序言
最近因为工作需要在阅读flink checkpoint处理机制,学习的过程中记录下来,并分享给大家。也算是学习并记录。
目前公司使用的flink版本为1.11。因此以下的分析都是基于1.11版本来的。
在分享前可以简单对flink checkpoint机制做一个大致的了解。
Flink checkpoint 机制介绍
Flink的checkpoint的过程依赖于异步屏障快照算法,该算法在《Lightweight Asynchronous Snapshots for Distributed Dataflows》这篇paper中被提出。理解了这篇paper也就明白了flink的chekpoint机制。paper整体来说比较简单易懂,下面简单介绍下paper的大体内容和核心的算法。
[1] 引用:Flink Checkpoint原理解析 - 知乎
代码分析
Flink checkpoint 的触发是通过CheckpointCoordinator 的定时线程完后。
private ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleTriggerWithDelay(long initDelay) {
return timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(
new ScheduledTrigger(),
initDelay, baseInterval, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
之后通过snapshotTaskState RPC的调用来实现触发checkpoint的
代码中遍历executions 来触发checkpoint,那么executions是什么东西呢?
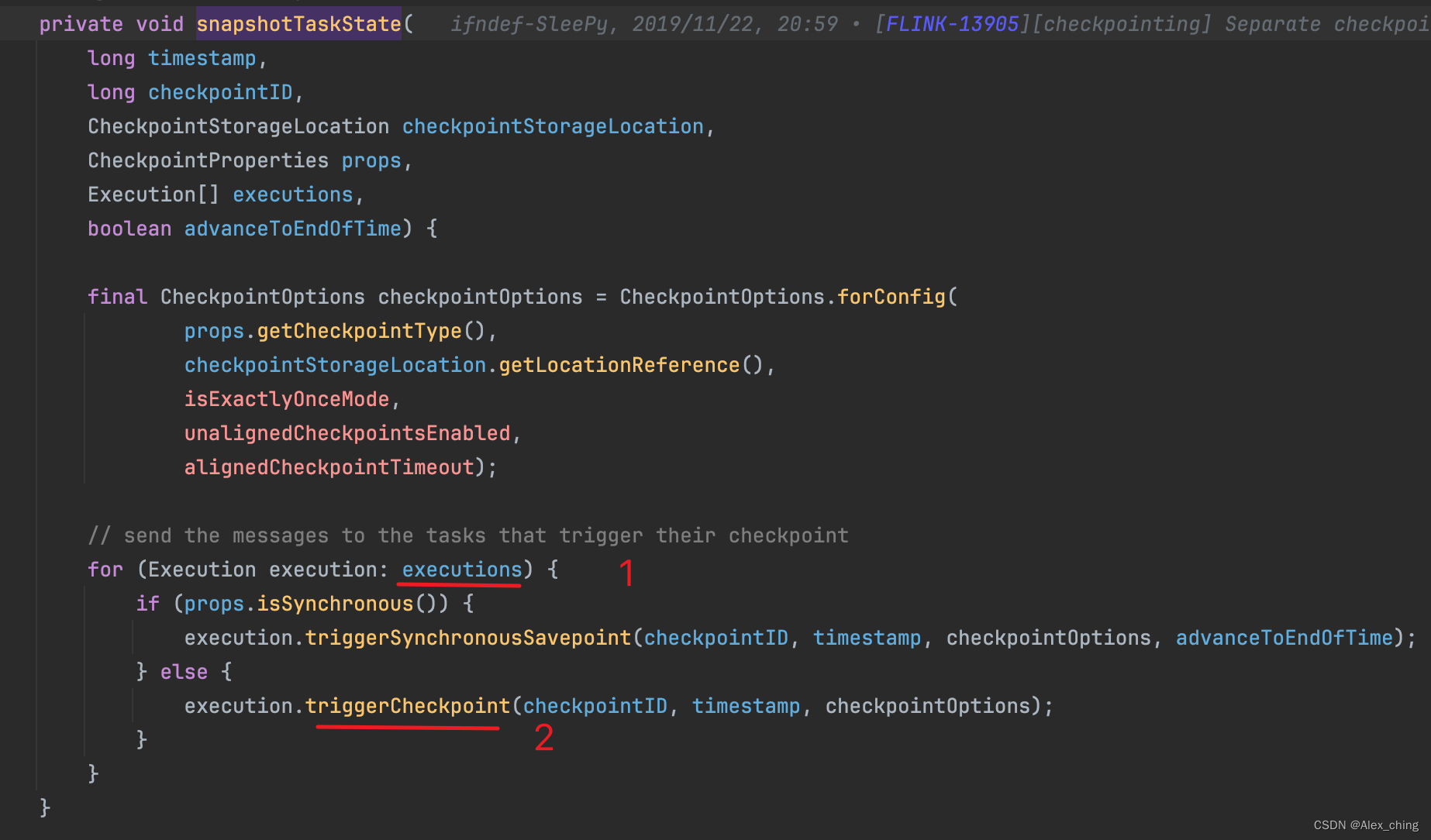
Flink 代码中维护了一个叫tasksToTrigger的数组。
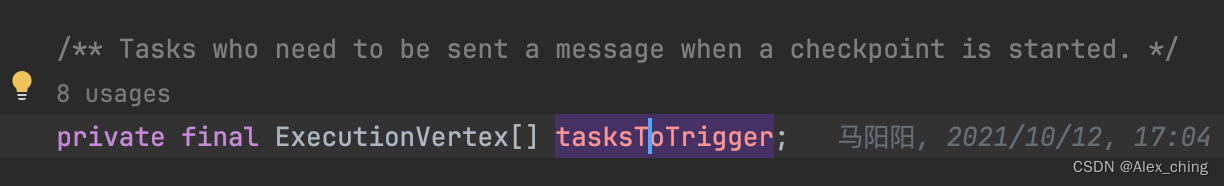
这个地方向前追溯,可以一直到jobgrap的生成。从名字和代码就可以看出,这个里面存的是没有inputchannel的节点,source节点没有inputchannel,所以回答上面的问题,executions 中是source节点,也就是做checkpoint 时 checkpointcoordinate 会给source节点发送rpc。

通过一个很长亮度的调用,最后到了SubtaskCheckpointCoordinatorImpl 中的
public void checkpointState(
CheckpointMetaData metadata,
CheckpointOptions options,
CheckpointMetricsBuilder metrics,
OperatorChain<?, ?> operatorChain,
Supplier<Boolean> isCanceled) throws Exception {
checkNotNull(options);
checkNotNull(metrics);
// All of the following steps happen as an atomic step from the perspective of barriers and
// records/watermarks/timers/callbacks.
// We generally try to emit the checkpoint barrier as soon as possible to not affect downstream
// checkpoint alignments
if (lastCheckpointId >= metadata.getCheckpointId()) {
LOG.info("Out of order checkpoint barrier (aborted previously?): {} >= {}", lastCheckpointId, metadata.getCheckpointId());
channelStateWriter.abort(
metadata.getCheckpointId(),
new CancellationException("checkpoint aborted via notification"),
true);
checkAndClearAbortedStatus(metadata.getCheckpointId());
return;
}
// Step (0): Record the last triggered checkpointId and abort the sync phase of checkpoint if necessary.
lastCheckpointId = metadata.getCheckpointId();
if (checkAndClearAbortedStatus(metadata.getCheckpointId())) {
// broadcast cancel checkpoint marker to avoid downstream back-pressure due to checkpoint barrier align.
operatorChain.broadcastEvent(new CancelCheckpointMarker(metadata.getCheckpointId()));
LOG.info("Checkpoint {} has been notified as aborted, would not trigger any checkpoint.", metadata.getCheckpointId());
return;
}
// if checkpoint has been previously unaligned, but was forced to be aligned (pointwise
// connection), revert it here so that it can jump over output data
if (options.getAlignment() == CheckpointOptions.AlignmentType.FORCED_ALIGNED) {
options = options.withUnalignedSupported();
initInputsCheckpoint(metadata.getCheckpointId(), options);
}
// Step (1): Prepare the checkpoint, allow operators to do some pre-barrier work.
// The pre-barrier work should be nothing or minimal in the common case.
operatorChain.prepareSnapshotPreBarrier(metadata.getCheckpointId());
// Step (2): Send the checkpoint barrier downstream
LOG.debug(
"Task {} broadcastEvent at {}, triggerTime {}, passed time {}",
taskName,
System.currentTimeMillis(),
metadata.getTimestamp(),
System.currentTimeMillis() - metadata.getTimestamp());
CheckpointBarrier checkpointBarrier =
new CheckpointBarrier(metadata.getCheckpointId(), metadata.getTimestamp(), options);
operatorChain.broadcastEvent(checkpointBarrier, options.isUnalignedCheckpoint());
// Step (3): Register alignment timer to timeout aligned barrier to unaligned barrier
registerAlignmentTimer(metadata.getCheckpointId(), operatorChain, checkpointBarrier);
// Step (4): Prepare to spill the in-flight buffers for input and output
if (options.needsChannelState()) {
// output data already written while broadcasting event
channelStateWriter.finishOutput(metadata.getCheckpointId());
}
// Step (5): Take the state snapshot. This should be largely asynchronous, to not impact
// progress of the
// streaming topology
Map<OperatorID, OperatorSnapshotFutures> snapshotFutures = new HashMap<>(operatorChain.getNumberOfOperators());
try {
if (takeSnapshotSync(snapshotFutures, metadata, metrics, options, operatorChain, isCanceled)) {
finishAndReportAsync(snapshotFutures, metadata, metrics, options);
} else {
cleanup(snapshotFutures, metadata, metrics, new Exception("Checkpoint declined"));
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
cleanup(snapshotFutures, metadata, metrics, ex);
throw ex;
}
}
代码中可以看到构造了CheckpointBarrier, source将barrier当成数据广播给下游的所有节点。使用的方法就是operatorChain.brodacastEvent()。这里就回到最开始提到的异步屏障快照算法。
下游收到了barrier,如何进行快照处理的?flink同时有多种类型的checkpoint,他们分别的处理时机是啥,后面我会进一步进行代码分析。
CheckpointBarrier checkpointBarrier =
new CheckpointBarrier(metadata.getCheckpointId(), metadata.getTimestamp(), options);
operatorChain.broadcastEvent(checkpointBarrier, options.isUnalignedCheckpoint());
版权归原作者 Alex_ching 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。
