Junit5+Mockito进行单元测试
文章目录
单元测试原则:分宏观微观
1.宏观层面:AIR原则
- A:Automatic(自动化) 全自动执行,输出结果无需人工检查,而是通过断言验证。
- I:Independent(独立性) 分层测试,各层之间不相互依赖。
- R:Repeatable(可重复) 可重复执行,不受外部环境( 网络、服务、中间件等)影响。
2.微观层面:BCDE原则
B: Border,边界值测试,包括循环边界、特殊取值、特殊时间点、数据顺序等。
C: Correct,正确的输入,并得到预期的结果。
D: Design,与设计文档相结合,来编写单元测试。
E : Error,单元测试的目标是证明程序有错,而不是程序无错。为了发现代码中潜在的错误, 我们需要在编写测试用例时有一些强制的错误输入(如非法数据、异常流程、非业务允许输入等)来得到预期的错误结果。
一.单元测试的概念
1.概念:
单元测试(unit testing),是指对软件中的最小可测试单元进行检查和验证。在Java中单元测试的最小单元是类。
单元测试是开发者编写的一小段代码,用于检验被测代码的一个很小的、很明确的功能是否正确。执行单元测试,就是为了证明这 段代码的行为和我们期望是否一致。
Spring提供了开发者用于单元测试的依赖包:
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId><scope>test</scope></dependency>
该依赖包含以下几个库
- Junit ——常用的单元测试库
- Spring Test & Spring Boot Test ——对Spring应用的集成测试支持
- AssertJ——一个断言库
- Hamcrest—— 一个匹配对象的库(主要用于校验的 Java 的单元测试框架,可以组合创建灵活的表达的匹配器进行断言)
- Mockito—— 一个Java模拟框架(对于某些不容易构造(如 HttpServletRequest 必须在Servlet 容器中才能构造出来)或者不容易获取比较复杂的对象(如 JDBC 中的ResultSet 对象),用一个虚拟的对象(Mock 对象)来创建以便测试的测试方法)
- JSONassert—— 一个针对JSON的断言库
- JsonPath—— 用于JSON的XPath((XML Path Language)用于确定Json位置)
二、单元测试的作用
1.写单元测试的两个动机:
- 验证功能的完整性,确保功能的可用性。
- 保护已经实现的功能不被破坏。
三、如何进行单元测试
1.Junit的变化
Spring Boot 2.2.0 版本开始引入 JUnit 5 作为单元测试默认库
JUnit 5官方文档
作为最新版本的JUnit框架,JUnit5与之前版本的JUnit框架有很大的不同。由三个不同子项目的几个不同模块组成。
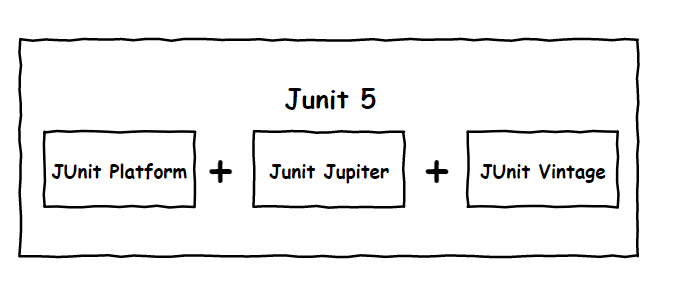
首先我们需要了解 Junit5
其中Junit5包含 Junit Platform、Junit Jupiter、Junit Vintage
①其中 Junit Platform 是Junit致力于打造跨平台测试而创建的测试平台
(在JVM上启动测试框架的基础,不仅支持Junit自制的测试引擎,其他测试引擎也都可以接入。)
②Junit Jupiter 是Junit5的核心所在
(提供了JUnit5的新的编程模型,是JUnit5新特性的核心。内部 包含了一个测试引擎,用于在Junit Platform上运行。)
③Junit Vintage主要是适配兼容Junit4的功能
(为了照顾老的项目,JUnit Vintage提供了兼容JUnit4.x,Junit3.x的测试引擎)
注意:SpringBoot 2.4 以上版本移除了默认对 Vintage 的依赖。如果需要兼容junit4需要自行引入(不能使用junit4的功能 @Test)
如果需要继续兼容junit4需要自行引入vintage
Junit5的基本单元测试模板**(区别于Junit4:Spring的JUnit4的是
@SpringBootTest
)**@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
importorg.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions;importorg.junit.jupiter.api.Test;//注意不是org.junit.Test(这是JUnit4版本的)importorg.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;importorg.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;@SpringBootTestclassSpringBootApplicationTests{@AutowiredprivateComponent component;@Test//@Transactional 标注后连接数据库有回滚功能publicvoidcontextLoads(){Assertions.assertEquals(5, component.getFive());}}
SpringBoot整合Junit以后
- 编写测试方法:@Test标注(注意需要使用junit5版本的注解)
- Junit类具有Spring的功能,@Autowired、比如 @Transactional 标注测试方法,测试完成后自动回滚
2.JUnit5常用注解
官方文档 - Annotations
@Test :表示方法是测试方法。但是与JUnit4的@Test不同,他的职责非常单一不能声明任何属性,拓展的测试将会由Jupiter提供额外测试
@ParameterizedTest: 表示方法是参数化测试
@RepeatedTest: 表示方法可重复执行
@DisplayName :为测试类或者测试方法设置展示名称
@BeforeEach :表示在每个单元测试之前执行
@AfterEach: 表示在每个单元测试之后执行
@BeforeAll :表示在所有单元测试之前执行
@AfterAll :表示在所有单元测试之后执行
@Tag: 表示单元测试类别,类似于JUnit4中的@Categories
@Disabled:表示测试类或测试方法不执行,类似于JUnit4中的@Ignore
@Timeout :表示测试方法运行如果超过了指定时间将会返回错误
@ExtendWith :为测试类或测试方法提供扩展类引用
importorg.junit.jupiter.api.*;@DisplayName("junit5功能测试类")publicclassJunit5Test{/**
*@displayName()括号内参数为方法或类别名
*
*
*/@DisplayName("测试displayname注解")@TestvoidtestDisplayName(){System.out.println(1);System.out.println(jdbcTemplate);}/**
* @ValueSource()后面参数化测试会再讲
* 声明一个源,该源将为每次调用提供参数,然后在测试方法中使用这些参数
* StringUtils.isPalindrome:用于判断是否为回文数
*/@ParameterizedTest@ValueSource(strings ={"racecar","radar","able was I ere I saw elba"})voidpalindromes(String candidate){assertTrue(StringUtils.isPalindrome(candidate));}/**
*@Disable:表示方法不执行。同Junit4中@Ignore
*
*
*/@Disabled@DisplayName("测试方法2")@Testvoidtest2(){System.out.println(2);}/**
*@RepeatedTest():修饰在方法上,表示会自动重复测试这个方法,比如@RepeatedTest(10),会自动执行10次
*
*
*/@RepeatedTest(5)@Testvoidtest3(){System.out.println(5);}/**
* 规定方法超时时间。超出时间测试出异常
*
* @throws InterruptedException
*/@Timeout(value =500, unit =TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)@TestvoidtestTimeout()throwsInterruptedException{Thread.sleep(600);}/**
*@BeforeEach:修饰在方法上,在每一个测试方法(所有@Test、@RepeatedTest、@ParameterizedTest或者@TestFactory注解的方 * 法)之前执行一次
*例如:一个测试类有2个测试方法testA()和testB(),还有一个@BeforeEach的方法,执行这个测试类,@BeforeEach的方法会在 * testA()之前执行一次,在testB()之前又执行一次。@BeforeEach的方法一共执行了2次。
*
*/@BeforeEachvoidtestBeforeEach(){System.out.println("测试就要开始了...");}/**
*@AfterEach:修饰在方法上,和@BeforeEach对应,在每一个测试方法(所有@Test、@RepeatedTest、@ParameterizedTest或 * 者@TestFactory注解的方法)之后执行一次。
*
*
*/@AfterEachvoidtestAfterEach(){System.out.println("测试结束了...");}/**
*@BeforeAll:修饰在方法上,使用该注解的方法在当前整个测试类中所有的测试方法之前执行,每个测试类运行时只会执行一次。
*
*
*/@BeforeAllstaticvoidtestBeforeAll(){System.out.println("所有测试就要开始了...");}/**
*修饰在方法上,与@BeforeAll对应,使用该注解的方法在当前测试类中所有测试方法都执行完毕后执行的,每个测试类运行时只会执行一 *次。
*
*
*/@AfterAllstaticvoidtestAfterAll(){System.out.println("所有测试以及结束了...");}}
3.断言(通俗的讲判断程序运行是否符合预期)
断言(assertions)是测试方法中的核心部分,用来对测试需要满足的条件进行验证。这些断言方法都是 org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions 的静态方法。JUnit 5 内置的断言可以分成如下几个类别:
检查业务逻辑返回的数据是否合理。
所有的测试运行结束以后,会有一个详细的测试报告;
JUnit 5 内置的断言可以分成如下几个类别:
①.简单断言
用来对单个值进行简单的验证。如:
方法****说明assertEquals判断两个对象或两个原始类型是否相等assertNotEquals判断两个对象或两个原始类型是否不相等assertSame判断两个对象引用是否指向同一个对象assertNotSame判断两个对象引用是否指向不同的对象assertTrue判断给定的布尔值是否为 trueassertFalse判断给定的布尔值是否为 falseassertNull判断给定的对象引用是否为 nullassertNotNull判断给定的对象引用是否不为 null
@Test@DisplayName("simple assertion")publicvoidsimple(){assertEquals(3,1+2,"simple math");assertNotEquals(3,1+1);assertNotSame(newObject(),newObject());Object obj =newObject();assertSame(obj, obj);assertFalse(1>2);assertTrue(1<2);assertNull(null);assertNotNull(newObject());}
②.数组断言
通过 assertArrayEquals 方法来判断两个对象或原始类型的数组是否相等
@Test@DisplayName("array assertion")publicvoidarray(){assertArrayEquals(newint[]{1,2},newint[]{1,2});}
③.组合断言
assertAll()
方法接受多个
org.junit.jupiter.api.Executable
函数式接口的实例作为要验证的断言,可以通过 lambda 表达式很容易的提供这些断言。
@Test@DisplayName("assert all")publicvoidall(){assertAll("Math",()->assertEquals(2,1+1),()->assertTrue(1>0));}
④.异常断言
在JUnit4时期,想要测试方法的异常情况时,需要用
@Rule
注解的
ExpectedException
变量还是比较麻烦的。而JUnit5提供了一种新的断言方式
Assertions.assertThrows()
,配合函数式编程就可以进行使用。
@Test@DisplayName("异常测试")publicvoidexceptionTest(){ArithmeticException exception =Assertions.assertThrows(//扔出断言异常ArithmeticException.class,()->System.out.println(1%0));}
⑤.超时断言
JUnit5还提供了Assertions.assertTimeout()为测试方法设置了超时时间。
@Test@DisplayName("超时测试")publicvoidtimeoutTest(){//如果测试方法时间超过1s将会异常Assertions.assertTimeout(Duration.ofMillis(1000),()->Thread.sleep(500));}
⑥.快速失败
通过 fail 方法直接使得测试失败。
@Test@DisplayName("fail")publicvoidshouldFail(){fail("This should fail");}
4.前置条件
JUnit 5 中的前置条件(assumptions【假设】)类似于断言,不同之处在于不满足的断言会使得测试方法失败,而不满足的前置条件只会使得测试方法的执行终止。前置条件可以看成是测试方法执行的前提,当该前提不满足时,就没有继续执行的必要。就跟@Ignore注解实现效果一样
前置条件可以看成是测试方法执行的前提,当该前提不满足时,就没有继续执行的必要。
@DisplayName("前置条件")publicclassAssumptionsTest{privatefinalString environment ="DEV";@Test@DisplayName("simple")publicvoidsimpleAssume(){assumeTrue(Objects.equals(this.environment,"DEV"));assumeFalse(()->Objects.equals(this.environment,"PROD"));}@Test@DisplayName("assume then do")publicvoidassumeThenDo(){assumingThat(Objects.equals(this.environment,"DEV"),()->System.out.println("In DEV"));}}
assumeTrue 和 assumFalse 确保给定的条件为 true 或 false,不满足条件会使得测试执行终止。
assumingThat 的参数是表示条件的布尔值和对应的 Executable 接口的实现对象。只有条件满足时,Executable 对象才会被执行;当条件不满足时,测试执行并不会终止。
5.嵌套测试
官方文档 - Nested Tests
什么是嵌套测试:项目包含多个模块,模块下又包含多个功能,也就是层层嵌套的,嵌套测试能表现出 层级关系,例如测试用例管理
Unit 5 可以通过 Java 中的内部类和@Nested 注解实现嵌套测试,从而可以更好的把相关的测试方法组织在一起。在内部类中可以使用@BeforeEach 和@AfterEach 注解,而且嵌套的层次没有限制。
@DisplayName("A stack")classTestingAStackDemo{Stack<Object> stack;@Test@DisplayName("is instantiated with new Stack()")voidisInstantiatedWithNew(){newStack<>();}@Nested@DisplayName("when new")classWhenNew{@BeforeEachvoidcreateNewStack(){
stack =newStack<>();}@Test@DisplayName("is empty")voidisEmpty(){assertTrue(stack.isEmpty());}@Test@DisplayName("throws EmptyStackException when popped")voidthrowsExceptionWhenPopped(){assertThrows(EmptyStackException.class, stack::pop);}@Test@DisplayName("throws EmptyStackException when peeked")voidthrowsExceptionWhenPeeked(){assertThrows(EmptyStackException.class, stack::peek);}@Nested@DisplayName("after pushing an element")classAfterPushing{String anElement ="an element";@BeforeEachvoidpushAnElement(){
stack.push(anElement);}@Test@DisplayName("it is no longer empty")voidisNotEmpty(){assertFalse(stack.isEmpty());}@Test@DisplayName("returns the element when popped and is empty")voidreturnElementWhenPopped(){assertEquals(anElement, stack.pop());assertTrue(stack.isEmpty());}@Test@DisplayName("returns the element when peeked but remains not empty")voidreturnElementWhenPeeked(){assertEquals(anElement, stack.peek());assertFalse(stack.isEmpty());}}}}
6.参数化测试
官方文档 - Parameterized Tests
参数化测试是JUnit5很重要的一个新特性,它使得用不同的参数多次运行测试成为了可能,也为我们的单元测试带来许多便利。
利用@ValueSource等注解,指定入参,我们将可以使用不同的参数进行多次单元测试,而不需要每新增一个参数就新增一个单元测试,省去了很多冗余代码。
利用**@ValueSource**等注解,指定入参,我们将可以使用不同的参数进行多次单元测试,而不需要每新增一个参数就新增一个单元测试,省去了很多冗余代码。
- @ValueSource: 为参数化测试指定入参来源,支持八大基础类以及String类型,Class类型
- @NullSource: 表示为参数化测试提供一个null的入参
- @EnumSource: 表示为参数化测试提供一个枚举入参
- @CsvFileSource:表示读取指定CSV文件内容作为参数化测试入参
- @MethodSource:表示读取指定方法的返回值作为参数化测试入参(注意方法返回需要是一个流)
当然如果参数化测试仅仅只能做到指定普通的入参还达不到让我觉得惊艳的地步。让我真正感到他的强大之处的地方在于他可以支持外部的各类入参。如:CSV,YML,JSON 文件甚至方法的返回值也可以作为入参。只需要去实现ArgumentsProvider接口,任何外部文件都可以作为它的入参。
参数化测试的七种方式
①:@ValueSource
@ValueSource
是最简单的参数化方式,它是一个数组,支持以下数据类型:
shortbyteintlongfloatdoublecharbooleanjava.lang.Stringjava.lang.Class
@ParameterizedTest@ValueSource(ints ={1,2,3})voidtestWithValueSource(int argument){assertTrue(argument >0&& argument <4);}
②:@Null and Empty Sources
表示为参数化测试提供一个null的入参
@ParameterizedTest
@DisplayName("测试NULL参数")
@NullSource
void test(Object i){
if (i==null){
System.out.println(1);
}else{
System.out.println(2);
}
}
③:@EnumSource: 表示为参数化测试提供一个枚举入参
@ParameterizedTest@EnumSourcevoidtestWithEnumSourceWithAutoDetection(ChronoUnit unit){assertNotNull(unit);}
其中的ChronoUnit是个日期枚举类。
ChronoUnit是接口TemporalUnit的实现类,如果测试方法的参数为TemporalUnit,那么需要给
@EnumSource
加上值:
@ParameterizedTest@EnumSource(ChronoUnit.class)voidtestWithEnumSource(TemporalUnit unit){assertNotNull(unit);}
因为JUnit5规定了
@EnumSource
的默认值的类型必须是枚举类型。
names属性用来指定使用哪些特定的枚举值:
@ParameterizedTest@EnumSource(names ={"DAYS","HOURS"})voidtestWithEnumSourceInclude(ChronoUnit unit){assertTrue(EnumSet.of(ChronoUnit.DAYS,ChronoUnit.HOURS).contains(unit));}
mode属性用来指定使用模式,比如排除哪些枚举值:
@ParameterizedTest@EnumSource(mode =EXCLUDE, names ={"ERAS","FOREVER"})voidtestWithEnumSourceExclude(ChronoUnit unit){assertFalse(EnumSet.of(ChronoUnit.ERAS,ChronoUnit.FOREVER).contains(unit));}
采用正则进行匹配
@ParameterizedTest@EnumSource(mode =MATCH_ALL, names ="^.*DAYS$")voidtestWithEnumSourceRegex(ChronoUnit unit){assertTrue(unit.name().endsWith("DAYS"));}
④:@MethodSource
参数值为factory方法,并且factory方法不能带参数。
@ParameterizedTest@MethodSource("stringProvider")voidtestWithExplicitLocalMethodSource(String argument){assertNotNull(argument);}staticStream<String>stringProvider(){returnStream.of("apple","banana");}
除非是@TestInstance(Lifecycle.PER_CLASS)生命周期,否则factory方法必须是static。factory方法的返回值是能转换为Stream的类型,比如Stream, DoubleStream, LongStream, IntStream, Collection, Iterator, Iterable, 对象数组, 或者基元类型数组,比如:
@ParameterizedTest@MethodSource("range")voidtestWithRangeMethodSource(int argument){assertNotEquals(9, argument);}staticIntStreamrange(){returnIntStream.range(0,20).skip(10);}
**
@MethodSource
的属性如果省略了,那么JUnit Jupiter会找跟测试方法同名的factory方法**
如果测试方法有多个参数,那么factory方法也应该返回多个:
@ParameterizedTest@MethodSource("stringIntAndListProvider")voidtestWithMultiArgMethodSource(String str,int num,List<String> list){assertEquals(5, str.length());assertTrue(num >=1&& num <=2);assertEquals(2, list.size());}staticStream<Arguments>stringIntAndListProvider(){returnStream.of(arguments("apple",1,Arrays.asList("a","b")),arguments("lemon",2,Arrays.asList("x","y")));}
⑤ :@CsvSource
参数化的值为csv格式的数据(默认逗号分隔),比如:
@ParameterizedTest@CsvSource({"apple, 1","banana, 2","'lemon, lime', 0xF1"})voidtestWithCsvSource(String fruit,int rank){assertNotNull(fruit);assertNotEquals(0, rank);}
delimiter属性可以设置分隔字符。delimiterString属性可以设置分隔字符串(String而非char)。
更多输入输出示例如下:

**注意,如果null引用的目标类型是基元类型,那么会报异常
ArgumentConversionException
。**
⑥:@CsvFileSource
顾名思义,选择本地csv文件作为数据来源。
**JUnit只在
classpath
中查找指定的CSV文件,因此,
test-capitalize.csv
这个文件要放到
test
目录下,内容如下**
@ParameterizedTest@CsvFileSource(resources ="/two-column.csv", numLinesToSkip =1)voidtestWithCsvFileSourceFromClasspath(String country,int reference){assertNotNull(country);assertNotEquals(0, reference);}@ParameterizedTest@CsvFileSource(files ="src/test/resources/two-column.csv", numLinesToSkip =1)voidtestWithCsvFileSourceFromFile(String country,int reference){assertNotNull(country);assertNotEquals(0, reference);}
delimiter属性可以设置分隔字符。delimiterString属性可以设置分隔字符串(String而非char)。**需要特别注意的是,
#
开头的行会被认为是注释而略过。**
⑦:@ArgumentsSource
如果JUnit内置的源代码无法满足您的所有用例,则可以自由创建自己的用例。 必须实现此接口。
publicinterfaceArgumentsProvider{Stream<?extendsArguments>provideArguments(ContainerExtensionContext context)throwsException;}
@ParameterizedTest@ArgumentsSource(MyArgumentsProvider.class)voidtestWithArgumentsSource(String argument){assertNotNull(argument);}
publicclassMyArgumentsProviderimplementsArgumentsProvider{@OverridepublicStream<?extendsArguments>provideArguments(ExtensionContext context){returnStream.of("apple","banana").map(Arguments::of);}}
本次主要以Json格式的入参为例:
JsonArgumentsProvider实现了ArgumentsProvider,AnnotationConsumer
packageorg.testerhome.junit5.json.params.test;importcom.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;importorg.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions;importorg.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;importorg.junit.jupiter.api.Test;importorg.junit.jupiter.params.ParameterizedTest;importorg.testerhome.junit5.json.params.JsonArgumentsProvider;importorg.testerhome.junit5.json.params.JsonSource;importjava.sql.SQLOutput;publicclassJsonArgumentsProviderTest{@Test@DisplayName("default constructor does not throw")voiddefaultConstructor(){Assertions.assertDoesNotThrow(JsonArgumentsProvider::new);}/**
* When passed <code>{"key":"value"}</code>, is executed a single time
* @param object the parsed JsonObject
*/@ParameterizedTest@JsonSource("{\"key\":\"value\"}")@DisplayName(",")voidsingleObject(JSONObject object){System.out.println(object);Assertions.assertEquals(object.getString("key"),"value");}/**
* When passed <code>[{"key":"value1"},{"key","value2"}]</code>, is
* executed once per element of the array
* @param object the parsed JsonObject array element
*/@ParameterizedTest@JsonSource("[{\"key\":\"value1\"},{\"key\":\"value2\"}]")@DisplayName("provides an array of objects")voidarrayOfObjects(JSONObject object){Assertions.assertTrue(object.getString("key").startsWith("value"));}/**
* When passed <code>[1, 2]</code>, is executed once per array element
* @param number the parsed JsonNumber for each array element
*/@ParameterizedTest@JsonSource("[1,2]")@DisplayName("provides an array of numbers")voidarrayOfNumbers(Integer number){Assertions.assertTrue(number >0);}/**
* When passed <code>["value1","value2"]</code>, is executed once per array
* element
* @param value the parsed JsonString for each array element
*/@ParameterizedTest@JsonSource("[\"value1\",\"value2\",\"value3\"]")@DisplayName("provides an array of strings")voidarrayOfStrings(String value){Assertions.assertTrue(value.startsWith("value"));}@ParameterizedTest@JsonSource("{'key':'value'}")@DisplayName("handles simplified json")voidsimplifiedJson(JSONObject object){Assertions.assertTrue(object.getString("key").equals("value"));}}
json参数格式泛型
package org.testerhome.junit5.json.params;
import org.junit.jupiter.params.provider.ArgumentsSource;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target({ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@ArgumentsSource(JsonArgumentsProvider.class)
public @interface JsonSource {
String value();
}
JsonFile文件形式作为入参
packageorg.testerhome.junit5.json.params.test;importcom.alibaba.fastjson.JSONArray;importcom.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;importorg.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions;importorg.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;importorg.junit.jupiter.api.Order;importorg.junit.jupiter.api.Test;importorg.junit.jupiter.params.ParameterizedTest;importorg.testerhome.junit5.json.params.JsonFileArgumentsProvider;importorg.testerhome.junit5.json.params.JsonFileSource;publicclassJsonFileArgumentsProviderTest{@Test@DisplayName("default constructor does not throw")voiddefaultConstructor(){Assertions.assertDoesNotThrow(JsonFileArgumentsProvider::new);}/**
* When passed <code>{"key":"value"}</code>, is executed a single time
*
* @param object the parsed JsonObject
*/@ParameterizedTest@JsonFileSource(resources ="/single-object.json")@DisplayName("provides a single object")voidsingleObject(JSONObject object){System.out.println(object.getString("key"));Assertions.assertEquals(object.getString("key"),"value");}/**
* When passed <code>[{"key":"value1"},{"key","value2"}]</code>, is
* executed once per element of the array
*
* @param object the parsed JsonObject array element
*/@ParameterizedTest@JsonFileSource(resources ="/array-of-objects.json")@DisplayName("provides an array of objects")voidarrayOfObjects(JSONObject object){Assertions.assertTrue(object.getString("key").startsWith("value"));}/**
* When passed <code>[1, 2]</code>, is executed once per array element
*
* @param number the parsed JsonNumber for each array element
*/@ParameterizedTest@JsonFileSource(resources ="/array-of-numbers.json")@DisplayName("provides an array of numbers")voidarrayOfNumbers(Integer number){Assertions.assertTrue(number >0);}/**
* When passed <code>["value1","value2"]</code>, is executed once per array
* element
*
* @param value the parsed JsonString for each array element
*/@ParameterizedTest@JsonFileSource(resources ="/array-of-strings.json")@DisplayName("provides an array of strings")voidarrayOfStrings(String value){Assertions.assertTrue(value.startsWith("value"));}/**
* @param jsonObject
*/@ParameterizedTest@Order(1)@JsonFileSource(resources ="/complex.json")@DisplayName("provides complex json case")voidcomplexJson(JSONObject jsonObject){JSONArray topics = jsonObject.getJSONArray("topics");for(Object t : topics){String title =((JSONObject) t).getString("title");System.out.println(title);}}}
json文件格式泛型
packageorg.testerhome.junit5.json.params;importorg.junit.jupiter.params.provider.ArgumentsSource;importjava.lang.annotation.*;@Target({ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE,ElementType.METHOD})@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Documented@ArgumentsSource(JsonFileArgumentsProvider.class)public@interfaceJsonFileSource{String[]resources();}
测试示例代码

//以json参数为例packageorg.testerhome.junit5.json.params.test;importcom.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;importorg.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions;importorg.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;importorg.junit.jupiter.api.Test;importorg.junit.jupiter.params.ParameterizedTest;importorg.testerhome.junit5.json.params.JsonArgumentsProvider;importorg.testerhome.junit5.json.params.JsonSource;importjava.sql.SQLOutput;publicclassJsonArgumentsProviderTest{@Test@DisplayName("default constructor does not throw")voiddefaultConstructor(){Assertions.assertDoesNotThrow(JsonArgumentsProvider::new);}/**
* When passed <code>{"key":"value"}</code>, is executed a single time
* @param object the parsed JsonObject
*/@ParameterizedTest@JsonSource("{\"key\":\"value\"}")@DisplayName(",")voidsingleObject(JSONObject object){System.out.println(object);Assertions.assertEquals(object.getString("key"),"value");}/**
* When passed <code>[{"key":"value1"},{"key","value2"}]</code>, is
* executed once per element of the array
* @param object the parsed JsonObject array element
*/@ParameterizedTest@JsonSource("[{\"key\":\"value1\"},{\"key\":\"value2\"}]")@DisplayName("provides an array of objects")voidarrayOfObjects(JSONObject object){Assertions.assertTrue(object.getString("key").startsWith("value"));}/**
* When passed <code>[1, 2]</code>, is executed once per array element
* @param number the parsed JsonNumber for each array element
*/@ParameterizedTest@JsonSource("[1,2]")@DisplayName("provides an array of numbers")voidarrayOfNumbers(Integer number){Assertions.assertTrue(number >0);}/**
* When passed <code>["value1","value2"]</code>, is executed once per array
* element
* @param value the parsed JsonString for each array element
*/@ParameterizedTest@JsonSource("[\"value1\",\"value2\",\"value3\"]")@DisplayName("provides an array of strings")voidarrayOfStrings(String value){Assertions.assertTrue(value.startsWith("value"));}@ParameterizedTest@JsonSource("{'key':'value'}")@DisplayName("handles simplified json")voidsimplifiedJson(JSONObject object){Assertions.assertTrue(object.getString("key").equals("value"));}}
//以参数文件为例packageorg.testerhome.junit5.json.params.test;importcom.alibaba.fastjson.JSONArray;importcom.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;importorg.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions;importorg.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;importorg.junit.jupiter.api.Order;importorg.junit.jupiter.api.Test;importorg.junit.jupiter.params.ParameterizedTest;importorg.testerhome.junit5.json.params.JsonFileArgumentsProvider;importorg.testerhome.junit5.json.params.JsonFileSource;publicclassJsonFileArgumentsProviderTest{@Test@DisplayName("default constructor does not throw")voiddefaultConstructor(){Assertions.assertDoesNotThrow(JsonFileArgumentsProvider::new);}/**
* When passed <code>{"key":"value"}</code>, is executed a single time
*
* @param object the parsed JsonObject
*/@ParameterizedTest@JsonFileSource(resources ="/single-object.json")@DisplayName("provides a single object")voidsingleObject(JSONObject object){System.out.println(object.getString("key"));Assertions.assertEquals(object.getString("key"),"value");}/**
* When passed <code>[{"key":"value1"},{"key","value2"}]</code>, is
* executed once per element of the array
*
* @param object the parsed JsonObject array element
*/@ParameterizedTest@JsonFileSource(resources ="/array-of-objects.json")@DisplayName("provides an array of objects")voidarrayOfObjects(JSONObject object){Assertions.assertTrue(object.getString("key").startsWith("value"));}/**
* When passed <code>[1, 2]</code>, is executed once per array element
*
* @param number the parsed JsonNumber for each array element
*/@ParameterizedTest@JsonFileSource(resources ="/array-of-numbers.json")@DisplayName("provides an array of numbers")voidarrayOfNumbers(Integer number){Assertions.assertTrue(number >0);}/**
* When passed <code>["value1","value2"]</code>, is executed once per array
* element
*
* @param value the parsed JsonString for each array element
*/@ParameterizedTest@JsonFileSource(resources ="/array-of-strings.json")@DisplayName("provides an array of strings")voidarrayOfStrings(String value){Assertions.assertTrue(value.startsWith("value"));}/**
* @param jsonObject
*/@ParameterizedTest@Order(1)@JsonFileSource(resources ="/complex.json")@DisplayName("provides complex json case")voidcomplexJson(JSONObject jsonObject){JSONArray topics = jsonObject.getJSONArray("topics");for(Object t : topics){String title =((JSONObject) t).getString("title");System.out.println(title);}}}
Mockito
1. 为什么要使用 mock
Mock 可以理解为创建一个虚假的对象,或者说模拟出一个对象,在测试环境中用来替换掉真实的对象
以达到我们可以:
- 验证该对象的某些方法的调用情况,调用了多少次,参数是多少
- 给这个对象的行为做一个定义,来指定返回结果或者指定特定的动作
大白话:主要是实现分层测试,减少结构之间的依赖,模拟你需要的其他层的数据,就像开发中你没有撰写Dao层代码,但是你想测试Service逻辑是否正确,那么你可以Mock(虚构)出Dao层的数据。
2. Mockito 中常用方法
2.1 Mock 方法
mock 方法来自
org.mockito.Mock
,它表示可以 mock 一个对象或者是接口。
publicstatic<T>Tmock(Class<T> classToMock)
- classToMock:待 mock 对象的 class 类。
- 返回 mock 出来的类
实例:使用 mock 方法 mock 一个类
Random random =Mockito.mock(Random.class);
大白话:我在Controller层要调用Service方法,但是我没写,可以使用Service MyService = Mockito.mock(xxxService.class);
2.2给 Mock 对象打桩
打桩可以理解为 mock 对象规定一行的行为,使其按照我们的要求来执行具体的操作。在 Mockito 中,常用的打桩方法为
方法含义when().thenReturn()Mock 对象在触发指定行为后返回指定值when().thenThrow()Mock 对象在触发指定行为后抛出指定异常when().doCallRealMethod()Mock 对象在触发指定行为后调用真实的方法
大白话:我在Controller层需要Service返回某个什么东西比如某个数据,我就new一个数据,然后对Service进行打桩,指定这个service调用这个方法的时候返回我new的数据。
thenReturn() 代码示例
@Testvoidcheck(){Random random =Mockito.mock(Random.class,"test");Mockito.when(random.nextInt()).thenReturn(100);//我希望我在调用random.nexInt()方法时,给我返回100,所以我对他进行打桩Assertions.assertEquals(100, random.nextInt());}
测试通过
注意:Mock后不对Mock出的对象进行打桩,那么Mock出的对象就是默认值。
2.3 Mock 静态方法
在Mockito 3.4.0后Mock实现了了模拟静态方法。
首先要引入 Mockito-Inline 的依赖。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mockito</groupId>
<artifactId>mockito-inline</artifactId>
<version>4.3.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
使用
mockStatic()
方法来 mock静态方法的所属类,此方法返回一个具有作用域的模拟对象。
@Testvoidrange(){MockedStatic<StaticUtils> utilities =Mockito.mockStatic(StaticUtils.class);
utilities.when(()->StaticUtils.range(2,6)).thenReturn(Arrays.asList(10,11,12));Assertions.assertTrue(StaticUtils.range(2,6).contains(10));}
@Testvoidname(){MockedStatic<StaticUtils> utilities =Mockito.mockStatic(StaticUtils.class);
utilities.when(StaticUtils::name).thenReturn("bilibili");Assertions.assertEquals("1",StaticUtils.name());}
执行整个测试类后会报错:
org.mockito.exceptions.base.MockitoException:
For com.echo.mockito.Util.StaticUtils, static mocking is already registered in the current thread
To create a new mock, the existing static mock registration must be deregistered
原因是因为 mockStatic() 方法是将当前需要 mock 的类注册到本地线程上(ThreadLocal),而这个注册在一次 mock 使用完之后是不会消失的,需要我们手动的去销毁。如过没有销毁,再次 mock 这个类的时候 Mockito 将会提示我们 :”当前对象 mock 的对象已经在线程中注册了,请先撤销注册后再试“。这样做的目的也是为了保证模拟出来的对象之间是相互隔离的,保证同时和连续的测试不会收到上下文的影响。
因此我们修改代码:
classStaticUtilsTest{@Testvoidrange(){try(MockedStatic<StaticUtils> utilities =Mockito.mockStatic(StaticUtils.class)){
utilities.when(()->StaticUtils.range(2,6)).thenReturn(Arrays.asList(10,11,12));Assertions.assertTrue(StaticUtils.range(2,6).contains(10));}}@Testvoidname(){try(MockedStatic<StaticUtils> utilities =Mockito.mockStatic(StaticUtils.class)){
utilities.when(StaticUtils::name).thenReturn("bilibili");Assertions.assertEquals("bilibili",StaticUtils.name());}}}
注:try()括号内流等对象会在程序运行结束后默认关闭。
3. Mockito 中常用注解
3.1 可以代替 Mock 方法的 @Mock 注解
Shorthand for mocks creation - @Mock annotation
Important! This needs to be somewhere in the base class or a test runner:
快速 mock 的方法,使用
@mock
注解。
mock 注解需要搭配 MockitoAnnotations.openMocks(testClass) 方法一起使用。
依据不同版本可能还会出现initMocks()未过期的情况。
@MockprivateRandom random;@Testvoidcheck(){MockitoAnnotations.openMocks(this);Mockito.when(random.nextInt()).thenReturn(100);Assertions.assertEquals(100, random.nextInt());}
3.2 Spy 方法与 @Spy 注解
spy() 方法与 mock() 方法不同的是
- 被 spy 的对象会走真实的方法,而 mock 对象不会
- spy() 方法的参数是对象实例,mock 的参数是 class
示例:spy 方法与 Mock 方法的对比
@Testvoidcheck(){CheckAuthorityImpl checkAuthority =Mockito.spy(newCheckAuthorityImpl());int res = checkAuthority.add(1,2);Assertions.assertEquals(3, res);CheckAuthorityImpl checkAuthority1 =Mockito.mock(CheckAuthorityImpl.class);int res1 = checkAuthority1.add(1,2);Assertions.assertEquals(3, res1);}
输出结果
// 第二个 Assertions 断言失败,因为没有给 checkAuthority1 对象打桩,因此返回默认值org.opentest4j.AssertionFailedError:Expected:3Actual:0
使用
@Spy
注解代码示例
@SpyprivateCheckAuthorityImpl checkAuthority;@BeforeEachvoidsetUp(){MockitoAnnotations.openMocks(this);}@Testvoidcheck(){int res = checkAuthority.add(1,2);Assertions.assertEquals(3, res);}
5.参数匹配
1.精准匹配
importorg.junit.Assert;importorg.junit.Test;importjava.util.List;importstaticorg.mockito.Mockito.*;publicclassMockitoDemo{@Testpublicvoidtest(){List mockList =mock(List.class);Assert.assertEquals(0, mockList.size());Assert.assertEquals(null, mockList.get(0));
mockList.add("a");// 调用 mock 对象的写方法,是没有效果的Assert.assertEquals(0, mockList.size());// 没有指定 size() 方法返回值,这里结果是默认值Assert.assertEquals(null, mockList.get(0));// 没有指定 get(0) 返回值,这里结果是默认值when(mockList.get(0)).thenReturn("a");// 指定 get(0)时返回 aAssert.assertEquals(0, mockList.size());// 没有指定 size() 方法返回值,这里结果是默认值Assert.assertEquals("a", mockList.get(0));// 因为上面指定了 get(0) 返回 a,所以这里会返回 aAssert.assertEquals(null, mockList.get(1));// 没有指定 get(1) 返回值,这里结果是默认值}}
其中
when(mockList.get(0)).thenReturn("a");
指定了
get(0)
的返回值,这个 0 就是参数的精确匹配。我们还可以让不同的参数对应不同的返回值,例如:
importorg.junit.Assert;importorg.junit.Before;importorg.junit.Test;importorg.mockito.Mock;importorg.mockito.MockitoAnnotations;importjava.util.List;importstaticorg.mockito.Mockito.*;publicclassMockitoDemo{@MockprivateList<String> mockStringList;@Beforepublicvoidbefore(){MockitoAnnotations.initMocks(this);}@Testpublicvoidtest(){
mockStringList.add("a");when(mockStringList.get(0)).thenReturn("a");when(mockStringList.get(1)).thenReturn("b");Assert.assertEquals("a", mockStringList.get(0));Assert.assertEquals("b", mockStringList.get(1));}}
2.模糊匹配
可以使用
Mockito.anyInt()
匹配所有类型为 int 的参数:
importorg.junit.Assert;importorg.junit.Before;importorg.junit.Test;importorg.mockito.Mock;importorg.mockito.MockitoAnnotations;importjava.util.List;importstaticorg.mockito.Mockito.*;publicclassMockitoDemo{@MockprivateList<String> mockStringList;@Beforepublicvoidbefore(){MockitoAnnotations.initMocks(this);}@Testpublicvoidtest(){
mockStringList.add("a");when(mockStringList.get(anyInt())).thenReturn("a");// 使用 Mockito.anyInt() 匹配所有的 intAssert.assertEquals("a", mockStringList.get(0));Assert.assertEquals("a", mockStringList.get(1));}}
anyInt 只是用来匹配参数的工具之一,目前 mockito 有多种匹配函数,部分如下:
函数名匹配类型any()所有对象类型anyInt()基本类型 int、非 null 的 Integer 类型anyChar()基本类型 char、非 null 的 Character 类型anyShort()基本类型 short、非 null 的 Short 类型anyBoolean()基本类型 boolean、非 null 的 Boolean 类型anyDouble()基本类型 double、非 null 的 Double 类型anyFloat()基本类型 float、非 null 的 Float 类型anyLong()基本类型 long、非 null 的 Long 类型anyByte()基本类型 byte、非 null 的 Byte 类型anyString()String 类型(不能是 null)anyList()
List<T>
类型(不能是 null)anyMap()
Map<K, V>
类型(不能是 null)anyCollection()
Collection<T>
类型(不能是 null)anySet()
Set<T>
类型(不能是 null)
any(Class<T> type)
type类型的对象(不能是 null)isNull()nullnotNull()非 nullisNotNull()非 null
6.Mockito 参数匹配顺序
如果参数匹配即声明了精确匹配,也声明了模糊匹配;又或者同一个值的精确匹配出现了两次,使用时会匹配哪一个?
会匹配符合匹配条件的最新声明的匹配。
例如下面这段代码
importorg.junit.Assert;importorg.junit.Test;importorg.junit.runner.RunWith;importorg.mockito.Mock;importorg.mockito.junit.MockitoJUnitRunner;importjava.util.List;importstaticorg.mockito.Mockito.*;@SpringbootTestpublicclassMockitoDemo{@MockprivateList<String> testList;@Testpublicvoidtest01(){// 精确匹配 0when(testList.get(0)).thenReturn("a");Assert.assertEquals("a", testList.get(0));// 精确匹配 0when(testList.get(0)).thenReturn("b");Assert.assertEquals("b", testList.get(0));// 模糊匹配when(testList.get(anyInt())).thenReturn("c");Assert.assertEquals("c", testList.get(0));Assert.assertEquals("c", testList.get(1));}@Testpublicvoidtest02(){// 模糊匹配when(testList.get(anyInt())).thenReturn("c");Assert.assertEquals("c", testList.get(0));Assert.assertEquals("c", testList.get(1));// 精确匹配 0when(testList.get(0)).thenReturn("a");Assert.assertEquals("a", testList.get(0));Assert.assertEquals("c", testList.get(1));}}
文章参考
BilibiliUP主:搞钱小王
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV15S4y1F7Xr/?spm_id_from=333.337.search-card.all.click
乐天笔记:Mockito入门
https://www.letianbiji.com/java-mockito/mockito-parameter-match.html
|
版权归原作者 感冒的方便面 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。