最近,我有幸接触到 medcl 大神的杰作:极限网关(INFINI GATEWAY)。INFINI Gateway 有很多优点,也有很多应用的场景。你可以在官方网站上进行阅读。简单说来,极限网关(INFINI Gateway)是一个面向 Elasticsearch 的高性能应用网关,它包含丰富的特性,使用起来也非常简单。极限网关工作的方式和普通的反向代理一样,我们一般是将网关部署在 Elasticsearch 集群前面, 将以往直接发送给 Elasticsearch 的请求都发送给网关,再由网关转发给请求到后端的 Elasticsearch 集群。因为网关位于在用户端和后端 Elasticsearch 之间,所以网关在中间可以做非常多的事情, 比如可以实现索引级别的限速限流、常见查询的缓存加速、查询请求的审计、查询结果的动态修改等等。
INFINI Gateway 它是如何和其它软件栈进行集成的呢?根据官方的介绍,网关通常是以这样的形式来进行接入的:
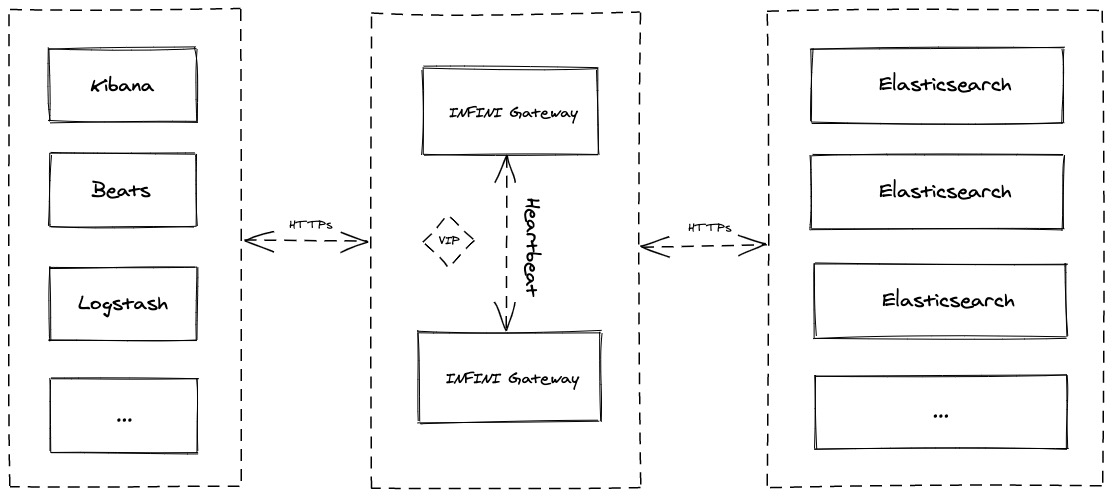
如上所示,INFINI 网关针对所有的请求是透明的。我们原本的发向 Elasticsearch 的请求,现在只要提交给网关就可以了。对于客户端开发者来说,你无需了解网关后面是如何连接 Elasticsearch 的。网关位于 Elasticsearch 的前端。所有的请求都发向网关,再由网关进行转发到 Elasticsearch。当然它不是简单的转发,它可以把请求分发至各个 Elasticsearch 节点或不同的 Elasticsearch 集群,也可以针对请求依据一些规则进行修改或者拒绝等操作,或者针对 _bulk 请求进行分析来提高摄入数据的速度。网关还可以实现负载均衡的功能,限流,使用 cache,甚至针对请求进行分析。也可以依据一定的条件进行修改或聚合来自其它数据源的数据。根据测评,极限网关相比同类主流网关类产品速度快 20% 以上。它对 Elasticsearch 做了细致的优化,并使得写入和查询的速度得到成倍的提升。
如上所示,在上面的架构中还采用了 VIP(浮动 IP)。我们可以在系统中部署2个 INFINI Gateway。一旦其中的一个由于一些原因不能正常工作,那么另外一个就会自动接管,从而避免 single point of failure。
在今天的展示中,我将使用最新的 Elastic Stack 8.1 来进行展示。
安装
Elastic Stack
如果你还没安装好自己的 Elasticsearch 及 Kibana,那么请参阅文章:
- 如何在 Linux,MacOS 及 Windows 上进行安装 Elasticsearch
- Kibana:如何在 Linux,MacOS 及 Windows 上安装 Elastic 栈中的 Kibana
特别地,你可以参考如下的文章来安装好 Elastic Stack 8.1:
- Elastic Stack 8.0 安装 - 保护你的 Elastic Stack 现在比以往任何时候都简单
- Elasticsearch:在多个机器上创建多节点的 Elasticsearch 集群 - Elastic Stack 8.0
当我们安装好自己的 Elasticsearch 后,我们可以使用如下的方式来进行查看:
curl -k -u elastic:_3DAof2=LryludRa5Zho -XGET "https://192.168.0.3:9200/"
$ curl -k -u elastic:_3DAof2=LryludRa5Zho -XGET "https://192.168.0.3:9200/"
{
"name" : "liuxgm.local",
"cluster_name" : "elasticsearch",
"cluster_uuid" : "SNZ_-EOOR8-tdb-I-BG_jA",
"version" : {
"number" : "8.1.1",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "tar",
"build_hash" : "d0925dd6f22e07b935750420a3155db6e5c58381",
"build_date" : "2022-03-17T22:01:32.658689558Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "9.0.0",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "7.17.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "7.0.0"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}
请注意上面的 _3DAof2=LryludRa5Zho 是我的集群超级用户 elastic 的密码,而 192.168.0.3 是我的 Elasticsearch 的访问地址。
INFINI Gateway
安装 INFINI Gateway 也非常简单。我们需要去 release.infinilabs.com 去下载我们需要的版本。
我们选择 gateway:

也许我比较喜欢尝鲜,我选择 snapshot。这里有每天的一个 build。它含有最新的功能,虽然可能会有 bug:
对于我的苹果电脑 Apple chipset 来说,我选择如上所示的 mac-arm6 版本。我们使用如下的命令来进行解压缩:
unzip gateway-1.6.0_SNAPSHOT-591-mac-arm64.zip
$ pwd
/Users/liuxg/gateway
$ ls -al
total 49976
drwxr-xr-x 6 liuxg staff 192 Apr 6 09:44 .
drwxr-xr-x+ 159 liuxg staff 5088 Apr 6 09:43 ..
-rw-r--r--@ 1 liuxg staff 6176162 Mar 24 15:21 gateway-1.6.0_SNAPSHOT-591-mac-arm64.zip
-rwxr-xr-x@ 1 liuxg staff 19401090 Mar 23 19:06 gateway-mac-arm64
-rw-r--r--@ 1 liuxg staff 4290 Mar 23 19:04 gateway.yml
drwxr-xr-x@ 21 liuxg staff 672 Mar 20 23:42 sample-configs
如上所示,当解压缩后,它含有一个默认的 gateway.yml 配置文件。它还含有一个 sample-configs 目录。这个目录含有多个实例配置文件。我们在命令行中运行 gateway:
gateway-mac-arm64 --help
$ pwd
/Users/liuxg/gateway
$ ls -al
total 49976
drwxr-xr-x 6 liuxg staff 192 Apr 6 09:44 .
drwxr-xr-x+ 159 liuxg staff 5088 Apr 6 09:43 ..
-rw-r--r--@ 1 liuxg staff 6176162 Mar 24 15:21 gateway-1.6.0_SNAPSHOT-591-mac-arm64.zip
-rwxr-xr-x@ 1 liuxg staff 19401090 Mar 23 19:06 gateway-mac-arm64
-rw-r--r--@ 1 liuxg staff 4290 Mar 23 19:04 gateway.yml
drwxr-xr-x@ 21 liuxg staff 672 Mar 20 23:42 sample-configs
$ ./gateway-mac-arm64 --help
Usage of ./gateway-mac-arm64:
-config string
the location of config file, default: gateway.yml (default "gateway.yml")
-debug
run in debug mode, gateway will quit with panic error
-log string
the log level, options: trace,debug,info,warn,error (default "info")
-service string
service management, options: install,uninstall,start,stop
-v version
如上所示,我们可以把 gateway 以 service 的方式来进行运行,这样当我们的系统启动后,我们不再需要手动来启动 gateway。在 macOS 下,我们可以这样运行:
sudo ./gateway-mac-arm64 -service install
$ sudo ./gateway-mac-arm64 -service install
Password:
Success
我们可以通过如下的方式来禁止以服务的方式来运行:
sudo ./gateway-mac-arm64 -service uninstall
$ sudo ./gateway-mac-arm64 -service uninstall
Success
当然,我们也可以使用 start 及 stop 选项来启动或停止服务的运行。
这样我们的安装就完成了。
运行 Gateway 的方式
我们有两种方式来运行 Gateway:
./gateway-mac-arm64
如果以这样的方式来运行 gateway,那么它的默认配置文件是在该目录下的 **gateway.yml **文件:
$ pwd
/Users/liuxg/gateway
$ ls
gateway-1.6.0_SNAPSHOT-591-mac-arm64.zip log
gateway-mac-arm64 sample-configs
gateway.yml
另外,我们也可以通过如下的方式来进行运行:
./gateway-mac-arm64 -config ./sample-configs/hello_world.yml
在上面,我们指定了一个配置文件。
$ ./gateway-mac-arm64 -config ./sample-configs/hello_world.yml
___ _ _____ __ __ __ _
/ _ \ /_\ /__ \/__\/ / /\ \ \/_\ /\_/\
/ /_\///_\\ / /\/_\ \ \/ \/ //_\\\_ _/
/ /_\\/ _ \/ / //__ \ /\ / _ \/ \
\____/\_/ \_/\/ \__/ \/ \/\_/ \_/\_/
[GATEWAY] A light-weight, powerful and high-performance elasticsearch gateway.
[GATEWAY] 1.6.0_SNAPSHOT, 2022-03-23 11:04:26, 2023-12-31 10:10:10, 6c3c047b27d353696da1454fc71bcc564103bf2f
[04-06 10:23:58] [INF] [app.go:174] initializing gateway.
[04-06 10:23:58] [INF] [app.go:175] using config: /Users/liuxg/gateway/sample-configs/hello_world.yml.
[04-06 10:23:58] [INF] [instance.go:72] workspace: /Users/liuxg/gateway/data/gateway/nodes/c96fjfl9so256esepqp0
[04-06 10:23:58] [INF] [app.go:283] gateway is up and running now.
[04-06 10:23:58] [INF] [api.go:262] api listen at: http://0.0.0.0:2900
[04-06 10:23:58] [INF] [entry.go:302] entry [my_es_entry] listen at: http://0.0.0.0:8000
[04-06 10:23:58] [INF] [module.go:116] all modules are started
上面的 hello_world.yml 文件非常简单:
sample-configs/hello_world.yml
path.data: data
path.logs: log
entry:
- name: my_es_entry
enabled: true
router: my_router
max_concurrency: 200000
network:
binding: 0.0.0.0:8000
flow:
- name: hello_world
filter:
- echo:
message: "hello world"
router:
- name: my_router
default_flow: hello_world
解释:
- 上面的 path.data 定义的是 data 的路径。比如在当前的 gateway 安装目录下,含有一个叫做 data 的目录。

- 上面的 path.logs 定义的是 日志的路径。如上所示,我们可以看到一个叫做 log 的目录。
- entry:定义网关的请求入口,极限网关支持 HTTP 和 HTTPS 两种模式,HTTPS 可以自动生成证书。可以有多个 entry。
- router:义请求的路由规则,根据 Method 和请求地址来进行路由到指定的 Flow 处理流程里面去。
- flow:定义数据的处理逻辑,每个请求会经过一系列的 Filter 操作,Flow 用来将这些 Filter 组织起来。
- filter:由若干个不同的 Filter 组件构成,每个 Filter 在设计的时候只处理一件事情,通过多个 Filter 组成变成一个 Flow。
整个极限网关的数据流是这样的:
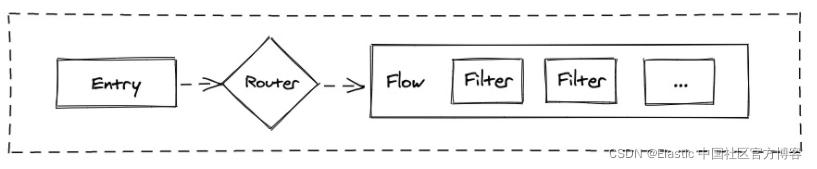
从上面的流中,我们可以看出来,数据是从 entry 进入,然后由 router 流向 flow。每个 flow 又含有各个不同的 filters。每个 filter 都有自己独特的功能。
我们下面来做一个简单的测试。如上面 gateway 启动的画面显示所示,我们看到 gateway 是在端口 0.0.0.0:8000 侦听的。0.0.0.0 意味着它绑定了当前电脑的所有网络接口。我们可以通过如下的命令来获得所有当前电脑的网络接口:
ifconfig
一般来说,它绑定了当前电脑的 localhost 及 privateIP 地址。我们使用如下的方式来访问 gateway:
$ curl http://localhost:8000
hello world$
从上面,我们可以看出来。这个是一个简单的 echo 命令。它返回 hello world。这说明我们的 gateway 的安装是没有任何问题的。细心的开发者发现 hello world 是没有换行符的。我们可以重新修正 hello_world.yml 文件如下:
sample-configs/hello_world.yml
path.data: data
path.logs: log
entry:
- name: my_es_entry
enabled: true
router: my_router
max_concurrency: 200000
network:
binding: 0.0.0.0:8000
flow:
- name: hello_world
filter:
- echo:
message: "hello world\n"
router:
- name: my_router
default_flow: hello_world
我们在上面的 message 中添加了一个换行符。重新启动 gateway,并再次运行上面的 curl 指令:
$ curl http://localhost:8000
hello world
这次,我们可以看到自动换行了。
如何连接到 Elasticsearch 和 Kibana
连接到 Elasticsearch 集群
我们可以参阅在安装目录中的 sample-configs/elasticsearch-proxy.yml 文件。如果你想创建多个节点的集群,请参阅我之前的文章 “Elasticsearch:在多个机器上创建多节点的 Elasticsearch 集群 - Elastic Stack 8.0”。我们可以通过如下的命令来验证集群含有的节点:
curl --insecure -u elastic:u7-KUuNhF2DcGCCtugU0 -XGET "https://192.168.0.3:9200/_cat/nodes"
$ curl --insecure -u elastic:u7-KUuNhF2DcGCCtugU0 -XGET "https://192.168.0.3:9200/_cat/nodes"
192.168.0.3 3 100 15 4.41 cdfhilmrstw * liuxgm.local
192.168.0.8 19 97 6 0.57 0.35 0.30 cdfhilmrstw - liuxg
在上面,它显示是有两个节点组成的集群。我们可以修改 elasticsearch-proxy.yml 文件如下:
sample-configs/elasticsearch-proxy.yml
path.data: data
path.logs: log
entry:
- name: my_es_entry
enabled: true
router: my_router
max_concurrency: 10000
network:
binding: 0.0.0.0:8000
flow:
- name: es-flow
filter:
- elasticsearch:
elasticsearch: es-server
router:
- name: my_router
default_flow: es-flow
elasticsearch:
- name: es-server
enabled: true
endpoints:
- https://192.168.0.3:9200
- https://192.168.0.8:9200
basic_auth:
username: elastic
password: u7-KUuNhF2DcGCCtugU0
请注意上面的 password 配置。你需要根据自己的设置而改变。
我们使用如下的方法来启动 gateway:
./gateway-mac-arm64 -config ./sample-configs/elasticsearch-proxy.yml
$ ./gateway-mac-arm64 -config ./sample-configs/elasticsearch-proxy.yml
___ _ _____ __ __ __ _
/ _ \ /_\ /__ \/__\/ / /\ \ \/_\ /\_/\
/ /_\///_\\ / /\/_\ \ \/ \/ //_\\\_ _/
/ /_\\/ _ \/ / //__ \ /\ / _ \/ \
\____/\_/ \_/\/ \__/ \/ \/\_/ \_/\_/
[GATEWAY] A light-weight, powerful and high-performance elasticsearch gateway.
[GATEWAY] 1.6.0_SNAPSHOT, 2022-03-23 11:04:26, 2023-12-31 10:10:10, 6c3c047b27d353696da1454fc71bcc564103bf2f
[04-06 12:26:45] [INF] [app.go:174] initializing gateway.
[04-06 12:26:45] [INF] [app.go:175] using config: /Users/liuxg/gateway/sample-configs/elasticsearch-proxy.yml.
[04-06 12:26:45] [INF] [instance.go:72] workspace: /Users/liuxg/gateway/data/gateway/nodes/c96fjfl9so256esepqp0
[04-06 12:26:45] [INF] [app.go:283] gateway is up and running now.
[04-06 12:26:45] [INF] [api.go:262] api listen at: http://0.0.0.0:2900
[04-06 12:26:45] [INF] [entry.go:302] entry [my_es_entry] listen at: http://0.0.0.0:8000
[04-06 12:26:45] [INF] [module.go:116] all modules are started
[04-06 12:26:45] [INF] [actions.go:280] elasticsearch [es-server] is available
如上所示,它显示 elasticsearch [es-server] is available 这个信息。如果你没有看到这个信息,则表明你的配置是有问题的。
为了能够通过 gateway 访问 Elasticsearch,我们通过如下的方式来进行访问。首先,我们把 Elasticsearch 安装目录下的证书文件拷贝过。这个证书在如下的地址:
$ pwd
/Users/liuxg/elastic/elasticsearch-8.1.1
$ ls config/certs/
http.p12 http_ca.crt transport.p12
在上面,显示的 http_ca.crt 就是所需要的证书。我们拷贝到下述命令运行的目录中,然后运行:
$ pwd
/Users/liuxg/gateway
$ ls
data http_ca.crt
gateway-1.6.0_SNAPSHOT-591-mac-arm64.zip log
gateway-mac-arm64 sample-configs
gateway.yml
$ curl --cacert ./http_ca.crt -u elastic:u7-KUuNhF2DcGCCtugU0 http://0.0.0.0:8000
{
"name" : "liuxg",
"cluster_name" : "elasticsearch",
"cluster_uuid" : "53aivEciQ-28pjjkYR-qlQ",
"version" : {
"number" : "8.1.2",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "deb",
"build_hash" : "31df9689e80bad366ac20176aa7f2371ea5eb4c1",
"build_date" : "2022-03-29T21:18:59.991429448Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "9.0.0",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "7.17.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "7.0.0"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}
如果你看到上面的输出则标明你的配置是成功的。我们可以通过如下的方法来获得所有的节点:
$ curl --cacert ./http_ca.crt -u elastic:u7-KUuNhF2DcGCCtugU0 http://0.0.0.0:8000/_cat/nodes
192.168.0.3 4 99 12 4.25 cdfhilmrstw * liuxgm.local
192.168.0.8 21 98 4 0.05 0.06 0.12 cdfhilmrstw - liuxg
由于是自签名证书,我们也可以使用如下的方式来获得:
$ curl -k -u elastic:u7-KUuNhF2DcGCCtugU0 http://0.0.0.0:8000/_cat/nodes
192.168.0.3 4 99 15 3.93 cdfhilmrstw * liuxgm.local
192.168.0.8 27 98 4 0.01 0.05 0.11 cdfhilmrstw - liuxg
或者:
$ curl --insecure -u elastic:u7-KUuNhF2DcGCCtugU0 http://0.0.0.0:8000/_cat/nodes
192.168.0.8 28 98 4 0.01 0.04 0.10 cdfhilmrstw - liuxg
192.168.0.3 4 99 15 8.63 cdfhilmrstw * liuxgm.local
之前没有网关的情况下,我们的请求都发向 Elasticsearch 的集群。现在有了网关的存在,我们直接把请求发向网关的地址就可以了。
连接到 Kibana
如同在文章一开始的架构图中所示,我们也可以把 Kibana 接入到 gateway 上去。我们按照通常的方法来安装 Kibana。具体步骤可以参阅文章 “Elasticsearch:在多个机器上创建多节点的 Elasticsearch 集群 - Elastic Stack 8.0”。为了测试方便,我们需要在 config/kibana.yml 文件中做如下的改动:
server.host: "0.0.0.0"
把 Kibana 绑定于电脑所有的网络接口上。我们可以通过 localhost:5601 及 privateIP:5601 的格式进行访问。
我们创建如下的一个 gateway.yml 文件:
path.data: data
path.logs: log
entry:
- name: my_es_entry
enabled: true
router: my_router
max_concurrency: 10000
network:
binding: 0.0.0.0:8000
- name: my_kibana_entry
enabled: true
router: my_kibana_router
network:
binding: 0.0.0.0:5602
flow:
- name: es-flow
filter:
- elasticsearch:
elasticsearch: es-server
- name: logout_flow
filter:
- set_response:
status: 401
body: "Success logout!"
- drop:
- name: replace_logo_flow
filter:
- redirect:
uri: https://elasticsearch.cn/uploads/event/20211120/458c74ca3169260dbb2308dd06ef930a.png
- name: kibana_flow
filter:
- basic_auth:
valid_users:
elastic: u7-KUuNhF2DcGCCtugU0 # super user elastic account
- http:
schema: "http" #https or http
host: "192.168.0.3:5601"
router:
- name: my_router
default_flow: es-flow
- name: my_kibana_router
default_flow: kibana_flow
rules:
- method:
- GET
- POST
pattern:
- "/_logout"
flow:
- logout_flow
- method:
- GET
pattern:
- "/plugins/kibanaReact/assets/illustration_integrations_lightmode.svg"
flow:
- replace_logo_flow
elasticsearch:
- name: es-server
enabled: true
endpoints:
- https://192.168.0.3:9200
- https://192.168.0.8:9200
basic_auth:
username: elastic
password: u7-KUuNhF2DcGCCtugU0
请注意我在上面使用了超级用户 elastic 来配置 Kibana。在实际的使用中,我们可以使用创建的账号来访问 Kibana。
我们使用如下的方法来启动 gateway:
./gateway-mac-arm64
我们可以看到:
$ ./gateway-mac-arm64
___ _ _____ __ __ __ _
/ _ \ /_\ /__ \/__\/ / /\ \ \/_\ /\_/\
/ /_\///_\\ / /\/_\ \ \/ \/ //_\\\_ _/
/ /_\\/ _ \/ / //__ \ /\ / _ \/ \
\____/\_/ \_/\/ \__/ \/ \/\_/ \_/\_/
[GATEWAY] A light-weight, powerful and high-performance elasticsearch gateway.
[GATEWAY] 1.6.0_SNAPSHOT, 2022-03-23 11:04:26, 2023-12-31 10:10:10, 6c3c047b27d353696da1454fc71bcc564103bf2f
[04-06 13:36:39] [INF] [app.go:174] initializing gateway.
[04-06 13:36:39] [INF] [app.go:175] using config: /Users/liuxg/gateway/gateway.yml.
[04-06 13:36:39] [INF] [instance.go:72] workspace: /Users/liuxg/gateway/data/gateway/nodes/c96fjfl9so256esepqp0
[04-06 13:36:39] [INF] [app.go:283] gateway is up and running now.
[04-06 13:36:39] [INF] [api.go:262] api listen at: http://0.0.0.0:2900
[04-06 13:36:39] [INF] [entry.go:302] entry [my_es_entry] listen at: http://0.0.0.0:8000
[04-06 13:36:39] [INF] [entry.go:302] entry [my_kibana_entry] listen at: http://0.0.0.0:5602
[04-06 13:36:39] [INF] [module.go:116] all modules are started
[04-06 13:36:39] [INF] [actions.go:280] elasticsearch [es-server] is available
从上面我们可以看到有两个 entry:my_es_entry 及 my_kibana_entry。
如何调试
在上面,我只对 gateway 的一个安装做了简单的介绍。在 gateway 的官方网站中,有许多的过滤器。这些是在请求发向 Elasticsearh 之前可以在网关做很多额外工作的地方。在开发的过程中,有一个良好的调试工具会给我们的开发带来很多的好处。在上面,我们除了可以使用 echo 来输出一些文字之外,我们还可以通过 dump 指令来查看请求及响应的内容。
下面,我们来做一个简单的展示。首先我们在 Elasticsearch 中创建如下的一个索引:
PUT twitter/_doc/1
{
"name": "liuxg",
"company": "elastic"
}
我们可以做如上所示的搜索:
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "liuxg"
}
}
}
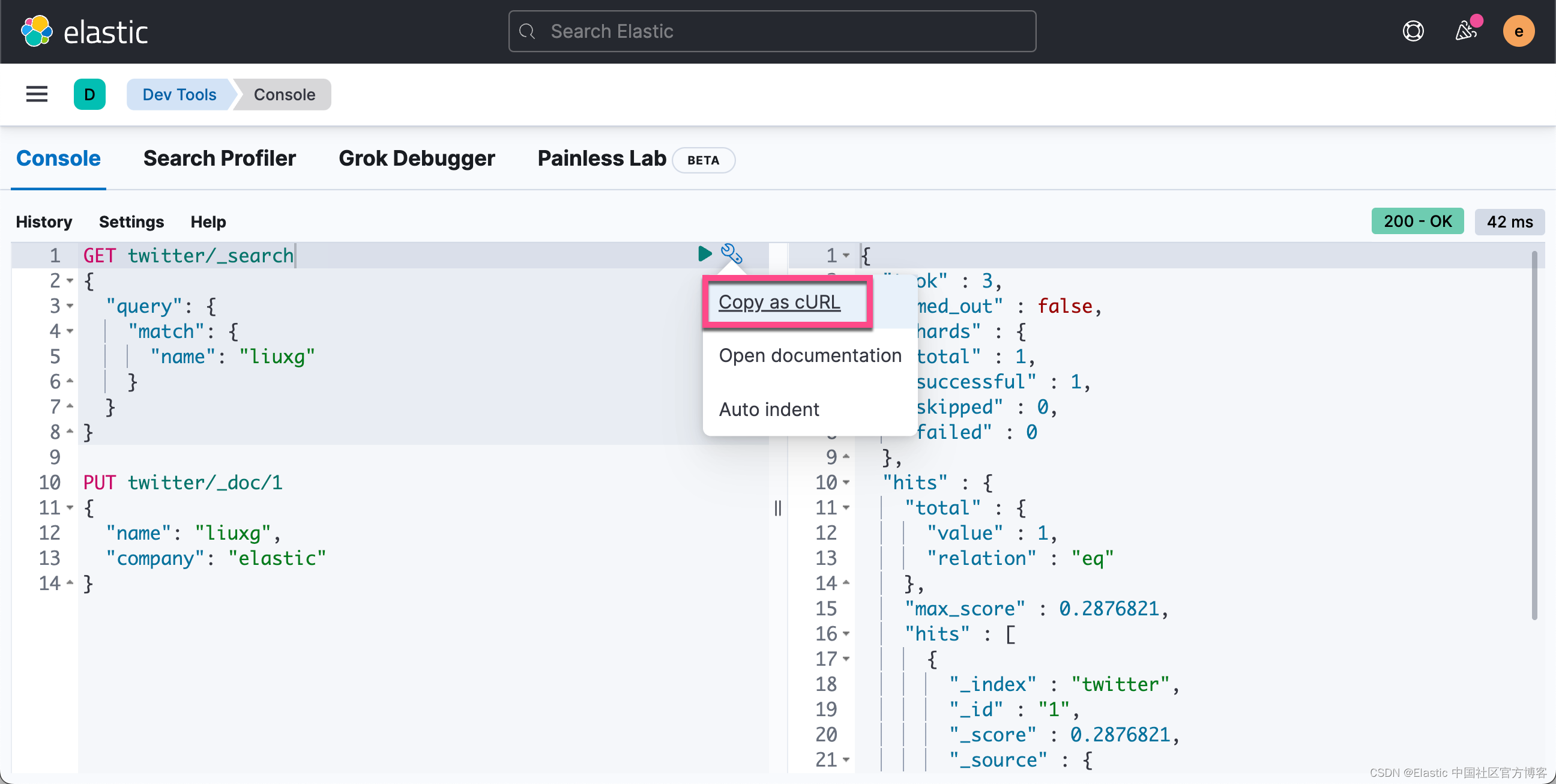
我们按照上面的方法点击 Copy as cURL。我们把拷贝下来的内容放入到下面的 curl 指令中去:
curl --insecure -u elastic:u7-KUuNhF2DcGCCtugU0 -XGET "http://0.0.0.0:8000/twitter/_search" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "liuxg"
}
}
}'
上面的结果为:
$ curl --insecure -u elastic:u7-KUuNhF2DcGCCtugU0 -XGET "http://0.0.0.0:8000/twitter/_search" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
> {
> "query": {
> "match": {
> "name": "liuxg"
> }
> }
> }'
{"took":2,"timed_out":false,"_shards":{"total":1,"successful":1,"skipped":0,"failed":0},"hits":{"total":{"value":1,"relation":"eq"},"max_score":0.2876821,"hits":[{"_index":"twitter","_id":"1","_score":0.2876821,"_source":{
"name": "liuxg",
"company": "elastic"
}
}]}
显然这个是我们想要的结果。
到目前位置,结果非常完美。我们可以使用 dump 过滤器来展示很多的细节。我们接着修改上面的 gateway.yml 文件。
gateway.yml
path.data: data
path.logs: log
entry:
- name: my_es_entry
enabled: true
router: my_router
max_concurrency: 10000
network:
binding: 0.0.0.0:8000
- name: my_kibana_entry
enabled: true
router: my_kibana_router
network:
binding: 0.0.0.0:5602
flow:
- name: es-flow
filter:
- echo:
message: "Before ES request\n"
- dump:
uri: true
request_header: true
request_body: true
response_body: true
status_code: true
context:
- _ctx.id
- _ctx.tls
- _ctx.remote_addr
- _ctx.local_addr
- _ctx.request.host
- _ctx.request.method
- _ctx.request.uri
- _ctx.request.path
- _ctx.request.body
- _ctx.request.body_length
- _ctx.request.query_args.from
- _ctx.request.query_args.size
- _ctx.request.header.Accept
- _ctx.request.user
- _ctx.response.status
- _ctx.response.body
- _ctx.response.content_type
- _ctx.response.body_length
- _ctx.response.header.Env
- elasticsearch:
elasticsearch: es-server
- echo:
message: "After ES request\n"
- dump:
uri: true
request_header: true
request_body: true
response_body: true
status_code: true
context:
- _ctx.id
- _ctx.tls
- _ctx.remote_addr
- _ctx.local_addr
- _ctx.request.host
- _ctx.request.method
- _ctx.request.uri
- _ctx.request.path
- _ctx.request.body
- _ctx.request.body_length
- _ctx.request.query_args.from
- _ctx.request.query_args.size
- _ctx.request.header.Accept
- _ctx.request.user
- _ctx.response.status
- _ctx.response.body
- _ctx.response.content_type
- _ctx.response.body_length
- _ctx.response.header.Env
- name: logout_flow
filter:
- set_response:
status: 401
body: "Success logout!"
- drop:
- name: replace_logo_flow
filter:
- redirect:
uri: https://elasticsearch.cn/uploads/event/20211120/458c74ca3169260dbb2308dd06ef930a.png
- name: kibana_flow
filter:
- basic_auth:
valid_users:
elastic: u7-KUuNhF2DcGCCtugU0 # super elastic account
- http:
schema: "http" #https or http
host: "192.168.0.3:5601"
router:
- name: my_router
default_flow: es-flow
- name: my_kibana_router
default_flow: kibana_flow
rules:
- method:
- GET
- POST
pattern:
- "/_logout"
flow:
- logout_flow
- method:
- GET
pattern:
- "/plugins/kibanaReact/assets/illustration_integrations_lightmode.svg"
flow:
- replace_logo_flow
elasticsearch:
- name: es-server
enabled: true
endpoints:
- https://192.168.0.3:9200
- https://192.168.0.8:9200
basic_auth:
username: elastic
password: u7-KUuNhF2DcGCCtugU0
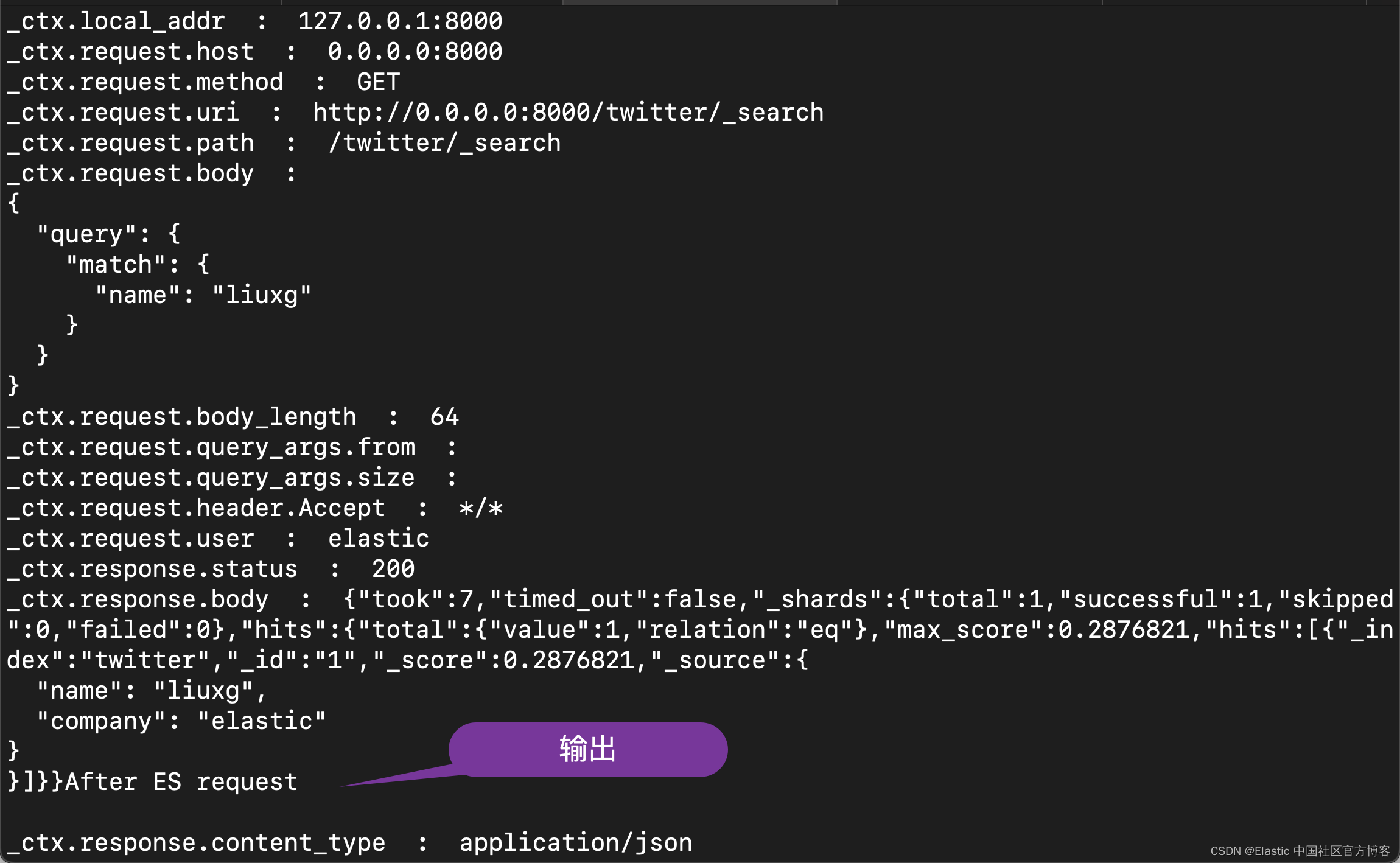
在上面,请注意 echo 和 dump 过滤器的部分。我们分别在 Elasticsearch 请求前后 dump 请求及响应的值。我们重新运行 gateway:
./gateway-mac-arm64
我们在 gateway 的 console 里可以看到如下的输出:

接下来,我们再创建一个文档:
PUT twitter/_doc/2
{
"name": "zhang san",
"company": "elastic"
}
如果我们使用如下的方式来搜索的话,应该是两个文档:
GET twitter/_search?filter_path=**.hits
{
"query": {
"match": {
"company": "elastic"
}
}
}
上面返回的结果将会是:
{
"hits" : {
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "twitter",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 0.13353139,
"_source" : {
"name" : "liuxg",
"company" : "elastic"
}
},
{
"_index" : "twitter",
"_id" : "2",
"_score" : 0.13353139,
"_source" : {
"name" : "zhang san",
"company" : "elastic"
}
}
]
}
}
接下来,我们来尝试修改请求,不管在任何情况下,返回的结果只有一个。我们修改 gateway.yml 文件如下:
gateway.yml
path.data: data
path.logs: log
entry:
- name: my_es_entry
enabled: true
router: my_router
max_concurrency: 10000
network:
binding: 0.0.0.0:8000
- name: my_kibana_entry
enabled: true
router: my_kibana_router
network:
binding: 0.0.0.0:5602
flow:
- name: es-flow
filter:
- echo:
message: "Before ES request\n"
- request_body_json_set:
path:
- size -> 1
- dump:
uri: true
request_header: true
request_body: true
response_body: true
status_code: true
context:
- _ctx.id
- _ctx.tls
- _ctx.remote_addr
- _ctx.local_addr
- _ctx.request.host
- _ctx.request.method
- _ctx.request.uri
- _ctx.request.path
- _ctx.request.body
- _ctx.request.body_length
- _ctx.request.query_args.from
- _ctx.request.query_args.size
- _ctx.request.header.Accept
- _ctx.request.user
- _ctx.response.status
- _ctx.response.body
- _ctx.response.content_type
- _ctx.response.body_length
- _ctx.response.header.Env
- elasticsearch:
elasticsearch: es-server
- set_response_header:
headers:
- Env -> Dev
- echo:
message: "After ES request\n"
- dump:
uri: true
request_header: true
request_body: true
response_body: true
status_code: true
context:
- _ctx.id
- _ctx.tls
- _ctx.remote_addr
- _ctx.local_addr
- _ctx.request.host
- _ctx.request.method
- _ctx.request.uri
- _ctx.request.path
- _ctx.request.body
- _ctx.request.body_length
- _ctx.request.query_args.from
- _ctx.request.query_args.size
- _ctx.request.header.Accept
- _ctx.request.user
- _ctx.response.status
- _ctx.response.body
- _ctx.response.content_type
- _ctx.response.body_length
- _ctx.response.header.Env
- name: logout_flow
filter:
- set_response:
status: 401
body: "Success logout!"
- drop:
- name: replace_logo_flow
filter:
- redirect:
uri: https://elasticsearch.cn/uploads/event/20211120/458c74ca3169260dbb2308dd06ef930a.png
- name: kibana_flow
filter:
- basic_auth:
valid_users:
elastic: u7-KUuNhF2DcGCCtugU0 # super elastic account
- http:
schema: "http" #https or http
host: "192.168.0.3:5601"
router:
- name: my_router
default_flow: es-flow
- name: my_kibana_router
default_flow: kibana_flow
rules:
- method:
- GET
- POST
pattern:
- "/_logout"
flow:
- logout_flow
- method:
- GET
pattern:
- "/plugins/kibanaReact/assets/illustration_integrations_lightmode.svg"
flow:
- replace_logo_flow
elasticsearch:
- name: es-server
enabled: true
endpoints:
- https://192.168.0.3:9200
- https://192.168.0.8:9200
basic_auth:
username: elastic
password: u7-KUuNhF2DcGCCtugU0
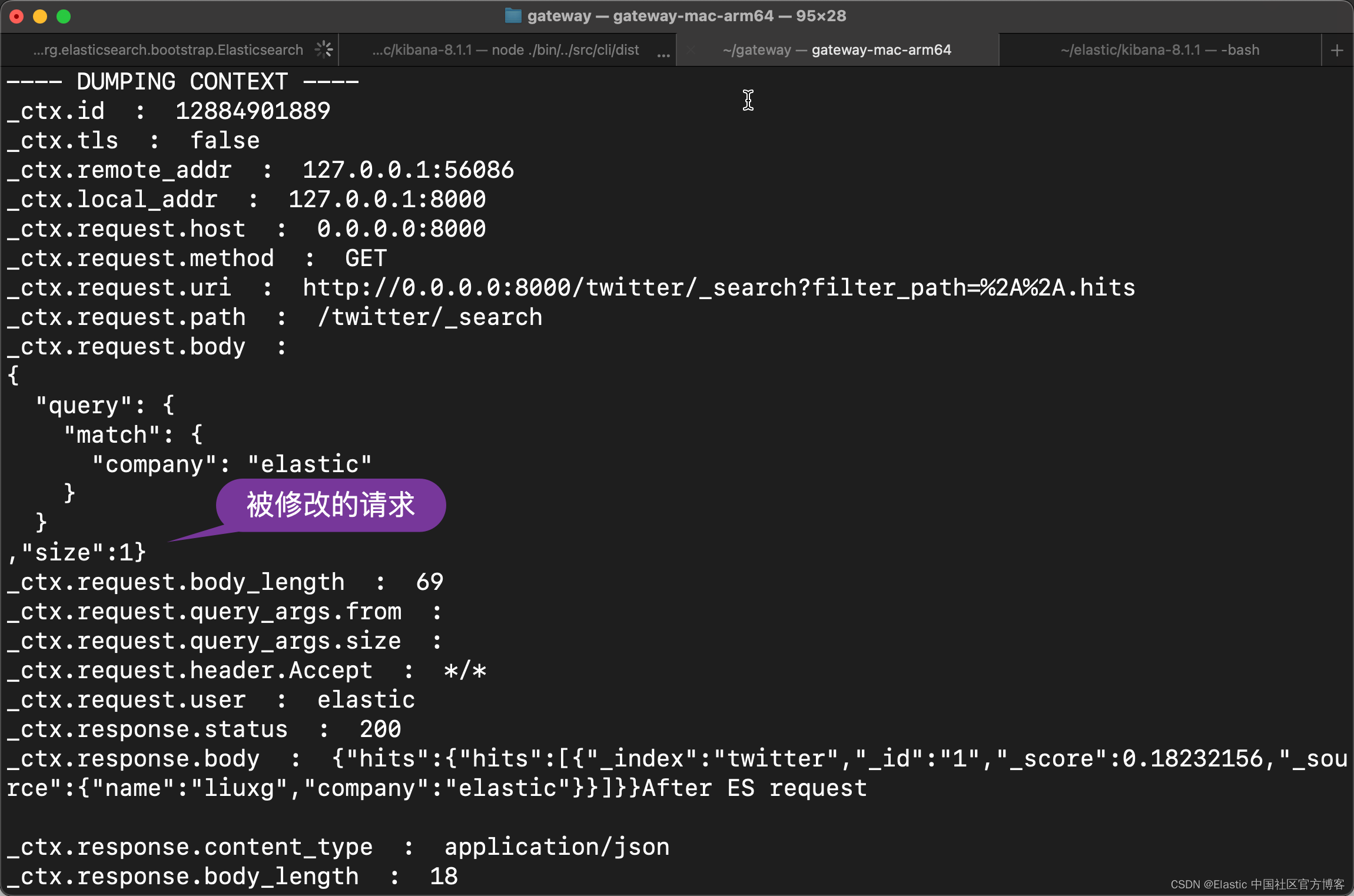
在上面,我们在请求之前,通过 request_body_json_set 过滤器把请求里的 body 进行修改。把 size 设置为 1。
- request_body_json_set:
path:
- size -> 1
这样我们的请求就变成了:
GET twitter/_search?filter_path=**.hits
{
"size": 1,
"query": {
"match": {
"company": "elastic"
}
}
}
虽然,在客户端,我们任然可以通过如下的方式来进行请求:
curl --insecure -u elastic:u7-KUuNhF2DcGCCtugU0 -XGET "http://0.0.0.0:8000/twitter/_search?filter_path=**.hits" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"query": {
"match": {
"company": "elastic"
}
}
}'
但是我们得到的结果是:
$ curl --insecure -u elastic:u7-KUuNhF2DcGCCtugU0 -XGET "http://0.0.0.0:8000/twitter/_search?filter_path=**.hits" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"query": {
"match": {
"company": "elastic"
}
}
}'
{"hits":{"hits":[{"_index":"twitter","_id":"1","_score":0.18232156,"_source":{"name":"liuxg","company":"elastic"}}]}}After ES request
我们只看到一个结果,而不是之前的两个尽管我们的请求没有设置 size 的值。
另外,我们也可以干预返回的响应。我们在请求之后,也添加了如下的过滤器:
- set_response_header:
headers:
- Env -> Dev
在我们的 gateway 运行的 console 中,我们可以看到:
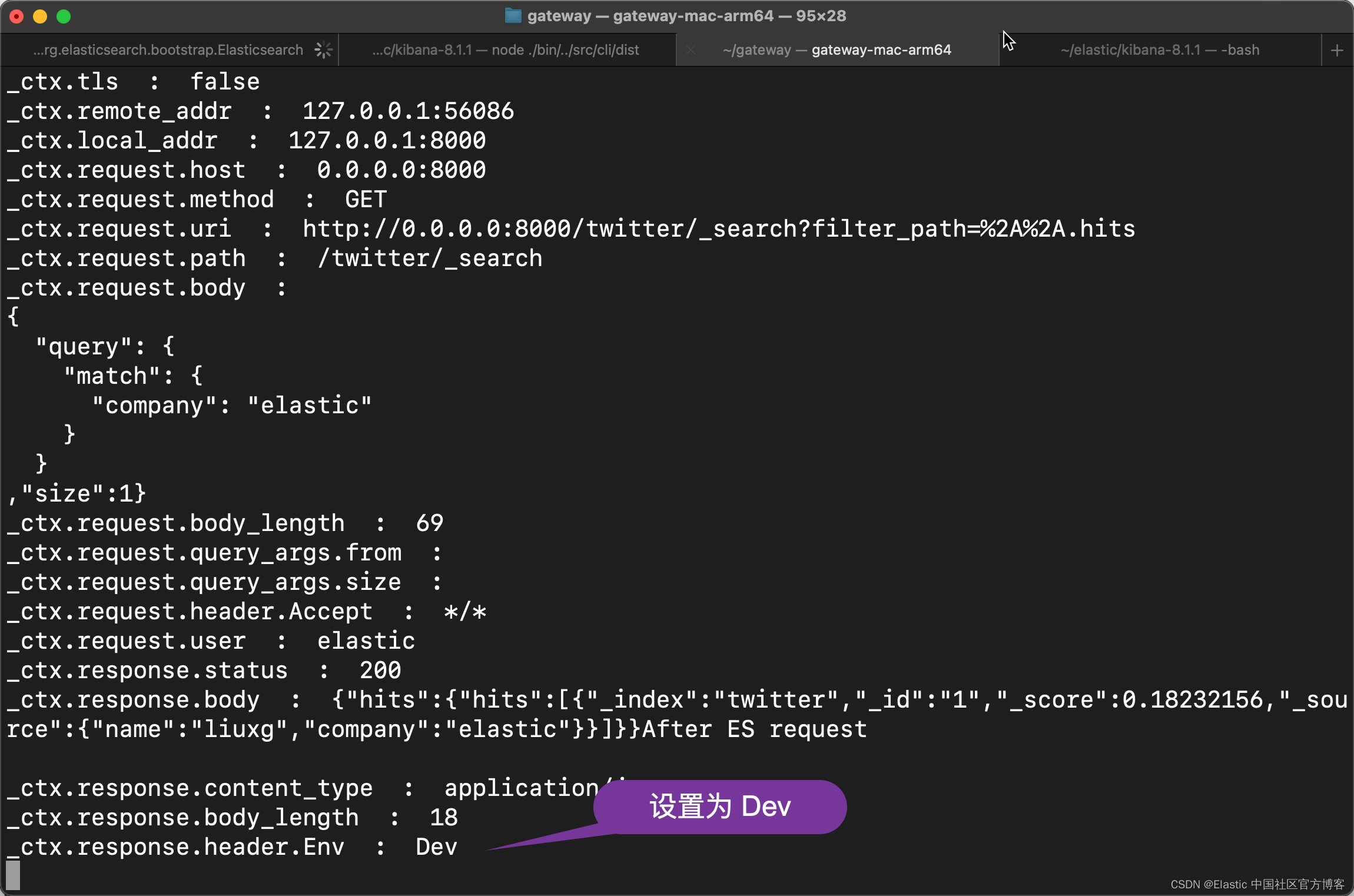
显然,我们针对 response 做了修改。
再举一个例子,我们可以利用网关提供的 request_client_ip_filter 过滤器来过滤一些不喜欢的 IP 地址的请求。比如,我们使用如下的 gateway.yml 文件:
path.data: data
path.logs: log
entry:
- name: my_es_entry
enabled: true
router: my_router
max_concurrency: 10000
network:
binding: 0.0.0.0:8000
- name: my_kibana_entry
enabled: true
router: my_kibana_router
network:
binding: 0.0.0.0:5602
flow:
- name: print_strangers
filter:
- echo:
message: "Hello, stranger\n"
- name: es-flow
filter:
- request_client_ip_filter:
action: redirect_flow
flow: print_strangers
exclude:
- 192.168.0.4
- echo:
message: "Before ES request\n"
- elasticsearch:
elasticsearch: es-server
- set_response_header:
headers:
- Env -> Dev
- echo:
message: "After ES request\n"
- name: logout_flow
filter:
- set_response:
status: 401
body: "Success logout!"
- drop:
- name: replace_logo_flow
filter:
- redirect:
uri: https://elasticsearch.cn/uploads/event/20211120/458c74ca3169260dbb2308dd06ef930a.png
- name: kibana_flow
filter:
- basic_auth:
valid_users:
elastic: u7-KUuNhF2DcGCCtugU0 # super elastic account
- http:
schema: "http" #https or http
host: "192.168.0.3:5601"
router:
- name: my_router
default_flow: es-flow
- name: my_kibana_router
default_flow: kibana_flow
rules:
- method:
- GET
- POST
pattern:
- "/_logout"
flow:
- logout_flow
- method:
- GET
pattern:
- "/plugins/kibanaReact/assets/illustration_integrations_lightmode.svg"
flow:
- replace_logo_flow
elasticsearch:
- name: es-server
enabled: true
endpoints:
- https://192.168.0.3:9200
- https://192.168.0.8:9200
basic_auth:
username: elastic
password: u7-KUuNhF2DcGCCtugU0
elastic:
elasticsearch: es-server
enabled: true
remote_configs: true
health_check:
enabled: false
availability_check:
enabled: false
metadata_refresh:
enabled: true
store:
enabled: true
orm:
enabled: true
init_template: true
template_name: ".infini"
index_prefix: ".infini_"
在上面,我们过滤来做 IP 地址 192.168.0.4 的请求。如果有来做这个 IP 地址的请求,我们返回信息为:Hello, stranger:
 我们在这里可以看到许多关于请求及响应的详细情况。我们可以根据这些 context,请求的类型,请求的 body,响应的 body 结合一些条件可以做出非常多的用户案例。比如在文章 “使用极限网关来处置 Elasticsearch 的 Apache Log4j 漏洞” 中介绍的那样,可以修复漏洞。拒绝一些请求。再比如,在文章 “在线查询修复的实现” 中,它实现对请求的修复。当然也可以对 response 进行修改。
我们在这里可以看到许多关于请求及响应的详细情况。我们可以根据这些 context,请求的类型,请求的 body,响应的 body 结合一些条件可以做出非常多的用户案例。比如在文章 “使用极限网关来处置 Elasticsearch 的 Apache Log4j 漏洞” 中介绍的那样,可以修复漏洞。拒绝一些请求。再比如,在文章 “在线查询修复的实现” 中,它实现对请求的修复。当然也可以对 response 进行修改。
结论
INFINI 网关置于 Elasticsearch 集群的前端。它是一个轻量级的高可用的网关。它可对客户端的请求动态地进行截获及分析。它含有丰富的过滤器供开发者使用。我们可以充分利用这些过滤器对来自客户端的请求进行分析,组装,拒绝,也可以针对响应做更改。当然,它还有很多其它的功能供开发者使用,比如,轻松实现跨集群搜索及备份。针对一些请求进行限流。有很多功能需要我们一起共同挖掘。
版权归原作者 Elastic 中国社区官方博客 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。