相关文章:
- OAuth2的定义和运行流程
- Spring Security OAuth实现Gitee快捷登录
- Spring Security OAuth实现GitHub快捷登录
- Spring Security的过滤器链机制
- Spring Security OAuth Client配置加载源码分析
文章目录
前言
根据前面的示例,我们已经知道启动时会加载18个过滤器,并且已经知道了请求会匹配到DefaultSecurityFilterChain并依次通过这18个过滤器。
DisableEncodeUrlFilter
WebAsyncManagerIntegrationFilter
SecurityContextPersistenceFilter
HeaderWriterFilter
CsrfFilter
LogoutFilter
OAuth2AuthorizationRequestRedirectFilter
OAuth2AuthorizationRequestRedirectFilter
OAuth2LoginAuthenticationFilter
DefaultLoginPageGeneratingFilter
DefaultLogoutPageGeneratingFilter
RequestCacheAwareFilter
SecurityContextHolderAwareRequestFilter
AnonymousAuthenticationFilter
OAuth2AuthorizationCodeGrantFilter
SessionManagementFilter
ExceptionTranslationFilter
FilterSecurityInterceptor
我们从OAuth2AuthorizationRequestRedirectFilter开始看,OAuth2开头这非常明显。
OAuth2AuthorizationRequestRedirectFilter
OAuth2 客户端认证核心过滤器,通过重定向到authorization_uri来获取code
该过滤器并没有doFilter()方法,只有doFilterInternal,而doFilter()存在于其父类OncePerRequestFilter过滤器中
如下是核心代码:
protectedvoiddoFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response,FilterChain filterChain)throwsServletException,IOException{try{//从request、ClientRegistration中构造出OAuth2的授权请求对象OAuth2AuthorizationRequest authorizationRequest =this.authorizationRequestResolver.resolve(request);if(authorizationRequest !=null){//重定向到authorizationUrithis.sendRedirectForAuthorization(request, response, authorizationRequest);return;}}catch(Exception ex){this.unsuccessfulRedirectForAuthorization(request, response, ex);return;}try{//执行下一个过滤器
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);}catch(IOException ex){throw ex;}catch(Exception ex){//判断是否有ClientAuthorizationRequiredException,如果有单独处理Throwable[] causeChain =this.throwableAnalyzer.determineCauseChain(ex);ClientAuthorizationRequiredException authzEx =(ClientAuthorizationRequiredException)this.throwableAnalyzer
.getFirstThrowableOfType(ClientAuthorizationRequiredException.class, causeChain);if(authzEx !=null){try{OAuth2AuthorizationRequest authorizationRequest =this.authorizationRequestResolver.resolve(request,
authzEx.getClientRegistrationId());if(authorizationRequest ==null){throw authzEx;}this.sendRedirectForAuthorization(request, response, authorizationRequest);this.requestCache.saveRequest(request, response);}catch(Exception failed){this.unsuccessfulRedirectForAuthorization(request, response, failed);}return;}if(ex instanceofServletException){throw(ServletException) ex;}if(ex instanceofRuntimeException){throw(RuntimeException) ex;}thrownewRuntimeException(ex);}}
OAuth2LoginAuthenticationFilter
说明:核心OAuth登录过滤器,首先从URL中提取code,然后使用code获取access_token,接着借助access_token获取用户信息,最终构建出OAuth2AuthenticationToken认 证对象,表明认证成功。
该过滤器会在授权服务器调用回调接口的时候起作用,本例中回调的URL为
/login/oauth2/code/gitee?code=c52e1e1f8ab954d680f4bb78e33ce303b15ed3cb1040bd47089067e9a8ed9ea5&state=k2Ci-0eyt0To1Me_ThgInRX2CPv2EtKSiu5xTrWyN3Y%3D
doFilter代码位于父类AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter中,核心代码如下:
@OverridepublicvoiddoFilter(ServletRequest request,ServletResponse response,FilterChain chain)throwsIOException,ServletException{doFilter((HttpServletRequest) request,(HttpServletResponse) response, chain);}privatevoiddoFilter(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response,FilterChain chain)throwsIOException,ServletException{//通过requestMatcher判断request请求是否需要处理if(!requiresAuthentication(request, response)){
chain.doFilter(request, response);return;}try{//获取身份认证结果,并创建认证对象,由子类实现,OAuth2 使用的是OAuth2LoginAuthenticationFilterAuthentication authenticationResult =attemptAuthentication(request, response);if(authenticationResult ==null){// return immediately as subclass has indicated that it hasn't completedreturn;}//对会话进行处理,防止会话固定攻击(session-fixation详情可网上查询)this.sessionStrategy.onAuthentication(authenticationResult, request, response);//认证成功后,是否继续执行后面的过滤器if(this.continueChainBeforeSuccessfulAuthentication){
chain.doFilter(request, response);}//处理认证成功后的处理逻辑,委托给AuthenticationSuccessHandler,此处为SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandlersuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, chain, authenticationResult);}catch(InternalAuthenticationServiceException failed){this.logger.error("An internal error occurred while trying to authenticate the user.", failed);//认证失败处理unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed);}catch(AuthenticationException ex){// Authentication failed//认证失败处理unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, ex);}}
其中attemptAuthentication处的代码量很大,作用是:获取身份认证结果,并创建认证对象,由子类实现,OAuth2 使用的是OAuth2LoginAuthenticationFilter,我们来看看这部分
publicAuthenticationattemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response)throwsAuthenticationException{//从授权服务器回调的URL请求中,将请求参数转换为map格式,key=参数名,value=参数值MultiValueMap<String,String> params =OAuth2AuthorizationResponseUtils.toMultiMap(request.getParameterMap());//根据code、status、error字段判断是否为返回请求if(!OAuth2AuthorizationResponseUtils.isAuthorizationResponse(params)){OAuth2Error oauth2Error =newOAuth2Error(OAuth2ErrorCodes.INVALID_REQUEST);thrownewOAuth2AuthenticationException(oauth2Error, oauth2Error.toString());}//返回OAuth2AuthorizationRequest,该对象在OAuth2LoginAuthenticationFilter中构建//removeAuthorizationRequest官方的话是,但不太理解为什么要remove//Removes and returns the OAuth2AuthorizationRequest associated to the provided //HttpServletRequest and HttpServletResponse or if not available returns null.OAuth2AuthorizationRequest authorizationRequest =this.authorizationRequestRepository
.removeAuthorizationRequest(request, response);if(authorizationRequest ==null){OAuth2Error oauth2Error =newOAuth2Error(AUTHORIZATION_REQUEST_NOT_FOUND_ERROR_CODE);thrownewOAuth2AuthenticationException(oauth2Error, oauth2Error.toString());}String registrationId = authorizationRequest.getAttribute(OAuth2ParameterNames.REGISTRATION_ID);ClientRegistration clientRegistration =this.clientRegistrationRepository.findByRegistrationId(registrationId);if(clientRegistration ==null){OAuth2Error oauth2Error =newOAuth2Error(CLIENT_REGISTRATION_NOT_FOUND_ERROR_CODE,"Client Registration not found with Id: "+ registrationId,null);thrownewOAuth2AuthenticationException(oauth2Error, oauth2Error.toString());}// @formatter:offString redirectUri =UriComponentsBuilder.fromHttpUrl(UrlUtils.buildFullRequestUrl(request)).replaceQuery(null).build().toUriString();// @formatter:on//构建OAuth2授权响应对象OAuth2AuthorizationResponse authorizationResponse =OAuth2AuthorizationResponseUtils.convert(params,
redirectUri);//从request构建一个完整的身份认证信息Object authenticationDetails =this.authenticationDetailsSource.buildDetails(request);//构建OAuth2认证TokenOAuth2LoginAuthenticationToken authenticationRequest =newOAuth2LoginAuthenticationToken(clientRegistration,newOAuth2AuthorizationExchange(authorizationRequest, authorizationResponse));
authenticationRequest.setDetails(authenticationDetails);//请求授权服务器的token-uri,进行身份认证,返回完整的OAuth2认证Token//请求user-info-uri,获取资源所有者主体信息//会轮询所有的provider,直到遇到支持的provider,该处为OAuth2LoginAuthenticationProviderOAuth2LoginAuthenticationToken authenticationResult =(OAuth2LoginAuthenticationToken)this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authenticationRequest);//转换成需要返回的OAuth2AuthenticationTokenOAuth2AuthenticationToken oauth2Authentication =this.authenticationResultConverter
.convert(authenticationResult);Assert.notNull(oauth2Authentication,"authentication result cannot be null");
oauth2Authentication.setDetails(authenticationDetails);//构建最终的OAuth2 授权客户端OAuth2AuthorizedClient authorizedClient =newOAuth2AuthorizedClient(
authenticationResult.getClientRegistration(), oauth2Authentication.getName(),
authenticationResult.getAccessToken(), authenticationResult.getRefreshToken());//保存授权相关信息,此处保存到本地this.authorizedClientRepository.saveAuthorizedClient(authorizedClient, oauth2Authentication, request, response);return oauth2Authentication;}
DefaultLoginPageGeneratingFilter
说明:默认的登录页面
当没有配置自定义登录页时,将使用该默认登录页
如下的doFilter核心代码:
@OverridepublicvoiddoFilter(ServletRequest request,ServletResponse response,FilterChain chain)throwsIOException,ServletException{doFilter((HttpServletRequest) request,(HttpServletResponse) response, chain);}privatevoiddoFilter(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response,FilterChain chain)throwsIOException,ServletException{//当前请求是否是failureUrl指定的地址boolean loginError =isErrorPage(request);//当前请求是否是logoutSuccessUrl指定的地址boolean logoutSuccess =isLogoutSuccess(request);//是否是登录请求,是否是重定向的错误请求,是否是登出地址if(isLoginUrlRequest(request)|| loginError || logoutSuccess){//生成一个默认的登录页String loginPageHtml =generateLoginPageHtml(request, loginError, logoutSuccess);
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
response.setContentLength(loginPageHtml.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8).length);
response.getWriter().write(loginPageHtml);return;}//否则执行下一个过滤器
chain.doFilter(request, response);}
DefaultLogoutPageGeneratingFilter
说明:默认的登出页面
当请求地址为GET请求,/logout时,生成一个默认的登出页面
核心代码如下:
@OverrideprotectedvoiddoFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response,FilterChain filterChain)throwsServletException,IOException{//地址是/logoutif(this.matcher.matches(request)){//生成一个登出页面renderLogout(request, response);}else{if(logger.isTraceEnabled()){
logger.trace(LogMessage.format("Did not render default logout page since request did not match [%s]",this.matcher));}
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);}}
界面如下: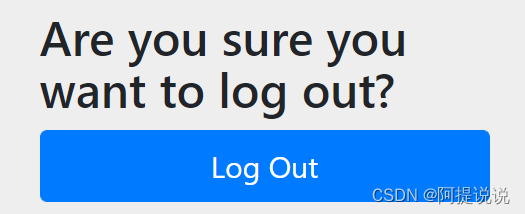
RequestCacheAwareFilter
说明:
从session中获取SavedRequest,如果当前请求信息和SaveRequest信息一致(一般是登录成功后重定向),则返回SavedRequestAwareWrapper的HttpServletRequest包装类
SecurityContextHolderAwareRequestFilter
说明:
通过HttpServletRequestFactory将HttpServletRequest请求包装成SecurityContextHolderAwareRequestWrapper,它实现了HttpServletRequest,并进行了扩展,添加一些额外的方法,比如:getPrincipal()方法等。这样就可以那些需要Principal等参数的Controller就可以接收到对应参数了。除了这个地方的应用,在其他地方,也可以直接调用request#getUserPrincipal()获取对应信息。
AnonymousAuthenticationFilter
说明:
匿名过滤器,如果执行到该过滤器时还没有主体,则创建一个匿名主体
OAuth2AuthorizationCodeGrantFilter
说明:
OAuth2授权码授权过滤器,跟OAuth2LoginAuthenticationFilter很像,不知道在这里的作用是什么?
是为了兜底?
SessionManagementFilter
Session管理过滤器
ExceptionTranslationFilter
处理过滤器链中抛出的AccessDeniedException和AuthenticationException 异常
FilterSecurityInterceptor
对资源的过滤处理
核心代码如下:
publicvoidinvoke(FilterInvocation filterInvocation)throwsIOException,ServletException{//该请求已经运行过该过滤,跳过,执行下一个过滤器if(isApplied(filterInvocation)&&this.observeOncePerRequest){// filter already applied to this request and user wants us to observe// once-per-request handling, so don't re-do security checking
filterInvocation.getChain().doFilter(filterInvocation.getRequest(), filterInvocation.getResponse());return;}// first time this request being called, so perform security checkingif(filterInvocation.getRequest()!=null&&this.observeOncePerRequest){
filterInvocation.getRequest().setAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED,Boolean.TRUE);}//获取当前的权限配置InterceptorStatusToken token =super.beforeInvocation(filterInvocation);try{
filterInvocation.getChain().doFilter(filterInvocation.getRequest(), filterInvocation.getResponse());}finally{//设置SecurityContextHolderStrategy contextsuper.finallyInvocation(token);}//最后的处理super.afterInvocation(token,null);}
获取当前 request 对应的权限配置,首先是调用基类的 beforeInvocation 方法 。
看一下基类的 beforeInvocation 方法,从配置好的 SecurityMetadataSource 中获取当前 request 所对应的 ConfigAttribute,即权限信息。
protectedInterceptorStatusTokenbeforeInvocation(Object object){......Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes =this.obtainSecurityMetadataSource().getAttributes(object);if(attributes ==null|| attributes.isEmpty()){if(rejectPublicInvocations){thrownewIllegalArgumentException("Secure object invocation "+ object
+" was denied as public invocations are not allowed via this interceptor. "+"This indicates a configuration error because the "+"rejectPublicInvocations property is set to 'true'");}......}}
这里需要注意一下 rejectPublicInvocations 属性,默认为 false。此属性含义为拒绝公共请求。如果从配置好的 SecurityMetadataSource 中获取不到当前 request 所对应的 ConfigAttribute 时,即认为当前请求为公共请求。如配置 rejectPublicInvocations 属性为 true,则系统会抛出 IllegalArgumentException 异常,即当前请求需要配置权限信息。
接下来,就要判断是否需要进行身份认证了,即调用 authenticateIfRequired 方法。
protectedInterceptorStatusTokenbeforeInvocation(Object object){......Authentication authenticated =authenticateIfRequired();......}
而判断及身份认证逻辑也并不复杂,首先会判断当前用户是否已通过身份认证,如果已通过身份认证,则直接返回;如果尚未通过身份认证,则调用身份认证管理器 AuthenticationManager 进行认证,就如同登录时一样。认证通过后,同样会在当前的安全上下文中存储一份认证后的 authentication。
privateAuthenticationauthenticateIfRequired(){Authentication authentication =SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();if(authentication.isAuthenticated()&&!alwaysReauthenticate){if(logger.isDebugEnabled()){
logger.debug("Previously Authenticated: "+ authentication);}return authentication;}
authentication = authenticationManager.authenticate(authentication);// We don't authenticated.setAuthentication(true), because each provider should do// thatif(logger.isDebugEnabled()){
logger.debug("Successfully Authenticated: "+ authentication);}SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authentication);return authentication;}
然后,使用获取到的 ConfigAttribute ,继续调用访问控制器 AccessDecisionManager 对当前请求进行鉴权。
protectedInterceptorStatusTokenbeforeInvocation(Object object){......// Attempt authorizationtry{this.accessDecisionManager.decide(authenticated, object, attributes);}catch(AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException){publishEvent(newAuthorizationFailureEvent(object, attributes, authenticated,
accessDeniedException));throw accessDeniedException;}if(debug){
logger.debug("Authorization successful");}if(publishAuthorizationSuccess){publishEvent(newAuthorizedEvent(object, attributes, authenticated));}}
注意,无论鉴权通过或是不通后,Spring Security 框架均使用了观察者模式,来通知其它Bean,当前请求的鉴权结果。
如果鉴权不通过,则会抛出 AccessDeniedException 异常,即访问受限,然后会被 ExceptionTranslationFilter 捕获,最终解析后调转到对应的鉴权失败页面。
如果鉴权通过,AbstractSecurityInterceptor 通常会继续请求。但是,在极少数情况下,用户可能希望使用不同的 Authentication 来替换 SecurityContext 中的 Authentication。该身份认证就会由 RunAsManager 来处理。这在某些业务场景下可能很有用,录入服务层方法需要调用远程系统并呈现不同的身份。因为 Spring Security 会自动将安全标识从一个服务器传播到另一个服务器(假设使用的是正确配置的 RMI 或 HttpInvoker 远程协议客户端),这就可能很有用。
在 AccessDecisionManager 鉴权成功后,将通过 RunAsManager 在现有 Authentication 基础上构建一个新的Authentication,如果新的 Authentication 不为空则将产生一个新的 SecurityContext,并把新产生的Authentication 存放在其中。这样在请求受保护资源时从 SecurityContext中 获取到的 Authentication 就是新产生的 Authentication。
protectedInterceptorStatusTokenbeforeInvocation(Object object){......// Attempt to run as a different userAuthentication runAs =this.runAsManager.buildRunAs(authenticated, object,
attributes);if(runAs ==null){if(debug){
logger.debug("RunAsManager did not change Authentication object");}// no further work post-invocationreturnnewInterceptorStatusToken(SecurityContextHolder.getContext(),false,
attributes, object);}else{if(debug){
logger.debug("Switching to RunAs Authentication: "+ runAs);}SecurityContext origCtx =SecurityContextHolder.getContext();SecurityContextHolder.setContext(SecurityContextHolder.createEmptyContext());SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(runAs);// need to revert to token.Authenticated post-invocationreturnnewInterceptorStatusToken(origCtx,true, attributes, object);}}
注意,AbstractSecurityInterceptor 默认持有的是 RunAsManager 的空实现 NullRunAsManager。
publicabstractclassAbstractSecurityInterceptorimplementsInitializingBean,ApplicationEventPublisherAware,MessageSourceAware{......privateRunAsManager runAsManager =newNullRunAsManager();......}
待请求完成后会在 finallyInvocation() 中将原来的 SecurityContext 重新设置给SecurityContextHolder。
protectedvoidfinallyInvocation(InterceptorStatusToken token){if(token !=null&& token.isContextHolderRefreshRequired()){if(logger.isDebugEnabled()){
logger.debug("Reverting to original Authentication: "+ token.getSecurityContext().getAuthentication());}SecurityContextHolder.setContext(token.getSecurityContext());}}
然而,无论正常调用,亦或是请求异常等,都会触发 finallyInvocation()。
publicvoidinvoke(FilterInvocation fi)throwsIOException,ServletException{if((fi.getRequest()!=null)......}else{......try{
fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse());}finally{// 无论是否成功、抛异常与否,均会执行super.finallyInvocation(token);}// 正常请求结束,最后也会执行(afterInvocation 内部会调用finallyInvocation )super.afterInvocation(token,null);}}
即便是正常执行结束,依然会执行 finallyInvocation()(afterInvocation 内部会调用finallyInvocation )。
protectedObjectafterInvocation(InterceptorStatusToken token,Object returnedObject){......finallyInvocation(token);// continue to clean in this method for passivity......}
此外,Spring Security 对 RunAsManager 有一个还有一个非空实现类 RunAsManagerImpl,其构造新 Authentication 的逻辑如下:
如果受保护对象对应的 ConfigAttribute 中拥有以“RUN_AS_”开头的配置属性,则在该属性前加上“ROLE_”,然后再把它作为一个 SimpleGrantedAuthority 赋给将要创建的 Authentication(如ConfigAttribute 中拥有一个“RUN_AS_ADMIN”的属性,则将构建一个“ROLE_RUN_AS_ADMIN”的SimpleGrantedAuthority),最后再利用原 Authentication 的 principal、权限等信息构建一个新的 Authentication 并返回;如果不存在任何以“RUN_AS_”开头的 ConfigAttribute,则直接返回null。
publicAuthenticationbuildRunAs(Authentication authentication,Object object,Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes){List<GrantedAuthority> newAuthorities =newArrayList<>();for(ConfigAttribute attribute : attributes){if(this.supports(attribute)){GrantedAuthority extraAuthority =newSimpleGrantedAuthority(getRolePrefix()+ attribute.getAttribute());
newAuthorities.add(extraAuthority);}}if(newAuthorities.size()==0){returnnull;}// Add existing authorities
newAuthorities.addAll(authentication.getAuthorities());returnnewRunAsUserToken(this.key, authentication.getPrincipal(),
authentication.getCredentials(), newAuthorities,
authentication.getClass());}
AccessDecisionManager 是在访问受保护的对象之前判断用户是否拥有该对象的访问权限。然而,有时候我们可能会希望在请求执行完成后对返回值做一些修改或者权限校验,当然,也可以简单的通过AOP来实现这一功能。
同样的,Spring Security 提供了 AfterInvocationManager 接口,它允许我们在受保护对象访问完成后对返回值进行修改或者进行权限校验,权限校验不通过时抛出 AccessDeniedException,并使用观察者模式通知其它Bean。
protectedObjectafterInvocation(InterceptorStatusToken token,Object returnedObject){......if(afterInvocationManager !=null){......catch(AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException){AuthorizationFailureEvent event =newAuthorizationFailureEvent(
token.getSecureObject(), token.getAttributes(), token
.getSecurityContext().getAuthentication(),
accessDeniedException);publishEvent(event);throw accessDeniedException;}}......}
其将由 AbstractSecurityInterceptor 的子类进行调用,如默认子类 FilterSecurityInterceptor 。
需要特别注意的是,AfterInvocationManager 需要在受保护对象成功被访问后才能执行。
类似于AuthenticationManager,AfterInvocationManager 同样也有一个默认的实现类AfterInvocationProviderManager,其中有一个由 AfterInvocationProvider 组成的集合属性。
publicclassAfterInvocationProviderManagerimplementsAfterInvocationManager,InitializingBean{......privateList<AfterInvocationProvider> providers;......}
非常有趣的是,AfterInvocationProvider 与 AfterInvocationManager 具有相同的方法定义。此一来,在调用AfterInvocationProviderManager 中的方法时,实际上就是依次调用其中成员属性 providers 中的AfterInvocationProvider 接口对应的方法。
publicObjectdecide(Authentication authentication,Object object,Collection<ConfigAttribute> config,Object returnedObject)throwsAccessDeniedException{Object result = returnedObject;for(AfterInvocationProvider provider : providers){
result = provider.decide(authentication, object, config, result);}return result;}
而 AfterInvocationProvider 的默认实现类 PostInvocationAdviceProvider 中的 PostInvocationAuthorizationAdvice,其默认实现类 ExpressionBasedPostInvocationAdvice,不正是对应着后置权限注解 @PostAuthorize 吗?
最后,关于 FILTER_APPLIED 常量,在 FilterSecurityInterceptor 中是这么使用的:
publicvoidinvoke(FilterInvocation fi)throwsIOException,ServletException{if((fi.getRequest()!=null)&&(fi.getRequest().getAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED)!=null)&& observeOncePerRequest){// filter already applied to this request and user wants us to observe// once-per-request handling, so don't re-do security checking
fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse());}else{// first time this request being called, so perform security checkingif(fi.getRequest()!=null&& observeOncePerRequest){
fi.getRequest().setAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED,Boolean.TRUE);}......}}
其主要作用,是用于阻止请求的重复安全检查。
原理也简单,第一次执行时,检查 request 中 FILTER_APPLIED 属性值为空,则放入值;后续该 request 再次请求时,FILTER_APPLIED 属性值不为空,代表已经进行过安全检查,则该请求直接通过,不再重复进行安全检查。
版权归原作者 阿提说说 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。