本篇会给大家举出各种
Spring属性依赖注入的例子,方便大家理解。
文章目录
1. setter属性注入
1.1 使用XML进行setter方法注入
我们在前面的文章中已经使用过
XML
进行
setter
方法的属性注入了,下面让我们再来回顾一下:
<beanid="userSetter"class="com.example.demo.bean.User"><propertyname="username"value="example-username-setter"/><propertyname="age"value="25"/></bean>
1.2 使用@Bean注解进行setter方法注入
我们在前面的文章中也学习过如何在
bean
创建时通过编程方式设置属性:
@BeanpublicUseruser(){User user =newUser();
user.setUsername("example-username-anno-setter");
user.setAge(25);return user;}
1.3 setter方法注入完整代码示例
- 使用XML进行setter方法注入
首先,我们需要创建一个
User
类,并在其中包含
username
和
age
两个属性,以及相应的
getter
、
setter
方法和构造器。
publicclassUser{privateString username;privateInteger age;publicUser(){}// 为了节省篇幅,getter和setter方法省略......@OverridepublicStringtoString(){return"User{username='"+ username +"', age="+ age +"}";}}
对于
XML
方式的
setter
注入和构造器注入,我们需要创建一个配置文件,比如叫
applicationContext.xml
。
<beansxmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"><!-- setter方法注入 --><beanid="userSetter"class="com.example.demo.bean.User"><propertyname="username"value="example-username-setter"/><propertyname="age"value="25"/></bean></beans>
然后,我们需要创建一个
DemoApplication
类,使用
ApplicationContext
来加载配置文件并获取
Bean
:
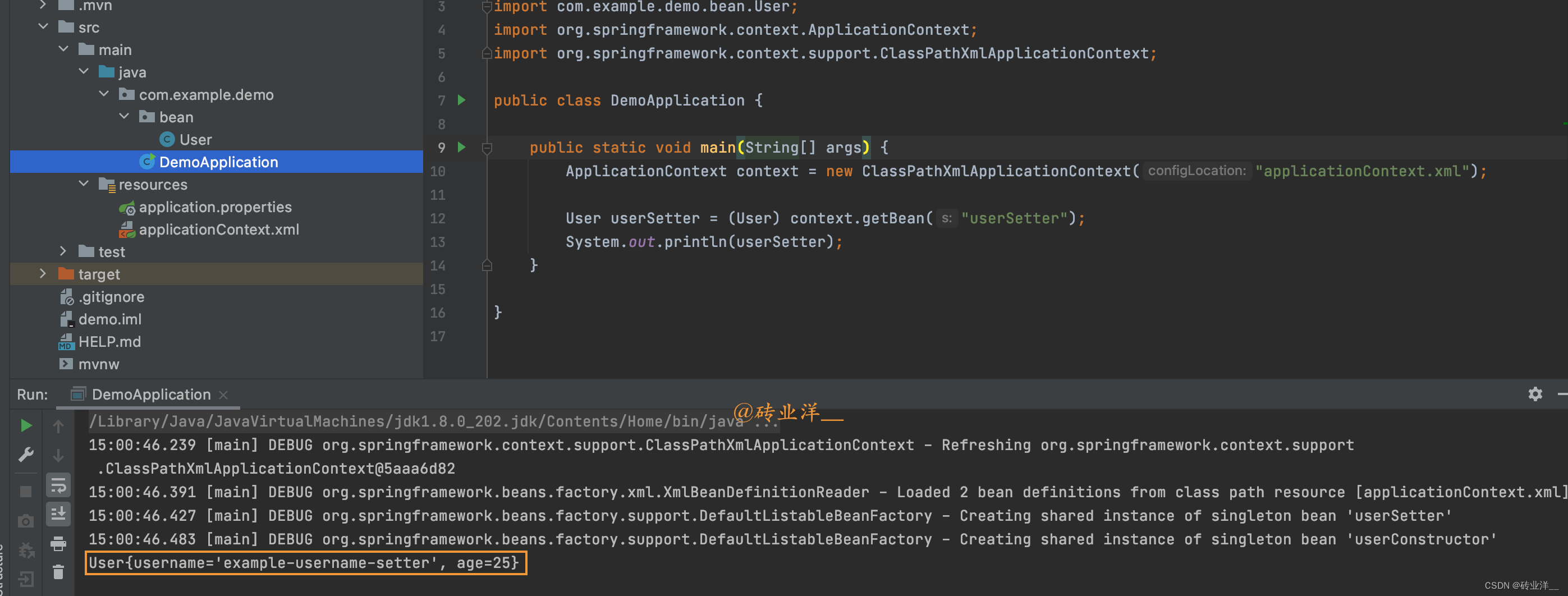
importcom.example.demo.bean.User;importorg.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;importorg.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;publicclassDemoApplication{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){ApplicationContext context =newClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");User userSetter =(User) context.getBean("userSetter");System.out.println(userSetter);}}
运行结果如下:
- 使用@Bean注解进行setter方法注入
我们需要创建一个配置类,例如叫
AppConfig.java
:
importorg.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;@ConfigurationpublicclassAppConfig{@BeanpublicUseruserSetter(){User user =newUser();
user.setUsername("example-username-anno-setter");
user.setAge(25);return user;}}
使用
@Bean
注解来定义
Bean
。每个
@Bean
方法对应于
XML
配置中的一个
<bean>
元素。这个方法的名称就是
Bean
的
id
,方法的返回值就是
Bean
的类型
然后修改主程序,这里使用
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
来创建
Spring
的应用上下文,并加载配置类。
Spring
会自动从配置类中获取所有的
Bean
定义,并创建相应的
Bean
实例。
packagecom.example.demo;importcom.example.demo.bean.User;importcom.example.demo.configuration.AppConfig;importorg.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;publicclassDemoApplication{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){ApplicationContext context =newAnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);User userSetter =(User) context.getBean("userSetter");System.out.println(userSetter);}}
运行结果如下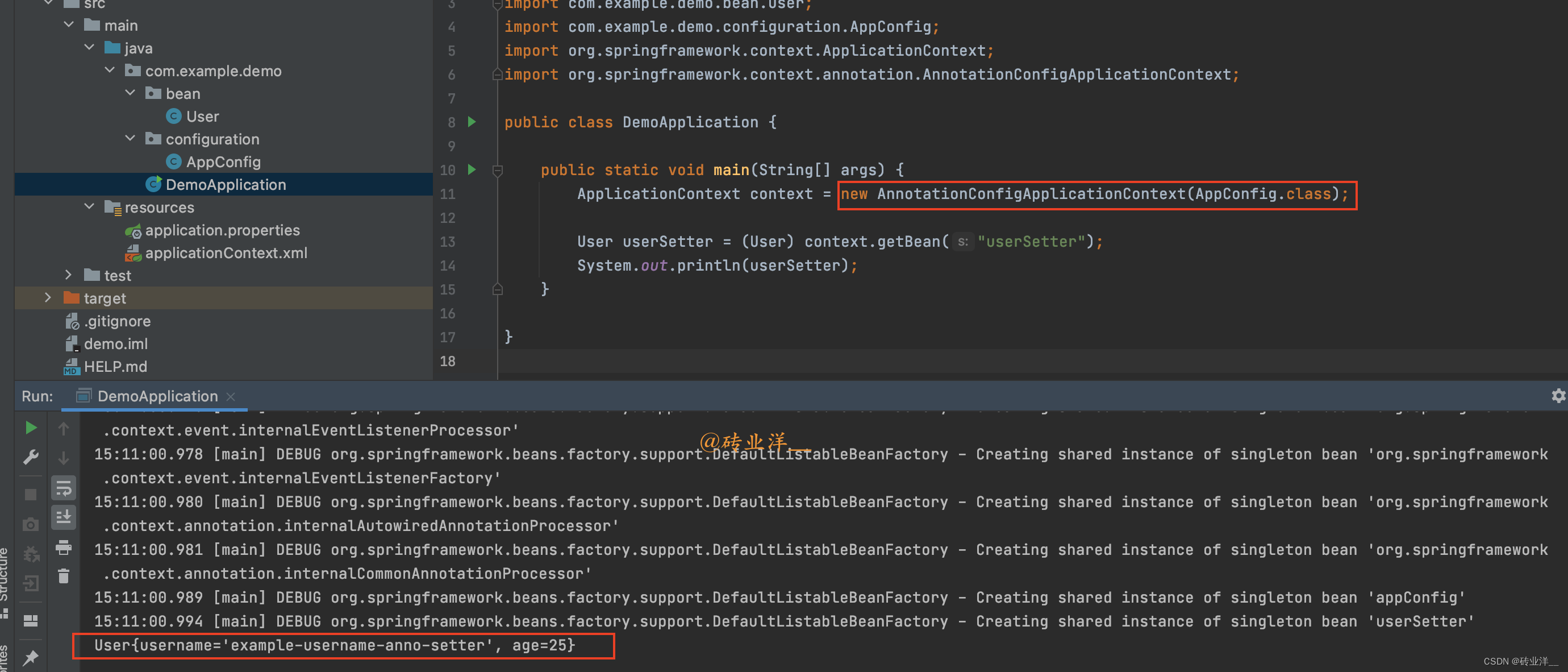
注意:
XML
配置方式已经相对陈旧,而且在
Spring Boot
项目中,主流的做法是使用注解和
Java
配置方式。对于
setter
注入,有时会引发循环依赖的问题。在
Spring
中,可以使用构造器注入来避免这种情况,这里了解即可。
2. 构造器注入
setter
注入是一种在对象被实例化之后(通过调用无参构造器创建实例)再通过
setter
方法注入依赖的方式。构造器注入则是在创建对象实例的时候就通过构造器参数来注入依赖。
为了演示构造器注入,我们需要给
User
添加一个全参数构造器:
publicUser(String username,Integer age){this.username = username;this.age = age;}
添加这个构造器后,
Java
不再提供默认的无参构造器,这会导致我们之前的
<bean>
标签创建时失败,因为它找不到默认的构造器。
2.1 使用XML进行构造器注入
我们可以在
<bean>
标签内部声明一个子标签:
constructor-arg
。它用于指定构造器的参数,来进行属性注入。
constructor-arg
标签的编写规则如下:
<beanid="userConstructor"class="com.example.demo.bean.User"><constructor-argindex="0"value="example-username-constructor"/><constructor-argindex="1"value="25"/></bean>
index
属性表示构造函数参数的位置,它的值是一个非负整数,其中
0
表示第一个参数,
1
表示第二个参数,以此类推。虽然
value
属性的值总是一个字符串,但是
Spring
会尝试将它转换为构造函数参数所需的类型。例如构造函数的第二个参数是
int
类型,那么
Spring
会尝试将字符串
"25"
转换为整数
25
。
使用
index
属性来指定构造函数参数的位置在大多数情况下是可以的,但是如果构造函数的参数数量或者顺序发生了改变,就可能会出错。另外一种更为可靠的方式是使用
name
属性来指定参数的名称,如:
<beanid="userConstructor"class="com.example.demo.bean.User"><constructor-argname="username"value="example-username-constructor"/><constructor-argname="age"value="25"/></bean>
这样无论参数的顺序如何,只要参数名称不变,就不会出错。
2.2 使用@Bean注解进行构造器属性注入
在注解驱动的
bean
注册中,我们也可以直接使用编程方式赋值:
@BeanpublicUseruser(){returnnewUser("example-username-anno-constructor",25);}
2.3 构造器注入的完整代码示例
- 使用XML进行构造器注入
首先,我们需要创建一个
User
类,并在其中包含
username
和
age
两个属性,以及相应的
getter
、
setter
方法和构造器。
publicclassUser{privateString username;privateInteger age;publicUser(){}publicUser(String username,Integer age){this.username = username;this.age = age;}// 为了节省篇幅,getter和setter方法省略......@OverridepublicStringtoString(){return"User{username='"+ username +"', age="+ age +"}";}}
对于
XML
方式的构造器注入,我们需要创建一个配置文件,比如叫
applicationContext.xml
,这里保留
setter
注入方便大家对比
<beansxmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"><!-- setter方法注入 --><!-- setter方法注入 --><!-- <bean id="userSetter" class="com.example.demo.bean.User">--><!-- <property name="username" value="example-username-setter"/>--><!-- <property name="age" value="25"/>--><!-- </bean>--><!-- 构造器注入 --><beanid="userConstructor"class="com.example.demo.bean.User"><constructor-argname="username"value="example-username-constructor"/><constructor-argname="age"value="25"/></bean></beans>
然后,我们需要创建一个
DemoApplication
类,使用
ApplicationContext
来加载配置文件并获取
Bean
:
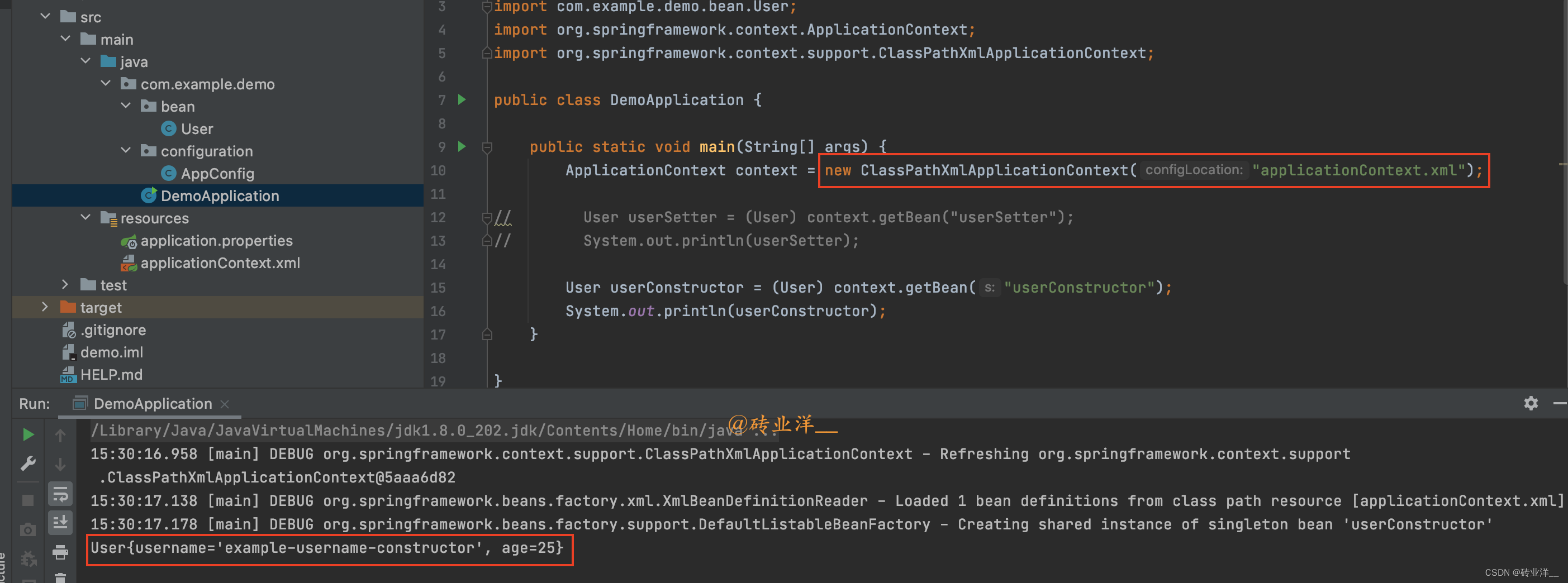
packagecom.example.demo;importcom.example.demo.bean.User;importorg.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;importorg.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;publicclassDemoApplication{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){ApplicationContext context =newClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");// User userSetter = (User) context.getBean("userSetter");// System.out.println(userSetter);User userConstructor =(User) context.getBean("userConstructor");System.out.println(userConstructor);}}
运行结果如下:
- 使用@Bean注解进行构造器属性注入
我们需要创建一个配置类,例如叫
AppConfig.java
:
importcom.example.demo.bean.User;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;@ConfigurationpublicclassAppConfig{// @Bean// public User userSetter() {// User user = new User();// user.setUsername("example-username-anno-setter");// user.setAge(25);// return user;// }@BeanpublicUseruserConstructor(){returnnewUser("example-username-anno-constructor",25);}}
同样,我们需要创建一个
DemoApplication
类,使用
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
来加载配置类并获取
Bean
:
importcom.example.demo.bean.User;importcom.example.demo.configuration.AppConfig;importorg.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;publicclassDemoApplication{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){ApplicationContext context =newAnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);// User userSetter = (User) context.getBean("userSetter");// System.out.println(userSetter);User userConstructor =(User) context.getBean("userConstructor");System.out.println(userConstructor);}}
运行结果:
注意:如果在类中同时使用构造器注入和
setter
注入,需要注意它们注入的顺序:先进行构造器注入,然后是
setter
注入。
3. 注解式属性注入
上面我们已经说过注解式的
setter
和构造器注入。我们又是如何处理那些通过
@Component
扫描而注册的
bean
的属性的呢?我们来仔细说说这个问题,同时展示如何在
xml
中进行相同的操作。
3.1 @Value注解式属性注入的应用
首先,让我们从最简单的属性注入方法:
@Value
开始。创建一个新的
White
类,并声明一些字段,但是这次我们不会设置
setter
方法:
@ComponentpublicclassWhite{@Value("white-value-annotation")privateString title;@Value("1")privateInteger rank;@OverridepublicStringtoString(){return"White{"+"title='"+ title +'\''+", rank="+ rank +'}';}}
要实现注解式属性注入,我们可以直接在需要注入的字段上添加
@Value
注解:
@Value("white-value-annotation")privateString title;@Value("1")privateInteger rank;
要注意的是,如果使用
@Value
注解来注入一个不存在的属性,那么应用程序会在启动时抛出异常。
然后,我们将通过组件扫描方式将这个
White
类扫描到
IOC
容器中,并将其取出并打印:
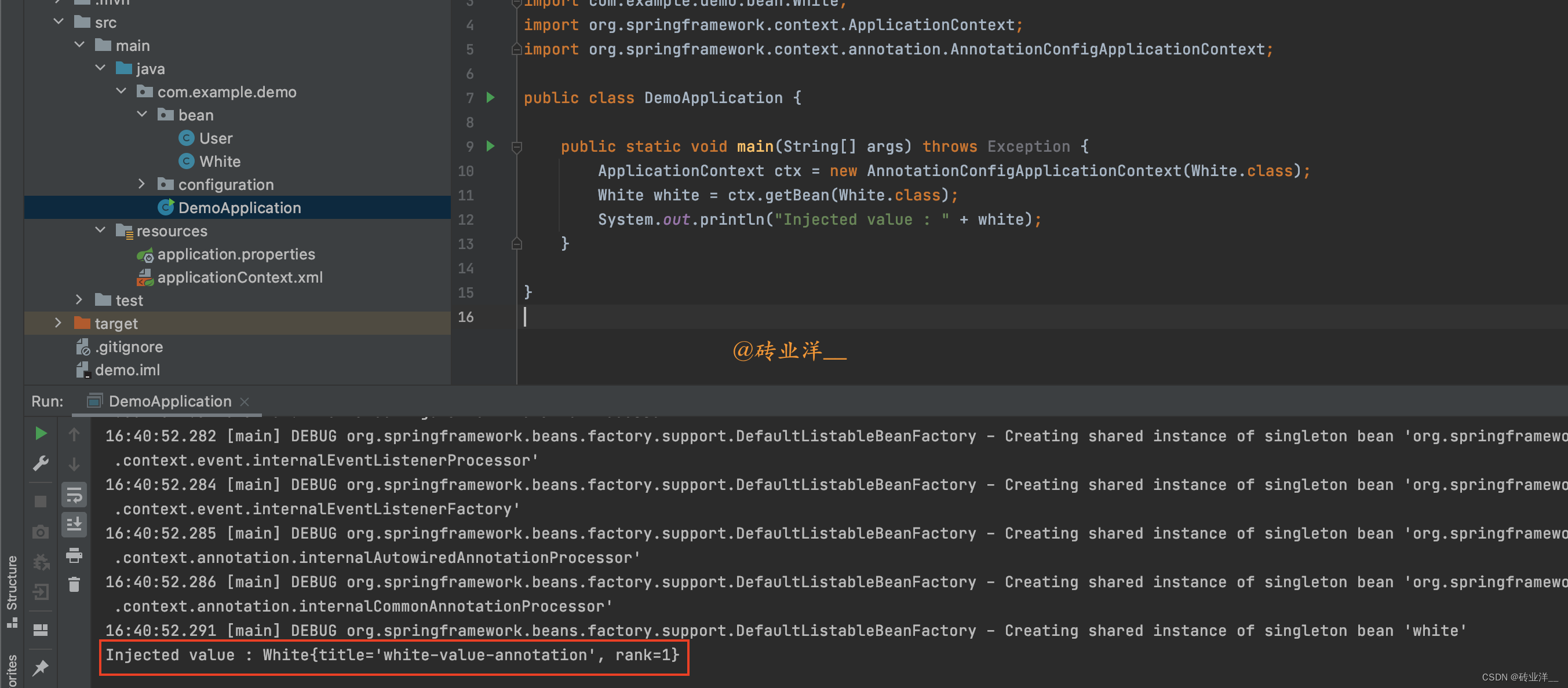
publicclassDemoApplication{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args)throwsException{ApplicationContext ctx =newAnnotationConfigApplicationContext(White.class);White white = ctx.getBean(White.class);System.out.println("Injected value : "+ white);}}
运行
main
方法会看到
White
的字段已经成功注入:
Injected value :White{title='white-value-annotation', rank=1}
3.2 引入外部配置文件@PropertySource
如果我们需要在
Spring
中使用
properties
文件,我们应该怎么办呢?
Spring
考虑到了这一点,并扩展了一个用于导入外部配置文件的注解:
@PropertySource
。
- 创建Bean和配置文件
创建一个新的
Blue
类,其结构与
White
类完全相同。然后在项目的
resources
目录下创建一个新的
blue.properties
文件,用于存储
Blue
类的属性配置:
blue.title=blue-value-properties
blue.rank=2
- 引入配置文件
使用
@PropertySource
注解将
properties
文件导入到配置类:
@Configuration@ComponentScan("com.example")@PropertySource("classpath:blue.properties")publicclassInjectValueConfiguration{}
这个
blue.properties
文件是一个键值对的列表,
Spring
将这些键值对加载到
Environment
中,我们可以通过
@Value
注解或者
Environment
类的方法来获取这些属性值。
@Value注解和
Environment类都可以用于读取
Spring上下文中的属性值。这些属性值可能来自于多个不同的源,包括但不限于:
Spring Boot的默认配置文件(application.properties或application.yml)。- 通过
@PropertySource注解加载的属性文件。- 系统环境变量。
Java系统属性(可以通过-D命令行参数设置)。
如果你想通过
@Value
注解来获取属性值,如下:
@ComponentpublicclassBlueConfig{@Value("${blue.title}")privateString title;@Value("${blue.rank}")privateint rank;// getters and setters...}
在
Spring
应用中使用
@PropertySource
注解来加载一个
.properties
文件时,这个文件中的所有配置项都会被读取,并存储在一个内部的
Map
结构中。这个
Map
的键是配置项的名称,值是配置项的值。
Spring
中的一些内置配置项也会被添加到这个
Map
中。
当我们使用
${...}
占位符语法来引用一个配置项时,
Spring
会查找这个
Map
,取出与占位符名称相应的配置项的值。例如有一个配置项
blue.title=blue-value-properties
,我们可以在代码中使用
${blue.title}
占位符来引用这个配置项的值。
如果想通过
Environment
类的方法来获取属性值,可以像下面这样做:
@ComponentpublicclassSomeComponent{@AutowiredprivateEnvironment env;publicvoidsomeMethod(){String title = env.getProperty("blue.title");int rank =Integer.parseInt(env.getProperty("blue.rank"));// ...}}
在上述代码中,
Environment
类的
getProperty
方法用于获取属性值。注意,
getProperty
方法返回的是
String
,所以如果属性是非字符串类型(如
int
),则需要将获取的属性值转换为适当的类型。
注意:**
@PropertySource
无法加载
YAML
格式的文件**,只能加载
properties
格式的文件。如果需要加载
YAML
格式的文件,而且使用的是
Spring Boot
框架,那么可以使用
@ConfigurationProperties
或
@Value
注解。例如以下的
YAML
文件:
application.yml
appTest:name: MyApp
version: 1.0.0
可以使用
@ConfigurationProperties
来加载这些属性:
@Configuration@ConfigurationProperties(prefix ="appTest")publicclassAppConfig{privateString name;privateString version;// getters and setters...}
@ConfigurationProperties
注解主要用于指定配置属性的前缀,
@ConfigurationProperties
注解本身并不直接指定配置文件的位置, 而是由
Spring Boot
的自动配置机制处理的。
这样,
name
字段就会被自动绑定到
appTest.name
配置属性,
version
字段就会被自动绑定到
appTest.version
配置属性。
默认情况下,
Spring Boot
会在启动时自动加载
src/main/resources
目录下的
application.properties
或
application.yml
文件。我们可以通过设置
spring.config.name
和
spring.config.location
属性来改变默认的配置文件名或位置。
注意:
@ConfigurationProperties
注解需要配合
@EnableConfigurationProperties
注解或
@Configuration
注解使用,以确保
Spring
能够发现并处理这些注解。
或者,你也可以使用
@Value
注解来加载这些属性:
@ComponentpublicclassAppConfig{@Value("${appTest.name}")privateString name;@Value("${appTest.version}")privateString version;// getters and setters...}
- Blue类的属性注入
对于
properties
类型的属性,我们这里选择
@Value
注解和占位符来注入属性:
@Value("${blue.title}")privateString title;@Value("${blue.rank}")privateInteger rank;
如果你熟悉
jsp
的
el
表达式,会发现这和它非常相似!
- 测试启动类
修改启动类,将配置类引入,然后取出并打印
Blue
:
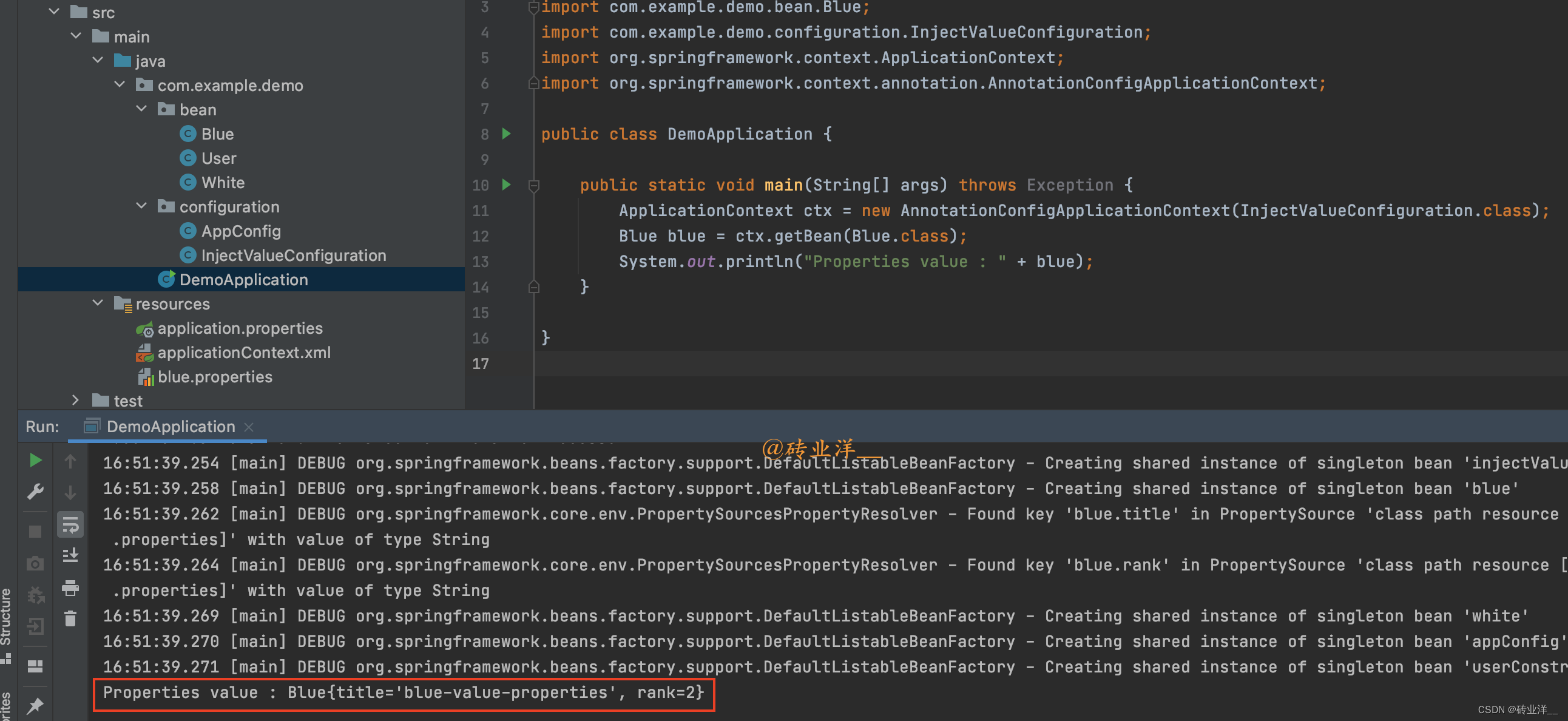
publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args)throwsException{ApplicationContext ctx =newAnnotationConfigApplicationContext(InjectValueConfiguration.class);Blue blue = ctx.getBean(Blue.class);System.out.println("Properties value : "+ blue);}
运行
main
方法会看到控制台已经成功打印出了配置文件的属性:
Properties value :Blue{title='blue-value-properties', rank=2}
3.3 在XML中引入外部配置文件
在
xml
中,我们可以和
@Value
相同的方式使用占位符:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beansxmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"><!-- 相当于注解中的 @PropertySource("classpath:blue.properties") --><context:property-placeholderlocation="classpath:blue.properties"/><beanclass="com.example.demo.bean.Blue"><propertyname="title"value="${blue.title}"/><propertyname="rank"value="${blue.rank}"/></bean></beans>
3.4 注解式属性注入完整代码示例
- @Value注解式属性注入的应用
创建
White
类:
packagecom.example.demo.bean;importorg.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;importorg.springframework.stereotype.Component;@ComponentpublicclassWhite{@Value("white-value-annotation")privateString title;@Value("1")privateInteger rank;@OverridepublicStringtoString(){return"White{"+"title='"+ title +'\''+", rank="+ rank +'}';}}
创建启动类
InjectValueAnnotationApplication
:
packagecom.example.demo;importcom.example.demo.bean.White;importorg.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;publicclassDemoApplication{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args)throwsException{ApplicationContext ctx =newAnnotationConfigApplicationContext(White.class);White white = ctx.getBean(White.class);System.out.println("Injected value : "+ white);}}
运行结果如下:
- 引入外部配置文件@PropertySource
创建
Blue
类和配置文件,没有
setter
和
getter
方法:
packagecom.example.demo.bean;importorg.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;importorg.springframework.stereotype.Component;@ComponentpublicclassBlue{@Value("${blue.title}")privateString title;@Value("${blue.rank}")privateInteger rank;@OverridepublicStringtoString(){return"Blue{"+"title='"+ title +'\''+", rank="+ rank +'}';}}
resources
目录下的
blue.properties
文件:
blue.title=blue-value-properties
blue.rank=2
创建配置类
InjectValueConfiguration
:
packagecom.example.demo.configuration;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;@Configuration@ComponentScan("com.example")@PropertySource("classpath:blue.properties")publicclassInjectValueConfiguration{}
修改启动类,引入配置类:
packagecom.example.demo;importcom.example.demo.bean.Blue;importcom.example.demo.configuration.InjectValueConfiguration;importorg.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;publicclassDemoApplication{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args)throwsException{ApplicationContext ctx =newAnnotationConfigApplicationContext(InjectValueConfiguration.class);Blue blue = ctx.getBean(Blue.class);System.out.println("Properties value : "+ blue);}}
运行结果如下:
- 在xml中引入外部配置文件
在使用
XML
配置的情况下,我们需要创建一个
XML
文件来替代
InjectValueConfiguration
类,我们可以先注释掉
InjectValueConfiguration
类的所有内容
下面是相应的
XML
文件内容:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beansxmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"><!-- 相当于注解中的 @PropertySource("classpath:blue.properties") --><context:property-placeholderlocation="classpath:blue.properties"/><beanclass="com.example.demo.bean.Blue"><propertyname="title"value="${blue.title}"/><propertyname="rank"value="${blue.rank}"/></bean></beans>
在这里我们使用了
context:property-placeholder
标签来导入外部的
properties
文件,然后使用
${...}
占位符语法来引用配置文件中的属性值。这样无论是选择用注解方式还是
XML
方式,都可以方便地在
Spring
中使用外部配置文件。
这里还需要修改下
Blue
类,因为通过
XML
方法注入属性需要提供相应的
setter
方法,修改后的
Blue
类如下:
packagecom.example.demo.bean;importorg.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;importorg.springframework.stereotype.Component;@ComponentpublicclassBlue{@Value("${blue.title}")privateString title;@Value("${blue.rank}")privateInteger rank;publicStringgetTitle(){return title;}publicvoidsetTitle(String title){this.title = title;}publicIntegergetRank(){return rank;}publicvoidsetRank(Integer rank){this.rank = rank;}@OverridepublicStringtoString(){return"Blue{"+"title='"+ title +'\''+", rank="+ rank +'}';}}
然后,我们需要修改启动类,使用
XmlApplicationContext
代替
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
:
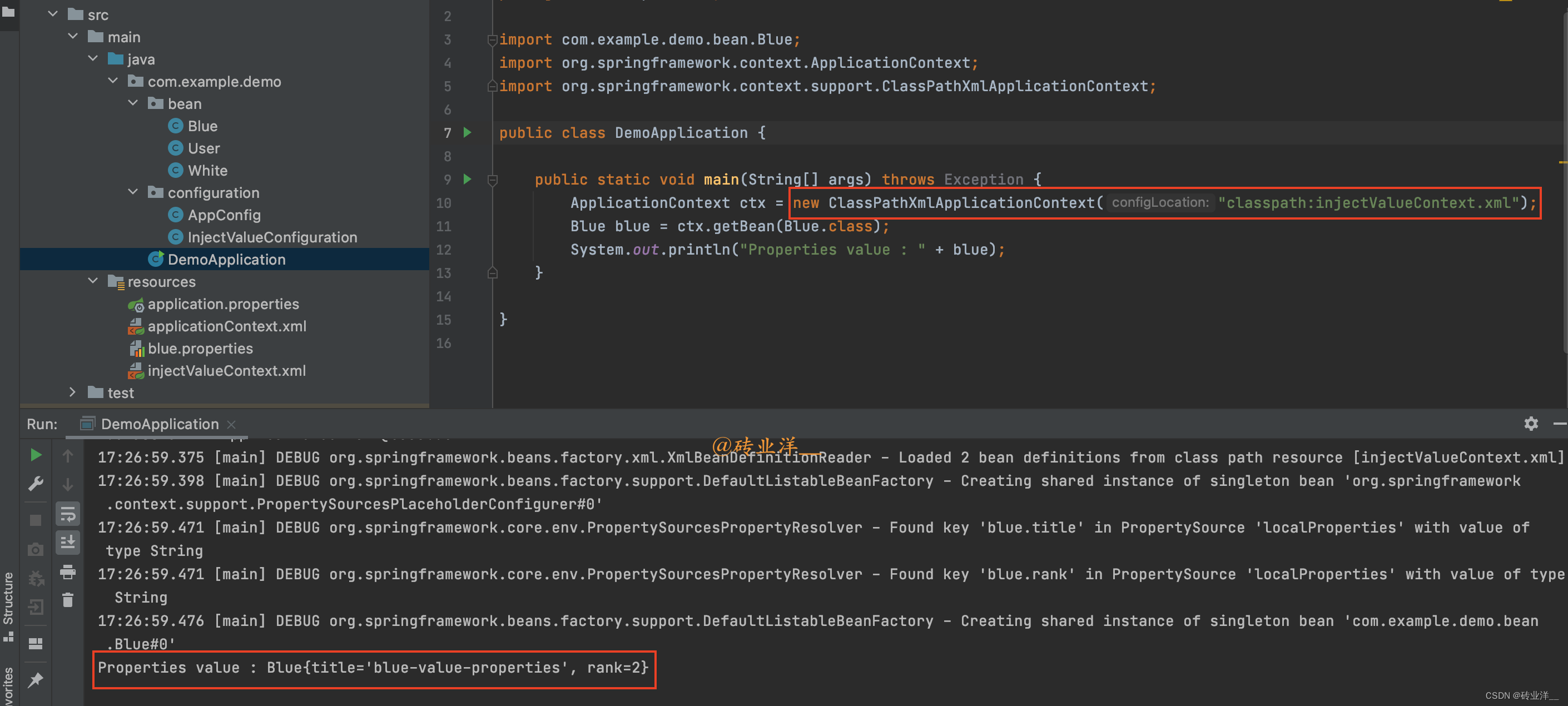
packagecom.example.demo;importcom.example.demo.bean.Blue;importorg.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;importorg.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;@ComponentScan("com.example")publicclassDemoApplication{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args)throwsException{ApplicationContext ctx =newClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:injectValueContext.xml");Blue blue = ctx.getBean(Blue.class);System.out.println("Properties value : "+ blue);}}
运行结果如下:
4. SpEL表达式
当我们谈到属性注入的时候,我们可能会遇到一些复杂的需求,例如我们需要引用另一个
Bean
的属性,或者我们需要动态处理某个属性值。这种需求无法通过使用
${}
的占位符方式实现,我们需要一个更强大的工具:
SpEL
表达式。
Spring Expression Language
(
SpEL
)是从
Spring
框架
3.0
开始支持的强大工具。
SpEL
不仅是
Spring
框架的重要组成部分,也可以独立使用。它的功能丰富,包括调用属性值、属性参数、方法调用、数组存储以及逻辑计算等。它与开源项目
OGNL
(
Object-Graph Navigation Language
)相似,但
SpEL
是
Spring
框架推出的,并默认内嵌在
Spring
框架中。
4.1 使用@Value注解和SpEL表达式实现属性注入
SpEL
的表达式用
#{}
表示,花括号中就是我们要编写的表达式。
我们创建一个
Bean
,命名为
Azure
,同样地,我们声明属性
name
和
priority
,并提供
getter
和
setter
方法以及
toString()
方法。然后我们使用
@Component
注解标注它。
使用
@Value
配合
SpEL
完成属性注入,如下:
@ComponentpublicclassAzure{@Value("#{'spel-for-azure'}")privateString name;@Value("#{10}")privateInteger priority;}
我们修改启动类,从
IOC
容器中获取
Azure
并打印,可以看到属性被成功注入:
Azure{name='spel-for-azure', priority=10}
SpEL
的功能远不止这些,它还可以获取
IOC
容器中其他
Bean
的属性,让我们来展示一下。
我们已经注册了
Azure Bean
,现在我们再创建一个
Bean
,命名为
Emerald
。我们按照上述方法对字段和方法进行声明,然后使用
@Component
注解标注。
我们希望
name
属性直接复制
Azure
的
name
属性,而
priority
属性则希望比
Azure
的
priority
属性大
1
,我们可以这样编写:
@ComponentpublicclassEmerald{@Value("#{'copy of ' + azure.name}")privateString name;@Value("#{azure.priority + 1}")privateInteger priority;}
在
Spring
的
SpEL
中可以通过
bean
的名称访问到对应的
bean
,并通过
.
操作符访问
bean
的属性。在这个例子中,
azure
就是一个
bean
的名称,它对应的
bean
就是
Azure
类的实例。所以,
azure.name
就是访问
Azure
类实例的
name
属性。
如果你在一个不涉及
Spring
的环境中使用
SpEL
,这个特性是不会生效的。这是因为这个特性依赖于
Spring
的
IoC
容器。
我们修改启动类,测试运行,可以看到
Azure
的属性已经成功被复制:
use spel bean property :Emerald{name='copy of spel-for-azure', priority=11}
SpEL
表达式不仅可以引用对象的属性,还可以直接引用类的常量,以及调用对象的方法。下面我们通过示例进行演示。
我们新建一个
Bean
,命名为
Ivory
。我们按照上述方法初始化属性、
toString()
方法、注解。
假设我们有一个需求,让
name
取
azure
属性的前
3
个字符,
priority
取
Integer
的最大值。那么我们可以使用
SpEL
这样写:
@ComponentpublicclassIvory{@Value("#{azure.name.substring(0, 3)}")privateString name;@Value("#{T(java.lang.Integer).MAX_VALUE}")privateInteger priority;}
注意,直接引用类的属性,需要在类的全限定名外面使用
T()
包围。
我们修改启动类,测试运行,可以看到
Ivory
的属性已经是处理之后的值:
use spel methods :Ivory{name='spe', priority=2147483647}
4.2 在XML中使用SpEL表达式实现属性注入:
<beanid="ivory"class="com.example.demo.bean.Ivory"><propertyname="name"value="#{azure.name.substring(0, 3)}"/><propertyname="priority"value="#{T(java.lang.Integer).MAX_VALUE}"/></bean>
学习
SpEL
表达式不需要花费大量的精力,掌握基础的使用方法即可。
4.3 SpEL表达式属性注入完整代码示例
- 使用@Value注解和SpEL表达式实现属性注入
创建三个
SpEL
表达式属性注入的
Bean
:
Azure.java
、
Emerald.java
和
Ivory.java
。
Azure.java:
packagecom.example.demo.bean;importorg.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;importorg.springframework.stereotype.Component;@ComponentpublicclassAzure{@Value("#{'spel-for-azure'}")privateString name;@Value("#{10}")privateInteger priority;publicStringgetName(){return name;}publicvoidsetName(String name){this.name = name;}publicIntegergetPriority(){return priority;}publicvoidsetPriority(Integer priority){this.priority = priority;}@OverridepublicStringtoString(){return"Azure{"+"name='"+ name +'\''+", priority="+ priority +'}';}}
Emerald.java:
packagecom.example.demo.bean;importorg.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;importorg.springframework.stereotype.Component;@ComponentpublicclassEmerald{@Value("#{'copy of ' + azure.name}")privateString name;@Value("#{azure.priority + 1}")privateInteger priority;publicStringgetName(){return name;}publicvoidsetName(String name){this.name = name;}publicIntegergetPriority(){return priority;}publicvoidsetPriority(Integer priority){this.priority = priority;}@OverridepublicStringtoString(){return"Emerald{"+"name='"+ name +'\''+", priority="+ priority +'}';}}
Ivory.java:
packagecom.example.demo.bean;importorg.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;importorg.springframework.stereotype.Component;@ComponentpublicclassIvory{@Value("#{azure.name.substring(0, 3)}")privateString name;@Value("#{T(java.lang.Integer).MAX_VALUE}")privateInteger priority;publicStringgetName(){return name;}publicvoidsetName(String name){this.name = name;}publicIntegergetPriority(){return priority;}publicvoidsetPriority(Integer priority){this.priority = priority;}@OverridepublicStringtoString(){return"Ivory{"+"name='"+ name +'\''+", priority="+ priority +'}';}}
MyBean.java
@ComponentpublicclassMyBean{@AutowiredprivateAzure azure;@AutowiredprivateEmerald emerald;@AutowiredprivateIvory ivory;publicvoidinit(){System.out.println(azure);System.out.println(emerald);System.out.println(ivory);}}
MyBean
是一个用于展示如何在
Spring
中通过
SpEL
表达式来注入属性的类,它聚合了三个对象
Azure
,
Emerald
和
Ivory
,并通过
Spring
的依赖注入机制将这三个对象注入到了
MyBean
类的实例中
主程序
DemoApplication
@SpringBootApplicationpublicclassDemoApplication{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){ApplicationContext applicationContext =SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);MyBean myBean = applicationContext.getBean(MyBean.class);
myBean.init();}}
运行结果: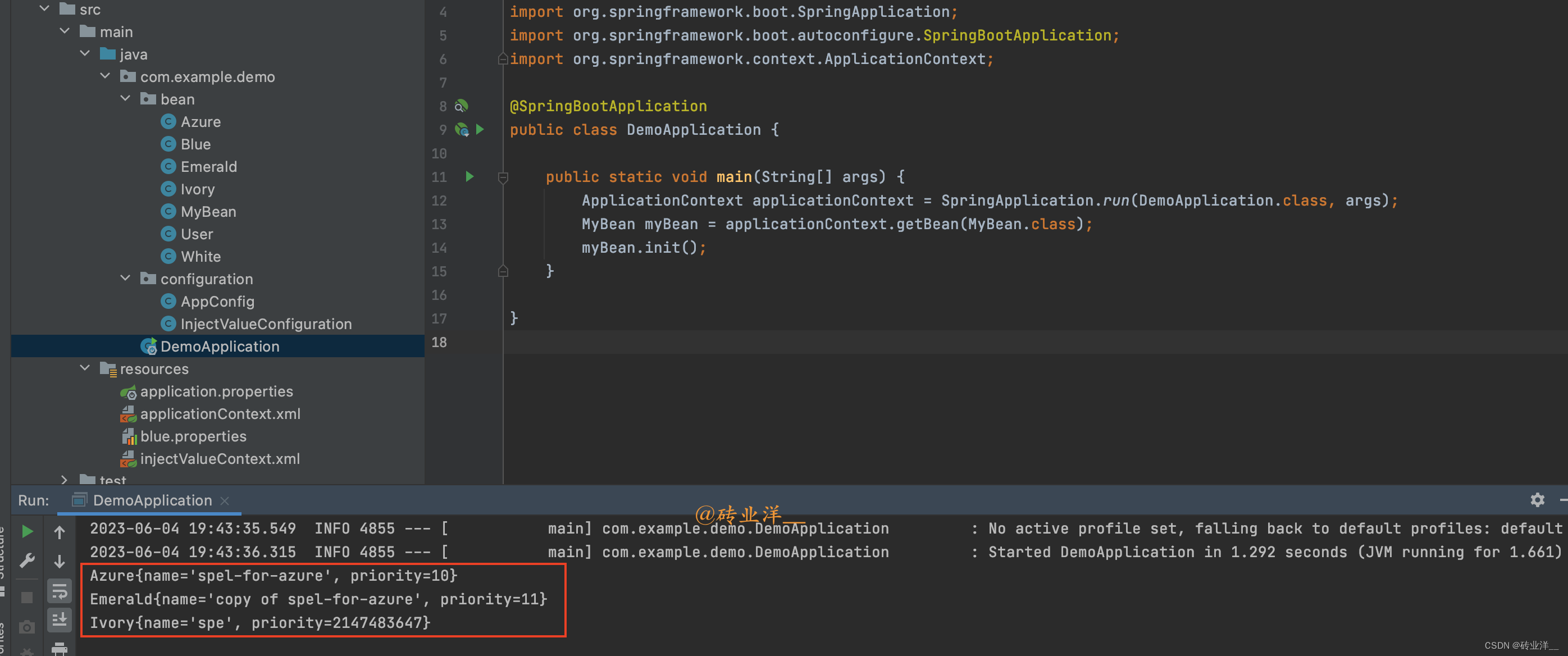
- 在XML中使用SpEL表达式实现属性注入
对于
XML
配置,
Spring
还支持在
bean
定义中使用
SpEL
。
首先,需要创建一个
Spring XML
配置文件,我们将其命名为
app-config.xml
:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beansxmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"><context:component-scanbase-package="com.example"/><beanid="azure"class="com.example.demo.bean.Azure"><propertyname="name"value="#{'spel-for-azure'}"/><propertyname="priority"value="#{10}"/></bean><beanid="emerald"class="com.example.demo.bean.Emerald"><propertyname="name"value="#{'copy of ' + azure.name}"/><propertyname="priority"value="#{azure.priority + 1}"/></bean><beanid="ivory"class="com.example.demo.bean.Ivory"><propertyname="name"value="#{azure.name.substring(0, 3)}"/><propertyname="priority"value="#{T(java.lang.Integer).MAX_VALUE}"/></bean></beans>
注意:在
XML
中使用
SpEL
需要使用
#{}
,而不是
${}
。
然后修改这
3
个
Bean
,如果是使用
XML
来配置
Spring
的
Bean
的话,那么在
Java
类中就不需要使用
@Component
注解了。因为
XML
配置文件已经明确地告诉
Spring
这些类是
Spring Bean
。
同样的,如果在
XML
文件中定义了
Bean
的属性值,那么在
Java
类中就不需要使用
@Value
注解来注入这些值了。因为
XML
配置文件已经明确地为这些属性赋了值。
Azure.java
packagecom.example.demo.bean;publicclassAzure{privateString name;privateInteger priority;publicStringgetName(){return name;}publicvoidsetName(String name){this.name = name;}publicIntegergetPriority(){return priority;}publicvoidsetPriority(Integer priority){this.priority = priority;}@OverridepublicStringtoString(){return"Azure{"+"name='"+ name +'\''+", priority="+ priority +'}';}}
Emerald.java
packagecom.example.demo.bean;publicclassEmerald{privateString name;privateInteger priority;publicStringgetName(){return name;}publicvoidsetName(String name){this.name = name;}publicIntegergetPriority(){return priority;}publicvoidsetPriority(Integer priority){this.priority = priority;}@OverridepublicStringtoString(){return"Emerald{"+"name='"+ name +'\''+", priority="+ priority +'}';}}
Ivory.java
packagecom.example.demo.bean;publicclassIvory{privateString name;privateInteger priority;publicStringgetName(){return name;}publicvoidsetName(String name){this.name = name;}publicIntegergetPriority(){return priority;}publicvoidsetPriority(Integer priority){this.priority = priority;}@OverridepublicStringtoString(){return"Ivory{"+"name='"+ name +'\''+", priority="+ priority +'}';}}
然后需要在主程序中导入这个
XML
配置文件,这可以通过在主程序中添加
@ImportResource
注解实现:
packagecom.example.demo;importcom.example.demo.bean.MyBean;importorg.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;importorg.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;importorg.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;importorg.springframework.context.annotation.ImportResource;@SpringBootApplication@ImportResource("classpath:app-config.xml")publicclassDemoApplication{publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args){ApplicationContext applicationContext =SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);MyBean myBean = applicationContext.getBean(MyBean.class);
myBean.init();}}
这样就可以在
Spring
的
XML
配置文件中使用
SpEL
了。
运行结果如下:
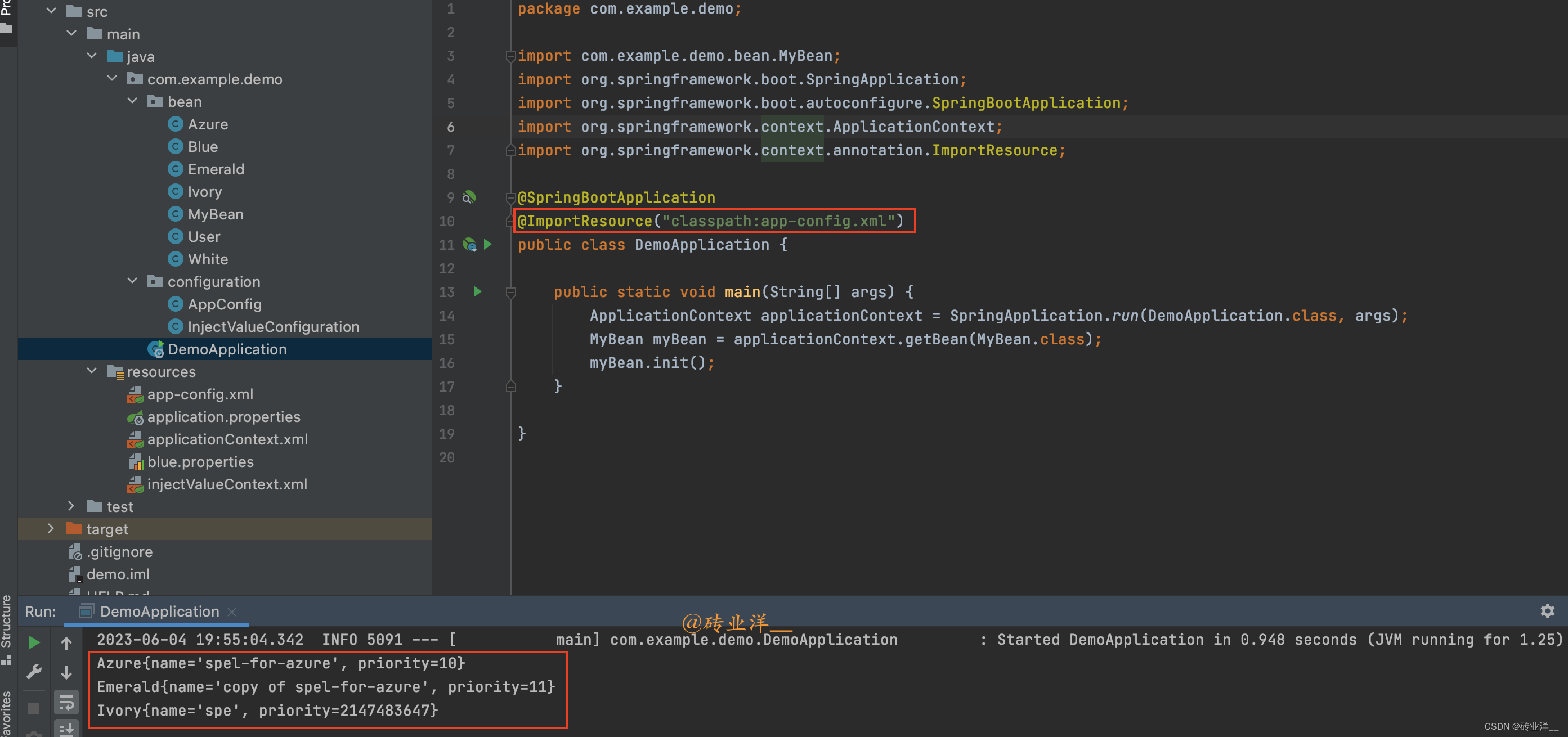
欢迎一键三连~
有问题请留言,大家一起探讨学习
----------------------Talk is cheap, show me the code-----------------------
版权归原作者 砖业洋__ 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。