一.Sring项目中关于MyBatis的配置
1.在pom.xml中引入框架依赖
这里手动进行添加,通过在已有的spring项目中的pom.xml文件中引入以下依赖
<!-- 添加 MyBatis 框架 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.1.4</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 添加 MySQL 驱动 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
2.配置文件配置相关信息
在application.properties中配置以下内容
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/blog?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
#配置mybatis的xml文件路径
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mapper/**Mapper.xml
这里关于xml文件路径配置的匹配规则是在当前mapper下所有文件名以Mapper.xml结尾的文件。
如下所示:

3.设置mapper中的xml文件内容
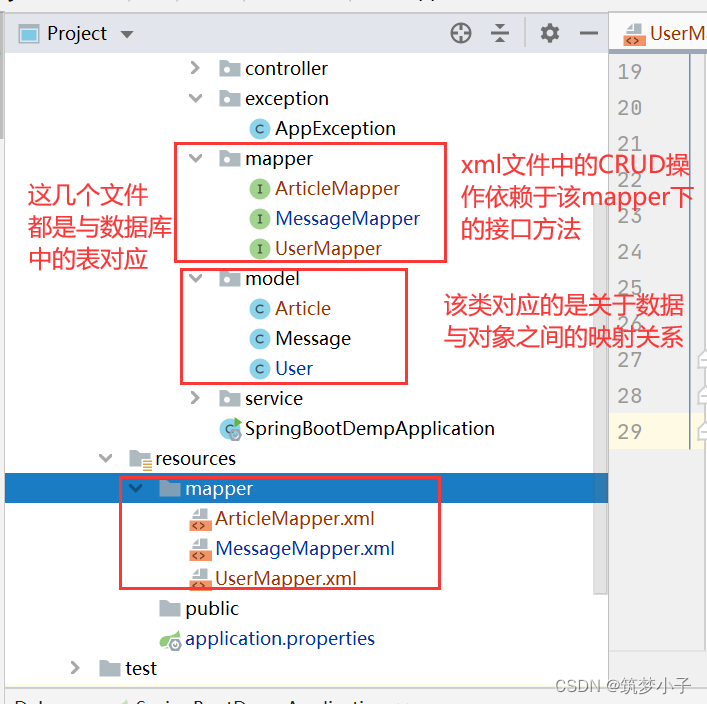
其中mapper中需要配置的内容有如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="org.example.mapper.UserMapper">
</mapper>
mapper里面就是对于CRUD操作的一些语句,只不过这些语句头需要遵守一些约束和规定,之后才能转化为java对象,并作为返回值返回给java中调用的方法。
4.根据以上配置实现的查询示例
查询前的配置:

(1)添加实体类
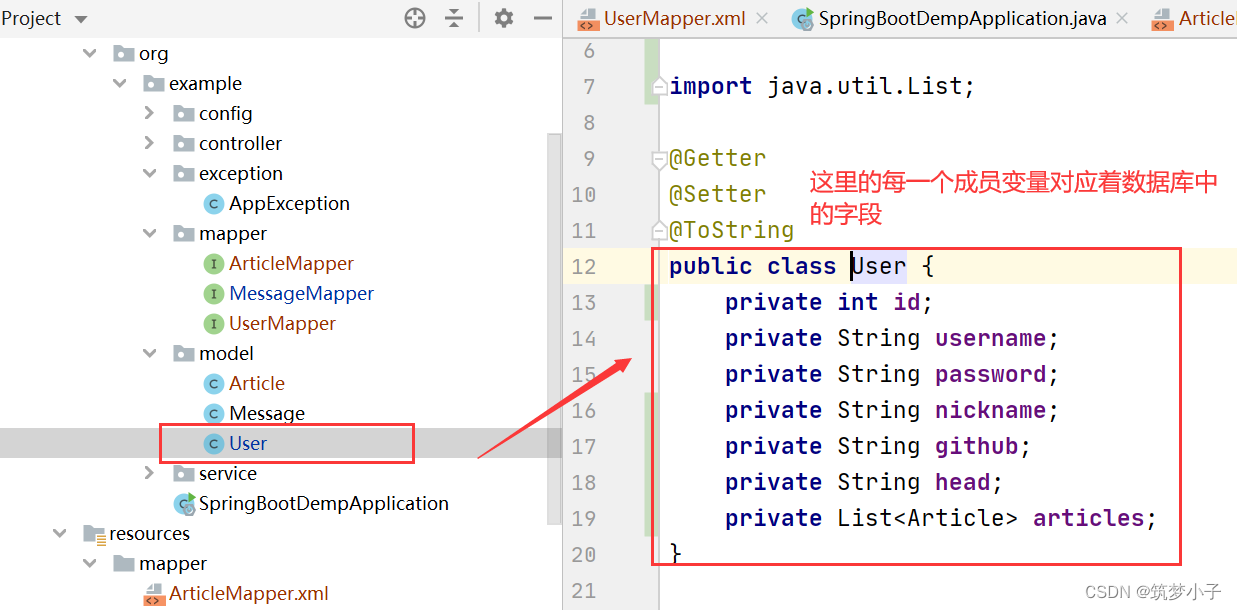
(2)添加mapper接口

(3)添加UserMapper.xml
将查询到的结果集会自动装配到配置的resultMap中

(4)server层的调用
mapper里面的指定方法被调用后会通过之前配置的xml和对应的路径会执行xml文件中的方法
(5)controller层的调用
定义service层,然后在该层调用mapper中的方法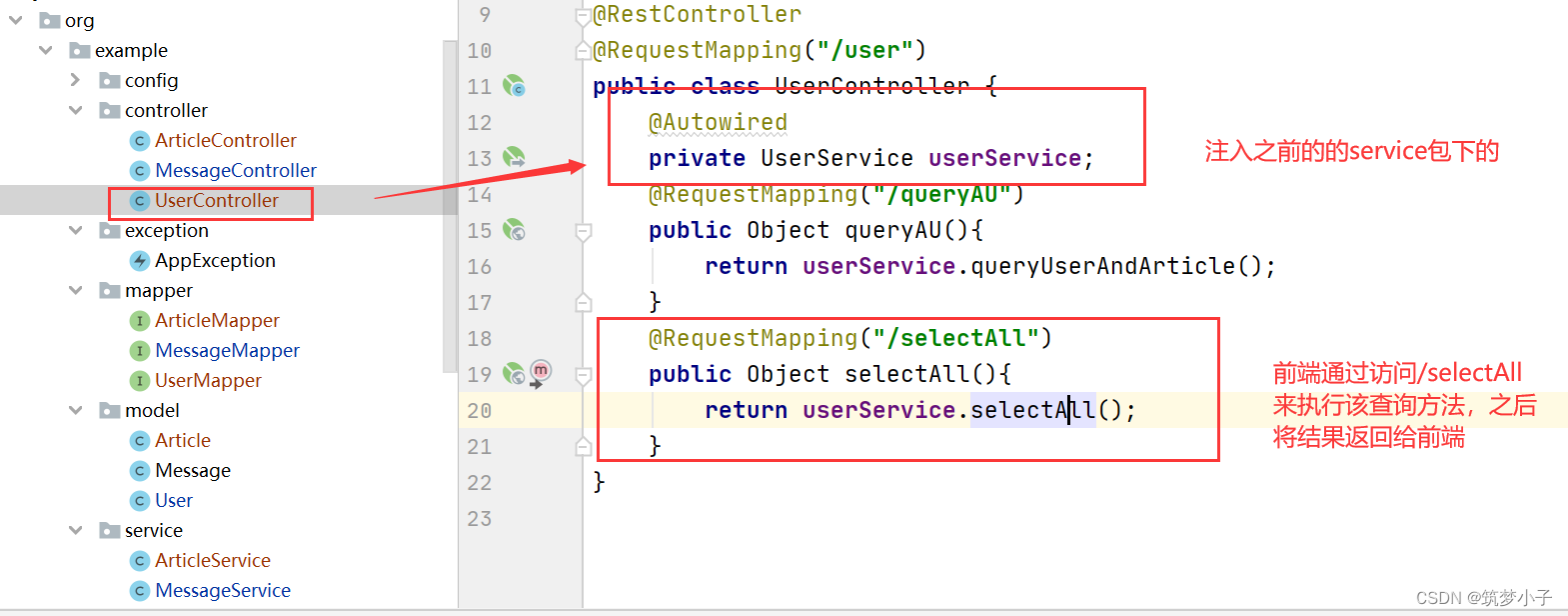
(6)前端访问后端路径
通过postman来通过url来访问该资源下的路径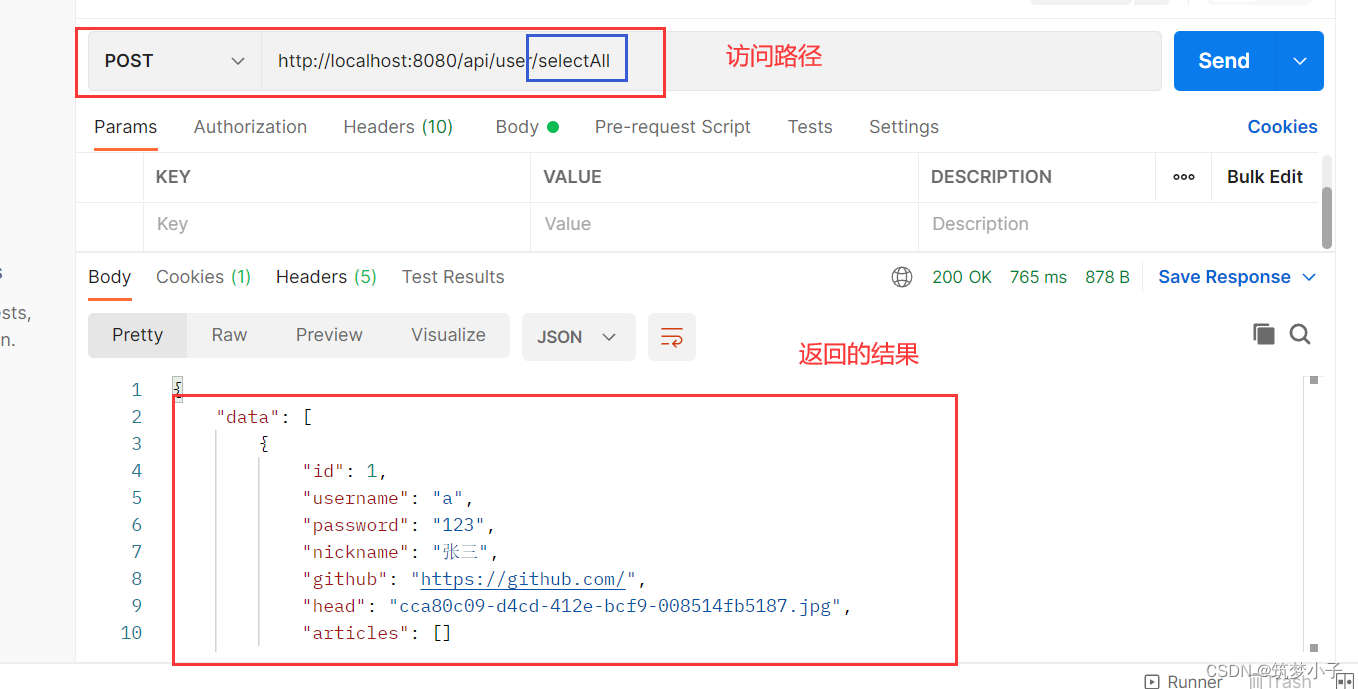
上面就是使用mybatis来对数据库操作的整个流程,接下来就是一些有关xml中关于CRUD语句的具体操作和配置。
二.有关mybatis中xml对于数据库操作的具体使用
1.插入操作
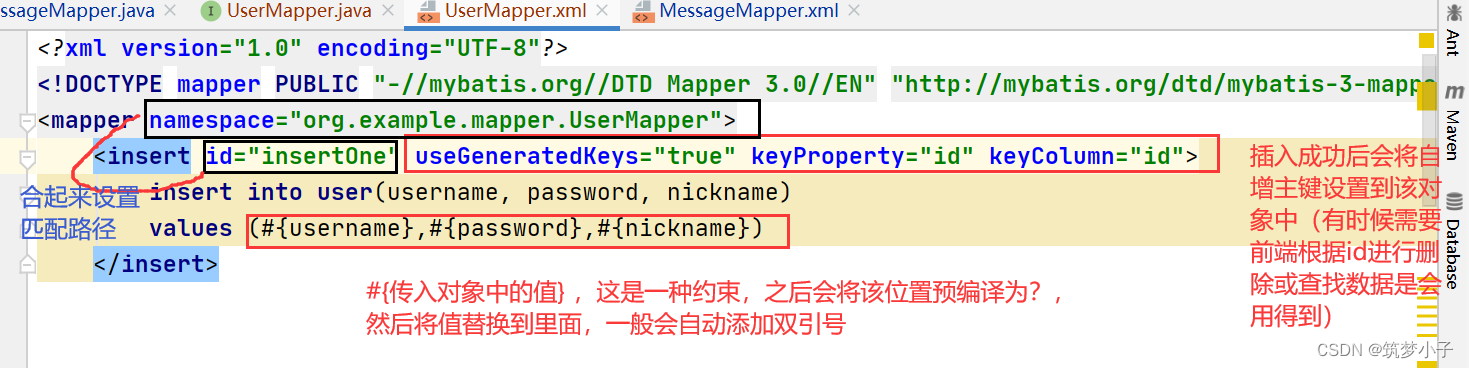
seGeneratedKeys: MyBatis 使用 JDBC 的 getGeneratedKeys 方法来取出由数据库内部生成的主键,默认值:false。
keyColumn:设置生成键值在数据库表中的列名;如果生成列不止一个,可以用逗号分隔多个属性名称。
keyProperty:指定能够唯一识别对象的属性,MyBatis 会使用 getGeneratedKeys 的返回值或 insert 语句的 selectKey 子元素设置它的值,默认值:未设置(unset)。如果生成列不止一个,可以用逗号分隔多个属性名称。
controller层

service层

mapper层
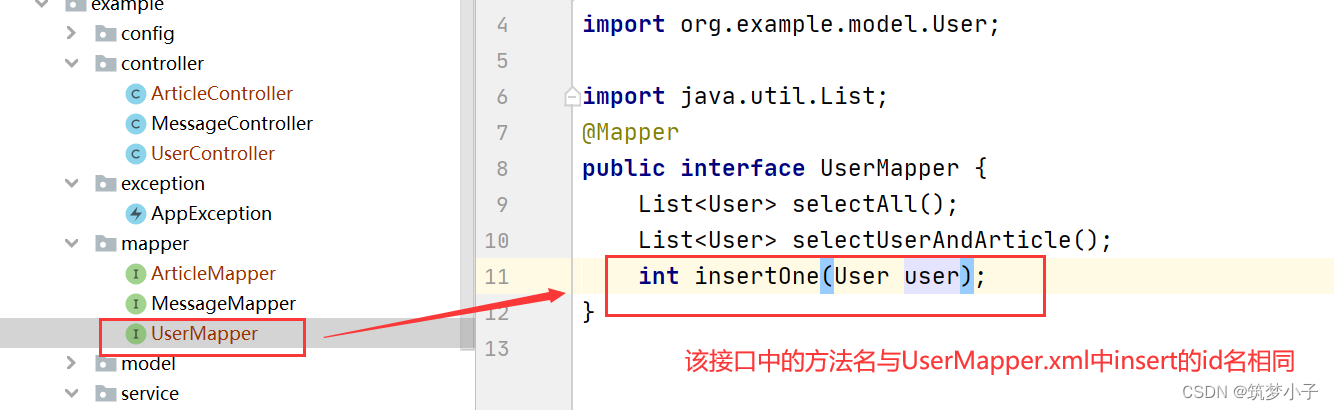
通过接口插入成功的显示

UserMapper.xml中的sql代码:
<insert id="insertOne" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id" keyColumn="id">
insert
into
user(username, password, nickname)
values (#{username},#{password},#{nickname})
</insert>
2.删除操作
基于xml文件配置好的前提下,然后在xml文件中写sql操作

通过构造前端接口,来调用mybatis中的sql来进行验证,执行顺序如下:

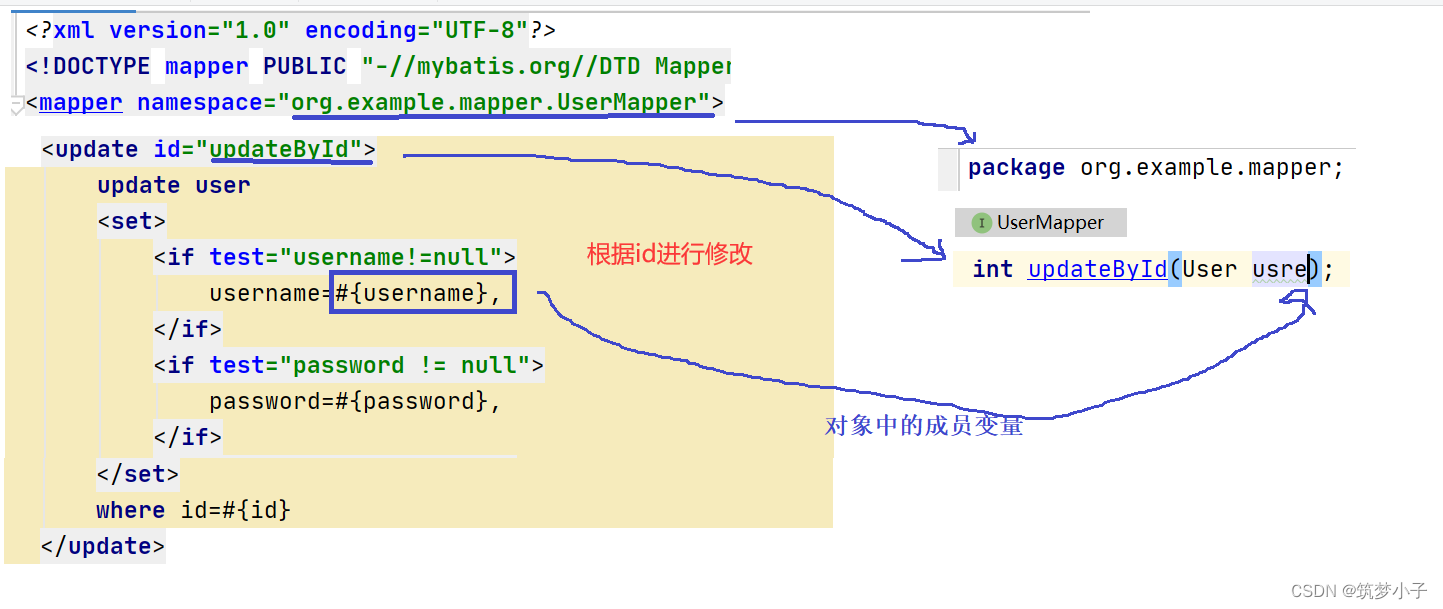
3.修改操作


4.查询操作
对于查询操作来说,需要在xml中配置结果集映射,因为需要将查找中的数据映射为一个java对象。
首先在xml文件中使用resultMap,然后设置id,之后的查询语句需要根据该id来进行转化为type中的对象,其中type中为model类的位置(类路径),然后里面就是关于映射关系的指定,其中id是数据库中关于主键的映射,如果不是主键,就使用result,对于属性中的参数,如column是数据库中的字段名,而property是类的成员变量。
<!-- 这里是配置有关查询到的结果集转化为哪一个-->
<!-- column代表数据库中的字段-->
<resultMap id="ResultBaseMap" type="org.example.model.User">
<id column="id" property="id"></id>
<result column="username" property="username"></result>
<result column="password" property="password"></result>
<result column="nickname" property="nickname"></result>
<result column="github" property="github"></result>
<result column="head" property="head"></result>
</resultMap>

三.Mybatis进阶操作
1.参数占位符
#{}是预编译占位符,在处理是,会将该位置的数据先转化为?,然后在执行PreparedStament中的set方法时,将?替换变量值。如果是字符串,会添加""。
${}是直接进行替换为变量的值,存在sql注入问题。
假如传递的数据是sort ,对于#{},最终会处理成"sort",而${}就是sort。
2.like查询
在使用like的时候,一般是模糊查询,在mybatis中需要使用concat函数来将%与#{变量值}来进行拼接。
concat(str1, str2, str3...)是将str1和str2和str3等全部进行拼接起来。
<!-- like查询-->
<select id="selectLike" resultMap="ResultBaseMap">
select
id,
username,
password
from
user
where password like concat('%',#{password},'%');
</select>
3.多表查询
(1)一对一查询
对于多表查询时,都需要使用resultMap来进行配置,在配置前还需要给对象中添加新的属性。例如一个用户登录表和用户信息表之间的关系是一对一,在进行关联查询的时候首先需要给User类中添加一个Message类型的成员变量,然后再在resultMap中除了配置有关User信息的属性外,还需要添加一个<association property="" resultMap="" columnPrefix="">属性.
property是在User中新添加的成员message, resultMap是需要关联的结果集的映射,而columnPrefix是对于查询的结果字段添加前缀,如果两个表中右重复字段,可以通过该字段进行区分,之后在associate中配置的resultMap中会去除掉前缀进行匹配。
<!-- 一对一关联自己的message信息-->
<resultMap id="ResultBaseMap2" type="org.example.model.User">
<id column="id" property="id"></id>
<result column="username" property="username"></result>
<result column="password" property="password"></result>
<result column="nickname" property="nickname"></result>
<result column="github" property="github"></result>
<result column="head" property="head"></result>
<association property="message" resultMap="org.example.mapper.UMMapper.BaseResultMap"
columnPrefix="m_"></association>
</resultMap>
<!-- 一对一关联查询-->
<select id="onebyone" resultMap="ResultBaseMap2">
select
u.id,
u.username,
m.id_card m_id_card,
m.id m_id,
m.user_id m_user_id
from user u left join message m on u.id=m.user_id;
</select>
查询和配置关系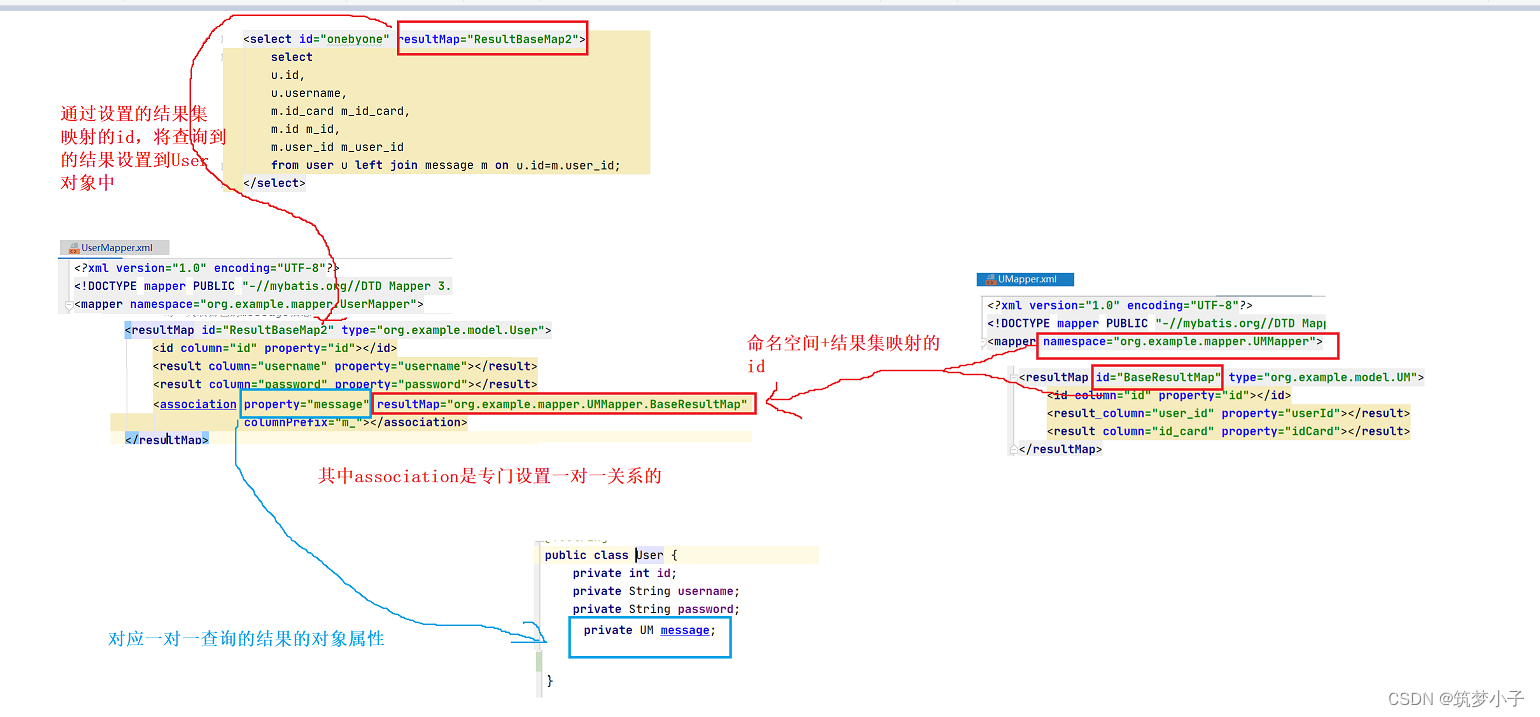
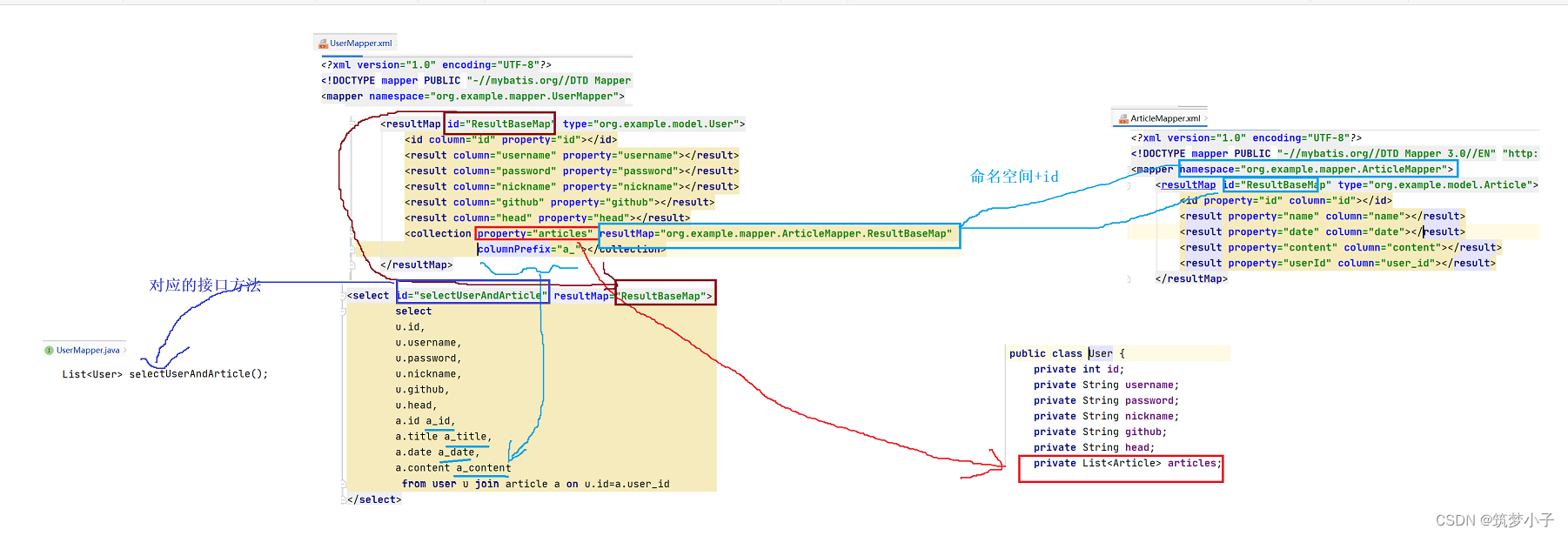
(2)一对多查询
对于一个用户表和文章表的关系是一对多,一个用户可以有多篇文章,Mybatis中也是通过resultMap来对查询结果集进行配置,然后再对查询结果中映射的对象中添加一个新的集合属性(因为是一对多关系),和一对一不同的是resultMap中设置的是collection属性,其他的配置规则基本不变。
<!-- 这里是配置有关查询到的结果集转化为哪一个-->
<!-- column代表数据库中的字段-->
<resultMap id="ResultBaseMap" type="org.example.model.User">
<id column="id" property="id"></id>
<result column="username" property="username"></result>
<result column="password" property="password"></result>
<result column="nickname" property="nickname"></result>
<result column="github" property="github"></result>
<result column="head" property="head"></result>
<collection property="articles" resultMap="org.example.mapper.ArticleMapper.ResultBaseMap"
columnPrefix="a_"></collection>
</resultMap>
<!--关联查询,一个用户对应多篇文章-->
<select id="selectUserAndArticle" resultMap="ResultBaseMap">
select
u.id,
u.username,
u.password,
u.nickname,
u.github,
u.head,
a.id a_id,
a.title a_title,
a.date a_date,
a.content a_content
from user u join article a on u.id=a.user_id
</select>
4.动态查询(if,trim,where,set,foreach的使用)
(1)if
标签为:<if test="属性值不为空"> </if>
如果对于一个参数是否传递是不确定的(可能为空或不为空),我们可以使用if来进行判断,如果传了就在sql中显示,没有传就不显示。
如注册用户时,有些信息可以不用传递,如头像等,这时候就可以在mybatis中使用if来进行过滤该参数。

<insert id="insertSelective">
insert into user(
username,
nickname,
password
<if test="head!=null"> ,head </if>
<if test="github!=null"> ,github </if>
)
values (
#{username},
#{nickname},
#{password}
<if test="head!=null"> ,#{head} </if>
<if test="github!=null"> ,#{github} </if>
)
</insert>
(2)trim
首先trim标签中有多个参数,分别为:
prefix=“” 表示整个语句块以prefix中的内容作为前缀
suffix=“” 表示整个语句块以suffix中的内容作为后缀
prefixOverrides=“” 表示整个语句块要去掉的前缀
suffixOverrides=“” 表示整个语句块要去掉的后缀
以之前的选择插入语句为例,来使用上面的参数:
<insert id="insertParam">
insert into user
<trim prefix="(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="username!=null">
username,
</if>
<if test="nickname!=null">
nickname,
</if>
<if test="password!=null">
password,
</if>
<if test="github!=null">github</if>
</trim>
<trim prefix="values(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="username!=null">
#{username},
</if>
<if test="nickname">
#{nickname},
</if>
<if test="password!=null">
#{password},
</if>
<if test="github!=null">
#{github},
</if>
</trim>
</insert>
(3)where
<where></where>是用在条件查询中(也可以使用上面的trim),对于where中的<if></if>里面的内容,写成and 属性名=属性值,之后会自动去掉第一个and。
如下所示,如果传递的password和username不为空,就根据这两个条件进行过滤:
<select id="selectByWhere" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select * from user
<where>
<if test="password!=null">
and password=#{password}
</if>
<if test="username!=null">
and username=#{username}
</if>
</where>
</select>
(4)set
用于sql修改中,会自动去除掉set中的if属性中的.
<update id="updateSet">
update user
<set>
<if test="username!=null">
username=#{username},
</if>
<if test="nickname!=null">
nickname=#{nickname},
</if>
<if test="password!=null">
password=#{password},
</if>
</set>
where id=#{id}
</update>
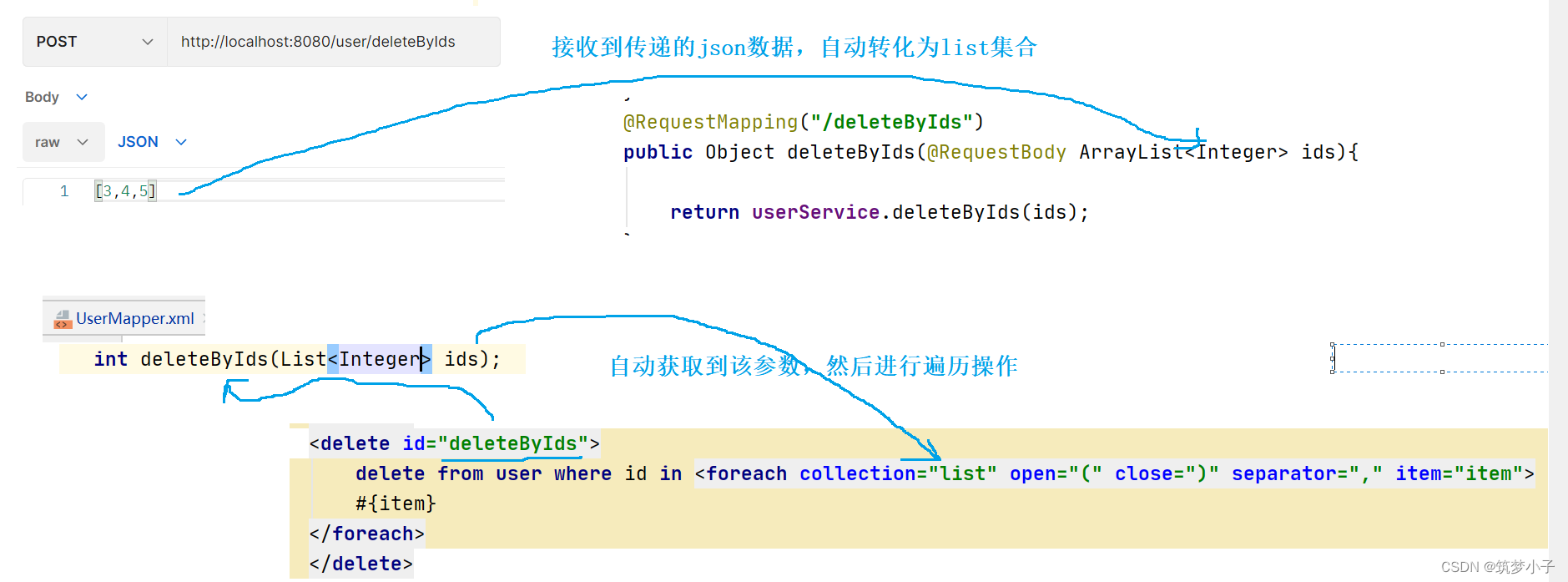
(5)foreach
可以对于传入的集合进行遍历,里面的参数如下所示:
collection:用于绑定方法参数中的集合
item:遍历时的每一个对象
open:语句块开头的字符串
close:语句块结束的字符串
separator:每次遍历之间的分隔符
示例,根据list中的id号来进行批量删除:
<delete id="deleteByIds">
delete from user where id in <foreach collection="list" open="(" close=")" separator="," item="item">
#{item}
</foreach>
</delete>
版权归原作者 筑梦小子 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。