最近学习用AFL(American Fuzzy Lop)进行漏洞挖掘,简单的记录一下AFL的QEMU模式的使用。
首先创建测试用例:test.c
#include<stdio.h>#include<stdlib.h>#include<unistd.h>#include<string.h>#include<signal.h>intvuln(char*str){int len =strlen(str);if(str[0]=='A'&& len ==66){raise(SIGSEGV);//如果输入的字符串的首字符为A并且长度为66,则异常退出}elseif(str[0]=='F'&& len ==6){raise(SIGSEGV);//如果输入的字符串的首字符为F并且长度为6,则异常退出}else{printf("it is good!\n");}return0;}intmain(int argc,char*argv[]){char buf[100]={0};gets(buf);//存在栈溢出漏洞printf(buf);//存在格式化字符串漏洞vuln(buf);return0;}
编译生成MIPS架构的可执行文件(需要建立MIPS交叉编译环境)
使用
mips-linux-gcc
编译
test.c
文件,
mips-linux-gcc -g -o mips-test test.c
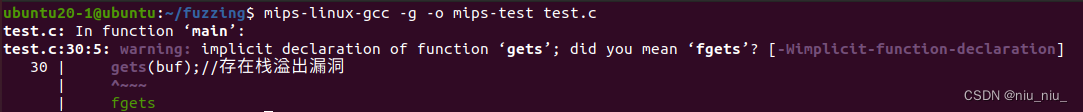
使用
file
命令查看文件类型
ubuntu20-1@ubuntu:~/fuzzing$ file mips-test
mips-test: ELF 32-bit MSB executable, MIPS, MIPS32 version 1(SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib/ld-uClibc.so.0, with debug_info, not stripped
在qemu模式下,AFL使用qemu用户模式来运行二进制文件。所以在使用afl进行fuzz前,先用qemu的用户模式测试MIPS文件能否正常运行
ubuntu20-1@ubuntu:~/fuzzing$ qemu-mips -L ./ mips-test
qemu-mips: Could not open'/lib/ld-uClibc.so.0': No such file or directory
-L
参数的作用:将elf解释器前缀设置为“path”,通常为
lib
文件夹的父目录
-L path QEMU_LD_PREFIX set the elf interpreter prefix to 'path'
报错:
qemu-mips: Could not open '/lib/ld-uClibc.so.0': No such file or directory
,缺少
lib
文件
解决方法:在当前目录创建
lib
文件夹,使用
locate
命令进行查找,并将
ld-uClibc.so.0
文件复制进
lib
文件夹
ubuntu20-1@ubuntu:~/fuzzing$ locate ld-uClibc.so.0
/home/ubuntu20-1/buildroot-mips/output/build/uclibc-1.0.39/lib/ld-uClibc.so.0
/home/ubuntu20-1/buildroot-mips/output/host/mips-buildroot-linux-uclibc/sysroot/lib/ld-uClibc.so.0
/home/ubuntu20-1/buildroot-mips/output/target/lib/ld-uClibc.so.0
ubuntu20-1@ubuntu:~/fuzzing$ mkdir lib
ubuntu20-1@ubuntu:~/fuzzing$ cp /home/ubuntu20-1/buildroot-mips/output/target/lib/ld-uClibc.so.0 ./lib
#再次执行qemu-mips,仍然报错,解决方法同上
ubuntu20-1@ubuntu:~/fuzzing$ qemu-mips -L ./ mips-test
/home/ubuntu20-1/fuzzing/mips-test: can't load library 'libc.so.0'
ubuntu20-1@ubuntu:~/fuzzing$ locate libc.so.0
/home/ubuntu20-1/buildroot-mips/output/build/uclibc-1.0.39/lib/ld-uClibc.so.0
/home/ubuntu20-1/buildroot-mips/output/build/uclibc-1.0.39/lib/libc.so.0
/home/ubuntu20-1/buildroot-mips/output/host/mips-buildroot-linux-uclibc/sysroot/lib/ld-uClibc.so.0
/home/ubuntu20-1/buildroot-mips/output/host/mips-buildroot-linux-uclibc/sysroot/lib/libc.so.0
/home/ubuntu20-1/buildroot-mips/output/target/lib/ld-uClibc.so.0
/home/ubuntu20-1/buildroot-mips/output/target/lib/libc.so.0
ubuntu20-1@ubuntu:~/fuzzing$ cp /home/ubuntu20-1/buildroot-mips/output/host/mips-buildroot-linux-uclibc/sysroot/lib/libc.so.0 ./lib
#再次执行qemu-mips
ubuntu20-1@ubuntu:~/fuzzing$ qemu-mips -L ./ mips-test
123
123it is good!#正常输出,可用afl-fuzz进行测试
进行fuzz
创建
afl-fuzz
的输入文件夹,并构造测试用例
mkdir afl-in
cd afl-in
echo abc > testcase
cd..
使用
afl-fuzz
进行fuzz,因为没有使用
afl-gcc
进行插桩编译,需要加上
-Q
参数,即使用QEMU模式进行fuzz测试
#初始化设置#需要设置core_pattern,若未设置会出现报错1,详情见后文sudosuecho core >/proc/sys/kernel/core_pattern
exit#设置AFL相关的环境变量#AFL_PATH为afl的安装路径#QEMU_LD_PREFIX 为 MIPS 的 lib/ 目录所在的目录,MIPS文件的根目录exportAFL_PATH=/home/ubuntu20-1/afl-2.52b
exportQEMU_LD_PREFIX=.
#若未设置 -m none,会出现报错2,详情见后文#若未设置export QEMU_LD_PREFIX=.,会出现报错3,详情见后文
afl-fuzz -i afl-in -o afl-out -m none -Q ./mips-test
参数解释:
-i afl-in
:输入文件夹为
afl-in
-o afl-out
:输出文件夹为
afl-out
-m none
:不限制内存大小
-Q
:使用afl的QEMU模式
./mips-test
:被fuzz测试的文件
开始fuzz
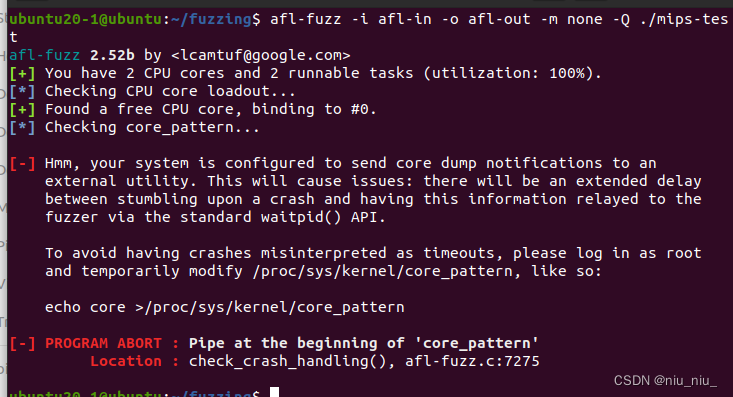
报错1:
[-] Hmm, your system is configured to send core dump notifications to an
external utility. This will cause issues: there will be an extended delay
between stumbling upon a crash and having this information relayed to the
fuzzer via the standard waitpid() API.
To avoid having crashes misinterpreted as timeouts, please log in as root
and temporarily modify /proc/sys/kernel/core_pattern, like so:
echo core >/proc/sys/kernel/core_pattern
[-] PROGRAM ABORT : Pipe at the beginning of 'core_pattern'
Location : check_crash_handling(), afl-fuzz.c:7275
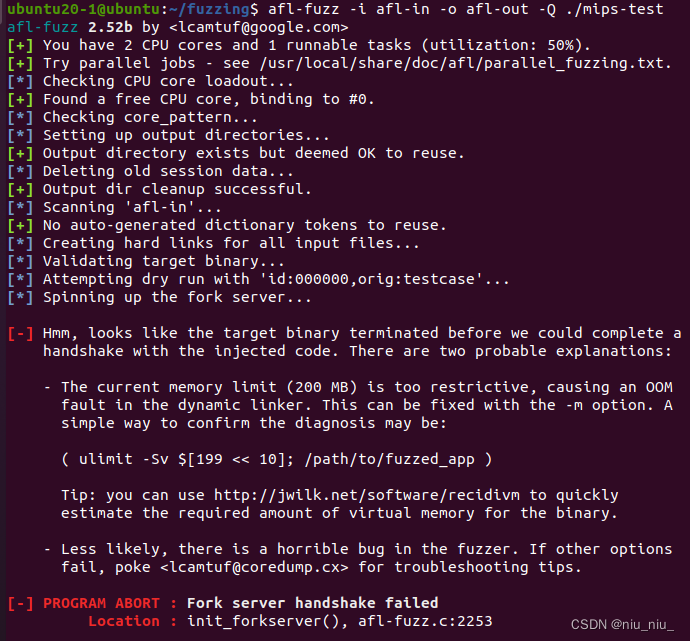
报错2:
[-] Hmm, looks like the target binary terminated before we could complete a
handshake with the injected code. There are two probable explanations:
- The current memory limit (200 MB) is too restrictive, causing an OOM
fault in the dynamic linker. This can be fixed with the -m option. A
simple way to confirm the diagnosis may be:
(ulimit -Sv $[199<<10]; /path/to/fuzzed_app )
Tip: you can use http://jwilk.net/software/recidivm to quickly
estimate the required amount of virtual memory for the binary.
- Less likely, there is a horrible bug in the fuzzer. If other options
fail, poke <[email protected]>for troubleshooting tips.
[-] PROGRAM ABORT : Fork server handshake failed
Location : init_forkserver(), afl-fuzz.c:2253
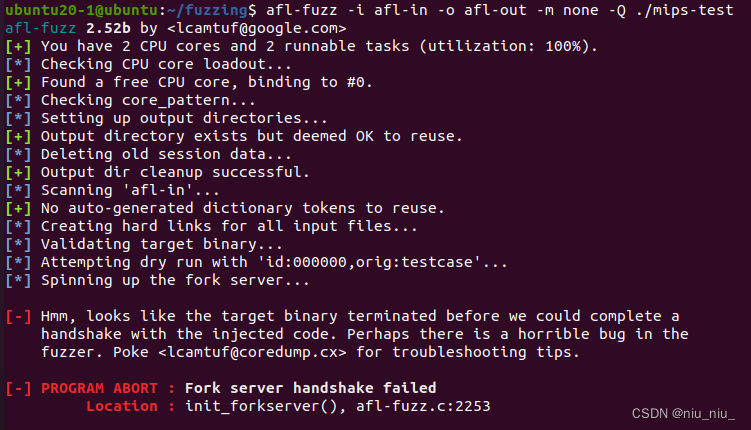
报错3:
[-] Hmm, looks like the target binary terminated before we could complete a
handshake with the injected code. Perhaps there is a horrible bug in the
fuzzer. Poke <[email protected]>for troubleshooting tips.
[-] PROGRAM ABORT : Fork server handshake failed
Location : init_forkserver(), afl-fuzz.c:2253
版权归原作者 niu_niu_ 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。