文章目录
概念:
- 数据库管理系统的一个重要功能就是数据查询,数据查询不应只是简单返回数据库中存储的数据,还应该根据需要对数据进行筛选以及确定数据以什么样的形式格式显示。
- MySQL提供了功能强大、灵活的语句来实现这些操作。
- MySQL数据库使用select语句来查询数据。
一. 基本查询
语法格式:
select[all|distinct]<目标列的表达式1>[别名],<目标列的表达式2>[别名]...from<表名或视图名>[别名],<表名或视图名>[别名]...[where<条件表达式>][groupby<列名>[having<条件表达式>]][orderby<列名>[asc|desc]][limit<数字或者列表>];
简化语法:
select*| 列名 from 表 where 条件
举例:
– 创建数据库
createdatabaseifnot exist mydb2;use mydb2;
– 创建商品表:
createtable product(
pid intprimarykeyauto_increment,-- 商品编号
pname varchar(20)notnull,-- 商品名字
price double,-- 商品价格
category_id varchar(20)-- 商品所属分类);
添加数据:
insertinto product values(null,'海尔洗衣机',5000,'c001');insertinto product values(null,'美的冰箱',3000,'c001');insertinto product values(null,'格力空调',5000,'c001');insertinto product values(null,'九阳电饭煲',200,'c001');insertinto product values(null,'啄木鸟衬衣',300,'c002');insertinto product values(null,'恒源祥西裤',800,'c002');insertinto product values(null,'花花公子夹克',440,'c002');insertinto product values(null,'劲霸休闲裤',266,'c002');insertinto product values(null,'海澜之家卫衣',180,'c002');insertinto product values(null,'杰克琼斯运动裤',430,'c002');insertinto product values(null,'兰蔻面霜',300,'c003');insertinto product values(null,'雅诗兰黛精华水',200,'c003');insertinto product values(null,'香奈儿香水',350,'c003');insertinto product values(null,'SK-II神仙水',350,'c003');insertinto product values(null,'资生堂粉底液',180,'c003');insertinto product values(null,'老北京方便面',56,'c004');insertinto product values(null,'良品铺子海带丝',17,'c004');insertinto product values(null,'三只松鼠坚果',88,null);
– 简单查询
-- 1.查询所有的商品select pid, pname, price, category_id from product;--或者select*from product;

-- 2.查询商品名和商品价格select pname, price from product;

– 3.别名查询,使用的关键字是as(as是可以省略的)
– 3.1 表别名:
select*from product as p;

– 3.2 列别名:
select pname as'商品名', price '商品价格'from product;

– 4.去掉重复值.
selectdistinct price from product;-- 按列进行比较,把该列相同的元组去掉

selectdistinct*from product;-- 按行(元组)进行比较,把相同行去掉

因为没有相同的行,所以不变。
– 5.查询结果是表达式(运算查询):将所有商品的价格加10元进行显示。
select pname, price +10as'new price'from product;-- 同时我们对price + 10取个别名

二. 运算符
数据库中的表结构确立后,表中的数据代表的意义就已经确定。通过MySQL运算符进行运算,就可以获取到表结构以外的另一种数据。
MySQL支持的四种运算符:
- 算术运算符
- 比较运算符
- 逻辑运算符
- 位运算符
2.1 算术运算符

举例:
select6+2;-- 8select6-2;-- 4select6*2;-- 12select6/2;-- 3select6%2;-- 0
– 将每件商品的价格加10
select name,price +10as new_price from product;

– 将所有商品的价格上调10%
select pname,price *1.1as new_price from product;

2.2 位运算符和逻辑运算符
位运算符:
位运算符是对二进制的一种运算,对二进制中的每一位进行一一运算后的出来的值,再把值以十进制的形式返回。

举例:
select3&5;-- 位与 = 1select3|5;-- 位或 = 7select3^5;-- 位异或 = 6select3>>1;-- 位左移 = 1select3<<1;-- 位右移 = 6select~3;-- 位取反 = 18446744073709551612
逻辑运算符
2.3 比较运算符

举例:
条件查询
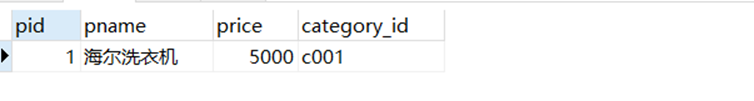
– 查询商品名称为“海尔洗衣机”的商品所有信息:
select*from product where pname ='海尔洗衣机';
– 查询价格为800商品
select*from product where price =800;
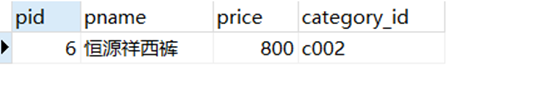
– 查询价格不是800的所有商品
select*from product where price !=800;select*from product where price <>800;select*from product wherenot(price =800);

– 查询商品价格大于60元的所有商品信息
select*from product where price >60;

– 查询商品价格在200到1000之间所有商品
select*from product where price >=200and price <=1000;select*from product where price between200and1000;

– 查询商品价格是200或800的所有商品
select*from product where price =200or price =800;select*from product where price =200|| price =800;select*from product where price in(200,800);
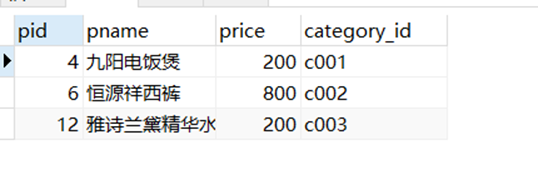
– 查询含有‘裤’字的所有商品
select*from product where pname like'%裤%';-- % 可以抵消任意多个字符

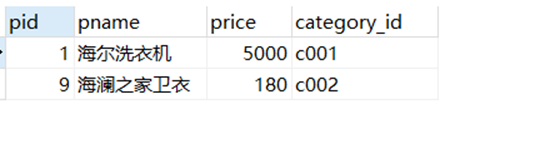
– 查询以’海’开头的所有商品
select*from product where pname like'海%';
– 查询第二个字为’蔻’的所有商品
select*from product where pname like'_蔻%';-- _ 可以抵消一个字符
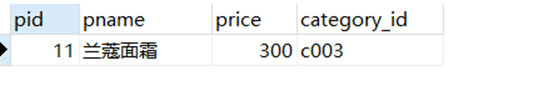
– 查询category_id为null的商品
select*from product where category_id isnull;

– 查询category_id不为null分类的商品
select*from product where category_id isnotnull;

– 使用least求最小值
select least(10,30,39,1,3);-- 1select least(10,null,30);-- null
– 使用greatest求最大值
select greatest(10,20,30);select greatest(10,null,30);-- null
三.排序查询
如果我们需要对读取的数据进行排序,我们就可以使用 MySQL 的 order by
子句来设定你想按哪个字段哪种方式来进行排序,再返回搜索结果
语法格式:
select
字段名1,字段名2,……
from 表名
orderby 字段名1[asc|desc],字段名2[asc|desc]……
特点:
1.asc代表升序,desc代表降序,如果不写默认升序
2.order by用于子句中可以支持单个字段,多个字段,表达式,函数,别名
3.order by子句,放在查询语句的最后面。LIMIT子句除外
举例:
– 1.使用价格排序(降序)
select*from product orderby price desc;

– 2.在价格排序(降序)的基础上,以分类排序(降序)
select*from product orderby price desc, pid desc;

– 3.显示商品的价格(去重复),并排序(降序)
selectdistinct price from product orderby price desc;

四.聚合查询
之前我们用的查询都是横向查询,也就是整行整行地进行判断,而聚合查询是纵向的查询,它是对一列的值进行计算,然后返回一个单一的值。同时聚合函数会忽略空值。

4.1 聚合查询举例:
– 1. 查询商品的总条数
selectcount(*)as'columns'from product;

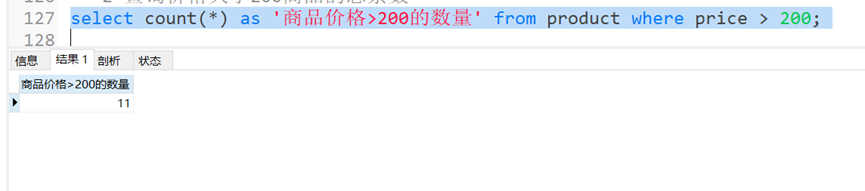
– 2. 查询价格大于200商品的总条数
selectcount(*)as'商品价格>200的数量'from product where price >200;
– 3 查询分类为’c001’的所有商品的总和
selectsum(price)from product where category_id ='c001';

– 4 查询商品的最大价格
selectmax(price)from product;

– 5 查询商品的最小价格
selectmin(price)from product;

– 6 查询分类为’c002’所有商品的平均价格
selectavg(price)from product where category_id ='c002';

4.2 NULL值处理
介绍:
1、count函数对null值的处理
如果count函数的参数为星号(*),则统计所有记录的个数。而如果参数为某字段,不统计含null值的记录个数。
2、sum和avg函数对null值的处理 这两个函数忽略null值的存在,就好象该条记录不存在一样。
3、max和min函数对null值的处理 max和min两个函数同样忽略null值的存在。
举例:
– 创建表
createtable test_null(
c1 varchar(20),
C2 int);
– 插入数据
insertinto test_null values('aaa',3);insertinto test_null values('bbb',3);insertinto test_null values('ccc',null);insertinto test_null values('ddd',6);
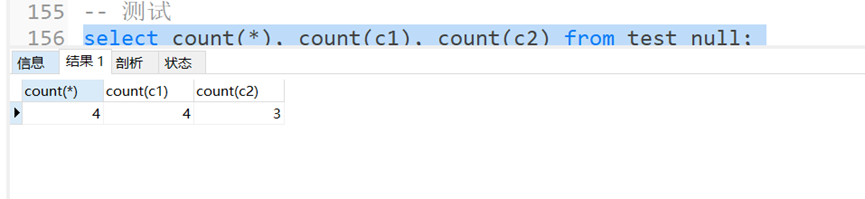
– 测试
selectcount(*),count(c1),count(c2)from test_null;
selectsum(c2),max(c2),min(c2),avg(c2)from test_null;

五.分组查询
分组查询使用group by字句对查询信息进行分组。
语法格式:
Select 字段1,字段2… from 表名 groupby 分组字段 having 分组条件;
举例:
– 1 统计各个分类商品的个数
select category_id,count(*)from product groupby category_id;

注意:
如果要进行分组的话,select语句后面只能出现分组的语句和统计函数,不能有其他字段出现。
分组查询之后的条件筛选
- 分组之后对统计结果进行筛选的话必须使用having,不能使用where
- where子句用来筛选 FROM 子句中指定的操作所产生的行
- group by 子句用来分组 WHERE 子句的输出。
- having 子句用来从分组的结果中筛选行
举例:
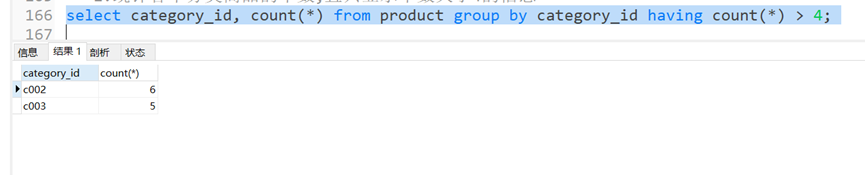
– 统计各个分类商品的个数,且只显示个数大于4的信息
select category_id,count(*)from product groupby category_id havingcount(*)>4;
六.分页查询
分页查询在项目开发中常见,由于数据量很大,显示屏长度有限,因此对数据需要采取分页显示方式。例如数据共有30条,每页显示5条,第一页显示1-5条,第二页显示6-10条。
语法格式:
– 方式1-显示前n条
select 字段1,字段2...from 表明 limit n
– 方式2-分页显示
select 字段1,字段2...from 表明 limit m,n
其中:
m: 整数,表示从第几条索引开始,计算方式 (当前页-1)*每页显示条数
n: 整数,表示查询多少条数据
举例:
– 查询product表的前5条记录
select*from product limit5;

– 从第4条开始显示,显示5条
select*from product limit3,5;

七. INSERT INTO SELECT语句
将一张表的数据导入到另一张表中,可以使用INSERT INTO SELECT语句 。
语法格式:
insertinto Table2(field1,field2,…)select value1,value2,… from Table1
orinsertinto Table2 select*from Table1
要求table2必须存在
八. SELECT INTO FROM语句
将一张表的数据导入到另一张表中,有两种选择 SELECT INTO 和 INSERT INTO SELECT 。
语法格式:
SELECT vale1, value2 into Table2 from Table1
要求目标表Table2不存在,因为在插入时会自动创建表Table2,并将Table1中指定字段数据复制到Table2中。
版权归原作者 友人苏 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。