RabbitMQ的安装与使用
介绍
RabbitMQ是一个在AMQP基础上完成的,可复用的企业消息系统。他遵循Mozilla Public License开源协议。开发语言为Erlang。
linux系统中安装RabbitMQ比较繁琐,这里使用的是Docker安装。
一、RabbitMQ的安装
1 查找镜像
docker search rabbitmq:management

2 拉取镜像
docker pull macintoshplus/rabbitmq-management
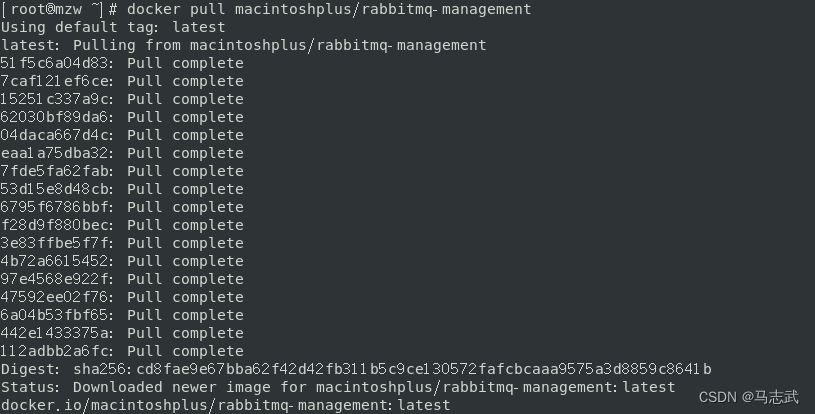
3 查看镜像
docker images

4 创建容器
docker run -d--hostname mzw-rabbitmq --name rabbitmq -eRABBITMQ_DEFAULT_USER=admin -eRABBITMQ_DEFAULT_PASS=admin -p15672:15672 -p5672:5672 c20
命令解读:
- 运行一个镜像
- -d 后台守护运行
- –hostname mzw-rabbitmq 指定主机名称
- –name 指定容器名称
- -e RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_USER=admin 指定用户名
- -e RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_PASS=admin 指定密码
- -p 15672:15672 -p 5672:5672 端口映射
- c20 镜像ID 简写

5 查看容器
dockerps

6 访问测试
访问地址:http://192.168.2.xx:15672/
输入启动容器时设置的用户密码登录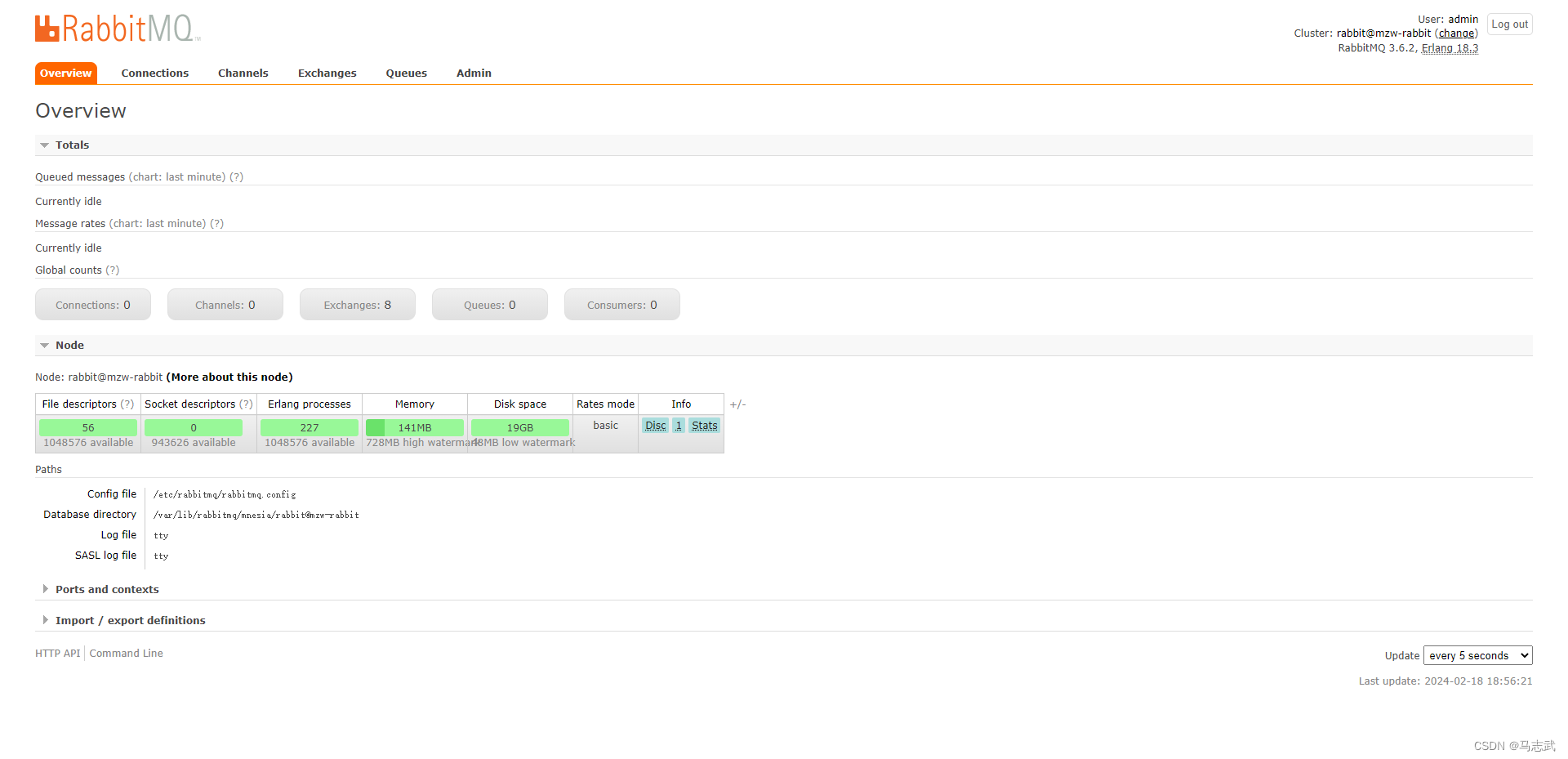
这就表示RabbitMQ安装成功了
二、RabbitMQ的使用
1 创建项目
创建SpringBoot项目并引入相关依赖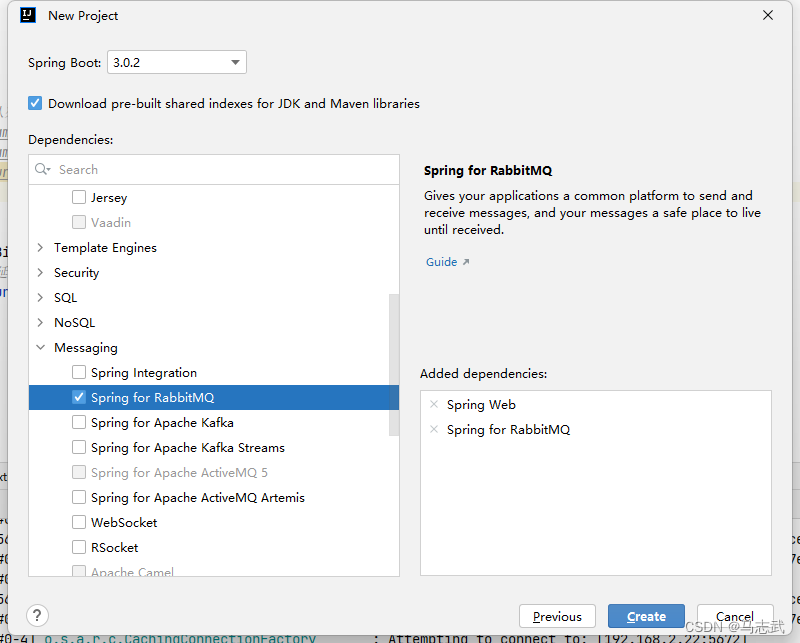
2 配置文件
# RabbitMQ 配置
spring.rabbitmq.name=rabbitmq-demo01
spring.rabbitmq.host=192.168.2.22
spring.rabbitmq.port=5672
spring.rabbitmq.username=admin
spring.rabbitmq.password=admin
# 自定义一个属性,设置队列的名称
mq.queue.name=hello-queue
3 队列配置文件
importorg.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;importorg.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;importorg.springframework.amqp.core.CustomExchange;importorg.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;importorg.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;importjava.util.HashMap;importjava.util.Map;// 添加@Configuration 注解,表示一个注解类@ConfigurationpublicclassQueueConfig{@Value("${mq.queue.name}")privateString queueName;/**
* 初始化短信队列
* @return
*/@BeanpublicQueuedelayedSmsQueueInit(){returnnewQueue(queueName);}}
4 消费者
importorg.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;importorg.springframework.stereotype.Component;/**
* 创建一个rabbitmq消费者
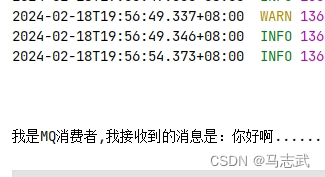
*/@ComponentpublicclassReceiver{// 接受MQ消息 并 处理消息@RabbitListener(queues ={"${mq.queue.name}"})publicvoidprocess(String msg){// 处理消息System.out.println("我是MQ消费者,我接收到的消息是:"+ msg );}}
5 生产者
importorg.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;importorg.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;importorg.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;importorg.springframework.stereotype.Component;/**
* 消息提供者
*/@ComponentpublicclassSender{@AutowiredprivateAmqpTemplate template;@Value("${mq.queue.name}")privateString queueName;// 发送消息publicvoidsend(String msg){// 队列名,消息内容
template.convertAndSend(queueName,msg);}}
6 测试
- 发送消息
@AutowiredprivateSender sender;@TestvoidcontextLoads(){ sender.send("你好啊......");} - 接收消息
三、交换器
RabbitMQ中有五种主要的交互器分别如下
交换器说明direct发布与订阅 完全匹配fanout广播topic主体,规则匹配fanout转发custom自定义
四、普通队列Demo
上边已经演示,这里不重复演示。
五、死信队列Demo
1 介绍
死信队列就是在某种情况下,导致消息无法被正常消费(异常,过期,队列已满等),存放这些未被消费的消息的队列即为死信队列。
2 示例
2.1 配置
- 配置文件
# RabbitMQ 配置
spring.rabbitmq.name=rabbitmq-demo01
spring.rabbitmq.host=192.168.2.22
spring.rabbitmq.port=5672
spring.rabbitmq.username=admin
spring.rabbitmq.password=admin
###死信队列
mq.dlx.exchange=mq_dlx_exchange
mq.dlx.queue=mq_dlx_queue
mq.dlx.routingKey=mq_dlx_key
###备胎交换机
mq.exchange=mq_exchange
mq.queue=mq_queue
mq.routingKey=routing_key
- 配置类
importorg.springframework.amqp.core.*;importorg.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;importjava.util.HashMap;importjava.util.Map;@ConfigurationpublicclassMQConfig{/**
* 普通交换机
*/@Value("${mq.exchange}")privateString mqExchange;/**
* 普通队列
*/@Value("${mq.queue}")privateString mqQueue;/**
* 普通路由key
*/@Value("${mq.routingKey}")privateString mqRoutingKey;/**
* 死信交换机
*/@Value("${mq.dlx.exchange}")privateString dlxExchange;/**
* 死信队列
*/@Value("${mq.dlx.queue}")privateString dlxQueue;/**
* 死信路由
*/@Value("${mq.dlx.routingKey}")privateString dlxRoutingKey;/**
* 声明死信交换机
* @return DirectExchange
*/@BeanpublicDirectExchangedlxExchange(){returnnewDirectExchange(dlxExchange);}/**
* 声明死信队列
* @return Queue
*/@BeanpublicQueuedlxQueue(){returnnewQueue(dlxQueue);}/**
* 声明普通业务交换机
* @return DirectExchange
*/@BeanpublicDirectExchangemqExchange(){returnnewDirectExchange(mqExchange);}/**
* 声明普通队列
* @return Queue
*/@BeanpublicQueuemqQueue(){// 普通队列绑定我们的死信交换机Map<String,Object> arguments =newHashMap<>(2);//死信交换机
arguments.put("x-dead-letter-exchange", dlxExchange);//死信队列
arguments.put("x-dead-letter-routing-key", dlxRoutingKey);returnnewQueue(mqQueue,true,false,false, arguments);}/**
* 绑定死信队列到死信交换机
* @return Binding
*/@BeanpublicBindingbinding(Queue dlxQueue,DirectExchange dlxExchange){returnBindingBuilder.bind(dlxQueue).to(dlxExchange).with(dlxRoutingKey);}/**
* 绑定普通队列到普通交换机
* @return Binding
*/@BeanpublicBindingmqBinding(Queue mqQueue,DirectExchange mqExchange){returnBindingBuilder.bind(mqQueue).to(mqExchange).with(mqRoutingKey);}}
2.2 生产者
importlombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;importorg.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;importorg.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;importorg.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;importorg.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;importorg.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;/**
* 生产者
*/@RestController@Slf4jpublicclassMQProducer{@AutowiredprivateRabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;/**
* 普通交换机
*/@Value("${mq.exchange}")privateString mqExchange;/**
* 普通路由key
*/@Value("${mq.routingKey}")privateString mqRoutingKey;@RequestMapping("/sendMsg")publicStringsendMsg(){String msg ="Hello RabbitMQ ......";//发送消息 参数一:交换机 参数二:路由键(用来指定发送到哪个队列)
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(mqExchange, mqRoutingKey, msg, message ->{// 设置消息过期时间 10秒过期 如果过期时间内还没有被消费 就会发送给死信队列
message.getMessageProperties().setExpiration("10000");return message;});
log.info("生产者发送消息:{}", msg);return"success";}}
2.3 消费者
importlombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;importorg.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;importorg.springframework.stereotype.Component;/**
* 消费者
*/@Component@Slf4jpublicclassMQConsumer{/**
* 监听队列回调的方法
*
* @param msg
*/@RabbitListener(queues ={"${mq.queue}"})publicvoidmqConsumer(String msg){
log.info("正常普通消费者消息MSG:{}", msg);}}
2.4 死信消费者
importlombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;importorg.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;importorg.springframework.stereotype.Component;/**
* 死信消费者
*/@Component@Slf4jpublicclassMQDlxConsumer{/**
* 死信队列监听队列回调的方法
*
* @param msg
*/@RabbitListener(queues ={"${mq.dlx.queue}"})publicvoidmqConsumer(String msg){
log.info("死信队列消费普通消息:msg{}", msg);}}
2.5 结果
访问:http://127.0.0.1:9023/sendMsg 会被 消费者 消费掉
将 消费者 代码注释掉,在访问http://127.0.0.1:9023/sendMsg,等待10秒钟后会被**死信队列**接收到。
六、延时队列Demo
- 两种方式: - 第一种:使用死信队列,将消息放入一个没有被监听的队列上,设置TTL(一条消息的最大存活时间)为延迟的时间,时间到了没有被消费,直接成为死信。监听死信队列来进行操作。- 第二种:使用rabbitmq官方提供的delayed插件来真正实现延迟队列。本文对第二种进行详解
1 安装延迟插件
官网下载:https://www.rabbitmq.com/community-plugins.html
我的RabbitMQ是3.12 b版本的,下载此插件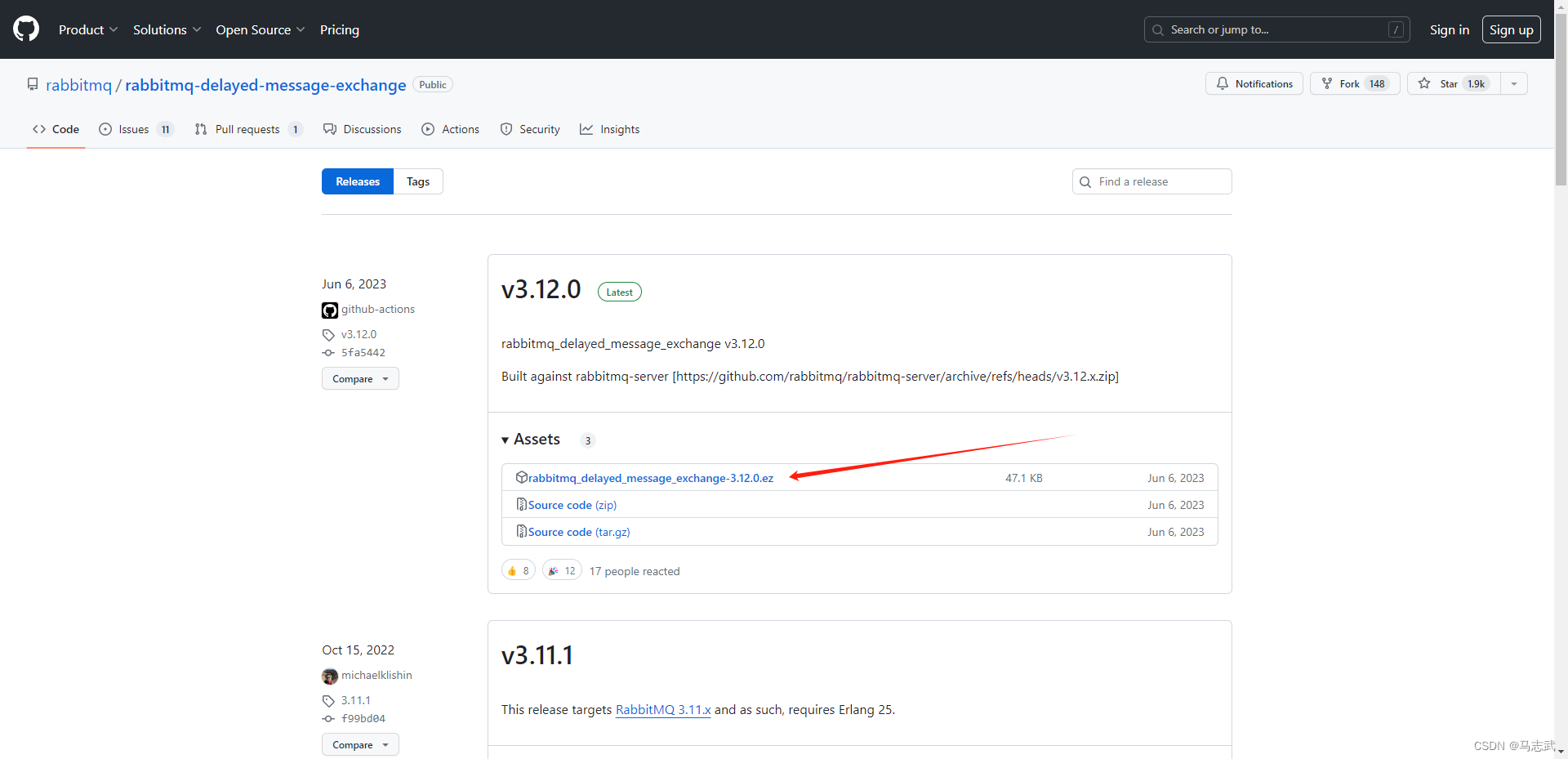
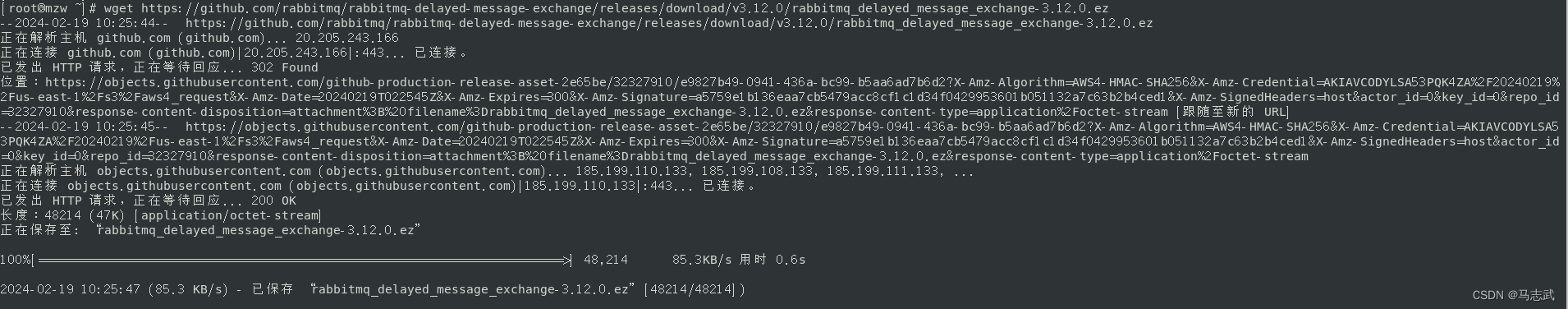
1.1 下载插件
wget https://github.com/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-delayed-message-exchange/releases/download/v3.12.0/rabbitmq_delayed_message_exchange-3.12.0.ez
1.2 将插件拷贝到RabbitMQ容器的插件目录
dockercp ./rabbitmq_delayed_message_exchange-3.12.0.ez de24369edeb4:/plugins

1.3 进入到容器
dockerexec-it de24369edeb4 /bin/bash
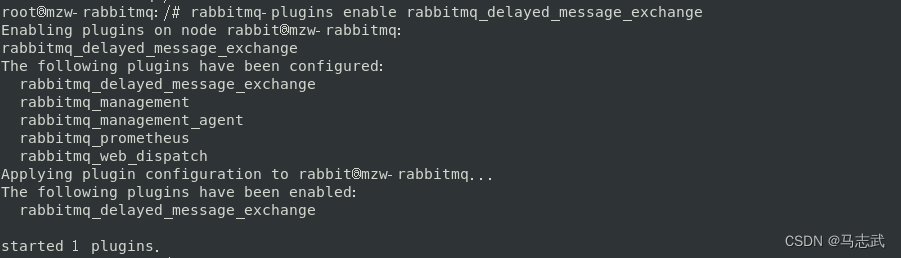
1.4 开启插件
rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_delayed_message_exchange
1.5 查看
rabbitmq-plugins list
E* 或 e* 代表 插件已启用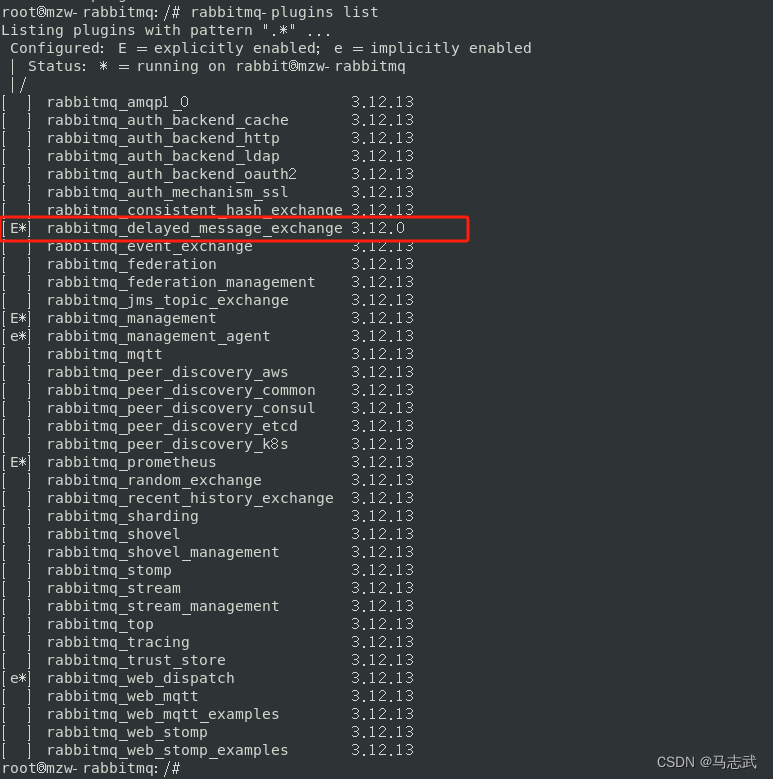
在RabbitMQ控制台可以看到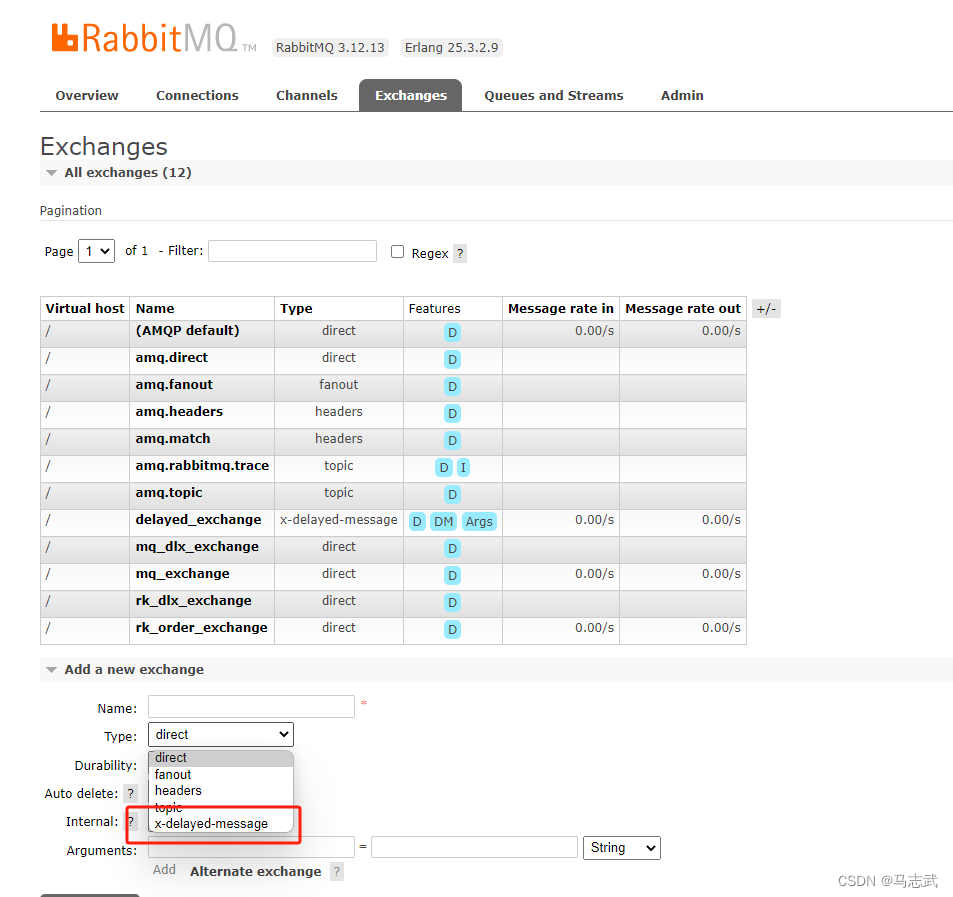
2 示例
2.1 配置
- 配置文件
# RabbitMQ 配置
spring.rabbitmq.name=rabbitmq-demo01
spring.rabbitmq.host=192.168.2.22
spring.rabbitmq.port=5672
spring.rabbitmq.username=admin
spring.rabbitmq.password=admin
# 自定义一个属性,设置队列的名称
mq.queue.name=hello-queue
- 配置类
importorg.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;importorg.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;importorg.springframework.amqp.core.CustomExchange;importorg.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;importorg.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;importjava.util.HashMap;importjava.util.Map;/**
* 使用x-delayed-message 延时队列插件
*/@ConfigurationpublicclassQueueConfig{@Value("${mq.queue.name}")privateString queueName;/**
* 初始化短信队列
* @return
*/@BeanpublicQueuedelayedSmsQueueInit(){returnnewQueue(queueName);}/**
* 初始化延迟交换机
* @return
*/@BeanpublicCustomExchangedelayedExchangeInit(){Map<String,Object> args =newHashMap<>();// 设置类型,可以为fanout、direct、topic
args.put("x-delayed-type","direct");// 第一个参数是延迟交换机名字,第二个是交换机类型,第三个设置持久化,第四个设置自动删除,第五个放参数returnnewCustomExchange("delayed_exchange","x-delayed-message",true,false,args);}/**
* 短信队列绑定到交换机
* @param delayedSmsQueueInit
* @param customExchange
* @return
*/@BeanpublicBindingdelayedBindingSmsQueue(Queue delayedSmsQueueInit,CustomExchange customExchange){// 延迟队列绑定延迟交换机并设置RoutingKey为smsreturnBindingBuilder.bind(delayedSmsQueueInit).to(customExchange).with("sms").noargs();}}
2.2 生产者
importlombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;importorg.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;importorg.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;importorg.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;importorg.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;importorg.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;/**
* 生产者
*/@RestController@Slf4jpublicclassSender{@AutowiredprivateAmqpTemplate template;@Value("${mq.queue.name}")privateString queueName;// 发送消息@RequestMapping("/sendMsg")publicvoidsend(){String msg ="Hello RabbitMQ ......";// 队列名,消息内容
template.convertAndSend(queueName,msg);
log.info("生产者发送消息:{}", msg);}@RequestMapping("/sendDelayedMsg")publicvoidsendDelayedMsg(){String msg ="Hello RabbitMQ Delayed ......";// 第一个参数是延迟交换机名称,第二个是Routingkey,第三个是消息主题,第四个是X,并设置延迟时间,单位 是毫秒
template.convertAndSend("delayed_exchange","sms",msg,a ->{
a.getMessageProperties().setDelay(2000);return a;});
log.info("生产者发送延时消息:{}", msg);}}
2.3 消费产者
importlombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;importorg.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;importorg.springframework.stereotype.Component;/**
* 消费者
*/@Component@Slf4jpublicclassReceiver{// 接受MQ消息 并 处理消息@RabbitListener(queues ={"${mq.queue.name}"})publicvoidprocess(String msg){// 处理消息
log.info("我是MQ消费者,我接收到的消息是:{}", msg);}}
2.4 结果
访问:http://127.0.0.1:9022/sendMsg
访问:http://127.0.0.1:9022/sendDelayedMsg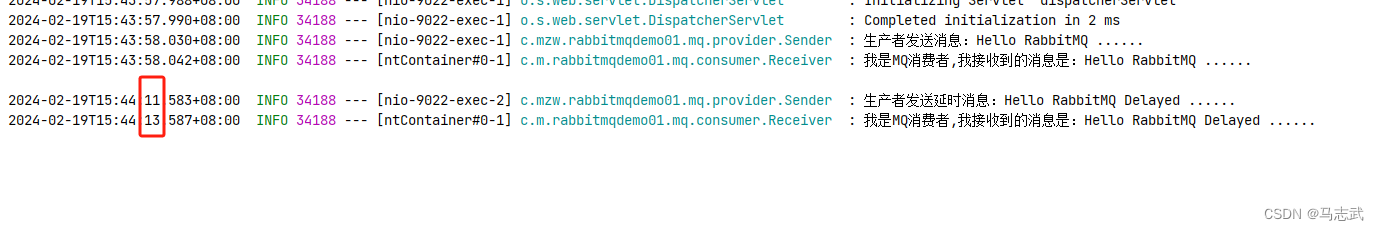
版权归原作者 马志武 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。