 1) rdd_mapRDD = flat_mapRDD.map(lambda word: (word, 1)) # print(type(rdd_mapRDD))#<class 'pyspark.rdd.PipelinedRDD'> # print(rdd_mapRDD.collect()) # [('hello', 1), ('you', 1), ('Spark', 1), ('Flink', 1), ('hello', 1), ('me', 1), ('hello', 1), ('she', 1), ('Spark', 1)] # 5 - reduceByKey将相同Key的Value数据累加操作 resultRDD = rdd_mapRDD.reduceByKey(lambda x, y: x + y) # print(type(resultRDD)) print(resultRDD.collect()) # [('Spark', 2), ('Flink', 1), ('hello', 3), ('you', 1), ('me', 1), ('she', 1)] # 6 - 将结果输出到文件系统或打印 # resultRDD.saveAsTextFile("D:\BigData\PyWorkspace\Bigdata25-pyspark_3.1.2\PySpark-SparkBase_3.1.2\data\output\wordsAdd") # 7-停止SparkContext sc.stop() # Shut down the SparkContext.
- 切记忘记上传python的文件,直接执行
- 注意1:自动上传设置
- 注意2:增加如何使用standalone和HA的方式提交代码执行
- 但是需要注意,尽可能使用hdfs的文件,不要使用单机版本的文件,因为standalone是集群模式
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Program function: Spark的第一个程序 # 1-思考:sparkconf和sparkcontext从哪里导保 # 2-如何理解算子?Spark中算子有2种, # 一种称之为Transformation算子(flatMapRDD-mapRDD-reduceBykeyRDD), # 一种称之为Action算子(输出到控制台,或文件系统或hdfs),比如collect或saveAsTextFile都是Action算子 >from pyspark import SparkConf, SparkContext > >if __name__ == '__main__': > ># 1 - 首先创建SparkContext上下文环境 > >conf = SparkConf().setAppName("FirstSpark").setMaster("spark://node1:7077,node2:7077") >sc = SparkContext(conf=conf) >sc.setLogLevel("WARN") # 日志输出级别 > ># 2 - 从外部文件数据源读取数据 > >fileRDD = sc.textFile("hdfs://node1:9820/pydata/input/hello.txt") > ># fileRDD = sc.parallelize(["hello you", "hello me", "hello spark"]) > ># 3 - 执行flatmap执行扁平化操作 > >flat_mapRDD = fileRDD.flatMap(lambda words: words.split(" ")) > ># print(type(flat_mapRDD)) > ># print(flat_mapRDD.collect()) > ># ['hello', 'you', 'Spark', 'Flink', 'hello', 'me', 'hello', 'she', 'Spark'] > ># # 4 - 执行map转化操作,得到(word, 1) > >rdd_mapRDD = flat_mapRDD.map(lambda word: (word, 1)) > ># print(type(rdd_mapRDD))#<class 'pyspark.rdd.PipelinedRDD'> > ># print(rdd_mapRDD.collect()) > ># [('hello', 1), ('you', 1), ('Spark', 1), ('Flink', 1), ('hello', 1), ('me', 1), ('hello', 1), ('she', 1), ('Spark', 1)] > ># 5 - reduceByKey将相同Key的Value数据累加操作 > >resultRDD = rdd_mapRDD.reduceByKey(lambda x, y: x + y) > ># print(type(resultRDD)) > >print(resultRDD.collect()) > ># [('Spark', 2), ('Flink', 1), ('hello', 3), ('you', 1), ('me', 1), ('she', 1)] > ># 6 - 将结果输出到文件系统或打印 > ># resultRDD.saveAsTextFile("D:\BigData\PyWorkspace\Bigdata25-pyspark_3.1.2\PySpark-SparkBase_3.1.2\data\output\wordsAdd") > ># 7-停止SparkContext > >sc.stop() # Shut down the SparkContext.
总结
- 函数式编程
#Python中的函数式编程#1-map(func, *iterables) --> map objectdeffun(x):return x*x#x=[1,2,3,4,5] y=map(fun,[1,2,3,4,5]) #[1, 4, 9, 16, 25]print(list(map(fun,[1,2,3,4,5])))#2-lambda 匿名函数 java: x=>x*x 表达式 Scala:x->x*xg=lambda x:x*xprint(g(10))print(list(map(lambda x:x*x,[1,2,3,4,5])))defadd(x,y):return x+yprint(list(map(add,range(5),range(5,10))))print(list(map(lambda x,y:x+y,range(5),range(5,10))))#3- [add(x,y) for x,y in zip(range(5),range(5,10))]# print(list(zip([1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6])))#[1,4],[2,5]# print(list(zip([1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6,7])))#[1,4],[2,5]# print(list(zip([1, 2, 3,6], [4, 5, 6])))#[1,4],[2,5]# 语法 lambda表达式语言:【lambda 变量:表达式】# 列表表达式 [表达式 for 变量 in 可迭代的序列中 if 条件]print([add(x, y)for x, y inzip(range(5),range(5))])#[0, 2, 4, 6, 8]#3-reducefrom functools importreduce# ((((1+2)+3)+4)+5)print(reduce(lambda x, y: x + y,[1,2,3,4,5]))# 4-filterseq1=['foo','x41','?1','***']deffunc(x):#Return True if the string is an alpha-numeric stringreturn x.isalnum()print(list(filter(func,seq1)))#返回 filter 对象# sorted()# 最后我们可以看到,函数式编程有如下好处:# 1)代码更简单了。# 2)数据集,操作,返回值都放到了一起。# 3)你在读代码的时候,没有了循环体,于是就可以少了些临时变量,以及变量倒来倒去逻辑。# 4)你的代码变成了在描述你要干什么,而不是怎么去干。### 后记
📢博客主页:https://manor.blog.csdn.net
📢欢迎点赞 👍 收藏 ⭐留言 📝 如有错误敬请指正!
📢本文由 Maynor 原创,首发于 CSDN博客🙉
📢感觉这辈子,最深情绵长的注视,都给了手机⭐
📢专栏持续更新,欢迎订阅:https://blog.csdn.net/xianyu120/category_12453356.html
版权归原作者 AI_Maynor 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。