最长异或路径:
题目大意:

思路解析:
现在假设有一棵这样的树,我们并不关心每条边的路径权值为多少,假设划红线的地方是异或值最大的一条路径,那我们可以发现我们只需要知道1-11的异或值,1-7路径的异或值,那我们在贪心的过程一定能得到最优答案
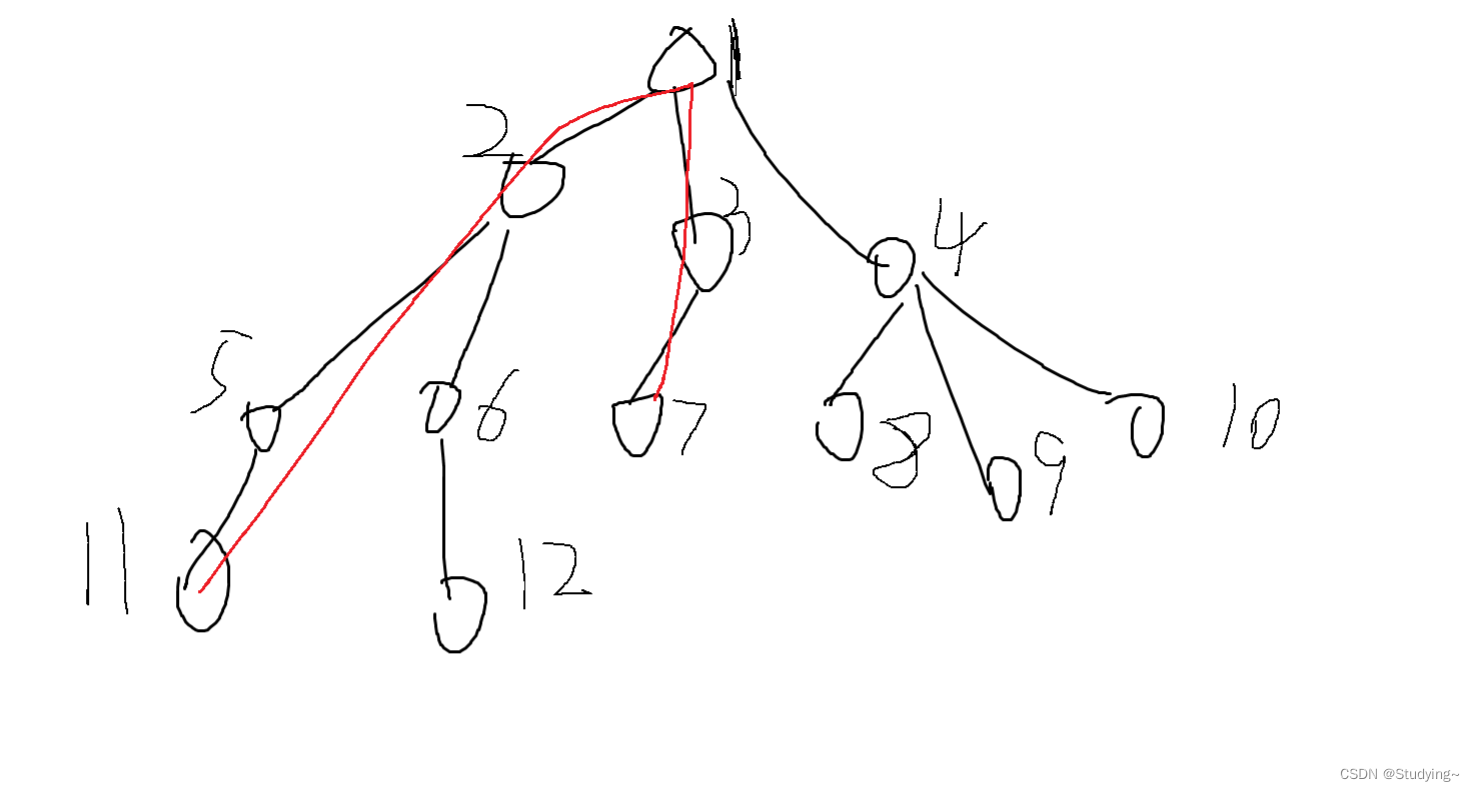
第二种情况,最大异或路径不经过顶点,但是我们发现 11 ^ 5 ^ 6 ^ 13 ^ 14等价于(2 ^ 5 ^ 11) ^ ( 2 ^ 6 ^ 13 ^ 14) ,可以发现还是相当于1--11的路径异或1-14的路径,所以我们只需要得到顶点到其他任意结点的路径即可,那我们在贪心选择时一定能得到最优解。
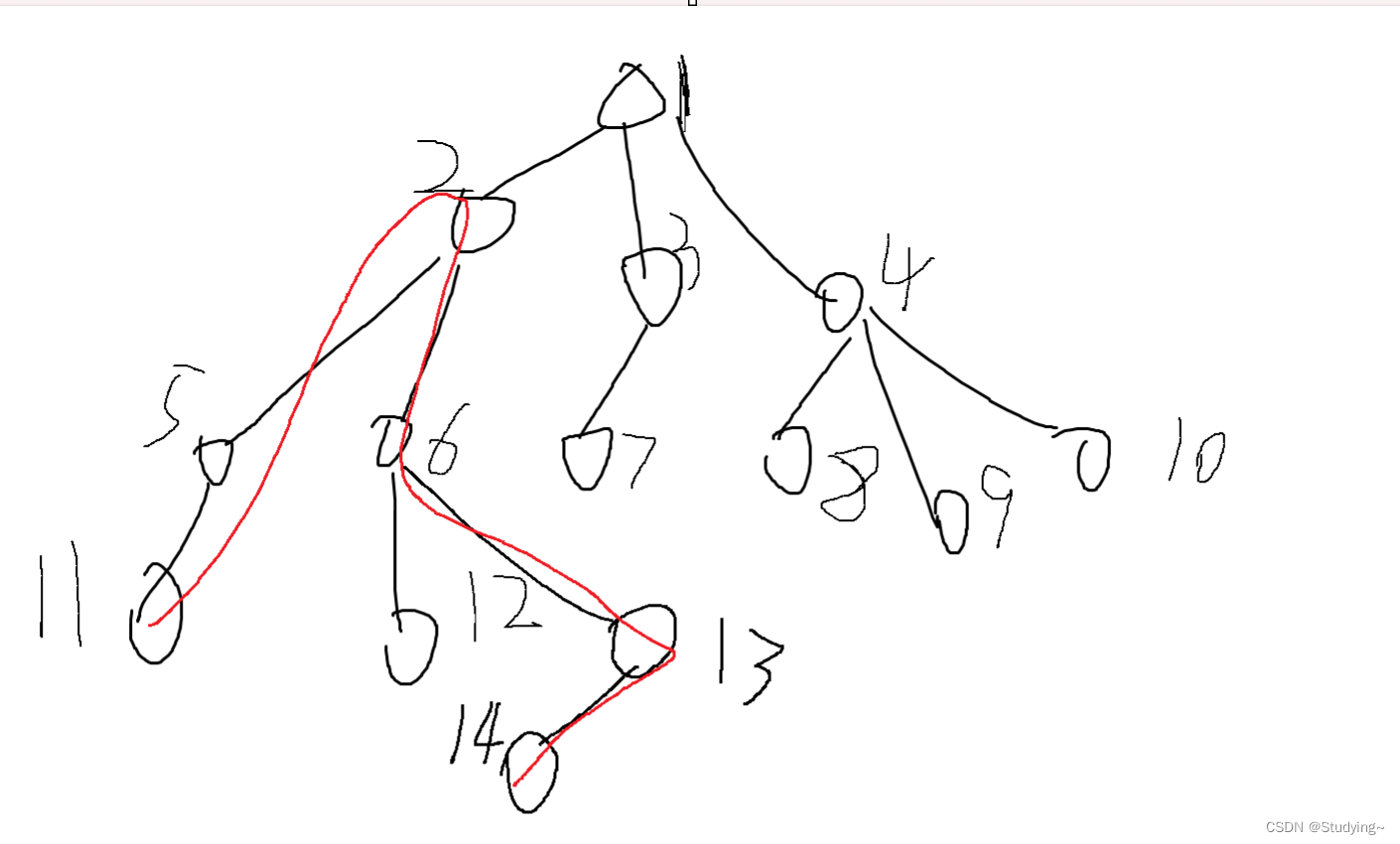
现在得到顶点到其他任意结点的异或路径值后,我们应该考虑我们如何贪心的选择。
假设我们现在路径的异或值为 2,曾经到过的路径异或值有(5 ,4,3,6)他们的二进制数分布为010,101,100,011,110,我们发现我们与5的路径异或后能得到最优答案。那么贪心选择为从二进制位的高位开始抉择,如果能有一个数能和当前值异或后在该位为1就选择这个数。
但是如果我们进行遍历选择,就会时间复杂度过高,那我们可以使用01字典树,这样就可以每次筛去大部分结果。
代码实现:
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import static java.lang.String.*;
public class Main {
static int MAXN = 100010;
static int n;
static int[][] tree = new int[MAXN << 3][2];
static int[] nxt = new int[MAXN << 1];
static int[] head = new int[MAXN];
static int[] to = new int[MAXN << 1];
static int[] weight = new int[MAXN << 1];
static int tot = 0;
static int ans = 0;
static int cnt;
static int[] dp = new int[MAXN];
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FastScanner f = new FastScanner();
PrintWriter w = new PrintWriter(System.out);
n = f.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
int x = f.nextInt();
int y = f.nextInt();
int v = f.nextInt();
add(x, y, v);
add(y,x,v);
}
dfs(1, 0);
w.println(ans);
w.flush();
w.close();
}
static void dfs(int x, int fa){
insert(dp[x]);
get(dp[x]);
for (int i = head[x]; i != 0; i = nxt[i]) {
int y = to[i];
if (y == fa) continue;
dp[y] = dp[x] ^ weight[i];
dfs(y, x);
}
}
static void insert(int x){
int p = 0;
for(int i = 30; i >= 0; i--){
int c = ((x >> i) & 1);
if (tree[p][c] == 0){
tree[p][c] = ++cnt;
}
p = tree[p][c];
}
}
static void get(int x){
int res = 0;
int p = 0;
for (int i = 30; i >= 0; i--) {
int c = ((x >> i) & 1);
if (tree[p][c ^ 1] != 0){
res |= (1 << i);
p = tree[p][c ^ 1];
}else {
p = tree[p][c];
}
}
ans = Math.max(ans, res);
}
static void add(int x, int y, int v){
nxt[++tot] = head[x];
head[x] = tot;
to[tot] = y;
weight[tot] = v;
}
private static class FastScanner {
final private int BUFFER_SIZE = 1 << 16;
private DataInputStream din;
private byte[] buffer;
private int bufferPointer, bytesRead;
private FastScanner() throws IOException {
din = new DataInputStream(System.in);
buffer = new byte[BUFFER_SIZE];
bufferPointer = bytesRead = 0;
}
private short nextShort() throws IOException {
short ret = 0;
byte c = read();
while (c <= ' ') c = read();
boolean neg = (c == '-');
if (neg) c = read();
do ret = (short) (ret * 10 + c - '0');
while ((c = read()) >= '0' && c <= '9');
if (neg) return (short) -ret;
return ret;
}
private int nextInt() throws IOException {
int ret = 0;
byte c = read();
while (c <= ' ') c = read();
boolean neg = (c == '-');
if (neg) c = read();
do ret = ret * 10 + c - '0';
while ((c = read()) >= '0' && c <= '9');
if (neg) return -ret;
return ret;
}
public long nextLong() throws IOException {
long ret = 0;
byte c = read();
while (c <= ' ') c = read();
boolean neg = (c == '-');
if (neg) c = read();
do ret = ret * 10 + c - '0';
while ((c = read()) >= '0' && c <= '9');
if (neg) return -ret;
return ret;
}
private char nextChar() throws IOException {
byte c = read();
while (c <= ' ') c = read();
return (char) c;
}
private String nextString() throws IOException {
StringBuilder ret = new StringBuilder();
byte c = read();
while (c <= ' ') c = read();
do {
ret.append((char) c);
} while ((c = read()) > ' ');
return ret.toString();
}
private void fillBuffer() throws IOException {
bytesRead = din.read(buffer, bufferPointer = 0, BUFFER_SIZE);
if (bytesRead == -1) buffer[0] = -1;
}
private byte read() throws IOException {
if (bufferPointer == bytesRead) fillBuffer();
return buffer[bufferPointer++];
}
}
}
版权归原作者 Studying~ 所有, 如有侵权,请联系我们删除。