文章目录
0 前言
🔥 这两年开始毕业设计和毕业答辩的要求和难度不断提升,传统的毕设题目缺少创新和亮点,往往达不到毕业答辩的要求,这两年不断有学弟学妹告诉学长自己做的项目系统达不到老师的要求。
为了大家能够顺利以及最少的精力通过毕设,学长分享优质毕业设计项目,今天要分享的是
🚩 基于大数据的共享单车数据分析与可视化
🥇学长这里给一个题目综合评分(每项满分5分)
- 难度系数:3分
- 工作量:3分
- 创新点:4分
1 课题背景
前几年共享单车项目在国内大热,五颜六色的单车一夜之间遍布城市的各个角落。其实,早在3年前国外就有类似的项目兴起:通过历史用车记录结合天气等数据预测共享单车项目在华盛顿的需求
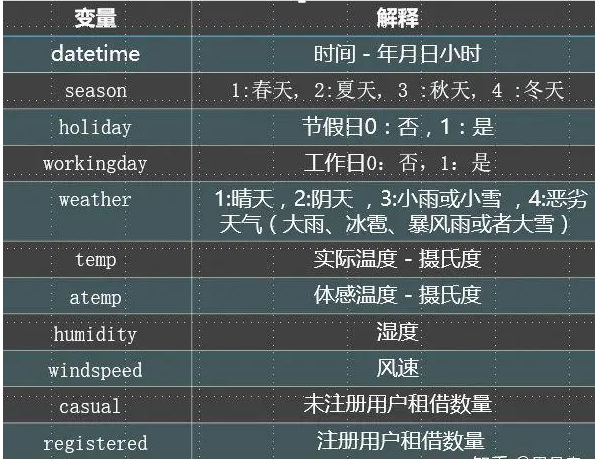
数据的特征解释
2 数据清洗
导库
import datetime
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pyecharts.charts import*import pyecharts.options as opts
from pyecharts.faker import Faker
from pyecharts.commons.utils import JsCode
读数据
df=pd.read_csv('data.csv')
提出假设
这里我们将研究决定单车租借的因素,上面给出了各个特征的解释,首先我们先大胆的提出假设:
- 租借数量可能时间有关
- .租借数量可能与天气的好坏有着很大的联系
- 租借的数量与是否为工作日有关
- 租借的数量可能与风速有关
查看有无缺失值和数据类型的情况
发现并无缺失值,不过时间的数据类型是object 需要转化为时间类型,同时为了更方便的分析数据,将datetime拆为 Year Month Weekday Hour
特征提取
#数据预处理
data['season']= data['season'].map({1:'spring',2:'summer',3:'fall',4:'winner'})
data['weather']= data['weather'].map({1:'Good',2:'Normal',3:'Bad',4:'ver Bad'})
#特征衍生
data['datetime']= pd.to_datetime(data['datetime'])
data['year']= data.datetime.apply(lambda d:d.year)
data['month']= data.datetime.apply(lambda d:d.month)
data['day']= data.datetime.apply(lambda d:d.day)
data['hour']= data.datetime.apply(lambda d:d.hour)
data['minute']= data.datetime.apply(lambda d:d.minute)
data.head()
查看一下各个特征的相关性*
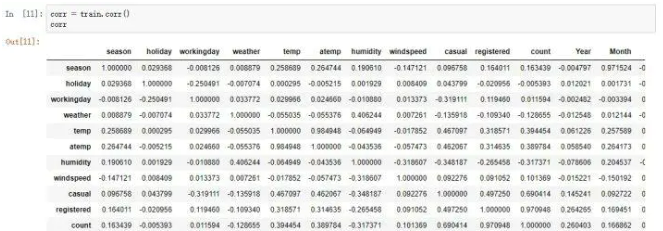
可以看出与count正相关最大的是temp 和atemp,holiday的相关性最小
3 数据可视化
通过Matplotlib、Seaborn等工具可视化理解数据,分析特征与标签之间的相关性。
热力图
为了更直观的表现出数据的背后意义,我们需要用可视化来做辅助,首先将上述的相关系数的数据可视化为热力图的呈现方式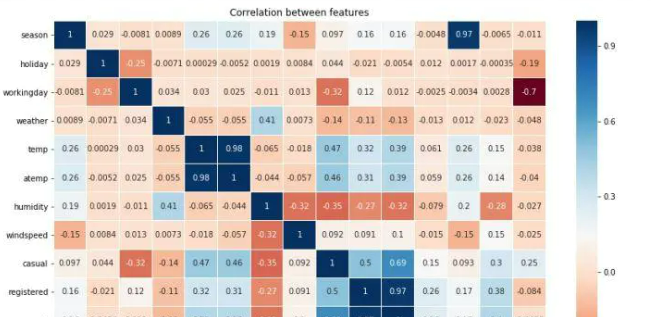
整体特征分布
sns.set_style('ticks')
plt.figure(figsize=(10,6))
sns.kdeplot(data['count'])
sns.despine(left=True)
plt.grid(linestyle='--',alpha=0.5,axis='y')
plt.title('Demand Distribution',fontsize=15)
plt.xlabel('Demand',fontsize=13)
plt.ylabel('Frequence',fontsize=13)
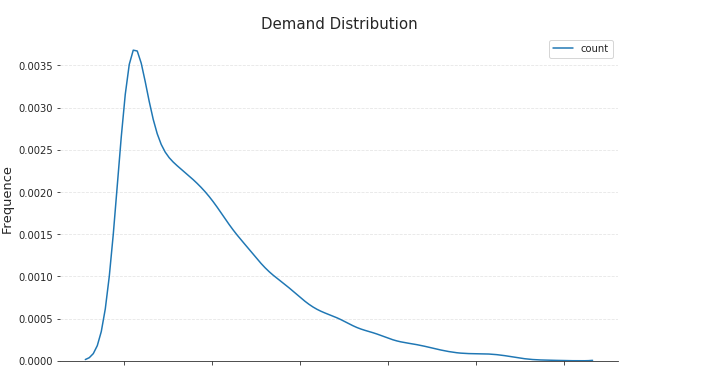
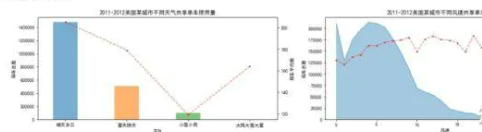
查看2011-2012间的单车租借情况
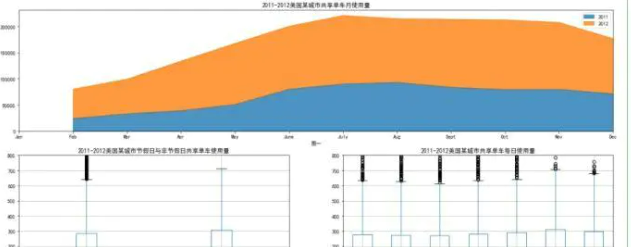
1.图一是2011-2012年的每月租借情况,较去年租借数量,2012同比上升较大,图示2012的面积是2011的2倍以上,各月的增长情况相类似,特别11-12月份成下坡趋势,猜测可能是温度的原因,季节属于冬季
2.图二是节假日和非节假日的租借数量的箱形图,不难看出,租借的数量的离散型情况相似。
3.图三是每星期的离散情况,周末有异常值,数量并不是很多,可能与活动有关,增加了出行的人数
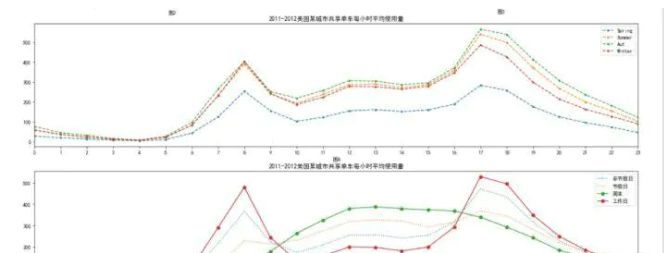
上述两图分别是季节和工作日的线形图
1.图一中,各季节的租借趋势相同,同时秋季最高,春季最低,租借的高峰时间7-9和16-18点正好是早晚高峰时间
2.图二也呈现出形式的趋势,在工作日租借的高峰时间7-9和16-18点,同时与此相反,非工作日,11-16点的租借人数最高,符合睡觉睡到自然醒。
附上代码
#绘制图像
fig,[ax1,ax2]= plt.subplots(2,1,figsize=(12,15))
plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.3)
Month_tendency_2011.plot(kind='line',linestyle='--',linewidth=2,colormap='Set1',ax=ax1)
ax1.set_title('2011 Demand Tendency',fontsize=15)
ax1.grid(linestyle='--',alpha=0.8)
ax1.set_ylim(0,150000)
ax1.set_xlabel('Month',fontsize=13)
ax1.set_ylabel('Count',fontsize=13)
Month_tendency_2012.plot(kind='line',linestyle='--',linewidth=2,colormap='Set1',ax=ax2)
ax2.set_title('2012 Demand Tendency',fontsize=15)
ax2.grid(linestyle='--',alpha=0.8)
ax2.set_ylim(0,150000)
ax2.set_xlabel('Month',fontsize=13)
ax2.set_ylabel('Count',fontsize=13)
sns.despine(left=True)
天气对于租借数量的影响
Weather_Demand=data.groupby(['weather','day'])[['count']].sum()
Weather_Demand.reset_index(inplace=True)
plt.figure(figsize=(12,6))
sns.stripplot(x='weather',y='count',data=Weather_Demand,palette='Set2',jitter=True,alpha=1.0)
sns.despine(left=True)
plt.xlabel('Season',fontsize=13)
plt.ylabel('Count',fontsize=13)
plt.title('Demand Distribution by Weather',fontsize=15)
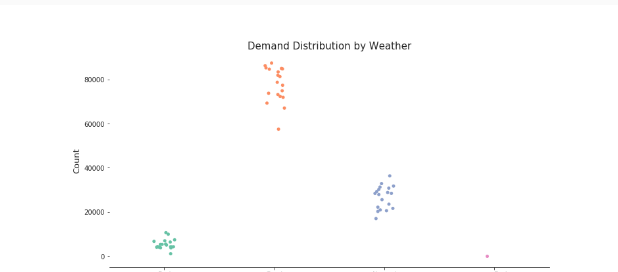
上述两图分别是4中天气情况下的租借总数,平均数和不同风速下的租借总数,平均数
1.晴天多云的租借总数最多平均数也最多,天气越好租借的概率越大,大雨大雪的租借平均数反倒上升,取出这个天气下的数据,发现只有一例,为特殊情况,不予分析
2.风速对于租借的影响还是很大的,风速超过25就少有租借情况,毕竟骑起来太累了,风速在10以下租借情况良好,同时当风速超过25后,平均租借数量上升,图中也能看出这种情况下的租借数量很少,不做考虑
湿度与温度对于租借数量的影响
plt.figure(figsize=(10,8))
sns.kdeplot(data['temp'],data['atemp'],shade=True,shade_lowest=False,cut=10,cmap='YlGnBu',cbar=True)
sns.despine(left=True)
plt.grid(linestyle='--',alpha=0.4)
plt.xlim(0,50)
plt.ylim(0,50)
plt.xlabel('Temperature',fontsize=13)
plt.ylabel('Atemp',fontsize=13)
plt.title('correlation of temp and atemp',fontsize=15)
# 温度与湿度的关系度量
plt.figure(figsize=(10,8))
sns.kdeplot(data['temp'],data['humidity'],shade=True,shade_lowest=False,cut=10,cmap='YlGnBu',cbar=True)
sns.despine(left=True)
plt.grid(linestyle='--',alpha=0.4)
plt.xlim(0,40)
plt.ylim(0,110)
plt.xlabel('Temperature',fontsize=13)
plt.ylabel('Humidity',fontsize=13)
plt.title('correlation of temp and humidity',fontsize=15)
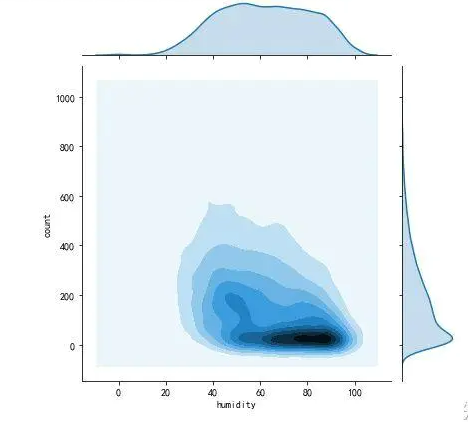
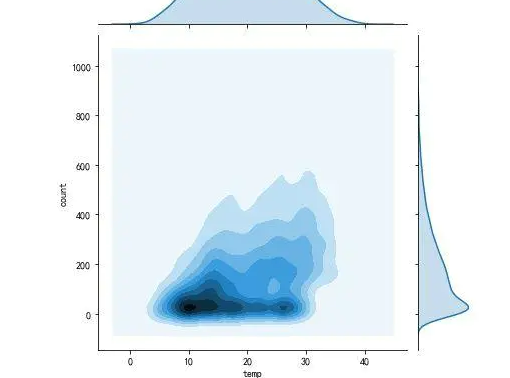
上述两图为温度与湿度对于租借情况的影响,温度和租借数量呈现正相关,湿度呈现负相关,租借数量在15-30度适应性最好,30度到35度租借数量没有低于100的情况,不多租借的数量不是很多,颜色较浅,湿度在30-60适应性最好
注册用户与未注册用户
# 衍生特征
data['dif']=data['registered']-data['casual']# 衍生特征注册用户与非注册用户的骑行需求差值
fig,axes=plt.subplots(2,2,figsize=(20,8))
plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.3,wspace=0.1)# 绘制子图1:月度差异
Month_Dif =data.groupby('month')[['casual','registered']].mean()
Month_Dif.plot(kind='line',linestyle='--',linewidth=2,colormap='Set1',ax=axes[0,0])
axes[0,0].set_title('Month Demand Tendency Dif',fontsize=15)
axes[0,0].grid(linestyle='--',alpha=0.8)
axes[0,0].set_xlabel('Month',fontsize=13)
axes[0,0].set_ylabel('Count',fontsize=13)#绘制子图2:小时差异
Hour_Dif = data.groupby('hour')[['casual','registered']].mean()
Hour_Dif.plot(kind='line',linestyle='--',linewidth=2,colormap='Set1',ax=axes[0,1])
axes[0,1].set_title('Hour Demand Tendency Dif',fontsize=15)
axes[0,1].grid(linestyle='--',alpha=0.8)
axes[0,1].set_xlabel('Hour',fontsize=13)
axes[0,1].set_ylabel('Count',fontsize=13)# 绘制子图3:工作日差异
H2_1 = data[data.workingday==1].groupby('hour')[['casual','registered']].mean()# 工作日
H2_0 = data[data.workingday==0].groupby('hour')[['casual','registered']].mean()# 非工作日
H2_1.plot(kind='line',linestyle='--',linewidth=2,colormap='Set1',ax=axes[1,0])
axes[1,0].set_title('Workingday Hour Demand Dif',fontsize=15)
axes[1,0].grid(linestyle='--',alpha=0.8)
axes[1,0].set_xlabel('Hour',fontsize=13)
axes[1,0].set_ylabel('Count',fontsize=13)# 绘制子图4:非工作日差异
H2_0.plot(kind='line',linestyle='--',linewidth=2,colormap='Set1',ax=axes[1,1])
axes[1,1].set_title('Holiday Hour Demand Dif',fontsize=15)
axes[1,1].grid(linestyle='--',alpha=0.8)
axes[1,1].set_xlabel('Hour',fontsize=13)
axes[1,1].set_ylabel('Count',fontsize=13)
sns.despine(left=True)
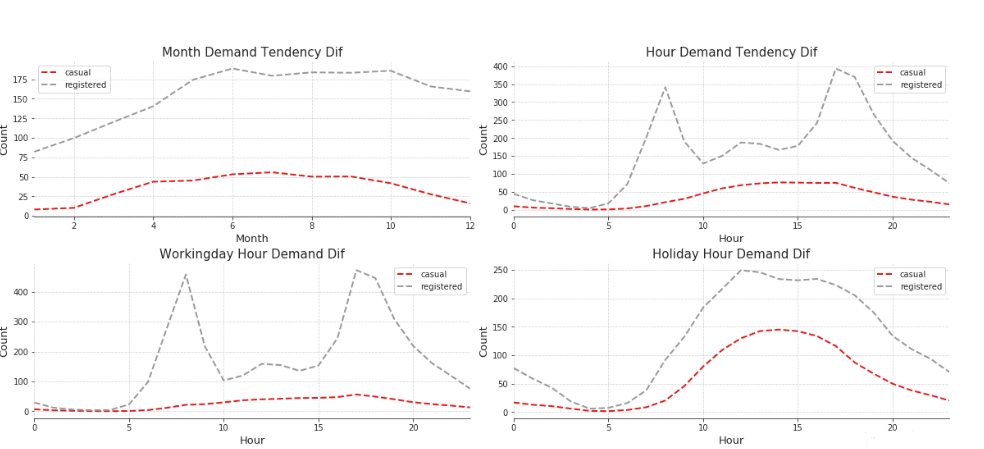
上面四幅为注册用户与非注册用户在各因素下的差异组合图(从左到右排序):
p1是月度差异图,整体趋势相同,注册用户远高于非注册用户;
p2是小时差异图,注册用户的小时规律明显,非注册用户则只在12am~5pm存在峰值,整体差异较大;
p3是工作日差异图,注册用户工作日小时规律明显,二非注册用户趋势平缓;
p4是非工作日差异图,非工作日两者差异相较于其他因素差异较小,且趋势相同。
总体来说,注册用户需求远高于非注册用户,注册用户的使用规律明显,而非注册用户受其他因素的影响相对较弱。
4 总结:
通过以上的可视化分析,我们可以清晰的发现印象租借数量的因素
1.温度对于租借的影响较大,15-30度间,租借数量最多,呈正相关
2.湿度在30-60的时候租借数量最大,呈负相关
3.早晚高峰时间段租借数量最多
4.早晚高峰时间段租借的用户较多为注册用户,注册用户周末租借量减少,相反,非租借用户周末租借量增加
5.天气情况和风速对于租借也有较大的影响,晴天租借最多,大雨大雪租借最少,风速在10以下租借的数量最多
6.共享单车前景良好,12较11年租借数量有增加2倍之多
5 最后
版权归原作者 caxiou 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。